Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 1632-1640.doi: 10.12307/2026.524
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of conditioned medium of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells on proliferation and apoptosis of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Yuan Xiaoshuang1, Yang Xu2, Yang Bo2, Chen Xiaoxu2, Tian Ting1, Wang Feiqing2, Li Yanju1, 3, Liu Yang2, Yang Wenxiu1, 3
- 1Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-15Revised:2025-03-05Accepted:2025-03-19Online:2026-03-08Published:2025-08-18 -
Contact:Liu Yang, PhD, Professor, First Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; Yang Wenxiu, PhD, Chief physician, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Yuan Xiaoshuang, Master candidate, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:“Discipline Outstanding Reserve Talents” Fund Project of Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, No. gyfyxkrc-2023-14 (to LYJ); Project of Science and Technology Department of Guizhou Province, No. [2021] 007 (to LY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yuan Xiaoshuang, Yang Xu, Yang Bo, Chen Xiaoxu, Tian Ting, Wang Feiqing, Li Yanju, Liu Yang, Yang Wenxiu. Effect of conditioned medium of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells on proliferation and apoptosis of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1632-1640.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
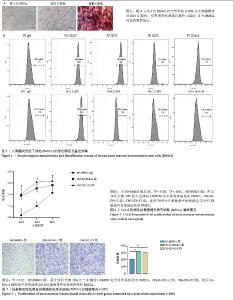
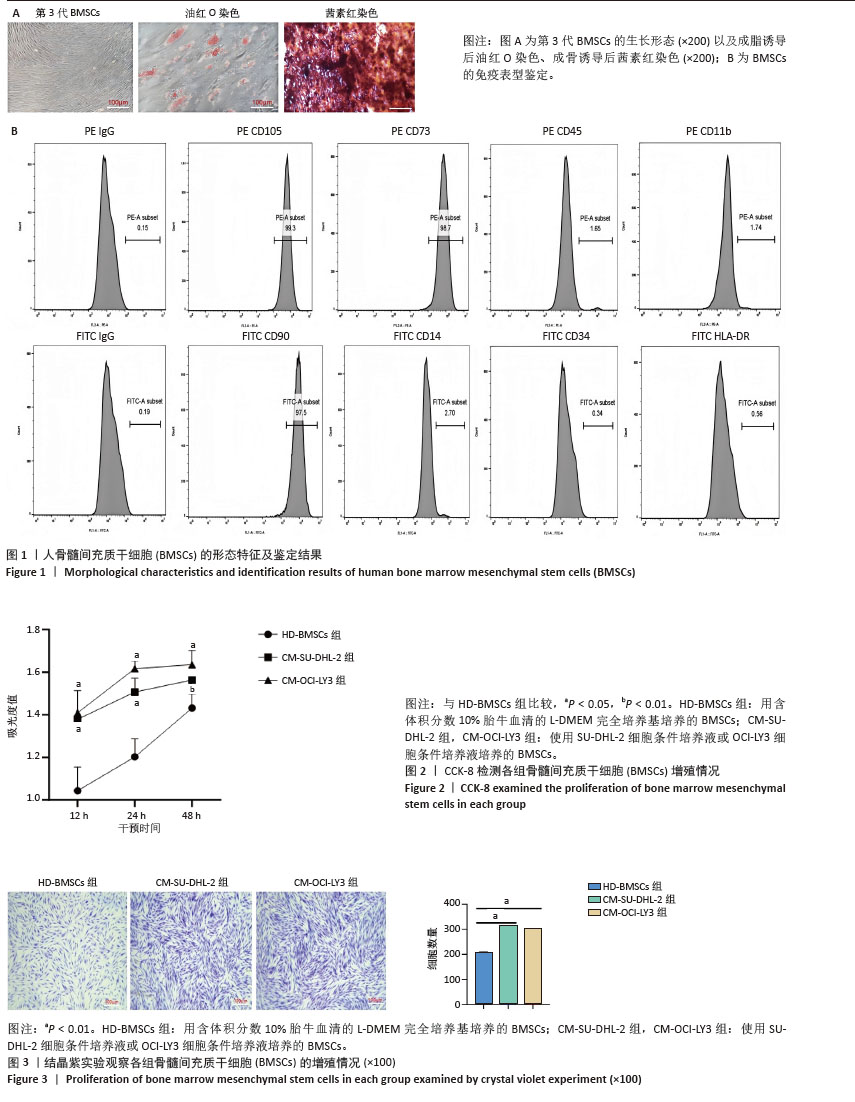
2.1 BMSCs的鉴定结果 如图1A所示,BMSCs呈贴壁生长;成骨诱导后,茜素红染色显示BMSCs中有致密的染色钙盐沉积;成脂诱导后,油红O染色显示BMSCs中形成油滴。如图1B所示,CD11b、CD34、CD14、CD45和HLA-DR在BMSCs中不表达,而CD90、CD105和CD73在BMSCs中高表达。 2.2 CCK-8检测BMSCs的增殖情况 在干预12,24,48 h后,CM-SU-DHL-2组和CM-OCI-LY3组BMSCs的吸光度值均显著高于HD-BMSCs组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图2。 2.3 结晶紫染色法观察BMSCs的形态和数量 干预24 h后,CM-SU-DHL-2组和CM-OCI-LY3组的染色细胞数量显著高于HD-BMSCs组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图3。 "
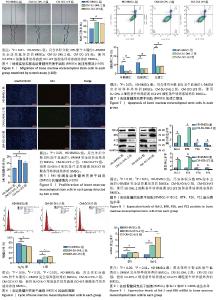
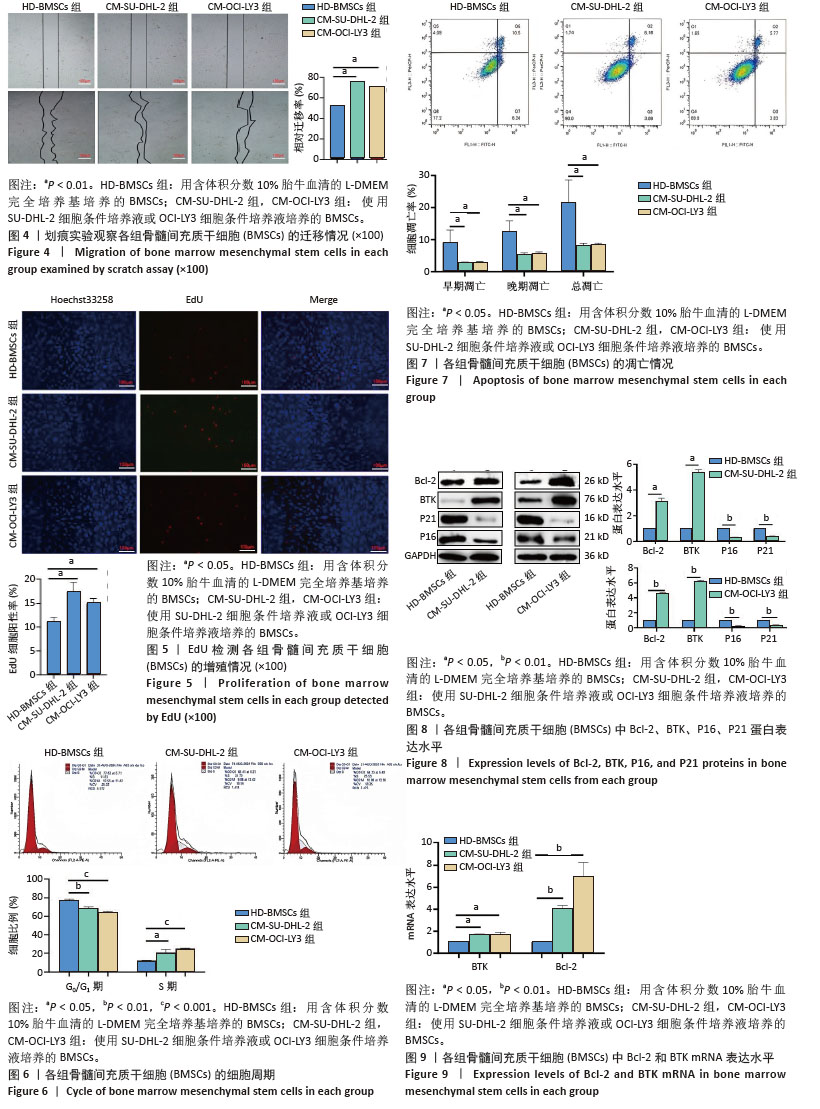
2.4 划痕实验观察BMSCs的迁移情况 干预24 h 后,划痕实验结果显示,CM-SU-DHL-2组和CM-OCI-LY3组细胞相对迁移率显著高于HD-BMSCs组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图4。 2.5 EdU荧光染色观察BMSCs的增殖情况 在干预24 h后,CM-SU-DHL-2组和CM-OCI-LY3组的EdU 阳性细胞率显著多于HD-BMSCs组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图5。 2.6 细胞周期 流式细胞术分析显示,与HD-BMSCs组相比,CM-SU-DHL-2组和CM-OCI-LY3组G0/G1期细胞数量显著减少(P < 0.05),而S期细胞数量则显著增加(P < 0.05),见图6。 2.7 细胞凋亡率 HD-BMSCs组、CM-SU-DHL-2组和CM-OCI-LY3组的BMSCs总凋亡率分别为(25.17±0.3)%,(8.20±0.55)%,(8.59±0.29)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图7。 2.8 Western blot检测Bcl-2、BTK、P21、P16蛋白的表达 与HD-BMSCs组相比,CM-SU-DHL-2组和CM-OCI-LY3组BMSCs中Bcl-2、BTK蛋白表达升高,P21、P16蛋白表达降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图8。 2.9 RT-PCR检测Bcl-2、BTK mRNA的表达 与HD-BMSCs组相比,CM-SU-DHL-2组和CM-OCI-LY3组BMSCs中Bcl-2、BTK mRNA表达升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图9。 "
