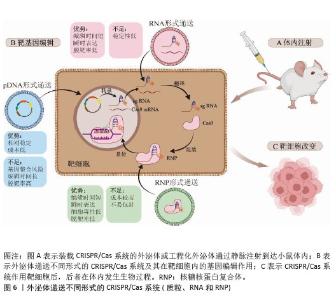
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 1839-1849.doi: 10.12307/2026.633
Previous Articles Next Articles
Exosome-delivered CRISPR/Cas system enables gene editing in target cells
Wang Baiyan1, 2, Yang Shu1, Wang Yiming1, Wu Mengqing3, Xiao Yu4, Guo Zixuan1, Zhang Boyi1, Feng Shuying1, 2
- 1Medical College, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Henan Engineering Research Center of Special Medical Food of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 3School of Pediatric Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 4School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2025-02-25Revised:2025-06-19Accepted:2025-07-03Online:2026-03-08Published:2025-08-21 -
Contact:Feng Shuying, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Medical College, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; Henan Engineering Research Center of Special Medical Food of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
About author:Wang Baiyan, MS, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Medical College, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; Henan Engineering Research Center of Special Medical Food of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Natural Science Foundation, No. 232300421164 (to FSY); Basic Research Project of Henan Provincial Key Scientific Research Project, No. 23ZX005 (to FSY); Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research and Development Joint Fund, No. 232301420070 (to FSY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Baiyan, Yang Shu, Wang Yiming, Wu Mengqing, Xiao Yu, Guo Zixuan, Zhang Boyi, Feng Shuying. Exosome-delivered CRISPR/Cas system enables gene editing in target cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1839-1849.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
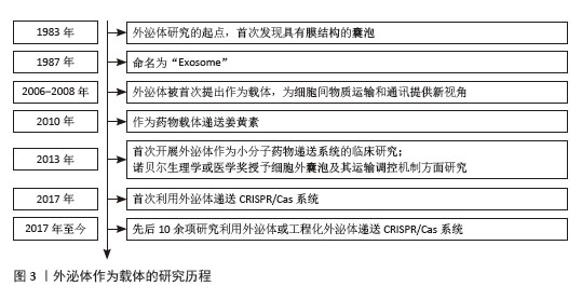
2.1 外泌体简介 2.1.1 外泌体及其作为载体的研究历程 1983年,在绵羊网织红细胞体外培养液中,Eberhard G. Trams和R.M.Johnstone通过电子显微镜首次发现具有膜结构的囊泡,这一发现标志着外泌体研究的起点[10]。在随后的1987年,Johnstone将其命名为“exosome”[11]。2006-2008年,首次提出外泌体可以作为载体,介导RNA和蛋白质在细胞间转移,为理解细胞间物质运输和通讯提供了新视 角[12-14]。2010年,外泌体作为药物载体,能够提高姜黄素的溶解度、稳定性和生物利用度,并增强其对特定细胞群的传递,从而发挥治疗作用[15]。 2013年,首次展开外泌体作为小分子(化疗)药物递送系统的临床试验(NCT01854866)。同年,James E. Rothman 等因在细胞外囊泡及其运输调控机制方面做出的巨大成就而获得诺贝尔生理学或医学奖。2013年后,大量学者投身于外泌体作为递送载体的研究并获得了许多重大突破,外泌体被广泛应用在癌症和感染性、心血管和神经退行性疾病领域[16]。2017年,研究者们首次使用来自卵巢癌细胞系SKOV3和人类胚胎肾细胞系HEK293T的天然外泌体作为载体,通过电穿孔的方式将靶向聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶1基因的CRISPR/Cas系统以质粒的形式进行装载,成功地靶向了SKOV3细胞并使得聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶1表达减少[17-18]。2017年至今,先后10余项研究利用外泌体及工程化外泌体作为CRISPR/Cas系统的递送载体,为CRISPR/Cas系统递送载体的发展提供了新的可能,见图3。"
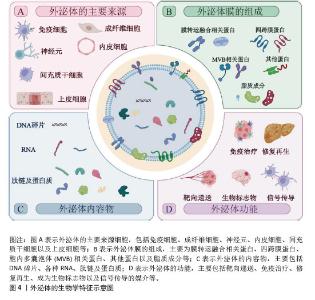
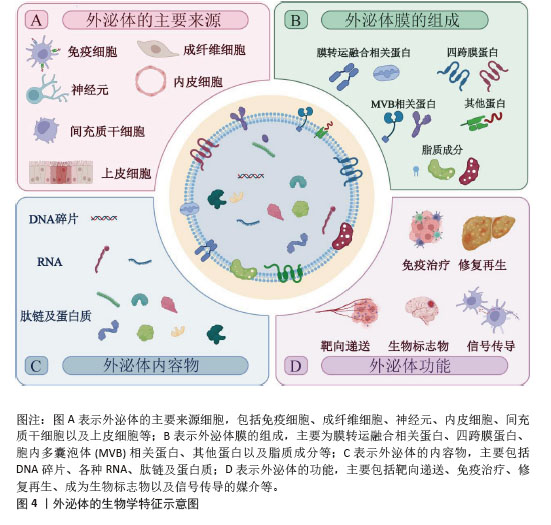
2.1.2 外泌体的生物学特征和功能 外泌体是一种由各种细胞(如免疫细胞、间充质干细胞、成纤维细胞、神经元、内皮细胞和上皮细胞等)分泌到细胞外液(如血液、脑脊液、尿液、唾液等)中的直径30-150 nm的脂质囊泡[19],这些囊泡中包裹着大量蛋白质、核酸和其他生物活性分子。根据外泌体数据库(http://www.exocarta.org)的最新列表,外泌体中包含13 472种蛋白质、4 946种mRNA、10 755种miRNA和3 946种脂质。其中,外泌体蛋白主要包括:①膜转运和融合相关蛋白,如膜联蛋白和热休克蛋白(HSP60、HSP70和HSP90);②四跨膜蛋白(CD9、CD63、CD81、CD82、CD106和细胞间黏附分子1);③胞内多囊泡体相关蛋白,例如ALIX和TSG101(外泌体表征的生物标志物);④其他蛋白质,如整合素(细胞黏附相关蛋白)、肌动蛋白和肌球蛋白[20-21]。 外泌体的脂质组成包括胆固醇、鞘磷脂、己糖神经酰胺、磷脂酰丝氨酸和饱和脂肪酸,这些都是质膜的组分[22]。核酸复合物(如DNA、mRNA和非编码RNA)也构成了外泌体内容物的一部分,其中miRNA是外泌体中最丰富的RNA种类之一,其他的外泌体RNA包括核糖体RNA、长链非编码RNA、转运RNA、核小RNA、小核仁RNA等[23]。 正是因为外泌体的生物特性及其所包含的大量内容物,使得外泌体功能众多,其中靶向递送是外泌体最基本、最重要的生物学功能;此外,外泌体在信号传导、免疫治疗、各种疾病模型中的修复和再生、作为多种疾病的生物标志物等方面表现出不俗的潜力[24-26],见图4。"

