Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1940-1951.doi: 10.12307/2026.607
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction of pH/near-infrared laser stimuli-responsive drug delivery system and its application in treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
Min Changqin1, Huang Ying2
- 1Chengdu Wenjiang District People’s Hospital, Chengdu 611100, Sichuan Province, China; 2Hospital of Chengdu Office of the People’s Government of Tibet Autonomous Region, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-09Accepted:2025-03-19Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-16 -
Contact:Huang Ying, Attending physician, Hospital of Chengdu Office of the People’s Government of Tibet Autonomous Region, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Min Changqin, MS, Attending physician, Chengdu Wenjiang District People’s Hospital, Chengdu 611100, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Min Changqin, Huang Ying. Construction of pH/near-infrared laser stimuli-responsive drug delivery system and its application in treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1940-1951.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
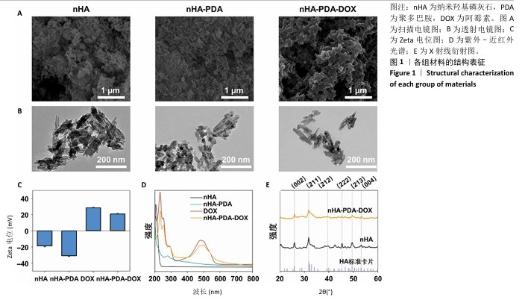
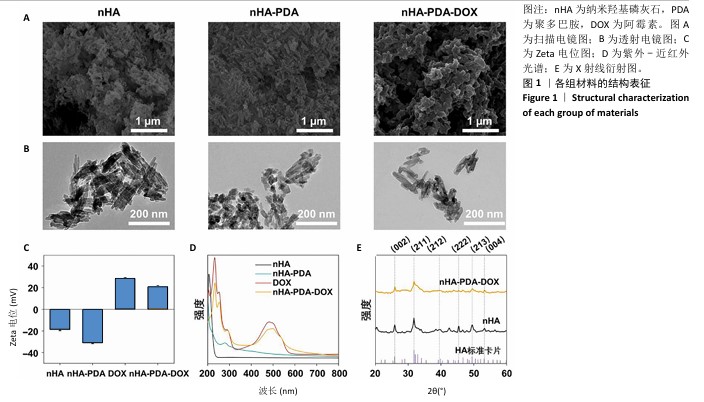
2.1 纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体的性能表征结果 使用液氮冻干纳米羟基磷灰石、纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体后喷金,利用扫描电镜测试3组材料形貌,结果如图1A所示,3组材料呈均匀的棒状结构。 透射电镜观察结果也显示纳米羟基磷灰石、纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体呈均匀的棒状结构,见图1B,粒径分别为(123.67±4.36),(129.13±6.44),(137.29± 9.51) nm,证实聚多巴胺和阿霉素成功包覆在纳米羟基磷灰石载体上。 采用动态激光粒度分析仪检测样品的Zeta电位和水合粒径,结果如图1C所示。纳米羟基磷灰石和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺均呈负电荷,Zeta电位分别为(-18.63±1.09) mV和(-31.07±0.76 ) mV,阿霉素溶液的Zeta电位为(27.57±0.85) mV,纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体的电位为(20.60±1.33) mV。纳米羟基磷灰石、纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体的水合粒径分别(156.12±8.91),(164.79±10.38),(171.82±7.72) nm。表面电荷和水合粒径的变化证实纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体制备成功。 使用紫外-可见光-近红外分光光度计检测样品光谱,结果如图1D所示。纳米羟基磷灰石在200-800 nm段未见明显吸收峰,纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺在279 nm处出现吸收峰,证实聚多巴胺被成功修饰。与阿霉素溶液相比较(在483 nm处出现明显吸收峰),纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体在497 nm处出现更宽、更低的吸收峰,表明阿霉素被成功负载到纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺上。 X射线衍射结果如图1E所示。制备的纳米羟基磷灰石与羟基磷灰石标准卡片(JCPDS 09-0432)的经典六方相晶型相匹配,纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体的结晶度下降,但未改变其晶相。纳米羟基磷灰石和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体在25.89°,31.75°,39.47°,46.64°,49.53°和53.31°处的衍射峰分别对应(002)(211)(212)(222)(213)和(004)晶面。 "
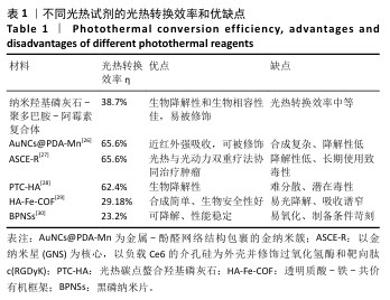
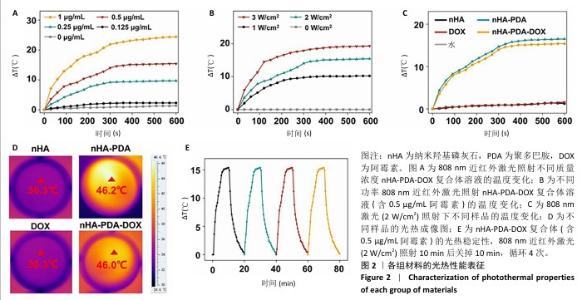
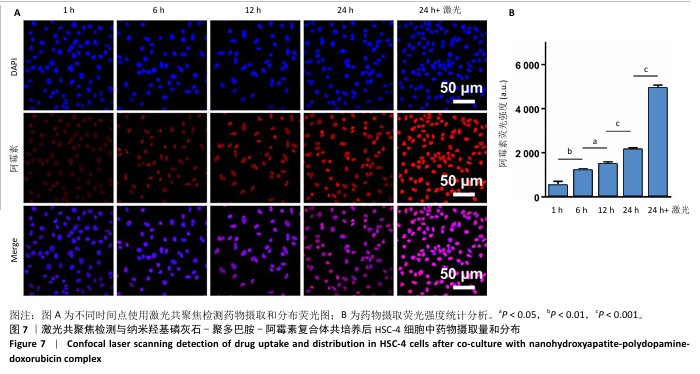
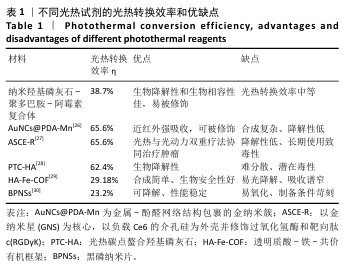
