Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1988-2000.doi: 10.12307/2026.565
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulatory mechanism of recombinant type III humanized collagen protein improving photoaging skin in rats
Yang Lixia1, Diao Liqin2, Li Hua1, Feng Yachan1, Liu Xin1, Yu Yuexin1, Dou Xixi3, Gu Huifeng1, Xu Lanju1
- 1Hebei NACOL Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shijiazhuang 050035, Hebei Province, China; 2Hebei Institute of Drug and Medical Device Inspection and Research, Shijiazhuang 050035, Hebei Province, China; 3Lushang Freda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Jinan 250101, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-25Accepted:2025-01-25Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-17 -
Contact:Xu Lanju, PhD, Principal senior engineer, Hebei NACOL Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shijiazhuang 050035, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Yang Lixia, MS, Senior engineer, Hebei NACOL Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shijiazhuang 050035, Hebei Province, China Diao Liqin, Senior engineer, Hebei Institute of Drug and Medical Device Inspection and Research, Shijiazhuang 050035, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:Hebei Province International Science and Technology Cooperation Demonstration Enterprise, No. 2022-1-1 (to XLJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Lixia, Diao Liqin, Li Hua, Feng Yachan, Liu Xin, Yu Yuexin, Dou Xixi, Gu Huifeng, Xu Lanju. Regulatory mechanism of recombinant type III humanized collagen protein improving photoaging skin in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1988-2000.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
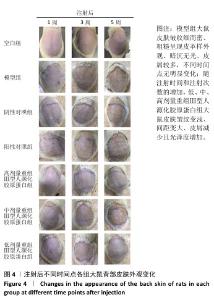
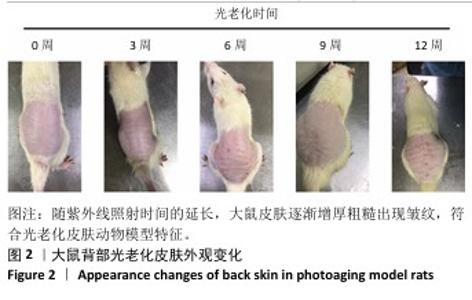
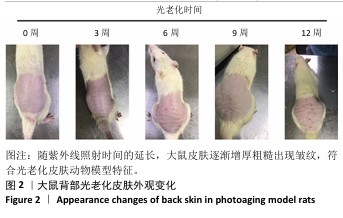
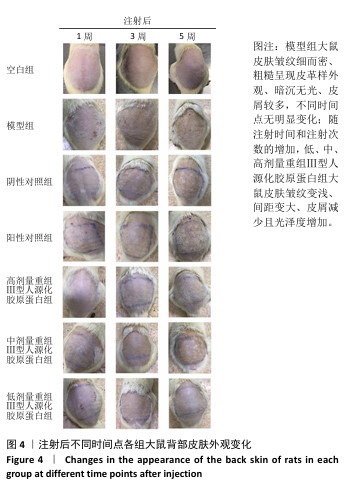
2.4 重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白改善大鼠光老化皮肤外观观察结果 见图4。 注射1周后,空白组大鼠皮肤柔软、无皮屑、无色素沉着;模型组大鼠皮肤粗糙、皮屑较多且局部伴有结痂,自然状态下皮肤皱纹密而深,皮肤暗沉;阴性对照组和阳性对照组大鼠皮肤粗糙、无光泽、皮屑较多、触感粗糙,其中阳性对照组皮肤呈现皱纹变宽变浅趋势,与模型组相比皮肤状态有所改善,但不明显;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组大鼠皮肤光泽度均明显增加、皮屑减少、皱纹变少变浅,色素沉着明显减轻,与模型组比较差异明显,并且改善程度与重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白剂量呈正比。 注射3周后,空白组皮肤外观同注射1周后皮肤外观基本相同;模型组大鼠皮肤粗糙、暗沉无光泽、皱纹密而深;阴性对照组仍可见细而深的皱纹,皮肤粗糙、无光泽、皮屑较多,皮肤色素沉着明显,皮肤外观和模型组相比无明显改善;阳性对照组皮肤皱纹进一步变浅,但仍可明显分辨皱纹痕迹,皮肤色素沉着明显、皮屑较多;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组皮肤外观较注射1周时均有进一步改善,主要表现为皮屑减少、皮肤皱纹变少变浅,其中高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组已经几乎看不出原皱纹存在的痕迹,色素沉着明显减轻,感官上皮肤光泽度和细腻度增加。 