Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 2044-2053.doi: 10.12307/2026.026
Applications and limitations of antioxidant nanomaterials in oral cavity
Yang Xuetao, Zhu Menghan, Zhang Chenxi, Sun Yimin, Ye Ling
- Department of Endodontics, National Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Prevention and Control & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-25Accepted:2025-01-24Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-18 -
Contact:Ye Ling, MD, Professor, Department of Endodontics, National Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Prevention and Control & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China Sun Yimin, MD, Associate professor, Department of Endodontics, National Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Prevention and Control & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Yang Xuetao, Master candidate, Department of Endodontics, National Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Prevention and Control & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. U21A20368 (to YL); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Project, No. BX20230240 (to SYM); Sichuan Province Science and Technology Plan, No. 2024NSFSC1581 (to SYM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Xuetao, Zhu Menghan, Zhang Chenxi, Sun Yimin, Ye Ling. Applications and limitations of antioxidant nanomaterials in oral cavity[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
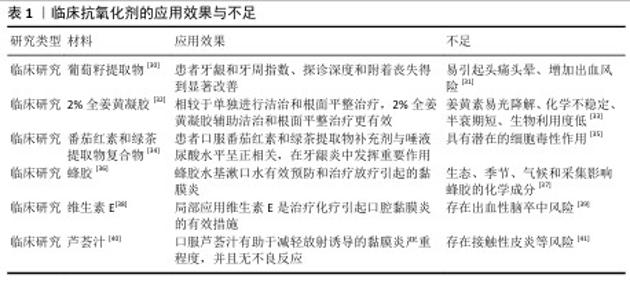
2.1 口腔疾病与氧化应激的关系 2.1.1 口腔疾病与氧化应激 氧化与抗氧化之间的微妙平衡对于维持口腔健康至关重要,氧化应激是口腔疾病的重要发病机制之一[9-11]。牙周病是受氧化应激影响最常见的口腔疾病之一[12]。在牙周病中,细菌感染会引起炎症,导致免疫细胞(如中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞)增多并产生较多活性氧[13-14],虽然活性氧水平增高对消除细菌具有重要作用[15],但是过高活性氧导致的氧化应激也造成了牙周支持组织的损伤和丧失[16]。临床研究发现,在牙周炎患者丙二醛和8-羟基脱氧鸟苷等氧化应激标志物水平增高[17]。龋齿也同样受到氧化应激的影响,变形链球菌等致龋细菌的代谢会促进活性氧的产生,过度增加的活性氧会损伤牙釉质和牙本质的有机质,同时诱导具有预防龋齿的唾液蛋白变性,加速龋病的进展[18-19]。研究证实,在口腔鳞状细胞癌中氧化应激标志物丙二醛和8-羟基脱氧鸟苷升高,并且升高水平和疾病预后密切相关[20]。 2.1.2 活性氧和氧化应激 活性氧是生物体内天然存在的含氧活性分子,主要由线粒体电子传递链和细胞质膜上的NADPH氧化酶复合体产生,部分由电离辐射等外界刺激产生,通常以氧自由基的形式存在[21-22]。常见的活性氧类型包括超氧阴离子、过氧化氢、单线态氧和羟基自由基等[23]。在生理状态下,活性氧在调节细胞的生长、分化、凋亡和基因表达等生理功能中发挥着重要作用[24]。 活性氧在机体内的生理水平主要依靠超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶等生物抗氧化酶以及维生素、类胡萝卜素和谷胱甘肽等抗氧化物调节[25-26]。然而,当机体受到病原体、损伤和炎症等刺激时,活性氧水平可能超过机体的调节能力,导致氧化与抗氧化平衡失调,从而引发氧化应激(图3)。氧化应激通过引起DNA碱基损伤和蛋白质结构与功能变性等方式诱导细胞损伤和凋亡,是多种疾病的共同发病机制[27]。 2.1.3 口腔疾病的传统治疗与抗氧化治疗 在口腔疾病治疗中,抗氧化主要是辅助传统治疗,以达到更好的治疗效果。传统的口腔疾病治疗主要是通过机械清创或者手术等方式去除导致疾病的直接因素,例如去除龋齿的龋坏组织、去除牙结石并消除细菌治疗牙周炎、手术切除癌变组织等,但是这些传统措施主要针对疾病的直接原因,并未及时缓解组织的损伤。相较于单纯的传统治疗,抗氧化辅助传统治疗可以从细胞、机制层面起作用,缓解氧化应激引起的损伤,加速疾病愈合的进展,因此,将抗氧化治疗与传统治疗相结合对于治愈氧化应激导致的口腔疾病至关重要。 2.1.4 针对口腔疾病氧化应激的措施 针对口腔疾病的氧化应激,目前临床上主要使用抗氧化剂消除过度增加的活性氧,常用的有辅酶Q10、维生素C、姜黄素和白藜芦醇等,然而,此类抗氧化剂在应用中又存在诸多问题[28]。随着纳米技术的不断发展,尤其是在抗氧化性能方向取得重大进展,具有抗氧化功能的纳米材料逐渐进入到生物医学研究视野[29],这些纳米材料具有特定的元素和结构,有望解决现有抗氧化剂的不足,维持更稳定的氧化与抗氧化平衡,进而恢复组织健康(表1)。 "
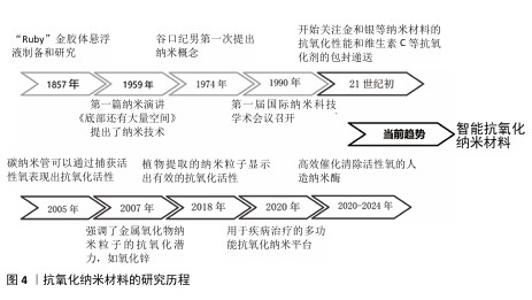
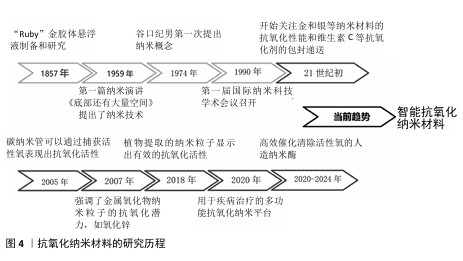
2.2 抗氧化纳米材料研究进展 2.2.1 纳米材料 纳米材料是尺寸介于原子、分子和宏观体系之间的纳米粒子组成的材料,其三维空间尺度至少有一维处于纳米量级(1-100 nm)。纳米材料具有更大的比表面积,因此,在吸附性能和催化性能方面具有更高的活性,同时纳米量级的尺寸可以赋予材料在光、热、声、电和磁等方面新的特性[42]。 2.2.2 抗氧化纳米材料的发展 抗氧化纳米材料的发展经历了漫长的演变(图4)。19世纪中期,胶体化学开始建立和发展促使科学家们开始对直径100 nm以下的粒子体系进行研究。到了20世纪60年代,科学家们对分离的纳米粒子进行了研究。1974年,日本的NORIO TANIGUCHI教授首次使用“纳米技术”一词来描述精细的机械加工。1990年,美国召开了第一届国际纳米科技学术会议,正式宣布纳米材料科学是材料科学的一个新分支。 随着对疾病发病机制认识的逐步深入,对抗氧化的要求也越来越高,为了更有效治疗氧化应激相关疾病,纳米技术与抗氧化剂的融合成为了一个新的研究方向,并不断发展创新。在21世纪初,研究人员首次研究了脂质体和聚合物纳米粒子等用于维生素C、维生素E和辅酶Q10等抗氧化剂的包封递送。金、银和铈等金属纳米材料的抗氧化能力也引起了广泛关注,并在生物体中进行了实验应用。为了实现更全面的疾病治疗,众多研究致力于构建多功能纳米复合材料,在高效抗氧化的同时发挥促进骨、血管和神经的再生功能。ZHAN等[43]制备了一种负载有氮杂双二甲基磷酸酯封端的磷树枝状聚合物,并且使用具有活性氧响应性的纤维蛋白涂覆聚合物纳米粒子,在炎症氧化微环境中发挥抗氧化、抗炎和促进骨修复的功能。RASOOL 等[44]开发了一种硫醇化的生物活性介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子,能够中和细胞中的活性氧来保护细胞,促进成骨和抑制破骨细胞的生成,在骨质疏松中具有显著治疗效果。近几年研究人员通过分析并模拟过氧化氢酶和超氧化物歧化酶等天然酶的金属配位结构,合成了催化活性氧清除的人造纳米酶,这类酶具有更高效的活性氧清除特性,并且催化活性可再生,在体内具有稳定持久的活性氧清除特性。SUN等[45]通过模拟天然过氧化氢酶的铁-氮活性中心,将具有低电负性、更多d电子以及足够空轨道的钌引入金属配位结构,开发了一种比天然抗氧化剂和先前报道的活性氧清除催化剂更有效的人造仿酶材料,对干细胞保护具有重要意义。ZHANG等[46]模拟过氧化氢酶中的活性位点,报道了一种配备铂簇的抗氧化酶样生物催化剂,具有高效的催化清除活性氧能力,在牙周炎治疗中具有显著的效果。最近,更符合生物学过程的智能抗氧化纳米材料陆续出现。XU等[47]用透明质酸和聚多巴胺修饰具有催化性能的铂纳米粒子,同时制作了一个由水核和脂质壳组成的脂质体纳米反应器,通过水核包裹水溶性的尿激酶和铂纳米粒子级联双酶,脂质壳包含亲脂性的白藜芦醇,发挥清除有害的尿酸和过氧化物酶功能,改善缺氧的炎症免疫微环境,最后通过巨噬细胞衍生的外泌体和巨噬细胞膜伪装、靶向和溶酶体逃逸将药物输送到炎症部位发挥功能。"