使用808 nm近红外激光照射不同质量浓度纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体溶液,记录温度变化,结果如图2A所示。随着复合体质量浓度的增加,溶液温度升高,光热升温能力呈浓度依赖性增加,当复合体(含0.5 μg/mL阿霉素)被照射10 min时温度为46 ℃,大于肿瘤消融阈值42 ℃,因此后续选择此质量浓度进行后续实验。 为进一步优化激光照射条件,使用不同效率的808 nm近红外激光照射纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体溶液,结果如图2B所示。随着激光功率的增加,溶液温度增加,照射10 min后,0,1,2,3 W/cm2激光照射后的溶液温度分别为41.2,46,49.7 ℃。由于41.2 ℃低于肿瘤消融阈值,并且文献报道温度在42-48 ℃范围内对肿瘤细胞有较强的杀伤作用而对正常细胞相对安全[25],49.7 ℃远高于正常细胞的安全温度,因此选择808 nm近红外激光(2 W/cm2)照射纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体(含0.5 μg/mL阿霉素)。 采用808 nm近红外激光以2 W/cm2的功率照射不同样品10 min,溶液温度变化如图2C所示。空白对照(水)组、纳米羟基磷灰石组和阿霉素组未见明显温度变化,纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺组和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体组随着照射时间的增加溶液温度逐渐升高,照射10 min后两者温度分别达到46.2 ℃和46.0 ℃(图2D)。 采用激光照射纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体10 min后关掉10 min,循环4次,记录温度变化,结果如图2E所示。4次循环中溶液温度变化趋势和最高温度没有明显变化,具有光热稳定性。根据公式计算纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体的光热转换效率约为38.7%。表1列举了常见光热试剂的光热转换效率及优缺点。综合评估光热试剂的光热转换效率、生物降解性和生物安全性等,纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素具有优异的临床应用前景。 "
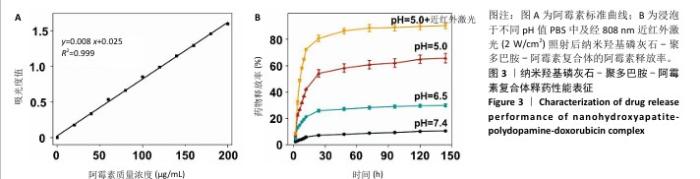
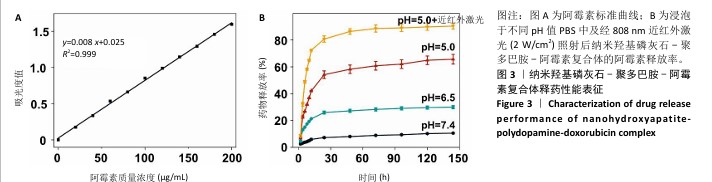
配制不同质量浓度的阿霉素溶液,通过紫外分光光度计检测吸光度值,并拟合得到阿霉素标准曲线:y=0.008 x+0.025(R2=0.999),见图3A。利用阿霉素标准曲线,计算出纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体的包封率和载药量分别为(72.27±3.29)%和(10.23±0.96) μg/mg。 浸泡于不同pH值PBS中及经808 nm近红外激光(2 W/cm2)照射后,纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体的阿霉素释放率结果如图3B所示。纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体可以持续释放144 h,前24 h药物快速释放,24 h后药物释放速度变慢;经过144 h,在pH=7.4,6.5,5.0 PBS中的药物释放率分别为(10.60±0.31)%,(29.96±1.16)%和(65.68±3.58)%。复合体中阿霉素的释放率随着浸泡液pH值的降低而增加,呈pH值刺激响应性释药;经过808 nm近红外激光照射后,复合体的药物释放率明显增加到(90.33±2.11)%,呈近红外激光刺激响应性释药。"
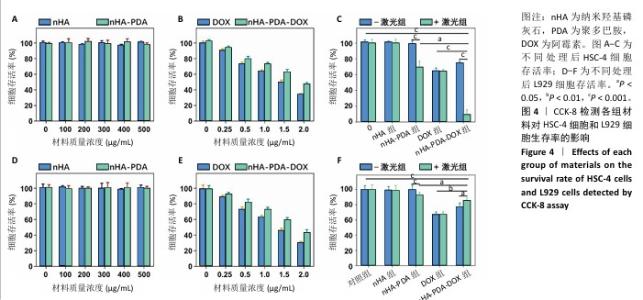
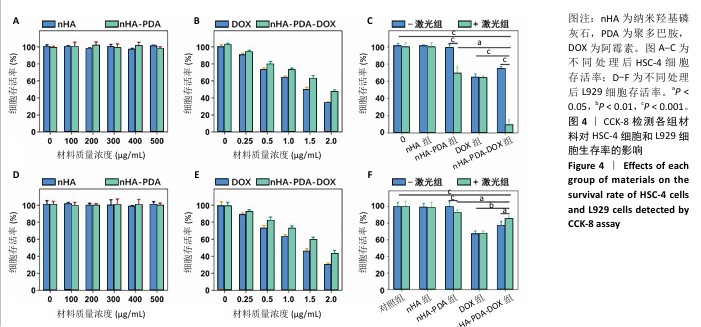
2.2 纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体的抗癌性能 采用CCK-8法检测各组样品对HSC-4细胞和L929细胞的毒性,结果如图4所示。不同质量浓度纳米羟基磷灰石和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺与细胞共培养24 h后,HSC-4细胞和L929细胞的存活率明显高于90%,说明纳米羟基磷灰石和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺无明显细胞毒性。不同质量浓度的阿霉素和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体与HSC-4细胞和L929细胞共培养后,随着阿霉素和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体质量浓度的增加,HSC-4细胞和L929细胞存活率下降,当阿霉素质量浓度为2 μg/mL时,阿霉素组和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体组HSC-4细胞存活率分别为(33.66±1.74)%和(47.17±2.26)%,L929细胞存活率分别为(30.32±1.67)%和(43.17±3.74)%。 将纳米羟基磷灰石、纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺、阿霉素和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体与HSC-4和L929细胞共培养12 h后,用808 nm近红外激光以2 W/cm2功率照射5 min后继续培养12 h,结果显示纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体+激光组HSC-4细胞存活率(9.02±6.43)%,明显低于光热治疗组[纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺+激光组,(69.54±7.51%)]和化学治疗组[阿霉素组,(64.57±3.89)%],说明光热-化学联合治疗组杀伤肿瘤的效果明显高于单一的光热治疗和化学治疗;纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体+激光组L929细胞存活率(85.69±3.12)%高于化学治疗组(66.90±3.63)%。 以上结果表明,在808 nm近红外激光照射下,纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体对肿瘤细胞具有较强的细胞毒性,而对正常细胞具有一定的保护作用。 "