2.1.3 外泌体的递送功能 外泌体的递送功能主要体现在生物信息传递、药物递送以及疫苗抗原呈递等方面。如外泌体装载HIV感染的T细胞所衍生的miR-155-5p,直接从感染T细胞转移到宫颈癌细胞,随后通过减少其靶基因AT丰富结合域2的表达来激活ERCC5-NF-κB信号通路,从而促进宫颈癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[27]。外泌体也可以充当体内外药物递送的载体,利用工程化外泌体将抗癌药物5-氟尿嘧啶和miR-21抑制剂寡核苷酸(miR-21i)递送到表达人表皮生长因子受体2的癌细胞中,结果显示出其强大的抗肿瘤作用[28]。此外,外泌体在充当疫苗载体方面也日渐成熟。装载新生抗原的工程化外泌体能够显著改善淋巴结运输和免疫原性,使得患黑色素瘤和结肠癌的小鼠产生了更高水平的肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素12,维持了患癌小鼠的免疫平衡,同时也显著促进了CD4+T和CD8+T细胞的增殖,展现了外泌体作为纳米疫苗递送平台的光明前景[29]。因此,外泌体强大的递送功能是其成为CRISPR/Cas系统递送载体的前提条件。 2.2 CRISPR/Cas系统的生物特征及现有递送载体的不足 2.2.1 CRISPR/Cas系统的生物特征 CRISPR/Cas系统是一种强大的基因编辑工具,为基因世界的发展带来了无限的可能性[30]。当前CRISPR/Cas系统因其靶向设计简单、编辑效率高、多路敲入/敲出能力、低成本和快速的循环时间已成为基因校正、转录调控、疾病建模和核酸成像的可靠基因组编辑平台[30-31]。CRISPR/Cas系统共计两大类6个型,其中最为成熟的为Ⅱ型CRISPR/Cas9系统,包含Cas9核酸酶、CRISPR RNA(crRNA)和反式激活RNA (trans-activating RNA,tracrRNA)3个核心元件[32-33]。crRNA和tracrRNA部分互补配对形成双链RNA,命名为gRNA (guide RNA),发挥引导Cas9靶向切割DNA的作用;Cas9具有2个不同的结构域:HNH结构域负责切割与crRNA互补的DNA链,而RuvC结构域则切割另一条DNA链。辅助元件PAM是一个短序列基序,与crRNA相邻,其不仅有助于单导向RNA(sgRNA)-Cas9对靶DNA的识别和初始结合,还能激发Cas9的活性[34]。 尽管该系统潜力巨大,但仍需解决靶向递送载体等一些挑战才能使其充分发挥作用;此外,潜在的脱靶效应,即发生目标外的基因组改变并导致不可预测且可能有害的后果,也成为CRISPR/Cas系统需要解决的困难之一[35]。 2.2.2 CRISPR/Cas系统递送载体的类型与比较 CRISPR/Cas系统的递送方法有病毒(慢病毒、腺病毒和腺相关病毒等)载体、非病毒(脂质纳米颗粒、细胞穿透肽、金纳米颗粒、聚合物和细胞外囊泡等)载体和其他物理性的递送方法(电穿孔和显微注射等)[36-37]。目前,物理递送方法更多的是在细胞水平而非生物体水平,更适合于体外应用而非体内递送,且不恰当的物理递送可能导致不可逆转的细胞损伤甚至细胞死亡[31]。相对而言,病毒载体在体内递送的研究更加深入,目前已有多项利用病毒载体递送CRISPR/Cas系统的试验顺利在临床中展开[38]。2023年,Casgevy成为FDA批准的首个利用CRISPR/Cas9系统的基因疗法。该疗法使用CRISPR/Cas9技术,通过基因组编辑对患者的造血干细胞进行修饰,用于治疗12岁及以上患有复发性血管闭塞危象患者的镰状细胞病。值得强调的是,慢病毒也因此成为临床上首个用于CRISPR/Cas9系统的递送载体[39]。尽管如此,病毒载体的应用仍然面临着重重障碍,如宿主产生针对腺相关病毒衣壳的中和抗体、递送CRISPR/Cas元件的表达异常、应用成本高以及封装能力有限等[40]。金纳米颗粒是非病毒载体的代表,在非病毒载体中的研究也最为充分,具有可以设计成任何尺寸结构且不会引起免疫反应等优势,在多种疾病中获得良好的疗效[41];聚合物纳米颗粒是另一种广泛使用的CRISPR/Cas系统递送的非病毒载体,聚合物载体通过内吞作用跨膜运输CRISPR/Cas系统成分,且聚合物表面可以很容易地进行靶向修饰,这使得它们能够将货物输送到靶组织进而控制货物的释放[42]。非病毒载体虽具有更好的安全性、易于合成、位点特异性、可递送大片段基因和低成本等优点,但也存在着特异性低、转染效率低、生物相容性差和细胞毒性等问题,成为临床应用的主要障碍[43]。可喜的是,外泌体及其衍生物因具有较长的半衰期、靶向能力高、生物相容性良好以及无固有毒性等特性,克服了大多数脂质纳米颗粒和细胞穿透肽等非病毒药物递送系统的局限性[44-45],具有开发为CRISPR/Cas系统新型递送载体的巨大潜力。 CRISPR/Cas系统主要递送方法,见表1[31,38,40-42,46-52]。"

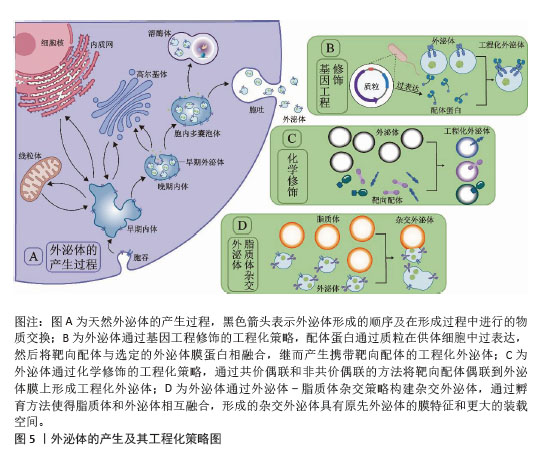
2.3 递送CRISPR/Cas系统的外泌体来源 递送CRISPR/Cas系统的外泌体主要来源于各种高产外泌体的细胞及组织。来源细胞如人卵巢腺癌细胞SKOV3[17]、人胚肾细胞HEK293T[18,53]、小鼠正常肝细胞AML12[54]、人肝星形细胞系LX-2[55]、树突状细胞[56]、子宫内膜间充质干细胞等[57],它们具有快速合成和分泌外泌体、易于进行基因转染、易于培养和增殖速率快等特点,可直接进行CRISPR/Cas系统的递送,通过装载并靶向转运CRISPR/Cas系统进而实现基因编辑。来源组织有肿瘤微环境和肿瘤组织[58-59],其中肿瘤组织可大量分泌外泌体,且这些外泌体对近处或远处的恶性细胞具有优先嗜性,因此在充当负载癌细胞凋亡相关的CRISPR/Cas系统载体方面大有作为[59]。在另一项研究中,研究者们提取并验证了来自肿瘤微环境中的天然外泌体,随后将靶向致癌基因N6-甲基腺苷阅读蛋白(YTHDF1)的CRISPR/Cas9质粒加载到该天然外泌体中并将其注射到荷瘤小鼠体内,体内示踪表明外泌体高度靶向肿瘤组织,并成功使小鼠黑色素瘤细胞B16/F10肿瘤生长受抑制[58]。值得注意的是,研究者们选择外泌体的来源并没有明确的标准,而是根据外泌体靶向细胞和CRISPR/Cas系统装载所需的条件而尽可能地选择合适来源的外泌体。 2.4 外泌体递送CRISPR/Cas系统的工程化策略 工程化外泌体是一种经过表面修饰或生物融合等技术处理的人工外泌体[60]。尽管天然外泌体作为CRISPR/Cas系统的递送载体满足了部分研究所需,但天然外泌体大规模生产困难、标准纯化方案未明确、表征成分复杂、质量控制和储存稳定性不足等主要缺陷限制了其更广泛的应用[55,61]。而工程化外泌体具有产量高、低成本、可控性和稳定性高等优势,在装载空间和药物可接受性等方面表现更为出色[61]。有研究利用CRISPR/Cas系统成功地将靶向M2型巨噬细胞的肽修饰到HEK 293T细胞来源外泌体表面,这种修饰使得该外泌体能够选择性地归巢于肿瘤组织并精确地靶向M2型巨噬细胞,实现了诱导M2型巨噬细胞向M1表型的极化。值得强调的是,该工程化外泌体在M2型巨噬细胞中的摄取率接近100%,而在非靶细胞中的摄取率不到20%,体现了工程化外泌体的优越性[62]。因此,部分研究通过对外泌体进行工程化设计,以提高外泌体的传递效率、靶向性和容量,并降低其免疫原性,更好地发挥载体作用[63]。 2.4.1 基因工程修饰策略 基因工程是外泌体表面修饰的一种常见手段,配体蛋白通过基因工程的方法在供体细胞中过表达,然后将靶向配体与选定的外泌体膜蛋白相融合,继而产生携带靶向配体的工程化外泌体[64]。有研究为提高AML12细胞来源外泌体对造血干细胞的靶向性,对AML12细胞来源外泌体进行Lamp2b-RBP4工程化,将已经构建好的Lamp2b-RBP4表达质粒转染到AML12细胞,进而使得分泌的外泌体表面携带Lamp2b-RBP4融合蛋白,从而提高AML12细胞来源外泌体对于造血干细胞的靶向性。在此基础上,将CRISPR/dCas9-SAM系统装载到该工程化外泌体中并在体内外靶向递送到造血干细胞中,成功使得造血干细胞转化为肝细胞样细胞[54]。GULEI等[59]将表达肿瘤坏死因子α蛋白的哺乳动物表达载体(pDisplay)转染到肿瘤细胞中,使得肿瘤细胞所分泌出的外泌体大量携带肿瘤坏死因子α,随后携带肿瘤坏死因子α的工程化外泌体靶向激活肿瘤坏死因子受体1以进一步激活死亡相关通路。通过这一基因工程的方法,装载CRISPR/Cas9系统的外泌体可以被设计为优先靶向肿瘤细胞,同时启动坏死性凋亡途径。 2.4.2 化学修饰策略 化学修饰也是一种常用的表面修饰技术,其通过共价偶联和非共价偶联的方法将靶向配体偶联到外泌体膜上,其中共价偶联方法更为常用[65]。为了提高外泌体-脂质体这种杂交外泌体对于人脐静脉内皮细胞的靶向性,有研究将胆固醇修饰的核酸适配体AS1411融合到杂交外泌体表面,这种化学修饰策略成功增强了AS1411修饰的杂交外泌体(CAELN)对于人脐静脉内皮细胞的靶向性。