| [1] SIEGEL RL, MILLER KD, FUCHS HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7-33. [2] HU W, ZANG L, FENG X, et al. Advances in epigenetic therapies for B-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2024;103(12):5085-5101. [3] TILLY H, MORSCHHAUSER F, SEHN LH, et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin in Previously Untreated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(4):351-363. [4] HUNG YS, HUNG CY, CHOU WC. Evaluating the cancer aging and research group model in predicting immunochemotherapy toxicity among elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;138:112544. [5] SEHN LH, HERRERA AF, FLOWERS CR, et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin in Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(2):155-165. [6] WU H, ZOU L, JIN Y, et al. Rituximab induces ferroptosis and RSL3 overcomes rituximab resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024;761:110188. [7] KUSOWSKA A, KUBACZ M, KRAWCZYK M, et al. Molecular Aspects of Resistance to Immunotherapies-Advances in Understanding and Management of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1501. [8] DUMONTET E, MANCINI SJC, TARTE K. Bone Marrow Lymphoid Niche Adaptation to Mature B Cell Neoplasms. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 784691. [9] ZAMÒ A, JOHNSTON P, ATTYGALLE AD, et al. Aggressive B-cell lymphomas with a primary bone marrow presentation. Histopathology. 2020;77(3):369-379. [10] BOGUN L, KOCH A, SCHERER B, et al. Overlapping Stromal Alterations in Myeloid and Lymphoid Neoplasms. Cancers (Basel). 2024;16(11):2071. [11] SALAME N, BIKORIMANA JP, EL-HACHEM N, et al. UM171A-induced ROS promote antigen cross-presentation of immunogenic peptides by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):16. [12] DUMONTET E, PANGAULT C, ROULOIS D, et al. Extracellular vesicles shed by follicular lymphoma B cells promote polarization of the bone marrow stromal cell niche. Blood. 2021;138(1):57-70. [13] PETINATI NA, BIGILDEEV AE, KARPENKO DS, et al. Humoral Effect of a B-Cell Tumor on the Bone Marrow Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2021;86(2):207-216. [14] CHAI M, SU G, CHEN W, et al. Effects of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Central Nervous System Diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 2024;61(10):7481-7499. [15] RADTKE AJ, ROSCHEWSKI M. The follicular lymphoma tumor microenvironment at single-cell and spatial resolution. Blood. 2024; 143(12):1069-1079. [16] LI M, ZHAI P, MU X, et al. Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal miR-652-3p promotes proliferation and metastasis of hepatocarcinoma cancer cells via targeting TNRC6A. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15(22): 12780-12793. [17] CAO Y, XU P, SHEN Y, et al. Exosomes and cancer immunotherapy: A review of recent cancer research. Front Oncol. 2023;12:1118101. [18] SIRCAR A, CHOWDHURY SM, HART A, et al. Impact and Intricacies of Bone Marrow Microenvironment in B-cell Lymphomas: From Biology to Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):904. [19] GOODARZI A, VALIKHANI M, AMIRI F, et al. The mechanisms of mutual relationship between malignant hematologic cells and mesenchymal stem cells: Does it contradict the nursing role of mesenchymal stem cells? Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):21. [20] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317. [21] WENIGER MA, SEIFERT M, KÜPPERS R. B Cell Differentiation and the Origin and Pathogenesis of Human B Cell Lymphomas. Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2865:1-30. [22] YE S, YING W, LIN Y, et al. LncRNA OR2A1-AS1 index predicts survival in germinal center-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022;36(10):e24680. [23] CARVALHO AS, BAETA H, HENRIQUES AFA, et al. Proteomic Landscape of Extracellular Vesicles for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Subtyping. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(20):11004. [24] PIROSA MC, STATHIS A, ZUCCA E. Tafasitamab for the treatment of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024;20(1):2309701. [25] MARTIN-MORO F, LOPEZ-JIMENEZ J, GARCIA-MARCO JA, et al. Comparative Review of the Current and Future Strategies to Evaluate Bone Marrow Infiltration at Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Diagnosis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024;14(6):658. [26] DOMA A, STUDEN A, JEZERŠEK NOVAKOVIĆ B. The Impact of Bone Marrow Involvement on Prognosis in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: An 18F-FDG PET/CT Volumetric Segmentation Study. Cancers (Basel). 2024;16(22):3762. [27] ZUO H, XIE X, SUN X, et al. Prognostic impact of concordant and discordant bone marrow involvement on diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Transl Cancer Res. 2024;13(10):5339-5346. [28] WEN HJ, ZHU SY, YANG HG, et al. Investigation on the molecular mechanism of SPA interference with osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):15600. [29] STONE AP, RAND E, THORNES G, et al. Extracellular matrices of stromal cell subtypes regulate phenotype and contribute to the stromal microenvironment in vivo. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):178. [30] VERYASKINA YA, TITOV SE, KOVYNEV IB, et al. MicroRNA Expression Profile in Bone Marrow and Lymph Nodes in B-Cell Lymphomas. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(20):15082. [31] AMIRPOUR M, KUHESTANI-DEHAGHI B, KHEYRANDISH S, et al. The impact of exosomes derived from B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia as a growth factor on bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):749. [32] BINDER M, SZALAT RE, TALLURI S, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells induce chromatin remodeling in multiple myeloma cells leading to transcriptional changes. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):4139. [33] LIU Z, LIU H, LI Y, et al. Multiple myeloma-derived exosomes inhibit osteoblastic differentiation and improve IL-6 secretion of BMSCs from multiple myeloma. J Investig Med. 2020;68(1):45-51. [34] ALLEGRA A, DI GIOACCHINO M, TONACCI A, et al. Multiple Myeloma Cell-Derived Exosomes: Implications on Tumorigenesis, Diagnosis, Prognosis and Therapeutic Strategies. Cells. 2021;10(11):2865. [35] WANG J, PANY, WAN Y, et al. SENEX gene promotes cell proliferation by activating RB/E2F pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells. Biocell. 2021;45(4):933-942. [36] SONG W, FEI F, QIAO F, et al. ALKBH5-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of TRERNA1 promotes DLBCL proliferation via p21 downregulation. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):25. [37] CZABOTAR PE, LESSENE G, STRASSER A, et al. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(1):49-63. [38] SARRO R, BISIG B, GUEY B, et al. Follicular Lymphoma Presenting With Symptomatic Bone Involvement: A Clinicopathologic and Molecular Analysis of 16 Cases. Mod Pathol. 2024;37(4):100440. [39] TAVAKOLI GM, YAZDANPANAH N, REZAEI N. Targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) as a signaling pathway in immune-mediated diseases: from molecular mechanisms to leading treatments. Adv Rheumatol. 2024;64(1):61. [40] JIANG C, SUN C, WANG X, et al. BTK Expression Level Prediction and the High-Grade Glioma Prognosis Using Radiomic Machine Learning Models. J Imaging Inform Med. 2024;37(4):1359-1374. |
| [1] | Wang Qisa, Lu Yuzheng, Han Xiufeng, Zhao Wenling, Shi Haitao, Xu Zhe. Cytocompatibility of 3D printed methyl acrylated hyaluronic acid/decellularized skin hydrogel scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1912-1920. |
| [2] | Sun Lei, Zhang Qi, Zhang Yu. Pro-osteoblastic effect of chlorogenic acid protein microsphere/polycaprolactone electrospinning membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1877-1884. |
| [3] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [4] | Jiang Xinghai, Song Yulin, Li Dejin, Shao Jianmin, Xu Junzhi, Liu Huakai, Wu Yingguo, Shen Yuehui, Feng Sicheng. Vascular endothelial growth factor 165 genes transfected into bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct a vascularized amphiphilic peptide gel module [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1903-1911. |