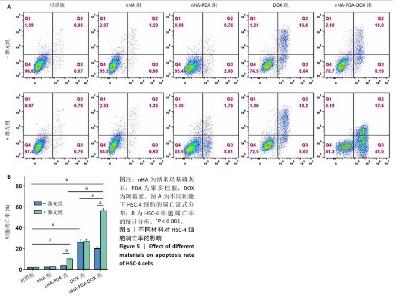
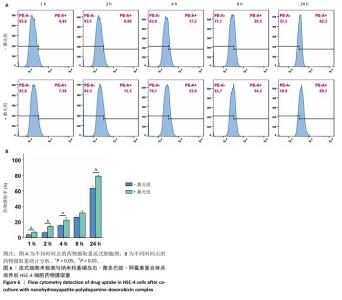
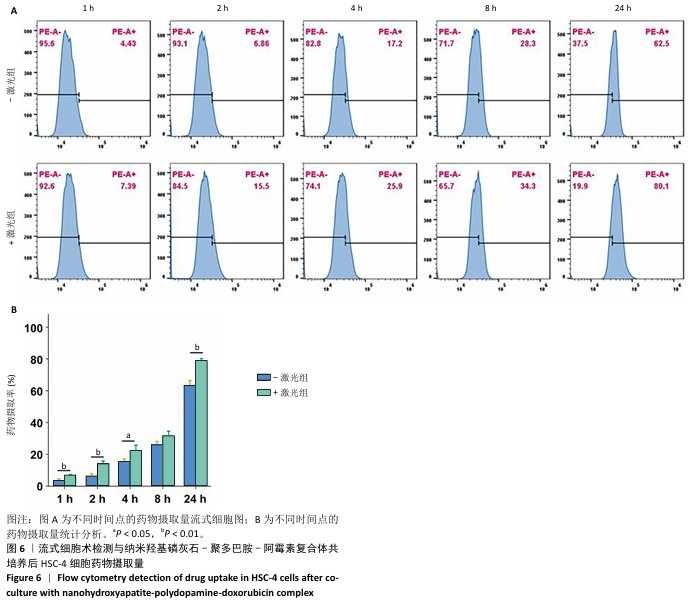
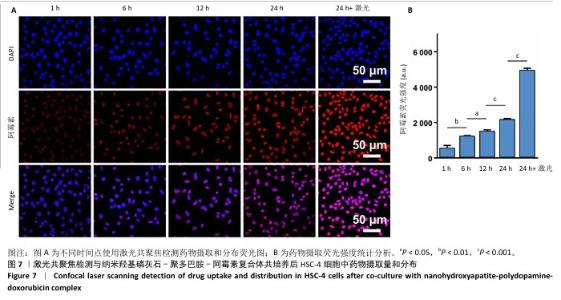
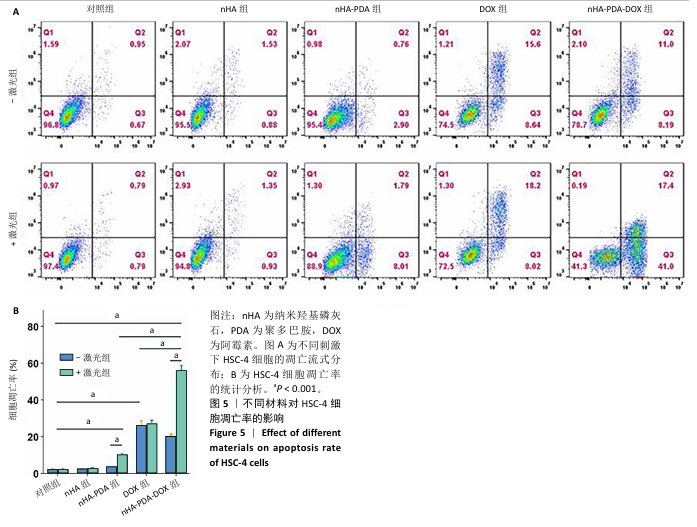
采用流式细胞术考察纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体对HSC-4细胞凋亡的影响,结果如图5所示。近红外激光组、纳米羟基磷灰石组、纳米羟基磷灰石+激光组和纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺组细胞凋亡率分别为(2.15±0.50)%,(2.53±0.11)%,(2.70±0.43)%和(3.72±0.06)%,与对照组细胞凋亡率(2.14±0.56)%比较无明显差异。单一光热治疗组(纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺+激光)和化学治疗组(阿霉素)细胞凋亡率增加到(10.18±0.42)%和(26.08±2.48)%,与对照组比较差异有显著性意义;此外,光热-化学联合治疗组(纳米羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-阿霉素复合体+激光)细胞凋亡率进一步增加,高达(55.93±2.79)%,明显高于任何单一治疗方式。"
| [1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. [2] TANG Q, XIE M, YU S, et al. Periodic Oxaliplatin Administration in Synergy with PER2-Mediated PCNA Transcription Repression Promotes Chronochemotherapeutic Efficacy of OSCC. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;6(21):1900667. [3] SMYTH EC, LAGERGREN J, FITZGERALD RC, et al. Oesophageal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17048. [4] TIAN Y, TANG C, SHI G, et al. Novel fluorescent GLUT1 inhibitor for precision detection and fluorescence image-guided surgery in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2022;151(3):450-462. [5] PIETZSCH S, WOHLAN K, THACKERAY JT, et al. Anthracycline-free tumor elimination in mice leads to functional and molecular cardiac recovery from cancer-induced alterations in contrast to long-lasting doxorubicin treatment effects. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021;116(1):61. [6] LIU T, ZHU M, CHANG X, et al. Tumor-Specific Photothermal-Therapy-Assisted Immunomodulation via Multiresponsive Adjuvant Nanoparticles. Adv Mater. 2023;35(18):e2300086. [7] REN Y, YAN Y, QI H. Photothermal conversion and transfer in photothermal therapy: From macroscale to nanoscale. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;308:102753. [8] PALMER LC, NEWCOMB CJ, KALTZ SR, et al. Biomimetic systems for hydroxyapatite mineralization inspired by bone and enamel. Chem Rev. 2008;108(11):4754-4783. [9] WANG R, HUA Y, WU H, et al. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles promote TLR4 agonist-mediated anti-tumor immunity through synergically enhanced macrophage polarization. Acta Biomater. 