注射5周后,空白组皮肤外观同注射1周后皮肤外观基本相同;模型组皮肤皱纹密而深,触感粗糙且局部伴有结痂,与注射1周后观察结果一致;阴性对照组皮肤皱纹仍清晰可辨,皮肤粗糙、无光泽、皮屑较多、皮肤色素沉着明显,与注射3周后观察结果相似;阳性对照组皮肤皱纹进一步变浅,但仍可明显分辨皱纹痕迹,皮肤色素沉着明显,皮屑较多,与注射3周后观察结果一致;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组大鼠皮肤较注射3周后进一步改善,皱纹进一步变浅,高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组几乎已经没有皱纹痕迹,色素沉淀减轻,皮肤触感柔软,毛发再生均匀和密集,低、中剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组仍可见皮肤皱纹痕迹,但皮屑减少,观感上皮肤光泽度和细腻度上升。 综上所述,模型组主要表现为皮肤皱纹细而密、粗糙呈现皮革样外观、皮肤暗沉无光、皮屑较多,同组内不同时间点外观无明显变化,说明紫外照射可加速皮肤老化,并且动物对光老化皮肤的自我修复缓慢;牛Ⅰ型胶原蛋白对光老化皮肤具有修复作用,但修复作用有限,不能彻底改善皮肤光老化现象;重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白具有修复皮肤光老化的作用,并且修复效果显著高于动物源性胶原蛋白。"
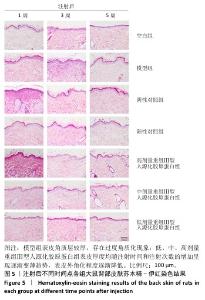
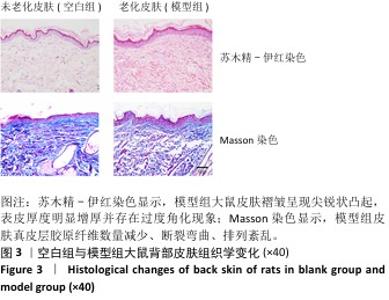
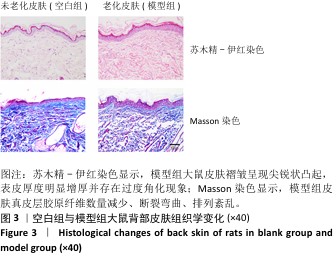
2.5 重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白改善大鼠光老化皮肤组织学染色观察结果 见图5,6。 2.5.1 苏木精-伊红染色 注射1周后,空白组表皮较薄、厚度均匀,表皮呈现平滑的波浪起伏状,真皮胶原纤维分布均匀,无断裂卷曲等,未见炎症细胞;与空白组相比,模型组表皮增厚,表皮层凹凸不平且伴有尖锐凸起,存在过度角质化现象,真皮层胶原纤维数量减少、变性断裂,排列紊乱、稀松,并且可见散落的炎症细胞;与模型组相比,阴性对照组表皮厚度仍较厚,表皮层凸起的尖锐程度有所减轻,皮屑较多,与该组皮肤外观一致,真皮层胶原纤维卷曲断裂、排列紊乱,真皮近表皮位置有疑似胶原增生现象,并能观察到散落的炎症细胞;阳性对照组表皮厚度仍较厚,但表皮尖锐状凸起减少,呈现相对平缓起伏状,能观察到皮肤角化情况,与该组皮肤外观一致,真皮层胶原纤维卷曲断裂、排列紊乱,并能观察到散落的炎症细胞;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组表皮厚度明显变薄且均匀,偶见尖锐状凸起,但整体趋于平缓,角化程度减轻,真皮层中未见胶原增生,但部分位置仍能观察到因胶原断裂、卷曲等形成的基质“空隙”,说明胶原排列不够紧密。 注射3周后,空白组表皮较薄平缓、厚度均匀,表皮外无角化现象,真皮胶原纤维分布均匀、无断裂卷曲等,未见炎症细胞;与空白组相比,模型组表皮较厚,表皮层凹凸不平且伴有尖锐凸起,并存在过度角质化现象,真皮层胶原纤维数量减少、变性断裂、排列紊乱稀松,并且可见散落的炎症细胞,与注射1周后表现类似;与模型组相比,阴性对照组表皮仍较厚,凸起的尖锐程度有所减轻,依然存在角化现象,与该组皮肤皮屑较多现象一致,真皮层胶原纤维卷曲断裂、排列紊乱,真皮近表皮位置有疑似胶原增生现象,并能观察到散落的炎症细胞;阳性对照组表皮厚度减小,但表皮仍不够平缓,表皮外仍存在角化现象,与该组皮肤外观一致,真皮层胶原卷曲减轻、排列略显紊乱,真皮层中仍能观察到散落的炎症细胞;除中剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组表皮厚度略大外,低、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组表皮厚度均明显变小,3组表皮均呈现出平缓的起伏状态,表皮外角化程度降低,真皮层中胶原纤维排列整齐、无断裂卷曲现象,真皮层中偶见少量炎症细胞。 注射5周后,空白组表皮薄而均匀,平缓无角化现象,真皮胶原纤维分布均匀,无断裂卷曲等、未见炎症细胞;与空白组相比,模型组表皮仍较厚,表皮层凹凸不平且伴有小的尖锐凸起,表皮存在过度角质化现象,真皮层胶原纤维数量减少、变性断裂、排列紊乱稀松,并且可见散落的炎症细胞,与注射1周后的表现类似;阴性对照组与模型组相似,表皮仍较厚,凸起的尖锐程度的有所减轻,依然存在角化现象,与该组皮肤皮屑较多一致,真皮层胶原纤维卷曲断裂、排列紊乱,真皮近表皮位置有疑似胶原增生现象,并能观察到散落的炎症细胞;阳性对照组表皮厚度与模型组类似,表皮外仍存在角化现象,与该组皮肤外观一致,真皮层胶原卷曲减轻、排列略显紊乱,真皮层中仍能观察到散落的炎症细胞;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组表皮薄且均匀,整体上表皮呈现平缓的波浪状,表皮外角化程度明显降低,真皮层中胶原纤维排列整齐、无断裂卷曲现象,真皮层中未见炎症细胞,以低剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组表皮形态最接近空白组,但低剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组真皮层中胶原分布显得疏松不够紧密,高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组真皮层胶原纤维排列紧密。综合分析,高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组对老化皮肤的修复效果更好,这与外观观察结果一致,说明重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白修复光老化皮肤的效果可能与实验剂量呈正比。 综上所述,空白组不同时间点均表现为表皮较薄,真皮层胶原分布均匀排列整齐;模型组表皮则持续性增厚,真皮层中胶原排列相对紊乱,可见炎症细胞分布;阴性对照组和阳性对照组对老化皮肤的修复效果不明显,尤其是阴性对照组观察到真皮近表皮位置出现了胶原增生现象,注射3周后表皮出现了短暂变薄现象,可能是实验动物的个体差异或者是真皮注射方式对表皮层的短暂刺激反应,但最终未改变阴性对照组和阳性对照组表皮厚度较大的趋势;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组表皮厚度均随注射时间和注射次数的增加呈现逐渐变薄趋势,表皮外角化程度逐渐降低,真皮层中胶原蛋白排列逐渐整齐、均匀、紧密,说明重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白可以逐渐修复光老化皮肤。 "

