Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1439-1449.doi: 10.12307/2026.601
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of EP300 on autophagy and apoptosis related to allergic rhinitis in rats
Jia Jinwen1, Airefate·Ainiwaer2, Zhang Juan1
- 1The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Xinjing Military Region General Hospital, Urumqi 830099, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-02-05Accepted:2025-03-26Online:2026-02-28Published:2025-07-16 -
Contact:Zhang Juan, Attending physician, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Jia Jinwen, Chief physician, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2022D01C326 (to JJW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jia Jinwen, Airefate·Ainiwaer, Zhang Juan. Effects of EP300 on autophagy and apoptosis related to allergic rhinitis in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1439-1449.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
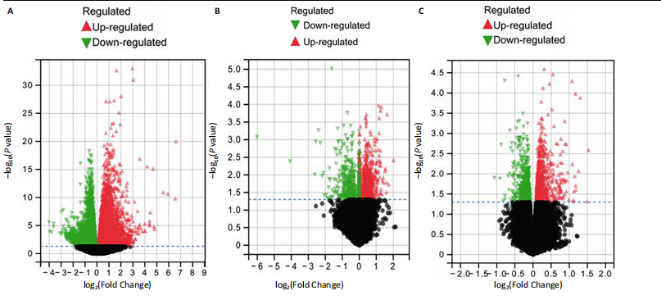
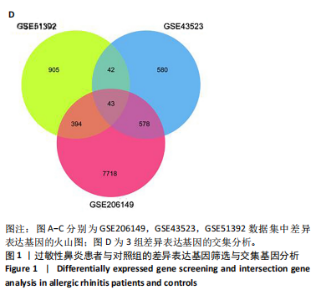
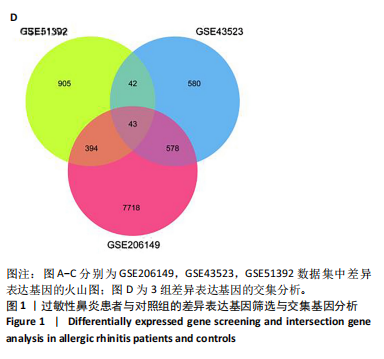
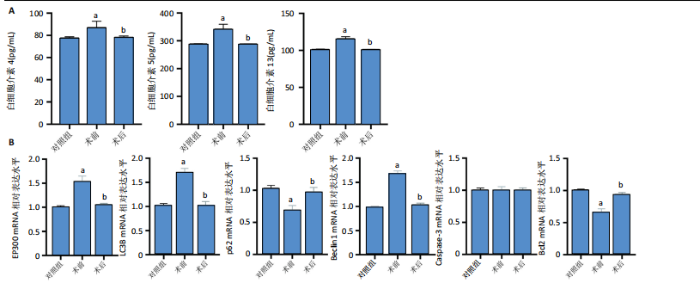
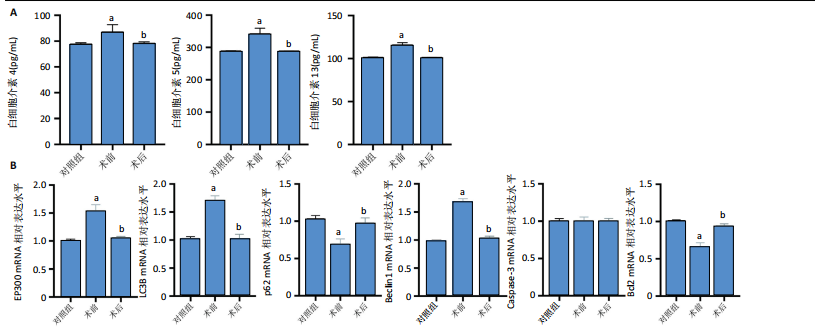
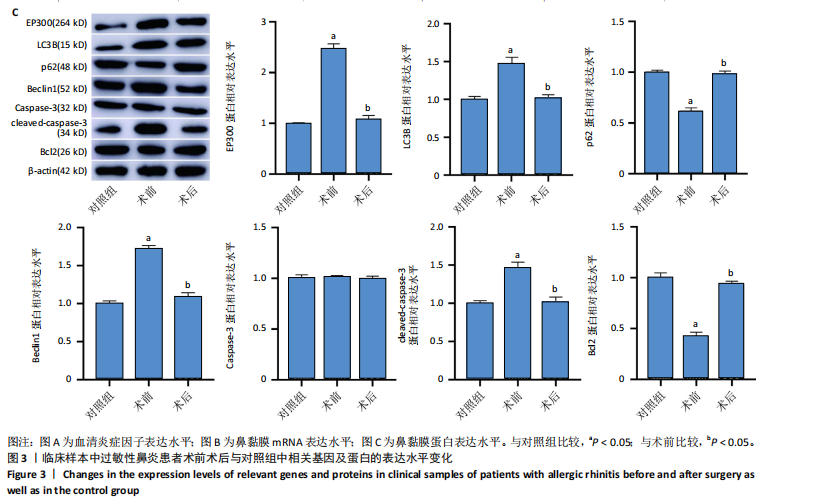
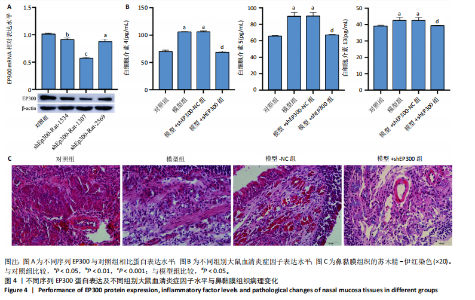
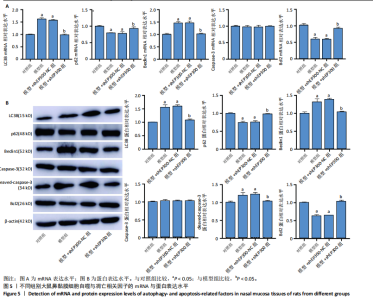
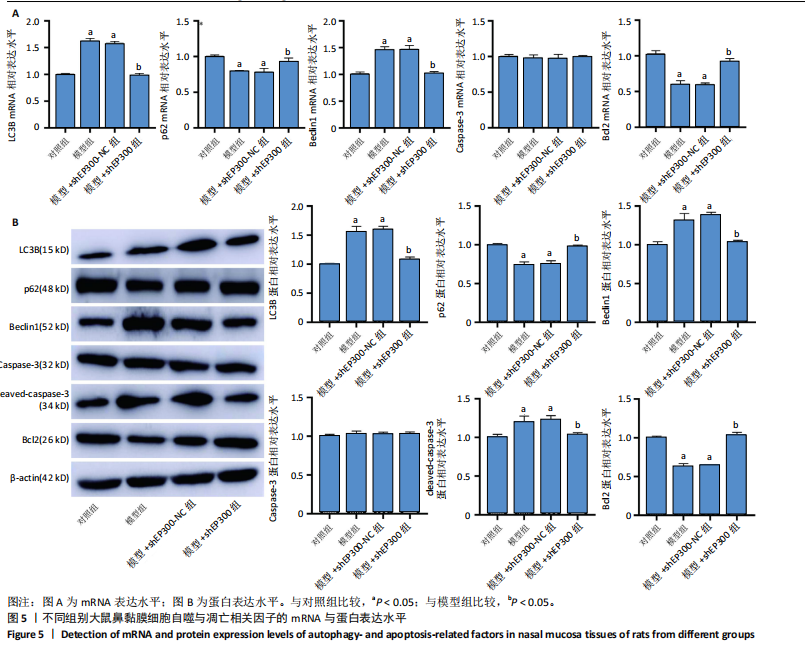
2.1 公共数据分析 2.1.1 差异表达基因筛选与交集基因分析 在GSE206149数据集中,通过差异表达分析共鉴定出8 733个差异表达基因,见图1A;在GSE43523数据集中鉴定出1 243个差异表达基因,见图1B;在GSE51392数据集中鉴定出1 384个差异表达基因,见图1C;将3个数据集进行交集后共发现43个共同差异表达基因,见图1D。 2.1.2 WGCNA对鼻炎相关基因模块特征及与程序性细胞死亡的分析 WGCNA结果共鉴定了4个共表达模块,见图2A;进一步的相关性分析发现,鼻炎与Green模块之间的相关性最强,相关系数为0.73,见图2B;将Green模块基因与程序性细胞死亡相关基因(Programmed cell death related genes,PCDRGs)进行交集共发现20个交集基因,见图2C;GSVA结果显示,与对照组相比,Cuproptosis、Entotic cell death、Netotic cell death、Pyroptosis与Alkaliptosis等细胞死亡方式在鼻炎组中相对更富集,见图2D。将43个共同差异表达基因与20个交集基因再次进行交集发现1个交集基因EP300,EP300参与细胞自噬和凋亡,见图2E。 2.2 临床样本验证过敏性鼻炎患者术前术后相关基因及蛋白的表达 2.2.1 ELISA检测结果 与对照组相比,患者术前血清白细胞介素4、白细胞介素5和白细胞介素13的质量浓度均显著升高;与术前比较,术后患者上述3项指标水平均降低(P < 0.05),见图3A。 2.2.2 RT-qPCR检测结果 与对照组相比,患者术前EP300、LC3B与Beclin1的mRNA表达水平均显著升高,p62与Bcl2的mRNA表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05);与术前比较,术后患者EP300、LC3B与Beclin1的mRNA表达水平均显著降低,p62与Bcl2的mRNA表达水平升高(P < 0.05),见图3B。 2.2.3 Western Blot检测结果 与对照组比较,患者术前EP300、LC3B、Beclin1与cleaved-caspase-3的蛋白表达水平显著升高,p62与Bcl2的蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05);与术前比,术后患者EP300、LC3B、Beclin1与cleaved-caspase-3蛋白表达水平降低,p62与Bcl2的蛋白表达水平升高(P < 0.05),见图3C。 2.3 大鼠实验结果 2.3.1 实验动物数量分析 选用40只SD大鼠开展实验,随机分为4组,每组10只。共有 36 只大鼠进入结果分析阶段,其中对照组大鼠未接受造模操作,均保持正常生理状态;模型组10只大鼠中有9只符合造模成功标准,模型+shEP300-NC组10只大鼠中有9只造模成功,模型+shEP300 组10只大鼠中有8只造模成功。 2.3.2 炎症因子水平与鼻黏膜组织病理改变在不同组别中的表现 (1)RT-qPCR检测:与对照组相比,不同序列EP300 mRNA表达水平中Ep300-Rat-1307降低显著(P < 0.001),见图4A。 (2)ELISA检测:与对照相比,模型组大鼠血清白细胞介素4、白细胞介素5和白细胞介素13的质量浓度均升高;与模型组相比,模型+shEP300组大鼠血清上述炎症因子水平均降低(P < 0.05),见图4B。 (3)苏木精-伊红染色结果:与对照组相比,模型组大鼠鼻腔黏膜结构紊乱,有明显炎症细胞浸润、血管扩张和腺体分泌增多等炎症表现;模型+shEP300-NC组与模型组大鼠情况类似,显示出炎症状态;模型+shEP300组相较于前2组,大鼠鼻腔黏膜结构有一定恢复,炎症细胞浸润减少,见图4C。 2.3.3 EP300调控自噬与凋亡相关因子的基因与蛋白表达 (1)qRT-PCR检测结果:与对照组相比,模型组与模型+shEP300-NC组中的LC3B和Beclin1的mRNA表达水平升高,p62和Bcl2的mRNA表达水平降低(P < 0.05),与模型组相比,模型+shEP300组LC3B和Beclin1的mRNA表达水平降低,p62和Bcl2的mRNA表达水平升高(P < 0.05),见图5A。 (2)Western Blot检测结果:与对照组相比,模型组与模型+shEP300-NC组中LC3B、Beclin1和cleaved caspase3的蛋白表达水平升高,p62和Bcl2的蛋白表达水平降低(P < 0.05),与模型组比较,模型+shEP300组LC3B、Beclin1和cleaved caspase3的蛋白表达水平降低,p62和Bcl2的蛋白表达水平升高(P < 0.05),见图5B。"
| [1] WISE SK, DAMASK C, ROLAND LT, et al. International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: Allergic rhinitis - 2023. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2023;13(4):293-859. [2] LETH-MOLLER KB, SKAABY T, LINNEBERG A. Allergic rhinitis and allergic sensitisation are still increasing among Danish adults. Allergy. 2020;75(3):660-668. [3] MA T, WANG X, ZHUANG Y, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for allergic rhinitis in adults and children living in different grassland regions of Inner Mongolia. Allergy. 2020;75(1):234-239. [4] ZHANG Y, LAN F, ZHANG L. Advances and highlights in allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 2021;76(11):3383-3389. [5] BERNSTEIN JA, BERNSTEIN JS, MAKOL R, et al. Allergic Rhinitis: A Review. JAMA. 2024;331(10):866-877. [6] LI Q, ZHANG X, FENG Q, et al. Common Allergens and Immune Responses Associated with Allergic Rhinitis in China. J Asthma Allergy. 2023;16:851-861. [7] LI Z, REN J, ZHANG J, et al. Association between IL1RL1 gene polymorphisms and allergic rhinitis risk in the Chinese Han population. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022;36(11):e24747. [8] DAI J, XIA K, HUAI D, et al. Identification of diagnostic signature, molecular subtypes, and potential drugs in allergic rhinitis based on an inflammatory response gene set. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1348391. [9] TAO Q, ZHU Y, WANG T, et al. Identification and analysis of lipid metabolism-related genes in allergic rhinitis. Lipids Health Dis. 2023; 22(1):105. [10] CAO K, ZHU J, LU M, et al. Analysis of multiple programmed cell death-related prognostic genes and functional validations of necroptosis-associated genes in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. EBioMedicine. 2024;99:104920. [11] SUN J, HUANG L, WANG J, et al. Programmed cell death in autoimmune diseases: ferroptosis. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2024;82(1):33-42. [12] LIU S, WANG C, ZHANG Y, et al. Polydatin inhibits mitochondrial damage and mitochondrial ROS by promoting PINK1-Parkin-mediated mitophagy in allergic rhinitis. FASEB J. 2023;37(4):e22852. [13] WANG M, YU F, ZHANG Y, et al. Programmed cell death in tumor immunity: mechanistic insights and clinical implications. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1309635. [14] RUBIO K, MOLINA-HERRERA A, PEREZ-GONZALEZ A, et al. EP300 as a Molecular Integrator of Fibrotic Transcriptional Programs. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(15):12302. [15] MA M, ZHAO S, LI C, et al. Transient receptor potential channel 6 knockdown prevents high glucose-induced Müller cell pyroptosis. Exp Eye Res. 2023;227:109381. [16] ZHANG Z, KANG H. Protective effect of Asarum sieboldii essential oil on ovalbumin induced allergic rhinitis in rat. Biosci Rep. 2020; 40(6):BSR20191370. [17] ŞAHIN A, SAKAT MS, KILIÇ K, et al, The protective effect of Naringenin against ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis in rats. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021;278(12):4839-4846. [18] SHOU Q, TAN T, XU F. Salvinorin A inhibits ovalbumin-stimulated allergic rhinitis and RBL-2H3 cells degranulation. FEBS Open Bio. 2021; 11(8):2166-2173. [19] WANG X, ZHANG H, DU L, et al. Influences of miR-378a-3p on the Pathogenesis of Allergic Rhinitis via GzmB-Mediated Inflammatory Reaction. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:5926834. [20] DRAZDAUSKAITE G, LAYHADI JA, SHAMJI MH. Mechanisms of Allergen Immunotherapy in Allergic Rhinitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020;21(1):2. [21] JIAO W E, XU S, QIAO YL, et al. Corrigendum to “Notch2-dependent GATA3+ Treg cells alleviate allergic rhinitis by suppressing the Th2 cell response” [Int. Immunopharmacol. 112 (2022) 109261]. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;136:112164. [22] JI T, LI H. T-helper cells and their cytokines in pathogenesis and treatment of asthma. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1149203. [23] WANG Y, ZHANG L, SHI B, et al. Trends and research foci in immunoregulatory mechanisms of allergic rhinitis: a bibliometric analysis (2014-2024). Front Immunol. 2024;15:1443954. [24] KANAGARATHAM C, EL ANSARI YS, LEWIS OL, et al. IgE and IgG Antibodies as Regulators of Mast Cell and Basophil Functions in Food Allergy. Front Immunol. 2020;11:603050. [25] SAVAS H B, GUNIZI H. Thiol-disulfide balance and trace element levels in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Afr Health Sci. 2022;22(3): 322-328. [26] FAN K, ZHOU S, JIN L, et al. Identification of key genes and the pathophysiology associated with allergen-specific immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis. BMC Immunol. 