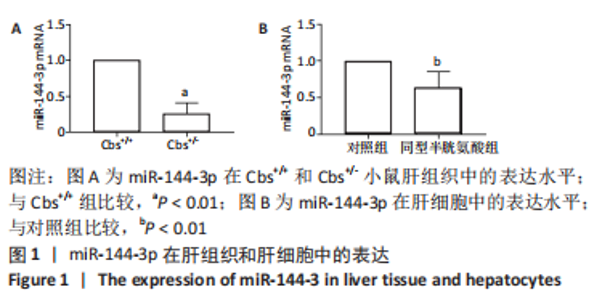
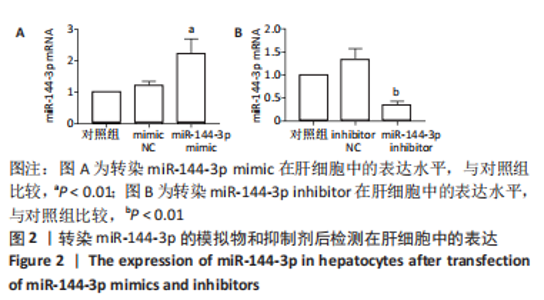
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (8): 1289-1294.doi: 10.12307/2024.201
Previous Articles Next Articles
Involvement of miR-144-3p in Cbs+/- mouse hepatocyte autophagy induced by high-methionine diet
Sheng Siqi1, 2, 3, Xie Lin1, 2, 3, Zhao Xiangyu1, 2, 3, Jiang Yideng1, 2, 3, Wu Kai1, 2, 3, Xiong Jiantuan1, 2, 3, Yang Anning1, 2, 3, Hao Yinju1, 2, 3, 4, Jiao Yun2, 4
- 1School of Basic Medical Sciences, 2NHC Key Laboratory of Metabolic Cardiovascular Diseases Research, Yinchuan 750004, 3Ningxia Key Laboratory of Vascular Injury and Repair Research, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 4General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-11-15Accepted:2022-12-26Online:2024-03-18Published:2023-07-19 -
Contact:Jiao Yun, Chief physician, NHC Key Laboratory of Metabolic Cardiovascular Diseases Research, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Sheng Siqi, Master candidate, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; NHC Key Laboratory of Metabolic Cardiovascular Diseases Research, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; Ningxia Key Laboratory of Vascular Injury and Repair Research, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82060110 (to JY); Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Key R&D Program, No. 2021BEG02033 (to XJT); Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Key R&D Program, No. 2020BFH02003 (to YAN); Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Key R&D Program, No. 2022BFH02013 (to HYJ); Basic Scientific Research Expense Project of the Central Public Welfare Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, No. 2019PT330002 (to JYD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sheng Siqi, Xie Lin, Zhao Xiangyu, Jiang Yideng, Wu Kai, Xiong Jiantuan, Yang Anning, Hao Yinju, Jiao Yun. Involvement of miR-144-3p in Cbs+/- mouse hepatocyte autophagy induced by high-methionine diet[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1289-1294.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
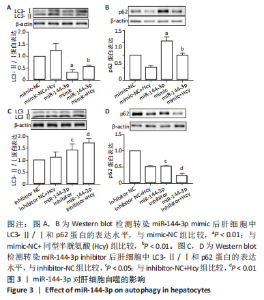
2.4 miR-144-3p对肝细胞自噬相关指标的影响 使用Western blot检测转染miR-144-3p模拟物和抑制剂后肝细胞中LC3-Ⅱ/Ⅰ和p62蛋白的表达,结果显示,转染miR-144-3p mimic后,与mimic-NC组相比,miR-144-3p mimic组中LC3B-Ⅱ/Ⅰ的蛋白表达水平降低,p62的蛋白表达水平升高(P < 0.01);与mimic-NC+同型半胱氨酸组比较,miR-144-3p mimic+同型半胱氨酸组中LC3B-Ⅱ/Ⅰ蛋白表达水平降低,p62的蛋白表达水平升高(P < 0.01),见图3A,B。转染miR-144-3p inhibitor后,与inhibitor-NC组比较,miR-144-3p inhibitor组中LC3B-Ⅱ/Ⅰ的蛋白表达水平升高,而p62的蛋白表达水平降低(P < 0.05);与inhibitor-NC+同型半胱氨酸组相比,miR-144-3p inhibitor+同型半胱氨酸组中LC3B-Ⅱ/Ⅰ的蛋白表达水平升高,而p62的蛋白表达水平降低(P < 0.01),见图3C,D。"

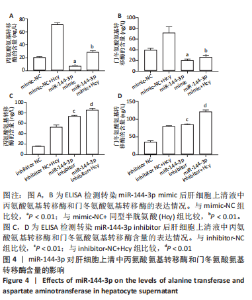
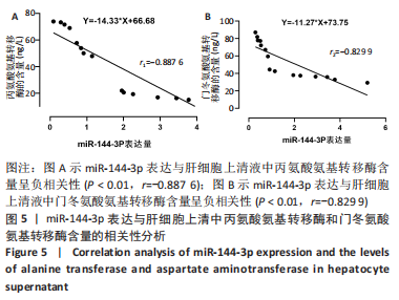
2.5 miR-144-3p对肝细胞上清中丙氨酸氨基转移酶和门冬氨酸氨基转移酶含量的影响 转染miR-144-3p mimic后,与mimic-NC组相比,miR-144-3p mimic组肝细胞上清液中丙氨酸氨基转移酶和门冬氨酸氨基转移酶的含量降低(P < 0.01);与mimic-NC+同型半胱氨酸组比较,miR-144-3p mimic+同型半胱氨酸组肝细胞上清液中丙氨酸氨基转移酶和门冬氨酸氨基转移酶的含量降低(P < 0.01),见图4A,B。转染miR-144-3p inhibitor后,与inhibitor-NC组比较,miR-144-3p inhibitor组肝细胞上清液中丙氨酸氨基转移酶和门冬氨酸氨基转移酶的含量升高(P < 0.01);与inhibitor-NC+同型半胱氨酸组相比,miR-144-3p inhibitor+同型半胱氨酸组肝细胞上清液中丙氨酸氨基转移酶和门冬氨酸氨基转移酶的含量升高(P < 0.01),见图4C,D。"