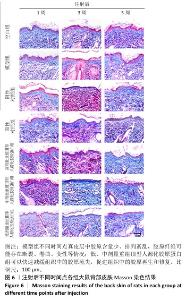
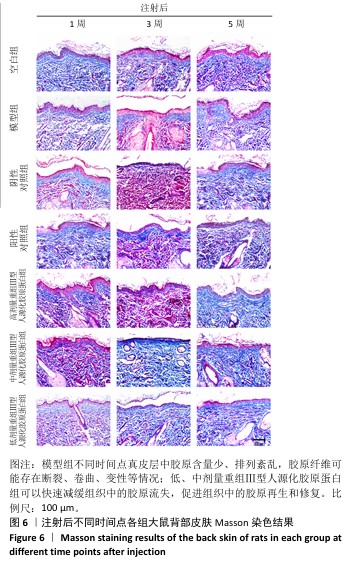
2.5.2 Masson染色 注射1周后,空白组真皮层中胶原含量丰富、分布均匀;模型组真皮层胶原数量减少、分布不均匀,胶原纤维断裂卷曲、排列稀疏,造成细胞外基质存在“空洞”现象;与模型组相比,阴性对照组胶原明显减少,分布主要集中在真皮层近表皮位置,说明注射生理盐水对胶原再生的促进作用不大;阳性对照组和低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组细胞外基质中的胶原增多,胶原卷曲、断裂现象有所缓解。 注射3周后,空白组整体趋势同注射1周后的结果;模型组真皮层胶原数量减少、分布不均匀,主要集中在真皮近表皮位置;与模型组相比,阴性对照组真皮层胶原含量明显减少,主要集中在真皮层近表皮位置;阳性对照组和低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组真皮层胶原含量增加,主要集中在真皮层中的近表皮位置,中、低剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组胶原含量甚至超过空白组,但是高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组胶原分布不均匀,主要分布在真皮层和表皮层交界处,以点状形式分布在真皮层中,分析可能是动物的个体差异或者是Masson染色脱色时间较长,但并未改变高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组中胶原含量增加的趋势。 注射5周后,空白组整体趋势同注射1周后的结果;模型组真皮层胶原含量升高,但多呈点状分布,说明胶原仍可能存在断裂、卷曲等现象,在真皮近表皮位置染色条带模糊,胶原可能存在增生或者是溶解现象,这与苏木精-伊红染色结果一致;与模型组相比,阴性对照组整体胶原含量升高,可能是持续的注射刺激胶原再生,也可能是动物个体差异,但表皮部分仍较厚、角化现象明显,真皮层变化未能改变皮肤老化外观;阳性对照组真皮层胶原含量升高,接近空白组;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组真皮层胶原含量随着剂量增加而增加,胶原呈现条索状分布均匀而密实,均优于模型组,并且无胶原增生现象,表皮层均平缓而薄,说明老化皮肤从内到外均得到修复。 综上所述,空白组不同时间点真皮层胶原均含量丰富、分布均匀,模型组不同时间点真皮层中胶原含量少、排列紊乱,胶原纤维可能存在断裂、卷曲、变性等情况;模型组、阴性对照组和阳性对照组注射3周后真皮层胶原被破坏的程度最大、流失最多,随着时间延长,大鼠自身的应激和修复能力也会促使自身组织中胶原的合成与再生,因此在注射5周后胶原含量有所增加;高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组可能并不能快速改善组织中的胶原流失速度,但中、低剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组可以快速减缓组织中的胶原流失,促进组织中的胶原再生和修复,由内而外修复光老化组织。"
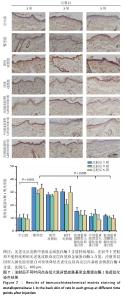
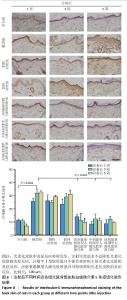
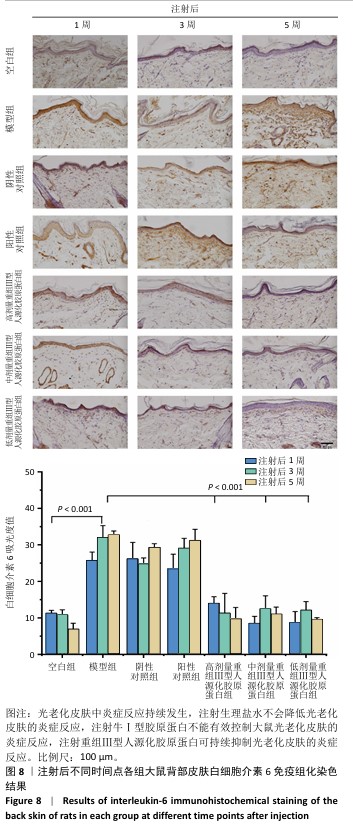
2.6 重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白影响光老化特征蛋白表达 2.6.1 重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白调控基质金属蛋白酶1/白细胞介素6表达 见图7,8。 为进一步探究重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白改善大鼠光老化皮肤的作用机制,利用免疫组化染色对基质金属蛋白酶1及白细胞介素6的表达进行定位检测。基质金属蛋白酶1是一种含锌内肽酶,可降解真皮胶原蛋白和其他细胞外基质分子,它被认为是细胞衰老和与年龄相关的皮肤变化的最重要指标之一[13]。基质基质金属蛋白酶1主要见于细胞质和真皮表层,呈散在或灶状分布。 (1)基质金属蛋白酶1含量:注射1周后,空白组基质金属蛋白酶1含量较少;模型组基质金属蛋白酶1含量较多,为空白组的两三倍;阴性对照组和阳性对照组基质金属蛋白酶1含量与模型组相比无显著差异,说明注射生理盐水或者牛Ⅰ型胶原蛋白均不能快速降低光老化皮肤组织中基质金属蛋白酶1含量;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组基质金属蛋白酶1含量较模型组显著降低,中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组基质金属蛋白酶1含量水平接近空白组。注射3周后,空白组基质金属蛋白酶1含量与注射1周后相当;模型组基质金属蛋白酶1含量较注射1周后减少,但仍明显高于空白组;阴性对照组基质金属蛋白酶1含量较注射1周后略降低,但与模型组相比无显著差异;阳性对照组基质金属蛋白酶1含量较模型组降低1/4,对胶原的降解能力减弱,这与注射3周后Masson蓝染增加结果一致;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组基质金属蛋白酶1含量约为模型组的一半。