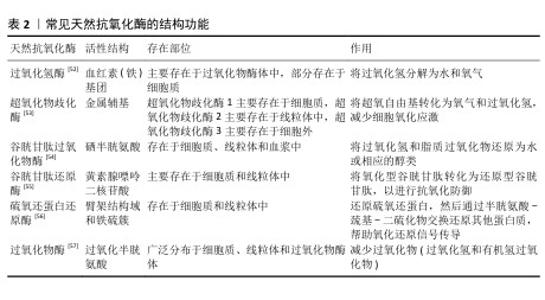
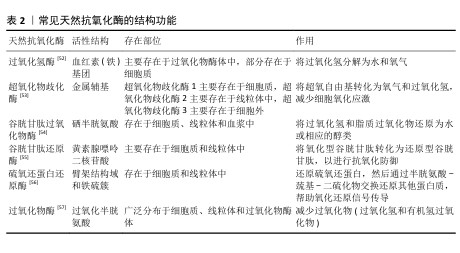
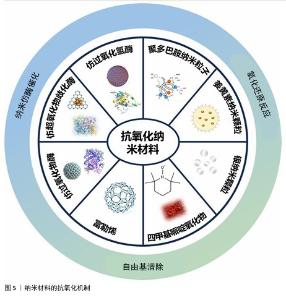
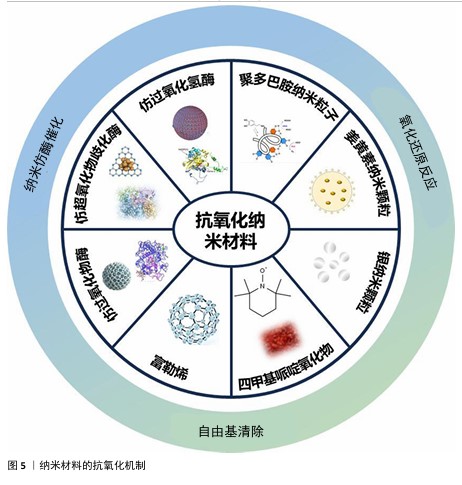
2.3 纳米材料的抗氧化机制 纳米材料的抗氧化机制见图5。 2.3.1 仿酶催化清除 机体自身主要有以下几种类型的氧化还原酶,包括过氧化物酶、过氧化氢酶和超氧化物歧化酶等,通过分析此类酶的化学结构,基于化学合成策略,衍生出了系列仿酶材料,这些纳米仿酶具有与天然酶类似的金属化学配位结构。受益于较大的比表面积,极小尺寸的纳米酶可以发挥高效、广谱的催化剂效果[48]。其中,类超氧化物歧化酶可以催化超氧阴离子歧化为氧气和过氧化氢,类过氧化氢酶可以将过氧化氢转换为氧气和水,类过氧化物酶能够还原过氧化物生成水。除此之外,部分纳米仿酶还可以通过电子供体的形式催化羟基自由基等自由基还原为水,从而减轻氧化应激[49-51]。常见天然抗氧化酶的结构功能,见表2。 2.3.2 氧化还原反应清除 自然界存在许多能够直接与活性氧反应来降低活性氧水平的物质。以姜黄素为基础的纳米粒子,能够通过自氧化消耗自由基,同时生成双环乙酰丙酮[58-59]。聚多巴胺纳米粒子邻位的醌结构可以发生H原子转移机制,与自由基直接进行反应[60]。银纳米粒子可以和超氧阴离子及羟基自由基等活性氧发生氧化还原反应,自身形成氧化银[61]。 2.3.3 自由基捕获 自由基捕获剂一般都是优良的电子受体,主要利用自身的单电子捕获氧自由基等自由基中不成对的电子,发生氧化还原反应,从而发挥抗氧化功能。2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶氧化物是一种哌啶类氮氧自由基,氮氧化物/氧代铵氧化还原对通过可逆的单电子氧化还原反应促进催化过程,羟胺作为氢原子供体,提供抗氧化功能[62]。富勒烯(C60)是一种“自由基海绵”,具有良好电子亲和力的共轭双键,可以接受自由基不成对的电子从而猝灭各种自由基,改善氧化应激[63]。 "
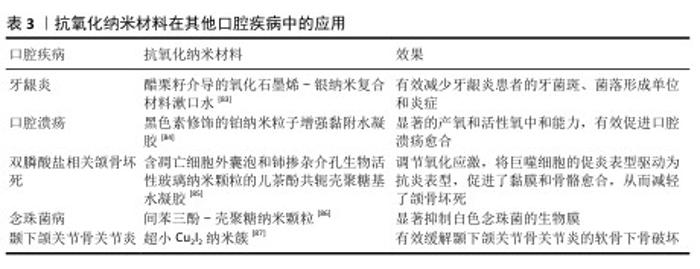
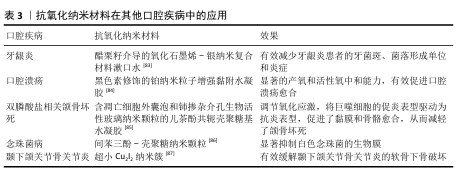
2.4 抗氧化纳米材料在口腔中的应用与不足 2.4.1 抗氧化纳米材料在口腔中的应用 龋齿:是口腔中发病率很高的疾病,可能与唾液氧化生物化学的变化及脂质过氧化增加有关。HENDI 等[64]通过临床试验发现,龋齿活跃的志愿者唾液中过氧化物酶、尿酸、过氧化氢酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶水平较高,超氧化物歧化酶水平较低。研究表明,硒纳米颗粒具有抗氧化和抗菌效果,可能具有抗染色和预防龋齿的效果[65]。 牙髓炎:龋病、磨损和创伤等因素都有可能导致不可复性牙髓炎症,目前临床针对不可复性牙髓炎的治疗方式主要是将牙髓杀死并去除,但失去牙髓营养的牙齿会变得更脆弱,同时失去感知功能[66]。人源牙髓干细胞具有高度繁殖、自我更新及多向分化潜能,目前已有相关研究将其移植在根管中再生牙髓,但是由于根管特殊的解剖结构,移植的牙髓干细胞容易发生急性缺氧[67]。香港大学利用低氧环境激发用作移植牙髓干细胞的保护性反应——氧化应激反应,增强移植干细胞的根管适应能力[68]。虽然这类方法能在一定程度上提高牙髓干细胞的适应能力,但是低氧环境条件并不完全与根管环境相同,并且无法解决移植后炎症可能再次发作的问题。ZHAO等[69]将具有抗氧化的二氧化铈纳米粒子和促进牙本质再生的牙本质基质蛋白1负载到可注射的Fmoc-三苯丙氨酸水凝胶中,将该水凝胶注入根管中发挥抗氧化、抗炎和促进牙本质生成的作用。 牙周炎:是由菌斑和牙结石等局部刺激因素引起的牙周支持组织破坏性疾病。病原微生物是破坏牙周组织的始动因子,机体免疫炎症反应也起到了重要作用,炎症状态下的人牙周组织会产生过量的活性氧物质,出现氧化应激。当前牙周炎的治疗以去除感染因素为主,通过龈上洁治、龈下刮治等物理疗法和局部使用派力奥等抗菌剂辅助治疗,对于较为严重的牙周炎,临床上还采用牙龈切除术、翻瓣术等手段进一步治疗,以尽可能去除感染因素,形成不利于牙菌斑堆积的解剖结构。然而,牙周炎造成的牙槽骨缺损往往难以恢复,导致患牙抵抗力差。因此,患者需要更加重视牙周健康的维护,以避免复发和牙齿进一步松动脱落[70]。临床研究表明,抗氧化疗法作为牙周病的单一疗法或者辅助治疗可以减少牙周炎症[71]。HUANG等[72]用阳离子聚酰胺胺树枝状大分子涂覆含硒的羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒,开创了一种清除与牙周炎高度相关的循环游离DNA的纳米材料,不仅可以抑制循环游离DNA的体外促炎作用,还可以缓解牙周炎症性骨丢失。XU等[73]提出了一种模拟超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化氢酶的铜基纳米酶,通过与甘油单硬酸酯和2,6-二叔丁基-4-甲基苯酚组装的水凝胶结合,实现牙周炎部位纳米酶的按需释放,便捷有效地缓解牙周炎症,促进组织再生。 口腔癌:口腔受到各种致癌因素刺激后,口腔黏膜中的活性氧会过度产生,损伤DNA和蛋白质等,导致突变和癌变。除此以外,活性氧增加还会降低T细胞和自然杀伤细胞的功能,促进巨噬细胞的募集、M2极化和肿瘤的发展[74]。其中,口腔鳞状细胞癌肿瘤微环境就以氧化应激为主要特征,不仅促进癌细胞存活增殖,而且不利于化疗和放疗。因此,抗氧化策略可能是治疗口腔癌的一种潜在方式。FAZLI等[75]将姜黄素和囊泡结合制备的纳米囊泡注射入动物体内发挥抗氧化动能,结果显示可有效防止严重形式的发育不良发展并抑制癌细胞的生长。然而,目前也有大量研究通过纳米材料产生大量活性氧抑制或杀死肿瘤细胞,用于口腔癌症或其他癌症的治疗。LUCKY等[76]开发了以近红外光激发的上转化纳米颗粒为基础的光动力纳米材料,可以特异性靶向过表达口腔癌细胞的上皮因子受体,在光照下产生活性氧,实现口腔癌细胞的破坏。ZHONG等[77]尝试在各种温度下煅烧控制钌纳米晶格的晶格间距以调节钌基纳米酶的电子状态,最大限度地提高纳米酶催化活性氧产生的能力,实现最佳的肿瘤治疗。活性氧在肿瘤中具有两面性,既可以表现为促进肿瘤发生,也可以抑制肿瘤。GLORIEUX等[78]通过总结众多研究结果认为,不同研究者得出的结论不同甚至相互矛盾可能是由于不同研究模型和方法造成的。活性氧的时空调控及在肿瘤发展不同阶段的动态效应,可能在一定程度上解释抗氧化剂在肿瘤中的作用。因此,如何利用活性氧治疗口腔癌症,需要从口腔癌症的具体类型、发展状态、分期分级及患者自身实际状况等方面综合考虑,制定出合理的活性氧治疗方案。 扁平苔藓:口腔扁平苔藓是口腔中常见的一种黏膜病变,主要表现为小丘疹样病损组成的线状、网状、树枝状或者斑块状病变,在中年女性中发病较高。相关研究表明,口腔扁平苔藓的发病机制与氧化应激相关[79],活性氧会诱导细胞凋亡,而角质形成细胞的凋亡是口腔扁平苔藓的标志[80]。系统评价结果表明,抗氧化治疗可以减轻口腔扁平苔藓患者的疼痛和临床评分,提高缓解率[81]。 ALIPOUR等[82]设计并制备了一种含有霉酚酸酯、氧化锌纳米粒子和芦荟的纳米纤维垫,患有双侧红斑/糜烂性口腔扁平苔藓的患者使用后与临床用的软膏疗效相同,并且症状得到明显改善。 除了龋齿、牙髓炎、牙周炎和口腔癌等口腔疾病,抗氧化纳米材料在其他口腔疾病中也有广泛应用(表3)。 2.4.2 抗氧化纳米材料口腔应用不足 潜在毒性:大多数具有活性氧清除效果的抗氧化纳米材料都含有过渡金属元素,在材料合成过程中的金属和杂质残留均容易引起生物毒性。纳米尺寸的材料容易进入全身循环系统,在肝脾等脏器积聚,同时也可能进入细胞而造成细胞凋亡。不同抗氧化纳米材料还具有丰富多样的形状,例如纳米球、纳米棒、纳米片等,不同形状的纳米材料可能位于细胞外,也可能锚定在细胞上或进入细胞,对细胞活力造成影响[88-89]。在过去的10年中,人们一直在探索纳米材料对生物系统的影响,纳米材料对细胞毒性的作用是动态的[90]。因此,系统评估抗氧化纳米材料的生物安全性至关重要,需要从合成原料、合成工艺以及纯化方面不断改进,从细胞、组织、个体和群体等方面长期综合评估抗氧化纳米材料的安全性[91]。 合成复杂:抗氧化纳米材料的合成需要昂贵的原材料、复杂的程序、精密的仪器设备和控制技术,并且纳米材料的形态、结构、电荷及成分都会影响材料的特性,最终影响细胞行为。目前大多数抗氧化纳米材料的合成都是通过不断试错筛选制备的,找到一种既具良好活性氧清除性能又能满足口腔组织相应部位效果和安全性的纳米材料很难[92]。 口腔保留稳定性:口腔是一个湿润的环境,不断有唾液分泌,并且龈沟内充满龈沟液,在说话咀嚼和吞咽时伴随骨、关节、肌肉和黏膜的运动,单纯抗氧化纳米材料应用于口腔时难以在疾病部位保持稳定,很容易流失或进入循环,因此,不得不增加口腔给药的频率,这可能带来潜在的生物毒性[93]。虽然目前也有许多研究将纳米抗氧化剂放入凝胶等聚合物材料中保持其在病变部位的稳定性,但是这种组合可能会对纳米抗氧化剂自身的性能产生影响。"