| [1] BUTZ LW, DUV INGEAUD V. The formation of a hamologue of cystine by the decomposition of methionine with sulfric acid. J Biol Chem. 1932;99(1):135-142. [2] Wang X, Zhang F, Guo L, et al. Significance of hyperhomocysteinaemia as an effective marker for vasculogenic erectile dysfunction: a cross-sectional study. Transl Androl Urol. 2022;11(3):397-406. [3] Xu B, Zhang L, Chen Q, et al. Case report: a case of late-onset combined methylmalonic acidemia and hyperhomocysteinemia induced by a vegetarian diet. Front Pediatr. 2022;10:896177. [4] Song J, Huh H, Bae E, et al. Association between homocysteinemia and mortality in CKD: A propensity-score matched analysis using NHANES-National Death Index. Medicine. 2022;101(36):e30334. [5] Zhang M, Dong R, Da J, et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia exacerbates acute kidney injury increased mitochondrial damage. Front Physiol. 2022;13:967104. [6] Weng H, Li Y, Fan F, et al. The association b etween total homocysteine and blood pressure in two independent Chinese populations. J Hum Hypertens. 2020;34(9): 657-665. [7] Lan T, Xu D, Huang M, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 prevents homocysteine-induced EPC dysfunction via VEGF/p38MAPK and SDF-1/CXCR4 activation. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):13061. [8] Kwon D, Son S, Kim S, et al. Effects of dietary restriction on hepatic sulfur-containing amino acid metabolism and its significance in acetaminophen-induced liver injury. J Nutr Biochem. 2022;108:109082. [9] Shen J, Jiao Y, Ding N, et al. Homocysteine facilitates endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis of hepatocytes by suppressing ERO1α expression via cooperation between DNMT1 and G9a. Cell Bio Int. 2022;46(8):1236-1248. [10] Xiao K, Ma S, Xu L, et al. Interaction between PSMD10 and GRP78 accelerates endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated hepatic apoptosis induced by homocysteine. Gut Pathog. 2021;13(1):63. [11] Vatsalya V, Gala K, Hassan A, et al. Characterization of early-stage alcoholic liver disease with hyperhomocysteinemia and gut dysfunction and associated immune response in alcohol use disorder patients. Biomedicines. 2020;9(1):7. [12] Yang A, Jiao Y, Yang S, et al. Homocysteine activates autophagy by inhibition of CFTR expression via interaction between DNA methylation and H3K27me3 in mouse liver. Death Dis. 2018;9(2):169. [13] 张宏红,谢琳,盛思琪,等. FoxO1在同型半胱氨酸诱导的肾脏足细胞损伤及凋亡中的作用研究[J]. 天津医药,2022,50(1):53-58. [14] 熊建团,顾铃毓,王青青,等. TLR4/NF-κB信号通路对Cbs+/-小鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝病的影响[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2021,37(7):1227-1232. [15] Zapletal D, Taborska E, Pasulka J, et al. Structural and functional basis of mammalian microRNA biogenesis by Dicer. Mol Cell. 2022;82(21):4064-4079. [16] Griñán R, Escolà-Gil J, Julve J, et al. Epigenetic regulation by microRNAs in hyperhomocysteinemia-accelerated atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12452. [17] Canning A, Chen X, Li J, et al. miRNA probe integrated biosensor platform using bimetallic nanostars for amplification-free multiplexed detection of circulating colorectal cancer biomarkers in clinical samples. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;220:114855. [18] BAO H, LI X, LI H, et al. MicroRNA-144 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion and migration by targeting ZFX. J Biosci. 2017;42(1):103-111. [19] Lv J, Kong Y, Gao Z, et al. LncRNA TUG1 interacting with miR-144 contributes to proliferation, migration and tumorigenesis through activating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;101:19-28. [20] Zhao J, Li H, Zhao S, et al. Epigenetic silencing of miR-144/451a cluster contributes to HCC progression via paracrine HGF/MIF-mediated TAM remodeling. Mol Cancer. 