| [5] | Hu Xiongke, Liu Shaohua, Tan Qian, Liu Kun, Zhu Guanghui. Shikonin intervention with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves microstructure of femur in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [6] | Li Zhenyu, Zhang Siming, Bai Jiaxiang, Zhu Chen. Osthole improves osteogenic differentiation function of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under high-glucose conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1641-1648. |
| [7] | Han Nianrong, Huang Yifei, Akram · Osman, Liu Yanlu, Hu Wei . Programmed cell death receptor-1 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a high-glucose microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1649-1657. |
| [8] | Jin Dongsheng, Zhao Zhanghong, Zhu Ziyin, Zhang Sen, Sun Zuyan, Deng Jiang. Effects of icariin-loaded microsphere-three-dimensional scaffold on osteogenic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1658-1668. |
| [9] | Zou Yulian, Chen Chaopei, Huang Haixia, Lan Yuyan, Liu Min, Huang Ting. Resveratrol promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1669-1678. |
| [10] | He Jiale, Huang Xi, Dong Hongfei, Chen Lang, Zhong Fangyu, Li Xianhui. Acellular dermal matrix combined with adipose-derived stem cell exosomes promotes burn wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1699-1710. |
| [11] | Cui Lianxu, Li Haomin, Xu Junrong, Tan Baodong, Lu Dahong, Peng Siwei, Wang Jinhui. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium on tissue repair after traumatic craniocerebral injury in miniature pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1730-1735. |
| [12] | Liu Anting, Lu Jiangtao, Zhang Wenjie, He Ling, Tang Zongsheng, Chen Xiaoling. Regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase by platelet lysate inhibits cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1800-1807. |
| [13] | Liu Xingyu, Li Lijie. Secretome of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth: a new hotspot in tissue engineering and stem cell therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1858-1868. |
| [14] | Jia Jinwen, Airefate·Ainiwaer, Zhang Juan. Effects of EP300 on autophagy and apoptosis related to allergic rhinitis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1439-1449. |
| [15] | Huang Liuyan, Zhang Wenxi, Chen Shuwen, Yu Shimei, Dai Zhong, Zuo Changqing. Forskolin promotes C2C12 myoblast differentiation via regulating the ERK and Akt signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1114-1121. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||