2023;164:626-640. [10] ZHANG K, ZHOU Y, XIAO C, et al. Application of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in tumor-associated bone segmental defect. Sci Adv. 2019;5(8):eaax6946. [11] YANG Y, YANG J, ZHU N, et al. Tumor-targeting hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for remodeling tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) by activating mitoDNA-pyroptosis pathway in cancer. J Nanobiotechnol. 2023;21(1):470. [12] KANG Y, SUN W, LI S, et al. Oligo Hyaluronan-Coated Silica/Hydroxyapatite Degradable Nanoparticles for Targeted Cancer Treatment. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;6(13):1900716. [13] CHENG X, XU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Glucose-Targeted Hydroxyapatite/Indocyanine Green Hybrid Nanoparticles for Collaborative Tumor Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(31):37665-37679. [14] CHANG L, HUANG S, ZHAO X, et al. Preparation of ROS active and photothermal responsive hydroxyapatite nanoplatforms for anticancer therapy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;125:112098. [15] ALFIERI ML, WEIL T, NG DYW, et al. Polydopamine at biological interfaces. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;305:102689. [16] FU Y, YANG L, ZHANG J, et al. Polydopamine antibacterial materials.Mater Horiz. 2021;8(6):1618-1633. [17] LIAO J, LI W, PENG J, et al. Combined cancer photothermal-chemotherapy based on doxorubicin/gold nanorod-loaded polymersomes. Theranostics. 2015;5(4):345-356. [18] NI W, WU J, FANG H, et al. Photothermal-Chemotherapy Enhancing Tumor Immunotherapy by Multifunctional Metal-Organic Framework Based Drug Delivery System. Nano Lett. 2021;21(18):7796-7805. [19] YANG G, LI M, SONG T, et al. Polydopamine-Engineered Theranostic Nanoscouts Enabling Intracellular HSP90 mRNAs Fluorescence Detection for Imaging-Guided Chemo-Photothermal Therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(23):e2201615. [20] DING T, XIAO Y, SAIDING Q, et al. Capture and Storage of Cell-Free DNA via Bio-Informational Hydrogel Microspheres. Adv Mater. 2024; 36(33):e2403557. [21] LIU L, ZHAO X. Preparation of environmentally responsive PDA&DOX@LAC live drug carrier for synergistic tumor therapy. Sci Rep.2024;14(1):15927. [22] CHEN Z, SUN Y, WANG J, et al. Dual-Responsive Triple-Synergistic Fe-MOF for Tumor Theranostics. ACS Nano. 2023;17(10):9003-9013. [23] ZHANG Y, KONG F, WU D, et al. Hydrothermal Extraction and Characterization of Natural Hydroxyapatite from Waste Bovine Femur Bone. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2023;29(11): 535-544. [24] HE S, ZHENG Q, MA L, et al. Mucin-Triggered Osmium Nanoclusters as Protein-Corona-Like Nanozymes with Photothermal-Enhanced Peroxidase-Like Activity for Tumor-Specific Therapy. Nano Lett. 2024; 24(45):14337-14345. [25] WU J, LIU J, LIN B, et al. Met-Targeted Dual-Modal MRI/NIR II Imaging for Specific Recognition of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(4):1640-1650. [26] YANG T, DAI L, LIU J, et al. Metal-phenolic-network-coated gold nanoclusters for enhanced photothermal/chemodynamic/immunogenic cancer therapy. Bioact Mater. 