2.5 口腔抗氧化纳米材料研究前沿 2.5.1 智能抗氧化纳米材料 生理水平的活性氧对于维持机体的正常功能是必须的,常常作为信号分子参与调控生物学过程,包括激活信号通路、调控细胞生长和影响生物体器官等。但是目前的抗氧化纳米材料只能单纯发挥抗氧化作用,并不能根据生理所需调控活性氧水平。当氧化应激解除以后,残留的抗氧化纳米材料可能继续清除生理水平的活性氧,影响正常的生理功能。除此以外,目前已经研究出了能够反复清除活性氧的纳米酶材料,这类材料随着循环进入到正常组织后仍然可以保持活性氧清除功能,对正常组织可能造成危害。 因此,未来可以尝试开发在具体疾病微环境中经过特定刺激激活抗氧化特性的智能纳米材料,避免对正常生理状态的干扰。除此以外,也可以将人工智能结合到纳米技术和生物医学领域,通过程序设计和计算机模拟、高通量筛选探索出更加科学的抗氧化纳米材料,同时借助人工智能收集抗氧化纳米材料应用在生物体中的各项实时生理参数,以便更准确的分析[94-95]。 2.5.2 安全容易代谢纳米材料 目前绝大多数抗氧化纳米材料都包含金属元素,例如银和锰等,同时纳米级尺寸使得材料更容易被细胞吞噬和进入全身循环系统,在肝脏和脾脏等部位聚集,对健康产生潜在的危害[96]。目前也有许多提高抗氧化纳米材料生物相容性的方法,例如,LI等[97]将多个乙二胺基团键合到富勒烯上获得水溶性的纳米粒子,不仅具有优异的活性氧清除能力,同时也具有良好的生物相容性;也有研究利用红细胞和中性粒细胞等细胞的胞膜对抗氧化纳米材料进行涂层,以改善其性能和生物安全性[98]。 但是从抗氧化纳米材料本身设计出发,构建自身更安全高效的抗氧化纳米材料,特别是容易被机体安全代谢并排泄的纳米材料,是未来需要不断努力的方向。 2.5.3 个性化抗氧化纳米材料 个性化医疗在近10年来取得了很大发展,尤其是在靶向药物等方面的突破,个性化医疗根据患者可监测的遗传信息和环境信息量身定做治疗计划,实现治疗效果最大化和不良反应最小化[99]。 对于不同患者、不同疾病状态以及不同的疾病阶段,氧化应激情况可能都不同,对药物的代谢能力也不同。为了尽可能发挥纳米材料的抗氧化效果以及减轻生物毒性,抗氧化纳米材料需要朝着更加精准的方向发展,具体可以从以下几个方面努力:①量身定制:根据不同的疾病类型及其氧化应激状态,从材料组分、给药方式和剂量等方面量身定制抗氧化纳米材料;②精准靶向:通过材料设计实现抗氧化纳米材料靶向特定部位或者细胞;③多学科交叉:促进医学、材料学、生物学和化学等领域的专家团队合作,创新改进抗氧化纳米材料治疗方式。 "
| [1] ROWIŃSKA I, SZYPERSKA-ŚLASKA A, ZARICZNY P, et al. The influence of diet on oxidative stress and inflammation induced by bacterial biofilms in the human oral cavity. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(6):1444. [2] SARDARO N, DELLA VELLA F, INCALZA MA, et al. Oxidative stress and oral mucosal diseases: an overview. In Vivo. 2019;33(2):289-296. [3] BIRBEN E, SAHINER UM, SACKESEN C, et al. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ J. 2012;5(1):9-19. [4] LANDETE JM. Dietary intake of natural antioxidants: vitamins and polyphenols. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2013;53(7):706-721. [5] LIU X, XU H, PENG H, et al. Advances in antioxidant nanozymes for biomedical applications. Coordin Chem Rev. 2024;502: 215610. [6] ABEDI N, SAJADI-JAVAN Z S, KOUHI M, et al. Antioxidant materials in oral and maxillofacial tissue regeneration: a narrative review of the literature. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023; 12(3):594. [7] SUI L, WANG J, XIAO Z, et al. ROS-scavenging nanomaterials to treat periodontitis. Front Chem. 2020;8:595530. [8] KUMAR H, BHARDWAJ K, NEPOVIMOVA E, et al. Antioxidant functionalized nanoparticles: A combat against oxidative stress. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(7):1334. [9] KESARWALA AH, KRISHNA MC, MITCHELL JB. Oxidative stress in oral diseases. Oral Dis. 2016;22(1):9-18. [10] MEYLE J, CHAPPLE IJP. Molecular aspects of the pathogenesis of periodontitis. Periodontol 2000. 2015;69(1):7-17. [11] 王雨,刘佳.氧化应激与口腔炎性疾病的相关性综述[J].现代口腔医学杂志, 2024,38(1):66-69. [12] 郑燕丹,黄翔.活性氧在牙周炎中病理作用的研究进展[J].安徽医药,2019,23(7): 1295-1298. [13] CEKICI A, KANTARCI A, HASTURK H, et al. Inflammatory and immune pathways in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000. 2014;64(1):57-80. [14] CANAKCI C, CICEK Y, CANAKCI VJB. Reactive oxygen species and human inflammatory periodontal diseases. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2005;70(6):619-628. [15] NATHAN C, CUNNINGHAM-BUSSEL A. Beyond oxidative stress: an immunologist’s guide to reactive oxygen species. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(5):349-361. [16] SCZEPANIK FSC, GROSSI ML, CASATI M, et al. Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of oxidative stress: We should treat it that way. Periodontol 2000. 