在随后的实验中,研究者通过电穿孔的方式,将靶向谷氨酸氨连接酶基因的质粒装载到CAELN中,在体内、外成功敲低了谷氨酸氨连接酶基因[66]。为了获得具有成像和治疗功能的神经胶质瘤靶向外泌体,研究者们运用点击化学的方法将外泌体膜与神经纤毛蛋白1靶向肽偶联,该工程化外泌体在体外对神经纤毛蛋白1阳性细胞具有显著的靶向能力,在体内可以顺利穿过血脑屏障,提高了神经胶质瘤靶向成像和治疗效果[67]。KIM等[68]将巨噬细胞来源外泌体修饰在聚乙二醇的冠状结构中,同时加载氨基乙酰胺,形成装载有抗癌剂紫杉醇的工程化外泌体(AA-PEG-exoPTX),该外泌体工程化过程中所形成的聚乙二醇和氨基乙酰胺复合物,高度靶向非小细胞肺癌高表达的σ受体。研究表明这种工程化外泌体具有更高的装载能力、更长的体内循环时间、可在肿瘤细胞内富集,且与肺癌转移灶的共定位率可达94.4%。 2.4.3 外泌体-脂质体杂交策略 外泌体容量小,能够运载的内容物少是外泌体成为CRISPR/Cas系统运送载体的一大障碍。脂质体和外泌体通过共孵育发生融合,杂化形成体积更大的外泌体-脂质体杂交外泌体,可以有效地包封CRISPR/Cas系统、大质粒等大分子物质,成功克服了CRISPR/Cas系统外泌体递送的体积挑战[61];此外,脂质体所带正电荷能使杂交外泌体更好地发生膜融合从而促进CRISPR/Cas系统与靶细胞的相互作用[69]。为了将非病毒S/MAR游离型载体(包含sgRNA、低氧诱导因子1敏感启动子、dCas9、转录激活结构域VP64、绿色荧光GFP基因序列、多西环素敏感基因以及2A肽序列)加载到外泌体中,研究者将来自子宫内膜间充质干细胞的衍生外泌体与表面偶联受体酪氨酸蛋白激酶ErbB4蛋白的脂质体在37 ℃下孵育12 h,成功地制造了外泌体-脂质体杂交外泌体并进行了内容物的封装。该杂交外泌体表面的ErbB4靶向滋养层膜,改善了细胞吸收以及位点特异性基因递送,有效证明了构建外泌体-脂质体杂交外泌体的可行性[57]。LIANG等[56]通过将外泌体表面蛋白Lamp2b融合软骨细胞亲和肽来构建靶向软骨细胞的外泌体(CAP-Exo),CAP-Exo再与脂质体的膜融合形成杂交CAP-Exo,杂交CAP-Exo具有更大的尺寸、更高的稳定性和相同的表面蛋白等优点。通过化学孵育将Cas9-sg-基质金属蛋白酶13(sg-MMP-13)质粒装载到杂交CAP-Exo中,在随后的实验中证明:该杂交外泌体载体成功使得Cas9-sgMMP-13基因编辑系统在体内外有效减少软骨细胞中基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,抑制软骨中细胞外基质蛋白的降解,见图5。"
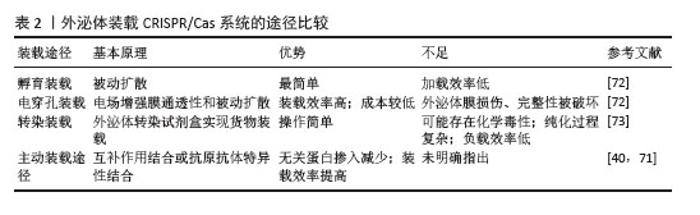
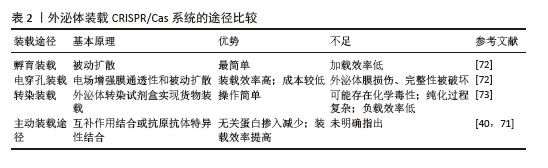
2.5 外泌体对CRISPR/Cas系统的装载 目前,外泌体装载CRISPR/Cas系统的方法包括电穿孔、孵育、转染以及主动装载途径等。选择合适的装载方法取决于被封装物质的理化性质。以往的大多数研究表明外泌体具有装载和交换小核酸(miRNAs、siRNA)至靶细胞和器官并表现出治疗效果的能力,而外泌体能否有效装载长度大于1 000碱基对的CRISPR/Cas系统质粒DNA或体积相对较大Cas蛋白,仍然是有待解决的难题[54]。 2.5.1 孵育装载 药物被装载到外泌体中最简单、侵入性最小的方法是孵育装载。为了将靶向Runt相关转录因子2基因的CRISPR干扰系统和靶向人类Catenin Beta-1基因(hCTNNB1)的CRISPR切割系统装载到HEK293T细胞外泌体中,LIN等[18]将外泌体、脂质体和CRISPR系统的混合物在37 ℃下孵育12 h,从而完成封装并证明12 h是该系统装载最佳的孵育时间,随后该外泌体成功靶向间充质干细胞并使得Runt相关转录因子2表达显著降低、hCTNNB1基因双链断裂。相似的是,为了将质粒Cas9-sg MMP-13装载到杂交CAP-Exo中,LIANG等[56]将外泌体、脂质体、质粒以及Lipofectamine2000转染试剂的混合物在37 ℃下孵育12 h,最终成功完成封装。孵育装载往往是为了将外泌体与脂质体融合以制造出更大的CRISPR/Cas系统纳米递送平台,并通过这种方法将CRISPR/Cas系统以质粒的形式加载到外泌体-脂质体杂交外泌体中。但孵育加载药物效率不高,可能与外泌体本身已携带大量的蛋白质和核酸有关。 2.5.2 电穿孔装载 电穿孔是利用施加外部电场而形成亲水孔的过程,通过形成“临时通道”将药物加载到外泌体中,然后在37 ℃下孵育使膜快速恢复完整[70]。与其他方法相比,电穿孔具有更高的加载效率和相对较低的成本,且电穿孔的参数易于控制,可将各种“货物”加载入外泌体中,装载完成后可通过计算得到载药率及装载效率。WAN等[55]将Cas9蛋白与sgRNA[p53上调凋亡调节因子单导RNA(sgPUMA)、细胞周期蛋白E1单导RNA(sgCcnE1)、组蛋白乙酰基转移酶单导RNA(sgKAT5)]混合后形成核糖核蛋白复合体(ribonucleoprotein complex,RNP),添加到外泌体悬液中,通过电穿孔有效地将混合物加载到LX-2细胞衍生外泌体中,该外泌体随后靶向库普弗细胞、肝窦内皮细胞、肝细胞和其他非实质细胞,成功上调了PUMA、CcnE1和KAT5的表达。非病毒S/MAR(支架/基质附着区)游离型载体所承载的内容物较多,包含sgRNA、低氧诱导因子1敏感启动子、dCas9、VP64、GFP基因序列、多西环素敏感基因以及基因之间2A肽序列(翻译成2A肽后,诱导细胞内重组蛋白自我剪切),YAGHOOBI等[57]通过电穿孔成功将设计的游离型S/MAR载体封装到脂质体-外泌体杂交体中。 2.5.3 转染装载 转染是利用市售的转染试剂有效地将相对应的物质加载到外泌体并成功传递至受体细胞。Mcandrew等[53]使用市售的外泌体转染试剂Exo-Fect将CRISPR/Cas9编码的质粒载体成功加载到HEK293T外泌体中,证明了该方案的可行性。但该方法与电穿孔相比,装载效率低,也无法从剩余的试剂中鉴定出成功负载的外泌体,且化学转染可能存在潜在毒性,不适用于临床治疗。 2.5.4 主动装载途径 虽然外泌体装载最常用的方式是电穿孔、孵育和转染技术,但随着一些新技术的出现解决了外泌体装载率低、无关蛋白掺入等难题,例如通过聚碳酸酯过滤器挤出和与膜透化剂孵育等方法。目前,有研究使用分裂绿色荧光蛋白互补系统来封装SaCas9和mPCSK9 sgRNA到Gectosomes[VSV-G蛋白(水泡性口炎病毒G蛋白)囊泡],随后将 Gectosomes注射到小鼠体内,成功地降低了小鼠肝脏中前蛋白转化酶枯草溶菌素9型(PCSK9)的表达。同时,分裂绿色荧光蛋白互补系统这一主动封装的方式也减少了无关蛋白的被动掺入以及提高了目标内容物的装载效率[71]。为了提高CRISPR-Cas系统内容物加载到外泌体中的效率,有研究使用GFP-GFP纳米抗体系统主动装载了靶向“stop-DsRed”序列[“stop-DsRed”序列可以用于控制下游基因(DsRed)的表达,当“stop”序列被删除,DsRed基因表达产物产生红色荧光信号]的CRISPR/Cas系统,结果表明肺癌A549细胞系“stop”序列被成功删除并产生红色荧光信号,然而,该研究并没有进一步探究GFP-GFP纳米抗体系统具体的主动装载效率[40],见表2[40,71-73]。"
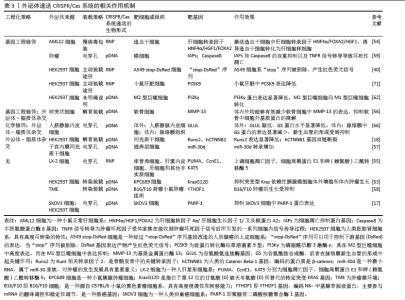
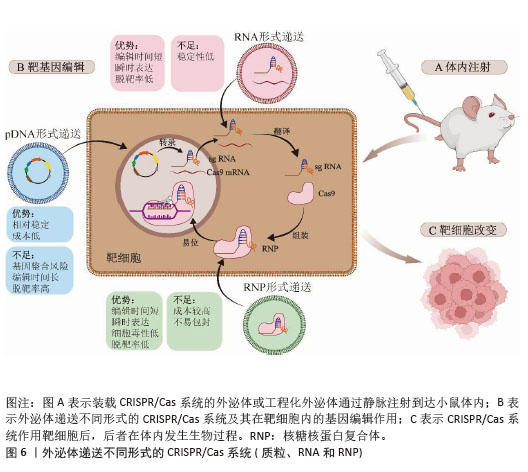
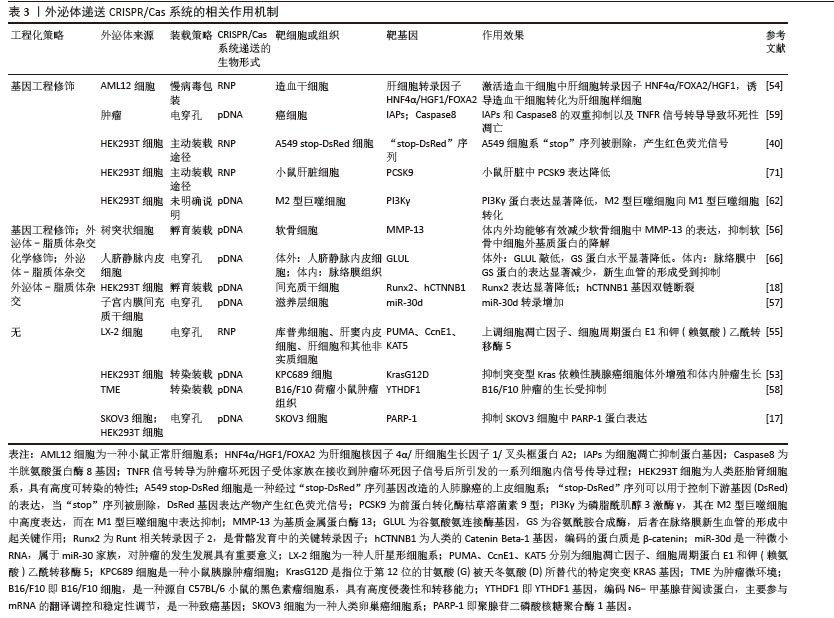