注射5周后,空白组基质金属蛋白酶1含量与注射1周后相当;与空白组相比,模型组基质金属蛋白酶1含量仍处于高水平表达;阴性对照组基质金属蛋白酶含量与模型组比无显著差异;阳性对照组基质金属蛋白酶1含量较注射3周后增加;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组基质金属蛋白酶1含量较模型组减少了2/3,中剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组基质金属蛋白酶1含量更趋近于空白组,说明该重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白可以显著抑制皮肤内基质金属蛋白酶1表达,从而减少基质金属蛋白酶1对胶原的降解,减缓真皮内胶原的流失速度。 结果表明,注射生理盐水不会降低光老化皮肤组织内基质金属蛋白酶1含量,注射牛Ⅰ型胶原不能持续抑制大鼠皮肤真皮层内基质金属蛋白酶1含量,分析可能是种间差异存在潜在的免疫反应或者应激反应;重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白对光老化皮肤的修复作用可能与抑制大鼠皮肤组织中基质金属蛋白酶1表达水平,从而减少其对胶原的破坏有关。 (2)白细胞介素6含量:从细胞层面上看,免疫细胞是衰老细胞的关键调控因子。随着年龄增长,大多数免疫细胞呈现出衰老特征,对内表现为难以清除衰老/受损细胞,对外表现为机体抵抗力减弱。其中白细胞介素6炎性细胞因子是调控皮肤局部炎症反应的重要细胞因子[14]。白细胞介素6主要分布于胞浆中。 注射1周后,空白组白细胞介素6含量不高;模型组白细胞介素6含量升高,为空白组的两三倍,说明光老化后皮肤炎症水平升高,这与苏木精-伊红染色结果中可见炎症细胞散落分布的结果一致;阴性对照组白细胞介素6含量与模型组相比无显著差异,但高于空白组;阳性对照组白细胞介素6含量与模型组相比差异不显著,说明补充牛Ⅰ型胶原蛋白不能有效控制白细胞介素6水平;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组白细胞介素6含量与模型组相比均显著较少,中、低剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组白细胞介素6含量甚至比空白组更少。注射3周后,空白组白细胞介素6含量与注射1周后相近;模型组中白细胞介素6含量进一步升高,说明光老化后皮肤炎症水平加剧;阴性对照组白细胞介素6含量低于模型组,但高于空白组;阳性对照组白细胞介素6含量较注射1周后升高;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组白细胞介素6含量均显著低于模型组,接近空白组水平。注射5周后,空白组白细胞介素6含量仍较低;模型组白细胞介素6含量较注射3周后略升高,提示光老化后的皮肤中白细胞介素6可能存在累积效应,这与苏木精-伊红染色结果持续观察到老化组织中的炎症细胞分布结果一致;阴性对照组白细胞介素6含量与模型组相当,显著高于空白组;阳性对照组白细胞介素6含量进一步升高,说明牛Ⅰ型胶原蛋白不能缓解老化皮肤的炎症反应;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组白细胞介素6含量显著低于模型组,接近空白组水平,说明组织中的炎症水平得到抑制,与苏木精-伊红染色结果一致。 "
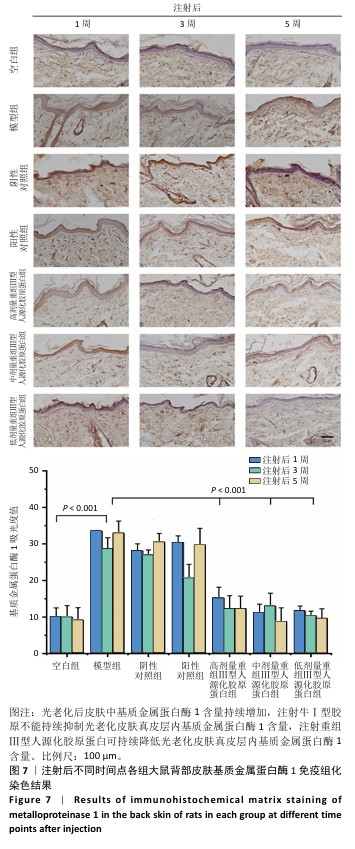
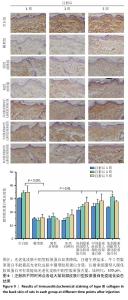
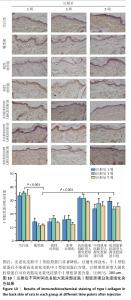
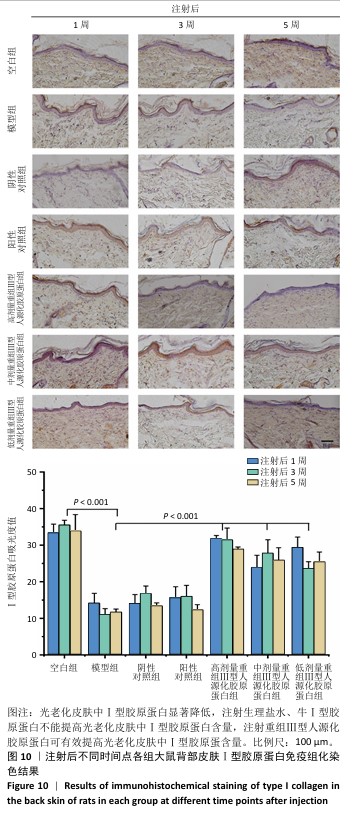
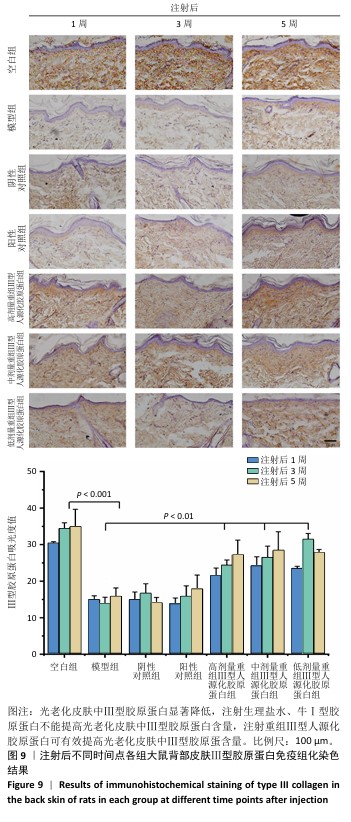
结果表明,光老化后皮肤组织中炎症反应持续发生,单纯注射生理盐水不会降低光老化皮肤的炎症反应,注射牛Ⅰ型胶原蛋白也不能有效控制大鼠光老化皮肤的炎症反应,注射重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋可持续抑制光老化皮肤的炎症反应,改善皮肤状态。 2.6.2 重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白促进Ⅰ型胶原蛋白/Ⅲ型胶原蛋白表达 见图9,10。 重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白可以通过减少基质金属蛋白酶1对胶原的降解作用以及白细胞介素6介导的组织炎症反应,进而抑制组织老化;此外,胶原蛋白含量多少是判断组织年轻化的重要依据之一,其中皮肤中含量较多的胶原蛋白为Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原蛋白,因此,实验进一步考察了重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白对皮肤中Ⅰ型胶原蛋白/Ⅲ型胶原蛋白表达水平的影响。 (1) Ⅲ型胶原蛋白含量:注射1,3,5周后,空白组Ⅲ型胶原蛋白含量丰富;模型组Ⅲ型胶原蛋白含量显著低于空白组;阴性对照组、阳性对照组Ⅲ型胶原蛋白含量与模型组相比无显著差别;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组Ⅲ型胶原蛋白含量显著高于模型组。说明光老化后皮肤内Ⅲ型胶原蛋白损失严重,注射生理盐水与牛Ⅰ型胶原蛋白不能有效提高光老化皮肤内Ⅲ型胶原蛋白含量,注射重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白可以提高光老化皮肤内Ⅲ型胶原蛋白含量,抑制组织衰老。 (2) Ⅰ型胶原蛋白含量:Ⅰ型胶原蛋白主要集中在细胞外基质及细胞质中,主要起到组织支撑作用。Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的减少会造成组织塌陷,宏观上表现出皮肤松弛、皱纹产生等老化特征,因此,此次研究探讨了注射重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白对组织中Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的影响。