2020;84(1):45-68. [17] FENTOĞLU Ö, KIRZIOĞLU F Y, BULUT MT, et al. Evaluation of lipid peroxidation and oxidative DNA damage in patients with periodontitis and hyperlipidemia. J Periodontol. 2015;86(5):682-688. [18] DE SOUSA NÉ YG, LIMA WF, MENDES PFS, et al. Dental caries and salivary oxidative stress: global scientific research landscape. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(2):330. [19] SOUTHWARD K. The systemic theory of dental caries. Gen Dent. 2011;59(5): 367-373;quiz 374-5. [20] AGHA‐HOSSEINI F, MIRZAII‐DIZGAH I, FARMANBAR N, et al. Oxidative stress status and DNA damage in saliva of human subjects with oral lichen planus and oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 2012;41(10):736-740. [21] MATOUGH FA, BUDIN SB, HAMID ZA, et al. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in diabetic complications. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2012;12(1):5-18. [22] ŻUKOWSKI P, MACIEJCZYK M, WASZKIEL D. Sources of free radicals and oxidative stress in the oral cavity. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;92:8-17. [23] SCHIEBER M, CHANDEL NAVDEEP S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 2014;24(10):R453-R462. [24] SIES H, BELOUSOV VV, CHANDEL NS, et al. Defining roles of specific reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cell biology and physiology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23(7):499-515. [25] JOMOVA K, RAPTOVA R, ALOMAR SY, et al. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Chronic diseases and aging. Arch Toxicol. 2023;97(10):2499-2574. [26] MATEEN S, MOIN S, KHAN AQ, et al. Increased reactive oxygen species formation and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0152925. [27] HAJAM YA, RANI R, GANIE SY, et al. Oxidative stress in human pathology and aging: molecular mechanisms and perspectives. Cells. 2022;11(3):552. [28] RATNAM DV, ANKOLA DD, BHARDWAJ V, et al. Role of antioxidants in prophylaxis and therapy: A pharmaceutical perspective. J Control Release. 2006; 113(3):189-207. [29] KUMAR H, BHARDWAJ K, NEPOVIMOVA E, et al. Antioxidant functionalized nanoparticles: A combat against oxidative stress. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(7):1334. [30] DAS M, DAS AC, PANDA S, et al. Clinical efficacy of grape seed extract as an adjuvant to scaling and root planing in treatment of periodontal pockets. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021;35:89-96. [31] BERRY AC, NAKSHABENDI R, ABIDALI H, et al. Adverse effects of grape seed extract supplement: a clinical case and long-term follow-up. J Diet Suppl. 2016;13(2):232-235. [32] BEHAL R, MALI AM, GILDA SS, et al. Evaluation of local drug-delivery system containing 2% whole turmeric gel used as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in chronic periodontitis: A clinical and microbiological study. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2011;15(1):35-38. [33] KARTHIKEYAN A, SENTHIL N, MIN T. Nanocurcumin: a promising candidate for therapeutic applications. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:487. [34] WASTI J, WASTI A, SINGH R. Efficacy of antioxidants therapy on progression of periodontal disease - A randomized control trial. Indian J Dent Res. 2021;32(2):187-191. [35] QU M, ZHOU Z, CHEN C, et al. Lycopene protects against trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons by inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Neurochem Int. 2011;59(8):1095-1103. [36] JAVADZADEH BOLOURI A, PAKFETRAT A, TONKABONI A, et al. Preventing and therapeutic effect of propolis in radiotherapy induced mucositis of head and neck cancers: a triple-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Iran J Cancer Prev. 2015;8(5):e4019. [37] SFORCIN JM, BANKOVA V. Propolis: is there a potential for the development of new drugs? J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;133(2): 253-260. [38] EL-HOUSSEINY AA, SALEH SM, EL-MASRY AA, et al. The effectiveness of vitamin “E” in the treatment of oral mucositis in children receiving chemotherapy. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2007;31(3):167-170. [39] MAGGIO E, BOCCHINI VP, CARNEVALE R, et al. Vitamin E supplementation (alone or with other antioxidants) and stroke: a meta-analysis. Nutr Rev. 2024;82(8):1069-1078. [40] AHMADI A. Potential prevention: Aloe vera mouthwash may reduce radiation-induced oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients. Chin J Integr Med. 2012;18(8):635-640. [41] FERREIRA M, TEIXEIRA M, SILVA E, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to Aloe vera. Contact Dermatitis. 2007;57(4):278-279. [42] SAHLE FF, GULFAM M, LOWE TL. Design strategies for physical-stimuli-responsive programmable nanotherapeutics. Drug Discov Today. 2018;23(5):992-1006. [43] ZHAN M, SUN H, WANG Z, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated multiple modulation of bone microenvironment To tackle osteoarthritis. ACS Nano. 2024; 18(15):10625-10641. [44] RASOOL N, NEGI D, SINGH Y. Thiol-functionalized, antioxidant, and osteogenic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for osteoporosis. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023; 9(6):3535-3545. [45] SUN Y, MU S, XING Z, et al. Catalase-mimetic artificial biocatalysts with Ru catalytic centers for ROS elimination and stem-cell protection. Adv Mater. 2022; 34(46):e2206208. [46] ZHANG C, YAN R, BAI M, et al. Pt-clusters-equipped antioxidase-like biocatalysts as efficient ROS scavengers for treating periodontitis. Small. 2024;20(17):e2306966. [47] XU J, WU M, YANG J, et al. Multimodal smart systems reprogramme macrophages and remove urate to treat gouty arthritis. Nat Nanotechnol. 2024;19(10):1544-1557. [48] YANG W, YANG X, ZHU L, et al. Nanozymes: Activity origin, catalytic mechanism, and biological application. Coordin Chem Rev. 2021;448:214170. [49] ZHAO H, ZHANG R, YAN X, et al. Superoxide dismutase nanozymes: an emerging star for anti-oxidation. J Mater Chem B. 2021; 9(35):6939-6957. [50] XU D, WU L, YAO H, et al. Catalase-like nanozymes: Classification, catalytic mechanisms, and their applications. Small. 2022;18(37):2203400. [51] ATTAR F, SHAHPAR MG, RASTI B, et al. Nanozymes with intrinsic peroxidase-like activities. J Mol Liq. 2019;278:130-144. [52] DÍAZ A, LOEWEN PC, FITA I, et al. Thirty years of heme catalases structural biology. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012;525(2): 102-110. [53] FUKAI T, USHIO-FUKAI M. Superoxide dismutases: role in redox signaling, vascular function, and diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(6):1583-1606. [54] WEAVER K, SKOUTA R. The Selenoprotein Glutathione Peroxidase 4: From Molecular Mechanisms to Novel Therapeutic Opportunities. Biomedicines. 2022;10(4): 891. [55] COUTO N, WOOD J, BARBER J. The role of glutathione reductase and related enzymes on cellular redox homoeostasis network. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;95:27-42. [56] LU J, HOLMGREN A. The thioredoxin antioxidant system. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;66:75-87. [57] SHEN C, WANG Y. Recent progress on peroxidase modification and application. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024;196(9): 5740-5764. [58] DOGGUI S, SAHNI JK, ARSENEAULT M, et al. Neuronal uptake and neuroprotective effect of curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles on the human SK-N-SH cell line. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;30(2):377-392. [59] GRIESSER M, PISTIS V, SUZUKI T, et al. Autoxidative and cyclooxygenase-2 catalyzed transformation of the dietary chemopreventive agent curcumin. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(2):1114-1124. [60] GUO Y, BASCHIERI A, MOLLICA F, et al. Hydrogen Atom Transfer from HOO. to ortho-Quinones Explains the Antioxidant Activity of Polydopamine. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(28):15220-15224. [61] BEDLOVIČOVÁ Z, STRAPÁČ I, BALÁŽ M, et al. A brief overview on antioxidant activity determination of silver nanoparticles. Molecules. 2020;25(14):3191. [62] SOULE BP, HYODO F, MATSUMOTO KI, et al. The chemistry and biology of nitroxide compounds. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007; 42(11):1632-1650. [63] LIN AMY, CHYI BY, WANG SD, et al. Carboxyfullerene prevents iron-induced oxidative stress in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1999;72(4):1634-1640. [64] HENDI SS, GOODARZI MT, MOGHIMBEIGI A, et al. Evaluation of the status of salivary antioxidants in dental caries. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2020;20(6):816-821. [65] ALMUQRIN A, KAUR IP, WALSH LJ, et al. Amelioration strategies for silver diamine fluoride: moving from black to white. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023;12(2):298. [66] YAN W, MONTOYA C, ØILO M, et al. Contribution of root canal treatment to the fracture resistance of dentin. J Endod. 2019;45(2):189-193. [67] DISSANAYAKA WL, HARGREAVES KM, JIN L, et al. The interplay of dental pulp stem cells and endothelial cells in an injectable peptide hydrogel on angiogenesis and pulp regeneration in vivo. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(3-4):550-563. [68] HAN Y, KOOHI-MOGHADAM M, CHEN Q, et al. HIF-1α stabilization boosts pulp regeneration by modulating cell metabolism. J Dent Res. 2022;101(10): 1214-1226. [69] ZHAO Y, SONG L, LI M, et al. Injectable CNPs/DMP1-loaded self-assembly hydrogel regulating inflammation of dental pulp stem cells for dentin regeneration. Materials Today Bio. 2023;24:100907. [70] ONUORA S. NETs implicated in periodontitis-associated bone loss. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023;19(8):463. [71] MATHUR A, MATHUR L, MANOHAR B, et al. Antioxidant therapy as monotherapy or as an adjunct to treatment of periodontal diseases. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2013; 17(1):21-24. [72] HUANG H, PAN W, WANG Y, et al. Nanoparticulate cell-free DNA scavenger for treating inflammatory bone loss in periodontitis. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1): 5925. [73] XU Y, LUO Y, WENG Z, et al. Microenvironment-responsive metal-Phenolic nanozyme release platform with antibacterial, ROS scavenging, and osteogenesis for periodontitis. ACS Nano. 2023;17(19):18732-18746. [74] HUANG R, CHEN H, LIANG J, et al. Dual role of reactive oxygen species and their application in cancer therapy. J Cancer. 2021;12(18):5543-5561. [75] FAZLI B, IRANI S, BARDANIA H, et al. Prophylactic effect of topical (slow-release) and systemic curcumin nano-niosome antioxidant on oral cancer in rat. BMC Complement Med. 2022;22(1):109. [76] LUCKY SS, IDRIS NM, HUANG K, et al. In vivo biocompatibility, biodistribution and therapeutic efficiency of titania coated upconversion nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy of solid oral cancers. Theranostics. 2016;6(11):1844-1865. [77] ZHONG S, ZHANG Z, ZHAO Q, et al. Lattice expansion in ruthenium nanozymes improves catalytic activity and electro-responsiveness for boosting cancer therapy. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):8097. [78] GLORIEUX C, LIU S, TRACHOOTHAM D, et al. Targeting ROS in cancer: rationale and strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024; 23(8):583-606. [79] UPADHYAY RB, CARNELIO S, SHENOY RP, et al. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid reaction. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2010;70(4):225-228. [80] SANKARI SL, BABU NA, RAJESH E, et al. Apoptosis in immune-mediated diseases. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2015;7:S200-202. [81] BAO J, CHEN C, YAN J, et al. Antioxidant therapy for patients with oral lichen planus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1030893. [82] ALIPOUR M, HABIBIVAND E, SEKHAVATI S, et al. Evaluation of therapeutic effects of nanofibrous mat containing mycophenolate mofetil on oral lichen planus: In vitro and clinical trial study. Biomater Investig Dent. 2023;10(1):2283177. [83] SOUNDARAJAN S, RAJASEKAR AJD, PROBLEMS M. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects of a novel herb-mediated nanocomposite mouthwash in plaque-induced gingivitis: a randomized controlled trial. Dent Med Probl. 2023;60(3): 445-451. [84] CAI E, QI X, SHI Y, et al. Immunomodulatory melanin@Pt nanoparticle-reinforced adhesive hydrogels for healing diabetic oral ulcers. Chem Eng J. 2024;488:150372. [85] LING Z, GUO S, XIE H, et al. Synergistic effects of cerium-containing bioactive glasses and apoptotic extracellular vesicles alleviate bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of jaw. Appl Mater Today. 2024;38:102177. [86] KHAN F, OH D, CHANDIKA P, et al. Inhibitory activities of phloroglucinol-chitosan nanoparticles on mono- and dual-species biofilms of Candida albicans and bacteria. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;211:112307. [87] WANG Y, DING X, ZHANG F, et al. Ultrasmall Cu2I2 nanoclusters trigger metabolic-epigenetic reprogramming and endogenous antioxidant systems for alleviating osteoarthritis. Chem Eng J. 2024;497:154568. [88] MEDICI S, PEANA M, PELUCELLI A, et al. An updated overview on metal nanoparticles toxicity. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;76:17-26. [89] HE X, FU P, AKER WG, et al. Toxicity of engineered nanomaterials mediated by nano-bio-eco interactions. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2018;36(1):21-42. [90] EFTEKHARI A, DIZAJ SM, CHODARI L, et al. The promising future of nano-antioxidant therapy against environmental pollutants induced-toxicities. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:1018-1027. [91] YAN L, ZHAO F, WANG J, et al. A safe-by-design strategy towards safer nanomaterials in nanomedicines. Adv Mater. 2019;31(45): 1805391. [92] YANG L, DONG S, GAI S, et al. Deep insight of design, mechanism, and cancer theranostic strategy of nanozymes. Nanomicro Lett. 2023;16(1):28. [93] CHEN Z, CHU Z, JIANG Y, et al. Recent advances on nanomaterials for antibacterial treatment of oral diseases. Materials Today Bio. 2023;20:100635. [94] WANG Z, WU J, ZHENG JJ, et al. Accelerated discovery of superoxide-dismutase nanozymes via high-throughput computational screening. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):6866. [95] KLEANDROVA VV, LUAN F, GONZÁLEZ-DÍAZ H, et al. Computational tool for risk assessment of nanomaterials: novel QSTR-perturbation model for simultaneous prediction of ecotoxicity and cytotoxicity of uncoated and coated nanoparticles under multiple experimental conditions. Environ Sci Technol. 2014;48(24):14686-14694. [96] SANCHEZ VC, PIETRUSKA JR, MISELIS NR, et al. Biopersistence and potential adverse health impacts of fibrous nanomaterials: what have we learned from asbestos? Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2009;1(5):511-529. [97] LI J, GUAN M, WANG T, et al. Gd@C(82)-(ethylenediamine)(8) nanoparticle: A new high-efficiency water-soluble ROS scavenger. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(39): 25770-25776. [98] LIU J, MA L, ZHANG G, et al. Recent progress of surface modified nanomaterials for scavenging reactive oxygen species in organism. Bioconjug Chem. 2021;32(11): 2269-2289. [99] JOHNSON KB, WEI WQ, WEERARATNE D, et al. Precision medicine, AI, and the future of personalized health care. Clin Transl Sci. 2021;14(1):86-93. [100] ABEDI N, SAJADI-JAVAN ZS, KOUHI M, et al. Antioxidant materials in oral and maxillofacial tissue regeneration: A narrative review of the literature. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(3):594. [101] BENZIAN H, WATT R, MAKINO Y, et al. WHO calls to end the global crisis of oral health. Lancet. 2022;400(10367): 1909-1910. [102] JAIN N, DUTT U, RADENKOV I, et al. WHO’s global oral health status report 2022: Actions, discussion and implementation. Oral Dis. 2024;30(2):73-79. [103] BELIBASAKIS GN, BOSTANCI N, MARSH PD, et al. Applications of the oral microbiome in personalized dentistry. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;104:7-12. |