2.6 外泌体递送CRISPR/Cas的形式及其在细胞内的作用 外泌体递送CRISPR/Cas系统的生物形式包括:在DNA水平上,递送表达Cas蛋白和sgRNA的质粒(pDNA);在RNA水平上,递送编码Cas蛋白的mRNA和sgRNA;在蛋白水平上,直接递送Cas蛋白和sgRNA所形成的核糖核蛋白复合体[74],见表3和图6。 2.6.1 pDNA形式递送 Cas和sgRNA被包装于同一pDNA,在核定位序列(NLS)的协助下进入细胞核转录成编码Cas蛋白的mRNA和sgRNA,mRNA再进入细胞质翻译成Cas蛋白,并在sgRNA的协同作用下实现基因编辑[75]。 基于这一原理,Mcandrews等[53]将Lenti CRISPR V2或PX458(二者均为Cas9编码质粒)和靶向KrasG12D[位于第12位的甘氨酸(G)被天冬氨酸(D)所替代的特定突变KRAS基因]的sgRNA1或sgRNA2所组成的共表达质粒通过外泌体递送到小鼠胰腺肿瘤细胞KPC689中,成功地抑制了突变型Kras依赖性胰腺癌细胞的体外增殖和体内肿瘤生长。LIN等[58]通过外泌体转运CRISPR/Cas9质粒DNA,靶向YTHDF1,YTHDF1的表达在运载pDNA外泌体的作用下明显耗尽,最终成功地激活了抗肿瘤免疫反应来抑制肿瘤生长。然而,pDNA递送成功后,需要在细胞质中经过转录及翻译过程才能进入细胞核从而编辑目的基因,易导致基因编辑时间延长、效率降低,从而使脱靶率增加。此外,递送外源质粒可能会整合到宿主基因组中,存在触发机体免疫反应的风险[75]。 2.6.2 RNA形式递送 CRISPR/Cas系统通过RNA形式进行递送时,Cas mRNA的翻译发生在细胞质中,随后生成的Cas蛋白与sgRNA进行组装,易位到细胞核后配合对靶基因进行编辑,该过程可以绕过DNA转录,提高基因编辑效率,并且Cas mRNA会实现瞬时表达并最终从体内完全去除,减少了脱靶效应[76]。但目前并没有研究采用RNA这一生物形式,以外泌体为载体将CRISPR/Cas系统递送到细胞内并执行任务。相关研究表明,可能是因为Cas mRNA通过外泌体递送时稳定性较差,易受到RNA酶的降解,导致基因编辑无法持续发挥作用,限制了其基因编辑的效果,因而并未在该领域得到广泛应用[77]。 2.6.3 核糖核蛋白复合体形式递送 核糖核蛋白复合体进入细胞后,无需转录或翻译就能快速实现基因编辑。与前两种递送方式相比,递送核糖核蛋白复合体的速度快、基因编辑效率高、在靶细胞停留时间短、脱靶量减少、细胞毒性更低[69]。因此,大多数研究者选择核糖核蛋白复合体作为外泌体递送CRISPR/Cas系统的生物形式。CRISPR/dCas9-SAM系统是核糖核蛋白复合体的一种形式,由dCas9、sg-肝细胞核因子4α/肝细胞生长因子1/叉头框蛋白A2(sg-HNF4α/HGF1/FOXA2)和P65-MS2构成,该系统通过外泌体递送到造血干细胞后,造血干细胞成功表达肝细胞核因子4α、抗去唾液酸糖蛋白受体1、角蛋白18和钙黏蛋白,而造血干细胞标志物CRBP1、α-SMA和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的表达明显减少,表明该系统能够体外诱导造血干细胞转化为肝细胞样细胞[54]。包含了sg-PUMA/CcnE1/KAT5和Cas9的核糖核蛋白复合体,通过外泌体递送后分别靶向上调了PUMA、CcnE1和KAT5,在急性肝损伤、慢性肝纤维化和肝细胞癌小鼠模型中显示出强大的治疗潜力[55]。但该形式递送的难点在于制备大量高活性的Cas蛋白有一定难度且核糖核蛋白复合体尺寸较大不易包封[78],因此探索其合适的递送载体尤为重要。"
| [1] LI L, SHEN G, WU M, et al. CRISPR-Cas-mediated diagnostics. Trends Biotechnol. 2022;40(11):1326-1345. [2] BHOKISHAM N, LAUDERMILCH E, TRAEGER LL, et al. CRISPR-Cas System: The Current and Emerging Translational Landscape. Cells. 2023;12(8):1103. [3] TAHA EA, LEE J, HOTTA A. Delivery of CRISPR-Cas tools for in vivo genome editing therapy: Trends and challenges. J Control Release. 2022;342:345-361. [4] BOUCHER P, CUI X, CURIEL DT. Adenoviral vectors for in vivo delivery of CRISPR-Cas gene editors. J Control Release. 2020; 327:788-800. [5] SADEGHI S, TEHRANI FR, TAHMASEBI S, et al. Exosome engineering in cell therapy and drug delivery. Inflammopharmacology. 2023;31(1):145-169. [6] 代月优,郭丹丹,王茜茜,等.工程化外泌体靶向递送药物的抗肿瘤效应[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(31):6753-6764. [7] TIAN J, HAN Z, SONG D, et al. Engineered Exosome for Drug Delivery: Recent Development and Clinical Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:7923-7940. [8] TAN D, LI G, FU W, et al. Exosomes: the next frontier in vaccine development and delivery. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1435426. [9] ZHANG Y, LUO J, GUI X, et al. Bioengineered nanotechnology for nucleic acid delivery. J Control Release. 2023;364:124-141. [10] JOHNSTONE RM, MATHEW A, MASON AB, et al. Exosome formation during maturation of mammalian and avian reticulocytes: evidence that exosome release is a major route for externalization of obsolete membrane proteins. J Cell Physiol. 1991; 147(1):27-36. [11] AL-MADHAGI H. The Landscape of Exosomes Biogenesis to Clinical Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:3657-3675. [12] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659. [13] BAJ-KRZYWORZEKA M, SZATANEK R, WEGLARCZYK K, et al. Tumour-derived microvesicles carry several surface determinants and mRNA of tumour cells and transfer some of these determinants to monocytes. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006;55(7):808-818. [14] SKOG J, WÜRDINGER T, VAN RIJN S, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(12):1470-1476. [15] SUN D, ZHUANG X, XIANG X, et al. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: the anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated in exosomes. Mol Ther. 2010;18(9):1606-1614. [16] TENCHOV R, SASSO JM, WANG X, et al. Exosomes─Nature’s Lipid Nanoparticles, a Rising Star in Drug Delivery and Diagnostics. ACS Nano. 2022;16(11):17802-17846. [17] KIM SM, YANG Y, OH SJ, et al. Cancer-derived exosomes as a delivery platform of CRISPR/Cas9 confer cancer cell tropism-dependent targeting. J Control Release. 