注射1,3,5周后,空白组Ⅰ型胶原蛋白含量丰富;模型组Ⅰ型胶原蛋白含量始终低于空白组,说明光老化皮肤中Ⅰ型胶原蛋白被破坏,大量流失;阴性对照组和阳性对照组Ⅰ型胶原蛋白含量与模型组相比无显著差异;低、中、高剂量重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白组Ⅰ型胶原蛋白含量均明显高于模型组。 结果表明,光老化皮肤中Ⅰ型胶原蛋白含量减少,还可能存在断裂、卷曲、变性等,导致Ⅰ型胶原蛋白对皮肤支撑作用减弱,最终造成皮肤外观松弛、皱纹产生;注射生理盐水、牛Ⅰ型胶原蛋白不能提高光老化皮肤内Ⅰ型胶原蛋白含量,注射重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白后可有效提高光老化皮肤内Ⅰ型胶原蛋白含量,宏观上表现为皮肤塌陷减轻、皮肤紧致、皱纹减少,这与观察到的皮肤外观相一致。"
| [1] FITSIOU E, PULIDO T, CAMPISI J, et al. Cellular Senescence and the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype as Drivers of Skin Photoaging. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141(4S):1119-1126. [2] ANSARY TM, HOSSAIN MR, KAMIYA K, et al. Inflammatory Molecules Associated with Ultraviolet Radiation-Mediated Skin Aging. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:3974. [3] GENDRISCH F, ESSER PR, SCHEMPP CM, et al. Luteolin as a modulator of skin aging and inflammation. Biofactors. 2021;47:170-80. [4] VIERKÖTTER A, KRUTMANN J. Environmental influences on skin aging and ethnic-specific manifestations. Dermatoendocrinol. 2012;4(3): 227-231. [5] YAO WZ, CHEN XY, LI X, et al. Current trends in the anti-photoaging activities and mechanisms of dietary non-starch polysaccharides from natural resources. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62:9021-9035. [6] SHARMA A, KUHAD A, BHANDARI R. Novel nanotechnological approaches for treatment of skin-aging. J Tissue Viabil. 2022;31(3): 374-386. [7] 马淑骅,孙娅楠,杨伟峰,等.重组人源胶原蛋白对激光损伤大鼠皮肤修复作用及机制研究[J].激光生物学报,2018,27(5):399-406. [8] HE Y, WANG J, SI Y, et al. A novel gene recombinant collagen hemostatic sponge with excellent biocompatibility and hemostatic effect. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;178:296-305. [9] YANG Y, RITCHIE AC, EVERITT NM. Using type Ⅲ recombinant human collagen to construct a series of highly porous scaffolds for tissue regeneration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;208:112139. [10] 范婷,赵健烽,常烨珺,等.重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白对皮肤功能性相关基因表达的影响[J].日用化学工业(中英文),2022,52(12): 1326-1332. [11] LIU T, HAO J, LEI H, et al. Recombinant collagen for the repair of skin wounds and photo-aging damage. Regen Biomater. 2024;11:rbae108. [12] LEE JE, OH J, SONG D, et al. Acetylated Resveratrol and Oxyresveratrol Suppress UVB-Induced MMP-1 Expression in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(8):1252. [13] 李张军,牛新武,肖生祥,等.大鼠皮肤光老化动物模型建立方法的改良[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2016,37(1):144-147,156. [14] 吴文伯,陈敏亮,吴焱秋,等.富血小板血浆对大鼠光老化皮肤的改善作用[J]. 中华医学美学美容杂志,2018,24(6):445-448. [15] 尹斌,蒋献.