| [1] | Haonan Yang, Zhengwei Yuan, Junpeng Xu, Zhiqi Mao, Jianning Zhang. Preliminary study on the mechanisms and efficacy of deep brain stimulation in treating depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Sun Lei, Zhang Qi, Zhang Yu. Pro-osteoblastic effect of chlorogenic acid protein microsphere/polycaprolactone electrospinning membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1877-1884. |
| [3] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [4] | Li Qingbin, Lin Jianhui, Huang Wenjie, Wang Mingshuang, Du Jiankai, Lao Yongqiang. Bone cement filling after enlarged curettage of giant cell tumor around the knee joint: a comparison of subchondral bone grafting and non-grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [5] | Jiang Xinghai, Song Yulin, Li Dejin, Shao Jianmin, Xu Junzhi, Liu Huakai, Wu Yingguo, Shen Yuehui, Feng Sicheng. Vascular endothelial growth factor 165 genes transfected into bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct a vascularized amphiphilic peptide gel module [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1903-1911. |
| [6] | Wang Qisa, Lu Yuzheng, Han Xiufeng, Zhao Wenling, Shi Haitao, Xu Zhe. Cytocompatibility of 3D printed methyl acrylated hyaluronic acid/decellularized skin hydrogel scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1912-1920. |
| [7] | Gao Yanguo, Guo Xu, Li Xiaohan, Chen Shiqi, Zhu Haitao, Huang Liangyong, Ye Fang, Lu Wei, Wang Qibin, Zheng Tao, Chen Li. Optimization of prescription ratio of “Honghuangbai” gel by orthogonal test in diabetic skin wound mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1921-1928. |
| [8] | Liu Hongjie, Mu Qiuju, Shen Yuxue, Liang Fei, Zhu Lili. Metal organic framework/carboxymethyl chitosan-oxidized sodium alginate/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes healing of diabetic infected wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [9] | Min Changqin, Huang Ying. Construction of pH/near-infrared laser stimuli-responsive drug delivery system and its application in treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1940-1951. |
| [10] | Shao Ziyu, Li Qian, Qumanguli·Abudukelimu, Han Youjun, Hu Yang. Preparation and characterization properties of three different ratios of biphasic calcium phosphate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1952-1961. |
| [11] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [12] | Zhou Hongli, Wang Xiaolong, Guo Rui, Yao Xuanxuan, Guo Ru, Zhou Xiongtao, He Xiangyi. Fabrication and characterization of nanohydroxyapatite/sodium alginate/polycaprolactone/alendronate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1962-1970. |
| [13] | Yang Lixia, Diao Liqin, Li Hua, Feng Yachan, Liu Xin, Yu Yuexin, Dou Xixi, Gu Huifeng, Xu Lanju. Regulatory mechanism of recombinant type III humanized collagen protein improving photoaging skin in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1988-2000. |
| [14] |
Dong Chunyang, Zhou Tianen, Mo Mengxue, Lyu Wenquan, Gao Ming, Zhu Ruikai, Gao Zhiwei.
Action mechanism of metformin combined with Eomecon chionantha Hance dressing in treatment of deep second-degree burn wounds#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013.
|
| [15] | Pan Zhiyi, Huang Jiawen, Xue Wenjun, Xu Jianda. Advantages of MXene-based flexible electronic sensors and their application in monitoring diabetic foot wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2023-2032. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||