2017;266:8-16. [18] LIN Y, WU J, GU W, et al. Exosome-Liposome Hybrid Nanoparticles Deliver CRISPR/Cas9 System in MSCs. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018; 5(4):1700611. [19] SINGH S, PAUL D, NATH V, et al. Exosomes: current knowledge and future perspectives. Tissue Barriers. 2024;12(2):2232248. [20] HAN QF, LI WJ, HU KS, et al. Exosome biogenesis: machinery, regulation, and therapeutic implications in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):207. [21] RÄDLER J, GUPTA D, ZICKLER A, et al. Exploiting the biogenesis of extracellular vesicles for bioengineering and therapeutic cargo loading. Mol Ther. 2023;31(5):1231-1250. [22] WANG C, LI Z, LIU Y, et al. Exosomes in atherosclerosis: performers, bystanders, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets. Theranostics. 2021;11(8):3996-4010. [23] GURUNG S, PEROCHEAU D, TOURAMANIDOU L, et al. The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun Signal. 2021;19(1):47. [24] YANG W, DING N, LUO R, et al. Exosomes from young healthy human plasma promote functional recovery from intracerebral hemorrhage via counteracting ferroptotic injury. Bioact Mater. 2023;27:1-14. [25] ZHAO Y, LIU L, SUN R, et al. Exosomes in cancer immunoediting and immunotherapy. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022;17(2):193-205. [26] CHENG H, YANG Q, WANG R, et al. Emerging Advances of Detection Strategies for Tumor-Derived Exosomes. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2):868. [27] LI J, ZHANG Y, LUO B. Effects of Exosomal Viral Components on the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers (Basel). 2022; 14(14):3552. [28] LIANG G, ZHU Y, ALI DJ, et al. Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):10. [29] LI J, LI J, PENG Y, et al. Dendritic cell derived exosomes loaded neoantigens for personalized cancer immunotherapies. J Control Release. 2023;353:423-433. [30] MENG X, WU TG, LOU QY, et al. Optimization of CRISPR-Cas system for clinical cancer therapy. Bioeng Transl Med. 2022;8(2):e10474. [31] FENG S, XIE X, LIU J, et al. A potential paradigm in CRISPR/Cas systems delivery: at the crossroad of microalgal gene editing and algal-mediated nanoparticles. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):370. [32] BAIRQDAR A, KARITSKAYA PE, STEPANOV GA. Expanding Horizons of CRISPR/Cas Technology: Clinical Advancements, Therapeutic Applications, and Challenges in Gene Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(24): 13321. [33] ALLEMAILEM KS, ALMATROUDI A, ALRUMAIHI F, et al. Current Updates of CRISPR/Cas System and Anti-CRISPR Proteins: Innovative Applications to Improve the Genome Editing Strategies. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:10185-10212. [34] WANG SW, GAO C, ZHENG YM, et al. Current applications and future perspective of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):57. [35] AZEEZ SS, HAMAD RS, HAMAD BK, et al. Advances in CRISPR-Cas technology and its applications: revolutionising precision medicine. Front Genome Ed. 2024;6: 1509924. [36] HORODECKA K, DÜCHLER M. CRISPR/Cas9: Principle, Applications, and Delivery through Extracellular Vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):6072. [37] KHOSHANDAM M, SOLTANINEJAD H, MOUSAZADEH M, et al. Clinical applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 genome-editing system: Delivery options and challenges in precision medicine. Genes Dis. 2023;11(1):268-282. [38] SONG X, LIU C, WANG N, et al. Delivery of CRISPR/Cas systems for cancer gene therapy and immunotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;168:158-180. [39] LESMANA H, KIM SY, CORADO AM, et al. Casgevy (exagamglogene autotemcel) and Lyfgenia (lovotibeglogene autotemcel) for individuals 12 years and older with sickle cell disease (SCD) and recurrent vaso-occlusive crises (VOC): A therapeutics bulletin of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet Med Open. 2024;2:101875. [40] YE Y, ZHANG X, XIE F, et al. An engineered exosome for delivering sgRNA:Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complex and genome editing in recipient cells. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(10):2966-2976. [41] KO WC, WANG SJ, HSIAO CY, et al. Pharmacological Role of Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles in Disease Applications. Molecules. 2022;27(5):1551. [42] HUANG J, ZHOU Y, LI J, et al. CRISPR/Cas systems: Delivery and application in gene therapy. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:942325. [43] SHAO J, ZARO J, SHEN Y. Advances in Exosome-Based Drug Delivery and Tumor Targeting: From Tissue Distribution to Intracellular Fate. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:9355-9371. [44] CHEN R, HUANG H, LIU H, et al. Friend or Foe? Evidence Indicates Endogenous Exosomes Can Deliver Functional gRNA and Cas9 Protein. Small. 2019;15(38):e1902686. [45] HA D, YANG N, NADITHE V. Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2016;6(4):287-296. [46] HE ZY, MEN K, QIN Z, et al. Non-viral and viral delivery systems for CRISPR-Cas9 technology in the biomedical field. Sci China Life Sci. 2017;60(5):458-467. [47] KANTOR B, O’DONOVAN B, RITTINER J, et al. The therapeutic implications of all-in-one AAV-delivered epigenome-editing platform in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):7259. [48] DEGTEV D, BRAVO J, EMMANOUILIDI A, et al. Engineered PsCas9 enables therapeutic genome editing in mouse liver with lipid nanoparticles. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):9173. [49] HU X, ENBAR T, TANG L. Delivery approaches of immunomodulatory nucleic acids for cancer therapy. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2024; 89:103182. [50] KAUPBAYEVA B, TSOY A, SAFAROVA YANTSEN Y, et al. Unlocking Genome Editing: Advances and Obstacles in CRISPR/Cas Delivery Technologies. J Funct Biomater. 2024;15(11):324. [51] MOLAEI Z, JABBARPOUR Z, OMIDKHODA A, et al. Exploring non-viral methods for the delivery of CRISPR-Cas ribonucleoprotein to hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):233. [52] XU W, ZHANG S, QIN H, et al. From bench to bedside: cutting-edge applications of base editing and prime editing in precision medicine. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):1133. [53] MCANDREWS KM, XIAO F, CHRONOPOULOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 for targeting of oncogenic KrasG12D in pancreatic cancer. Life Sci Alliance. 2021;4(9):e202000875. [54] 罗年安.基于CRISPR/dCas9靶向递送系统的HSCs重编程策略及其在肝纤维化治疗中的应用[D].西安:中国人民解放军空军军医大学,2023. [55] WAN T, ZHONG J, PAN Q, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complexes for tissue-specific gene therapy of liver diseases. Sci Adv. 2022;8(37):eabp9435. [56] LIANG Y, XU X, XU L, et al. Chondrocyte-specific genomic editing enabled by hybrid exosomes for osteoarthritis treatment. Theranostics. 2022;12(11):4866-4878. [57] YAGHOOBI A, NAZERIAN Y, MEYMAND AZ, et al. Hypoxia-sensitive miRNA regulation via CRISPR/dCas9 loaded in hybrid exosomes: A novel strategy to improve embryo implantation and prevent placental insufficiency during pregnancy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;10:1082657. [58] LIN W, CHEN L, ZHANG H, et al. Tumor-intrinsic YTHDF1 drives immune evasion and resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors via promoting MHC-I degradation. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):265. [59] GULEI D, BERINDAN-NEAGOE I. Activation of Necroptosis by Engineered Self Tumor-Derived Exosomes Loaded with CRISPR/Cas9. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;17:448-451. [60] BAHADORANI M, NASIRI M, DELLINGER K, et al. Engineering Exosomes for Therapeutic Applications: Decoding Biogenesis, Content Modification, and Cargo Loading Strategies. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:7137-7164. [61] LI YJ, WU JY, LIU J, et al. Artificial exosomes for translational nanomedicine. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):242. [62] ZHANG L, LIN Y, LI S, et al. In Situ Reprogramming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages with Internally and Externally Engineered Exosomes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023;62(11):e202217089. [63] 黄春满,李丽薇,黄勇彬,等.外泌体靶向修饰的研究进展[J].科学通报,2023, 68(33):4532-4543. [64] LIANG Y, IQBAL Z, LU J, et al. Cell-derived nanovesicle-mediated drug delivery to the brain: Principles and strategies for vesicle engineering. Mol Ther. 2023;31(5):1207-1224. [65] AKBARI A, NAZARI-KHANAMIRI F, AHMADI M, et al. Engineered Exosomes for Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery: A Focus on Genetic and Chemical Functionalization. Pharmaceutics. 2022;15(1):66. [66] ZHANG M, LU X, LUO L, et al. Targeting glutamine synthetase with AS1411-modified exosome-liposome hybrid nanoparticles for inhibition of choroidal neovascularization. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):703. [67] JIA G, HAN Y, AN Y, et al. NRP-1 targeted and cargo-loaded exosomes facilitate simultaneous imaging and therapy of glioma in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials. 2018;178:302-316. [68] KIM MS, HANEY MJ, ZHAO Y, et al. Engineering macrophage-derived exosomes for targeted paclitaxel delivery to pulmonary metastases: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Nanomedicine. 2018;14(1):195-204. [69] SONG Z, TAO Y, LIU Y, et al. Advances in delivery systems for CRISPR/Cas-mediated cancer treatment: a focus on viral vectors and extracellular vesicles. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1444437. [70] YOSHIDA Y, AOKI M, NAGASE K, et al. Plasmid DNA Delivery into the Skin via Electroporation with a Depot-Type Electrode. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(9):1219. [71] ZHANG X, XU Q, ZI Z, et al. Programmable Extracellular Vesicles for Macromolecule Delivery and Genome Modifications. Dev Cell. 2020;55(6):784-801.e9. [72] PALAKURTHI SS, SHAH B, KAPRE S, et al. A comprehensive review of challenges and advances in exosome-based drug delivery systems. Nanoscale Adv. 2024;6(23): 5803-5826. [73] HUYAN T, LI H, PENG H, et al. Extracellular Vesicles - Advanced Nanocarriers in Cancer Therapy: Progress and Achievements. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6485-6502. [74] DU Y, LIU Y, HU J, et al. CRISPR/Cas9 systems: Delivery technologies and biomedical applications. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023;18(6):100854. [75] KAZEMIAN P, YU SY, THOMSON SB, et al. Lipid-Nanoparticle-Based Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 Genome-Editing Components. Mol Pharm. 2022;19(6):1669-1686. [76] ROSENBLUM D, GUTKIN A, DAMMES N, et al. Progress and challenges towards CRISPR/Cas clinical translation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;154-155:176-186. [77] HUANG X, LI A, XU P, et al. Current and prospective strategies for advancing the targeted delivery of CRISPR/Cas system via extracellular vesicles. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):184. [78] LIN Y, WAGNER E, LÄCHELT U. Non-viral delivery of the CRISPR/Cas system: DNA versus RNA versus RNP. Biomater Sci. 2022; 10(5):1166-1192. |