端粒与皮肤老化[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志,2009,23(5): 313-315. [16] 曹迪,陈瑾,黄琨,等.皮肤光老化 SD大鼠模型的构建及评价标准的探讨[J].重庆医科大学学报,2016,41(4):379-383. [17] LEE YI, LEE SG, JUNG I, et al. Topical Application of Peptide Nucleic Acid Antisense Oligonucleotide for MMP-1 and Its Potential Anti-Aging Properties. J Clin Med. 2023;12(7):2472. [18] PALDOR M, LEVKOVITCH-SIANY O, EIDELSHTEIN D, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals a senescence-associated IL-6/CCR6 axis driving radiodermatitis. EMBO Mol Med. 2022;14(8):e15653. [19] BHARDWAJ SK, SINGH H, DEEP A, et al. UVC-based photoinactivation as an efficient tool to control the transmission of coronaviruses. Sci Total Environ. 2021;792:148548. [20] BATTIE C, JITSUKAWA S, BERNERD F, et al. New insights in photoaging, UVA induced damage and skin types. Exp Dermatol. 2014;1:7-12. [21] KIM DJ, IWASAKI A, CHIEN AL, et al. UVB-mediated DNA damage induces matrix metalloproteinases to promote photoaging in an AhR-and SP1-dependent manner. JCI Insight. 2022;7(9):e156344. [22] JEONG EH, YANG H, KIM JE, et al. Safflower Seed Oil and Its Active Compound Acacetin Inhibit UVB-Induced Skin Photoaging. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;30(10):1567-1573. [23] CSEKES E, RACKOVÁ L. Skin Aging, Cellular Senescence and Natural Polyphenols. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:12641. [24] WANG YJ, OUYANG QQ, CHANG XF, et al. Anti-photoaging effects of flexible nanoliposomes encapsulated Moringa oleifera Lam. isothiocyanate in UVB-induced cell damage in HaCaT cells. Drug Deliv. 2022;29:871-881. [25] MCCARTY MF, BENZVI C, VOJDANI A, et al. Nutraceutical strategies for alleviation of UVB phototoxicity. Exp Dermatol, 2023;32(6):722-730. [26] 孙侠,刘香梅,庞增雄,等.不同时间紫外线照射对SD大鼠的皮肤光毒性损伤作用[J].实验动物与比较医学,2019,39(2):124-130. [27] BORUMAND M, SIBILLA S. Daily consumption of the collagen supplement Pure Gold Collagen® reduces visible signs of aging. Clin Interv Aging. 2014;9:1747-1758. [28] LIU H, DONG J, DU R, et al. Collagen study advances for photoaging skin. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2024;40(1):e12931. [29] WANG J, QIU H, XU Y, et al. The biological effect of recombinant humanized collagen on damaged skin induced by UV-photoaging: An in vivo study. Bioact Mater. 2021;11:154-165. [30] ZHANG Y, WANG Y, LI Y, et al. Application of Collagen-Based Hydrogel in Skin Wound Healing. Gels. 2023;9(3):185. [31] KIM YU, GI H, JEONG EK, et al. Development of a highly effective recombinant protein from human collagen type Ⅲ Alpha 1 (COL3A1) to enhance human skin cell functionality. BMB Rep. 2024;57(9):424-429. [32] WALIMBE T, CALVE S, PANITCH A, et al. Incorporation of types I and III collagen in tunable hyaluronan hydrogels for vocal fold tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2019;87:97-107. [33] YOU S, LIU S, DONG X, et al. Intravaginal administration of human type III collagen-derived biomaterial with high cell-adhesion activity to treat vaginal atrophy in rats. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(4):1977-1988. [34] HUA C, ZHU Y, XU W, et al. Characterization by high-resolution crystal structure analysis of a triple-helix region of human collagen type III with potent cell adhesion activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508(4):1018-1023. [35] FRANK M, ALBUISSON J, RANQUE B, et al. The type of variants at the COL3A1 gene associates with the phenotype and severity of vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015;23:1657-1664. [36] QIAN H, SHAN Y, GONG R, et al. Mechanism of action and therapeutic effects of oxidative stress and stem cell-based materials in skin aging: Current evidence and future perspectives. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;10:1082403. [37] PITTAYAPRUEK P, MEEPHANSAN J, PRAPAPAN O, et al. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Photoaging and Photocarcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(6):868. [38] LEE MJ, AGRAHARI G, KIM HY, et al. Extracellular Superoxide Dismutase Prevents Skin Aging by Promoting Collagen Production through the Activation of AMPK and Nrf2/HO-1 Cascades. J Invest Dermatol. 2021; 141:2344-2353.e7. [39] LI X, LI C, ZHANG W, et al. Inflammation and aging: signaling pathways and intervention therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):239. [40] DOMASZEWSKA-SZOSTEK A, PUZIANOWSKA-KUZNICKA M, KURYLOWICZ A. Flavonoids in Skin Senescence Prevention and Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:6814. [41] SHIN SM, BAEK EJ, KIM KH, et al. Polydeoxyribonucleotide exerts opposing effects on ERK activity in human skin keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Mol Med Rep. 2023;28(2):148. |
| [1] | Haonan Yang, Zhengwei Yuan, Junpeng Xu, Zhiqi Mao, Jianning Zhang. Preliminary study on the mechanisms and efficacy of deep brain stimulation in treating depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Sun Lei, Zhang Qi, Zhang Yu. Pro-osteoblastic effect of chlorogenic acid protein microsphere/polycaprolactone electrospinning membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1877-1884. |