2025;44:447-460. [27] ZHANG L, YANG XQ, WEI JS, et al. Intelligent gold nanostars for in vivo CT imaging and catalase-enhanced synergistic photodynamic & photothermal tumor therapy. Theranostics. 2019;9(19):5424-5442. [28] LIU G, LI B, LI J, et al. Photothermal Carbon Dots Chelated Hydroxyapatite Filler: High Photothermal Conversion Efficiency and Enhancing Adhesion of Hydrogel. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023; 15(48):55335-55345. [29] CHEN Y, FENG T, ZHU X, et al. Ambient Synthesis of Porphyrin-Based Fe-Covalent Organic Frameworks for Efficient Infected Skin Wound Healing. Biomacromolecules. 2024;25(6): 3671-3684. [30] LI S, ZHANG Y, WEN W, et al. A high-sensitivity thermal analysis immunochromatographic sensor based on au nanoparticle-enhanced two-dimensional black phosphorus photothermal-sensing materials. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;133:223-229. [31] KATO K, MACHIDA R, ITO Y, et al. Doublet chemotherapy, triplet chemotherapy, or doublet chemotherapy combined with radiotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment for locally advanced oesophageal cancer (JCOG1109 NExT): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2024;404(10447):55-66. [32] ZHANG Z, SUN D, TANG H, et al. PER2 binding to HSP90 enhances immune response against oral squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting IKK/NF-κB pathway and PD-L1 expression. J Immunother Cancer. 2023;11(11):e007627. [33] FAROKHI M, MOTTAGHITALAB F, SAEB MR, et al. Functionalized theranostic nanocarriers with bio-inspired polydopamine for tumor imaging and chemo-photothermal therapy. J Control Release. 2019; 309:203-219. [34] POUSTCHI F, AMANI H, AHMADIAN Z, et al. Combination Therapy of Killing Diseases by Injectable Hydrogels: From Concept to Medical Applications. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(3):e2001571. [35] RATZIU V, CHARLTON M. Rational combination therapy for NASH: Insights from clinical trials and error. J Hepatol. 2023;78(5):1073-1079. [36] FANE M, WEERARATNA AT. How the ageing microenvironment influences tumour progression. Nature reviews Cancer 2020;20(2):89-106. [37] CHEN J, XIANG Y, BAO R, et al. Combined Photothermal Chemotherapy for Effective Treatment Against Breast Cancer in Mice Model. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:9973-9987. [38] 李璐,刘怡萌,李楠楠,等.多功能19F磁共振/CT成像及光热/化学联合治疗纳米平台用于肿瘤诊疗[J]. 化学试剂,2023,45(9):47-55. [39] CHEN T, ZHUANG B, HUANG Y, et al. Inhaled curcumin mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles against radiation pneumonitis. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12(5):2522-2532. [40] YUAN Z, LIN C, HE Y, et al. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Nitric-Oxide-Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy and Low-Temperature Photothermal Therapy for Biofilm Elimination. ACS Nano. 2020;14(3):3546-3562. [41] WANG Z, LI Z, SHI Y, et al. Mesoporous polydopamine delivery system for intelligent drug release and photothermal-enhanced chemodynamic therapy using MnO(2) as gatekeeper. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbad087. [42] NIEZNI D, HARRIS Y, SASON H, et al. Polydopamine Copolymers for Stable Drug Nanoprecipitation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12420. [43] VIGER ML, SANKARANARAYANAN J, DE GRACIA LUX C, et al. Collective activation of MRI agents via encapsulation and disease-triggered release. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135(21):7847-7850. [44] HANH L, VAN HAI L, THE HOANG N, et al. In vitro biodegradation behavior of biodegradable hydroxyapatite coated AZ31 alloy treated at various pH values. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2021;19: 22808000211010037. [45] LI D, HUANG X, WU Y, et al. Preparation of pH-responsive mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for intracellular controlled release of an anticancer drug. Biomater Sci. 2016;4(2):272-280. [46] CHEN W, MENG F, CHENG R, et al. pH-Sensitive degradable polymersomes for triggered release of anticancer drugs: a comparative study with micelles. J Control Release. 2010;142(1):40-46. [47] LIU J, HUANG Y, KUMAR A, et al. pH-sensitive nano-systems for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32(4):693-710. [48] ESKANDANI M, JAHANBAN-ESFAHLAN R, SADUGHI MM, et al. Thermal-responsive β-cyclodextrin-based magnetic hydrogel as a de novo nanomedicine for chemo/hyperthermia treatment of cancerous cells. Heliyon. 2024;10(11):e32183. [49] WU D, JI W, XU S, et al. Near-infrared Light-Triggered Size-Shrinkable theranostic nanomicelles for effective tumor targeting and regression. Int J Pharm. 2024;658:124203. [50] ZHOU T, WU L, MA N, et al. Photothermally responsive theranostic nanocomposites for near-infrared light triggered drug release and enhanced synergism of photothermo-chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023;8(1):e10368. [51] SHIN HH, CHOI HW, LIM JH, et al. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Thermo-responsive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Pyrrole Nanocomposites for Chemo-photothermal Cancer Therapy. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2020; 15(1):214. [52] BAE Y, FUKUSHIMA S, HARADA A, et al. Design of environment-sensitive supramolecular assemblies for intracellular drug delivery: polymeric micelles that are responsive to intracellular pH change. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2003;42(38):4640-4643. [53] GE R, LIN M, LI X, et al. Cu(2+)-Loaded Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided pH- and Near-Infrared-Light-Stimulated Thermochemotherapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(23):19706-19716. [54] WANG H, HAN Z, LIU Y, et al. Recyclable Composite Membrane of Polydopamine and Graphene Oxide-Modified Polyacrylonitrile for Organic Dye Molecule and Heavy Metal Ion Removal. Membranes (Basel). 2022;12(10):938. [55] RENNICK JJ, JOHNSTON APR, PARTON RG. Key principles and methods for studying the endocytosis of biological and nanoparticle therapeutics. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021;16(3):266-276. [56] ZHANG S, GAO H, BAO G. Physical Principles of Nanoparticle Cellular Endocytosis. ACS Nano. 2015;9(9):8655-8671. [57] BATTAGLINI M, CARMIGNANI A, CIOBANU DZ, et al. Detailed Profiling of Protein Corona Formed by Polydopamine Nanoparticles in Human Plasma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025;17(7):10485-10498. [58] HAN M, LI Y, LU S, et al. Amyloid Protein-Biofunctionalized Polydopamine Nanoparticles Demonstrate Minimal Plasma Protein Fouling and Efficient Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(11):13743-13757. [59] ZHU Z, SU M. Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Combined Chemo- and Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017;7(7):160. [60] LI X, YANG C, TAO Y, et al. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Thermosensitive Liposomes Modified with Membrane Peptides for the Local Chemo/Photothermal Therapy of Melanoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2021;14:1317-1329. [61] BORDAT A, BOISSENOT T, NICOLAS J, et al. Thermoresponsive polymer nanocarriers for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019; 138:167-192. [62] XU C, ZHANG J, ZHANG J, et al. Near Infrared-Triggered Nitric Oxide-Release Nanovesicles with Mild-Photothermal Antibacterial and Immunomodulation for Healing MRSA-Infected Diabetic Wounds. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(31):e2402297. |
| [1] | Haonan Yang, Zhengwei Yuan, Junpeng Xu, Zhiqi Mao, Jianning Zhang. Preliminary study on the mechanisms and efficacy of deep brain stimulation in treating depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Yang Xuetao, Zhu Menghan, Zhang Chenxi, Sun Yimin, Ye Ling. Applications and limitations of antioxidant nanomaterials in oral cavity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
| [3] | Sun Lei, Zhang Qi, Zhang Yu. Pro-osteoblastic effect of chlorogenic acid protein microsphere/polycaprolactone electrospinning membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1877-1884. |