| [1] | Wang Qisa, Lu Yuzheng, Han Xiufeng, Zhao Wenling, Shi Haitao, Xu Zhe. Cytocompatibility of 3D printed methyl acrylated hyaluronic acid/decellularized skin hydrogel scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1912-1920. |
| [2] | Wang Songpeng, Liu Yusan, Yu Huanying, Gao Xiaoli, Xu Yingjiang, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Min. Bidirectional regulation of reactive oxygen species based on zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanomaterials: from tumor therapy and antibacterial activity to cytoprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2033-2013. |
| [3] | Liu Yang, Liu Donghui , Xu Lei, Zhan Xu, Sun Haobo, Kang Kai. Role and trend of stimuli-responsive injectable hydrogels in precise myocardial infarction therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2072-2080. |
| [4] | Lai Yu, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Research hotspots and frontier trends of bioactive materials in treating bone infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2132-2144. |
| [5] | Ding Yifan, Yin Wenjie, Zhang Li, Yuan Shuya, Sun Guoju, Zhang Naili, Zhao Dongmei, Ma Lina. Repair of segmental bone defect of rabbit radius by decalcified bone matrix loaded with adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1679-1686. |
| [6] | Zhu Jing, Zhai Xiguo, Wu Qizhen, Wang Yupei, Lyu Ling, Hou Qinzheng. Development and application of human amniotic membrane in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1818-1827. |
| [7] | Liu Xingyu, Li Lijie. Secretome of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth: a new hotspot in tissue engineering and stem cell therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1858-1868. |
| [8] | Wang Mingqi, Feng Shiya, Han Yinhe, Yu Pengxin, Guo Lina, Jia Zixuan, Wang Xiuli. Construction and evaluation of a neuralized intestinal mucosal tissue engineering model in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 892-900. |
| [9] | Yu Shiyu, Yu Sutong, Xu Yang, Zhen Xiangyan, Han Fengxuan. Advances in research and application of tissue engineering therapeutic strategies in oral submucous fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 936-948. |
| [10] | Yang Hu, Zheng Yu, Jia Chengming, Wang Tong, Zhang Guangfei, Ji Yaoyao. Immune microenvironment regulates bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 701-710. |
| [11] | Gu Jianmei, Yuan Kunshan, Zhou Qiang, Zhang Haijun, , . Application of laser microporous decellularized scaffolds in tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 499-507. |
| [12] | Yang Fengli, Zhou Chao, Xiong Wei, Zhou Yuxiang, Li Dengshun, Wang Xin, Li Zhanzhen. 3D printed poly-L-lactic acid bone scaffolds in repair of bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 507-515. |
| [13] | Jiang Kan, Alimujiang·Abudourousuli, Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Biomaterials and bone regeneration: research hotspots and analysis of 500 influential papers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| [14] | Wang Zhuo, Sun Panpan, Cheng Huanzhi, Cao Tingting. Application of chitosan in repair and regeneration of oral hard and soft tissues [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 459-468. |
| [15] | Wang Yu, Fan Minjie, Zheng Pengfei. Application of multistimuli-responsive hydrogels in bone damage repair: special responsiveness and diverse functions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 469-479. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||