| [3] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [4] | Li Qingbin, Lin Jianhui, Huang Wenjie, Wang Mingshuang, Du Jiankai, Lao Yongqiang. Bone cement filling after enlarged curettage of giant cell tumor around the knee joint: a comparison of subchondral bone grafting and non-grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [5] | Jiang Xinghai, Song Yulin, Li Dejin, Shao Jianmin, Xu Junzhi, Liu Huakai, Wu Yingguo, Shen Yuehui, Feng Sicheng. Vascular endothelial growth factor 165 genes transfected into bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct a vascularized amphiphilic peptide gel module [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1903-1911. |
| [6] | Yang Xuetao, Zhu Menghan, Zhang Chenxi, Sun Yimin, Ye Ling. Applications and limitations of antioxidant nanomaterials in oral cavity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
| [7] | Gao Yanguo, Guo Xu, Li Xiaohan, Chen Shiqi, Zhu Haitao, Huang Liangyong, Ye Fang, Lu Wei, Wang Qibin, Zheng Tao, Chen Li. Optimization of prescription ratio of “Honghuangbai” gel by orthogonal test in diabetic skin wound mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1921-1928. |
| [8] | Liu Hongjie, Mu Qiuju, Shen Yuxue, Liang Fei, Zhu Lili. Metal organic framework/carboxymethyl chitosan-oxidized sodium alginate/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes healing of diabetic infected wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [9] | Min Changqin, Huang Ying. Construction of pH/near-infrared laser stimuli-responsive drug delivery system and its application in treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1940-1951. |
| [10] | Shao Ziyu, Li Qian, Qumanguli·Abudukelimu, Han Youjun, Hu Yang. Preparation and characterization properties of three different ratios of biphasic calcium phosphate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1952-1961. |
| [11] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [12] | Zhou Hongli, Wang Xiaolong, Guo Rui, Yao Xuanxuan, Guo Ru, Zhou Xiongtao, He Xiangyi. Fabrication and characterization of nanohydroxyapatite/sodium alginate/polycaprolactone/alendronate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1962-1970. |
| [13] | Wang Qisa, Lu Yuzheng, Han Xiufeng, Zhao Wenling, Shi Haitao, Xu Zhe. Cytocompatibility of 3D printed methyl acrylated hyaluronic acid/decellularized skin hydrogel scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1912-1920. |
| [14] |
Dong Chunyang, Zhou Tianen, Mo Mengxue, Lyu Wenquan, Gao Ming, Zhu Ruikai, Gao Zhiwei.
Action mechanism of metformin combined with Eomecon chionantha Hance dressing in treatment of deep second-degree burn wounds#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013.
|
| [15] | Pan Zhiyi, Huang Jiawen, Xue Wenjun, Xu Jianda. Advantages of MXene-based flexible electronic sensors and their application in monitoring diabetic foot wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2023-2032. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||