2023;24(1):19. [27] HUANG H, REN Y, LIANG H, et al. Mechanism of TCONS_00147848 regulating apoptosis of nasal mucosa cells and alleviating allergic rhinitis through FOSL2-mediated JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):15991. [28] LIN R, FOGARTY CE, MA B, et al. Identification of ferroptosis genes in immune infiltration and prognosis in thyroid papillary carcinoma using network analysis. BMC Genomics. 2021;22(1):576. [29] SUEN HC, RAO S, LUK ACS, et al. The single-cell chromatin accessibility landscape in mouse perinatal testis development. Elife. 2023;12:e75624. [30] HE R, LIU Y, FU W, et al. Mechanisms and cross-talk of regulated cell death and their epigenetic modifications in tumor progression. Mol Cancer. 2024;23(1): 267. [31] TANG D, KANG R, BERGHE TV, et al. The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res. 2019;29(5):347-364. [32] WANG X, WANG Z, GUO Z, et al. Exploring the Role of Different Cell-Death-Related Genes in Sepsis Diagnosis Using a Machine Learning Algorithm. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(19):14720. [33] PIAO CH, FAN Y, NGUYEN TV, et al. PM(2.5) Exacerbates Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response through the Nrf2/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway in OVA-Induced Allergic Rhinitis Mouse Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8173. [34] LEON B. Understanding the development of Th2 cell-driven allergic airway disease in early life. Front Allergy. 2022;3:1080153. [35] SHI J, WANG Q H, WEI X, et al. Histone acetyltransferase P300 deficiency promotes ferroptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells by activating the HIF-1alpha/HMOX1 axis. Mol Med. 2023;29(1): 91. [36] CRAWFORD MC, TRIPU DR, BARRITT SA, et al. Comparative Analysis of Drug-like EP300/CREBBP Acetyltransferase Inhibitors. ACS Chem Biol. 2023;18(10):2249-2258. [37] LI F, LI J, WANG PH, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike promotes inflammation and apoptosis through autophagy by ROS-suppressed PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021;1867(12):166260. [38] HU X, ZHANG H, ZHANG Q, et al. Emerging role of STING signalling in CNS injury: inflammation, autophagy, necroptosis, ferroptosis and pyroptosis. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):242. [39] HSU SK, LI CY, LIN IL, et al. Inflammation-related pyroptosis, a novel programmed cell death pathway, and its crosstalk with immune therapy in cancer treatment. Theranostics. 2021;11(18):8813-8835. [40] CHEN L, YANG L, LI Y, et al. Autophagy and Inflammation: Regulatory Roles in Viral Infections. Biomolecules. 2023;13(10):1454. [41] XU Y, WAN W. Acetylation in the regulation of autophagy. Autophagy. 2023;19(2):379-387. [42] REYES A, SIDDIQI T. Targeting BCL2 pathways in CLL: a story of resistance and ingenuity. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023;6(4):828-837. [43] KALONI D, DIEPSTRATEN S T, STRASSER A, et al. BCL-2 protein family: attractive targets for cancer therapy. Apoptosis. 2023;28(1-2):20-38. [44] ASADI M, TAGHIZADEH S, KAVIANI E, et al. Caspase-3: Structure, function, and biotechnological aspects. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2022;69(4):1633-1645. |