| [4] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [5] | Li Qingbin, Lin Jianhui, Huang Wenjie, Wang Mingshuang, Du Jiankai, Lao Yongqiang. Bone cement filling after enlarged curettage of giant cell tumor around the knee joint: a comparison of subchondral bone grafting and non-grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [6] | Jiang Xinghai, Song Yulin, Li Dejin, Shao Jianmin, Xu Junzhi, Liu Huakai, Wu Yingguo, Shen Yuehui, Feng Sicheng. Vascular endothelial growth factor 165 genes transfected into bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct a vascularized amphiphilic peptide gel module [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1903-1911. |
| [7] | Wang Qisa, Lu Yuzheng, Han Xiufeng, Zhao Wenling, Shi Haitao, Xu Zhe. Cytocompatibility of 3D printed methyl acrylated hyaluronic acid/decellularized skin hydrogel scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1912-1920. |
| [8] | Gao Yanguo, Guo Xu, Li Xiaohan, Chen Shiqi, Zhu Haitao, Huang Liangyong, Ye Fang, Lu Wei, Wang Qibin, Zheng Tao, Chen Li. Optimization of prescription ratio of “Honghuangbai” gel by orthogonal test in diabetic skin wound mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1921-1928. |
| [9] | Liu Hongjie, Mu Qiuju, Shen Yuxue, Liang Fei, Zhu Lili. Metal organic framework/carboxymethyl chitosan-oxidized sodium alginate/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes healing of diabetic infected wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [10] | Shao Ziyu, Li Qian, Qumanguli·Abudukelimu, Han Youjun, Hu Yang. Preparation and characterization properties of three different ratios of biphasic calcium phosphate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1952-1961. |
| [11] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [12] | Zhou Hongli, Wang Xiaolong, Guo Rui, Yao Xuanxuan, Guo Ru, Zhou Xiongtao, He Xiangyi. Fabrication and characterization of nanohydroxyapatite/sodium alginate/polycaprolactone/alendronate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1962-1970. |
| [13] | Yang Lixia, Diao Liqin, Li Hua, Feng Yachan, Liu Xin, Yu Yuexin, Dou Xixi, Gu Huifeng, Xu Lanju. Regulatory mechanism of recombinant type III humanized collagen protein improving photoaging skin in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1988-2000. |
| [14] |
Dong Chunyang, Zhou Tianen, Mo Mengxue, Lyu Wenquan, Gao Ming, Zhu Ruikai, Gao Zhiwei.
Action mechanism of metformin combined with Eomecon chionantha Hance dressing in treatment of deep second-degree burn wounds#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013.
|
| [15] | Pan Zhiyi, Huang Jiawen, Xue Wenjun, Xu Jianda. Advantages of MXene-based flexible electronic sensors and their application in monitoring diabetic foot wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2023-2032. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||