| [1] | Lai Jiaming, , Song Yuling, Chen Zixi, Wei Jinghuan, Cai Hao, , Li Guoquan, . Screening of diagnostic markers for endothelial cell Senescence in mice with radiation-induced heart disease and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1450-1463. |
| [2] | You Huijuan, Wu Shuzhen, Rong Rong, Chen Liyuan, Zhao Yuqing, Wang Qinglu, Ou Xiaowei, Yang Fengying. Macrophage autophagy in lung diseases: two-sided effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526. |
| [3] | Liu Kexin, , Hao Kaimin, Zhuang Wenyue, , Li Zhengyi. Autophagy-related gene expression in pulmonary fibrosis models: bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1129-1138. |
| [4] | Hu Jing, Zhu Ling, Xie Juan, Kong Deying, Liu Doudou. Autophagy regulates early embryonic development in mice via affecting H3K4me3 modification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1147-1155. |
| [5] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [6] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [7] | Bao Zhuoma, Hou Ziming, Jiang Lu, Li Weiyi, Zhang Zongxing, Liu Daozhong, Yuan Lin. Effect and mechanism by which Pterocarya hupehensis skan total flavonoids regulates the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 816-823. |
| [8] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [9] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Mechanism by which vascular endothelial growth factor A targets regulation of angiogenesis in the treatment of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 671-679. |
| [10] | Chen Ling, Mao Qiuhua, Xu Pu, Zhang Wenbo. Effect of water-soluble matrix of nano-pearl powder on proliferation, migration and apoptosis of mouse fibroblasts#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 338-344. |
| [11] | Zhao Yang, Li Jialin, Wu Xiao, Zou Yourui, Liu Yang, Ma Hui. Choline kinase alpha silencing affects proliferation and apoptosis in glioma cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 130-138. |
| [12] | Lu Yongheng, Zhu Shuang, Zhao Feiyan, Ai Fujun, Liu Yanjie, Dong Yangting, Guan Zhizhong, Wei Na. Effect of fluoride exposure on endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial calcium transfer and apoptosis in primary nerve cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 111-119. |
| [13] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [14] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [15] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||