2021;20(1):46. [21] Chen Y, Xu N, Hong C, et al. Myo1b promotes tumor progression and angiogenesis by inhibiting autophagic degradation of HIF-1α in colorectal cancer. Death Dis. 2022;13(11):939. [22] van Vliet A, Chiduza G, Maslen S, et al. ATG9A and ATG2A form a heteromeric complex essential for autophagosome formation. Mol Cell. 2022;82(22):4324-4339.e8. [23] 曾征鹏,蔡金文,廖毓梅,等. MicroRNA-21通过自噬影响疾病的研究进展[J]. 中南大学学报,2022,47(7):936-941. [24] 张宏红,谢琳,盛思琪,等. miR-195-3p在同型半胱氨酸诱导的肝氧化应激损伤中的调控作用研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2022,38(17):2044-2048. [25] Wong CKH, Mak LY, Au ICH, et al. Risk of acute liver injury following the mRNA (BNT162b2) and inactivated (CoronaVac) COVID-19 vaccines. J Hepatol. 2022; 77(5):1339-1348. [26] Jacobs RL, Jiang H, Kennelly JP, et al. Cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency alters hepatic phospholipid and choline metabolism: Post-translational repression of phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase is a consequence rather than a cause of liver injury in homocystinuria. Mol Genet Metab. 2017;120(4):325-336. [27] 孙磊,郭伟,马鹏俊,等. miR-30a-5p启动子区DNA甲基化在同型半胱氨酸致肝损伤中的作用[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2020,36(1):119-126. [28] Palma Reis R. Homocysteinemia and vascular disease: Where we stand in 2022. Rev Port Cardiol. 2022;41(10):821-822. [29] Omorou M, Liu N, Huang Y, et al. Cystathionine beta-Synthase in hypoxia and ischemia/reperfusion: A current overview. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022;718:109149. [30] 罗婷玉,杨玉辉,许云聪,等.蛋氨酸限制对高脂饮食诱导的肥胖小鼠胰岛功能损伤的改善作用[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(3):111-119. [31] Han C, Yang J, Zhang E, et al. Metabolic labeling of cardiomyocyte-derived small extracellular-vesicle (sEV) miRNAs identifies miR-208a in cardiac regulation of lung gene expression. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022;11(10):e12246. [32] Dhuppar S, Murugaiyan G. miRNA effects on gut homeostasis: therapeutic implications for inflammatory bowel disease. Trends Immunol. 2022;43(11):917-931. [33] 殷荷,吴琪瑞,高丽娜,等. 环状RNA circRBM39在缺氧致胎盘滋养细胞凋亡中的作用及其分子机制[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2021,37(16):2180-2183. [34] Kooshkaki O, Rezae Z, Rahmati M, et al. MiR-144: A New Possible Therapeutic Target and Diagnostic/Prognostic Tool in Cancers. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2578. [35] Zhang G, Wan Z, Liu Z, et al. Exosomes Derived from BMSCs Ameliorate Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Regulating miR-144-3p-Mediated Oxidative Stress. Dig Dis Sci. 2022;67(11):5090-5106. [36] 胡滨,袁金金. circPUM1靶向调控miR-144-3p对宫颈癌细胞放射抵抗的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报,2022,51(2):215-224. [37] Kennedy L, Meadows V, Sybenga A, et al. Mast cells promote nonalcoholic fatty liver disease phenotypes and microvesicular steatosis in mice fed a western diet. Hepatology. 2021;74(1):164-182. [38] Zhang D, Pan A, Gu J, et al. Upregulation of miR-144-3p alleviates doxorubicin-induced heart failure and cardiomyocytes apoptosis via SOCS2/PI3K/AKT axis. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022;10.1111/cbdd.14104. doi:10.1111/cbdd.14104. [39] Qian R, Cao G, Su W, et al. Enhanced sensitivity of Tumor cells to autophagy inhibitors using fasting-mimicking diet and targeted lysosomal delivery. Nano Lett. 2022;22(22):9154-9162. [40] Luo M, Ye L, Chang R, et al. Multi-omics characterization of autophagy-related molecular features for therapeutic targeting of autophagy. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):6345. [41] 高源,揭育祯,马天龙,等. miR-488-3p靶向调控RAP1A在同型半胱氨酸介导肝细胞自噬的作用研究[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2022,32(9):1-9. [42] 马芳,张辉,沈江涌,等. 同型半胱氨酸通过激活beclin1调节的自噬激活分子(AMBRA1)促进人肝细胞自噬[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2022,38(9):813-818. [43] 刘圆,张辉,焦运,等. 基质金属蛋白酶2 DNA甲基化在同型半胱氨酸诱导肝细胞凋亡中的作用[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2022,38(1):14-17. [44] 董小艳,刘达越,徐灵博,等. 脂肪酸结合蛋白4在同型半胱氨酸致大鼠心肌细胞焦亡中的作用[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2022,47(1):33-38. [45] 顾铃毓,徐灵博,杨安宁,等. 长链非编码RNA生长停滞特异性转录本5 (lncGAS5)促进同型半胱氨酸致肝细胞自噬作用[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2021,37(3):240-245. [46] Yan Y, Wu X, Wang P, et al. Homocysteine promotes hepatic steatosis by activating the adipocyte lipolysis in a HIF1α-ERO1α-dependent oxidative stress manner. Redox Biol. 2020;37:101742. [47] Zhang D, Lou J, Zhang X, et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia results from and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma via CYP450 metabolism by CYP2J2 DNA methylation. Oncotarget. 2017;8(9):15377-15392. [48] 宋鹏书,张燕华,张奕梅,等. 自噬相关蛋白LC3-Ⅱ和p62在不明原因复发性流产患者绒毛组织中的表达和临床意义[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2021, 42(13):1602-1605. [49] 江利亚,张玉想,张志华,等. 自噬在劳力性热射病大鼠急性肺损伤中的作用[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2022,47(5):427-434. [50] 姚雅兰,蒋廷旺,张敏. 血清溶酶体相关膜蛋白2A和转移酶在原发性胆汁性胆管炎中的表达[J]. 临床血液学杂志,2020,33(10):674-677. [51] Pan B, Han B, Zhu X, et al. Dysfunctional microRNA-144-3p/ZBTB20/ERK/CREB1 signalling pathway is associated with MK-801-induced schizophrenia-like abnormalities. Brain Res. 2022;1798:148153. [52] Li S, Shao J, Lou G, et al. MiR-144-3p-mediated dysregulation of EIF4G2 contributes to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma through the ERK pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40(1):53. |
| [1] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Li Wenbo, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. Effect of aerobic exercise on glycolipid metabolism, skeletal muscle inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [2] | Zhou Bangyu, Li Jie, Ruan Yushang, Geng Funeng, Li Shaobo. Effects of Periplaneta americana powder on motor function and autophagic protein Beclin-1 in rats undergoing spinal cord hemisection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1223-1228. |
| [3] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [4] | Huang Yuxin, Liang Wenzi, Chen Xiuwen, Ni Na, Zhao Yinglin, Lin Changmin. Role of autophagy in hair regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1112-1117. |
| [5] | Liu Qiwei, Zhang Junhui, Yang Yuan, Wang Jinjuan. Role and mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [6] | Xue Jingwen, Wang Fangfang, Zhang Xin, Pang Ruifeng, Wang Xiaoye, Ma Xiaoru. Effect of ganoderma spore on mitochondrial autophagy and apoptosis in testicular tissue of diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 562-568. |
| [7] | Yan Binghan, Li Zhichao, Su Hui, Xue Haipeng, Xu Zhanwang, Tan Guoqing. Mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine monomers in the treatment of osteoarthritis by targeting autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 627-632. |
| [8] | Guo Xiangying, Peng Zifu, He Yimin, Fang Hongbo, Jiang Ning. MiRNA-122 contributes to the effect of exercise on non-alcoholic fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 272-279. |
| [9] | Wang Jingfeng, Wen Dengtai, Wang Shijie, Gao Yinghui. Atg-mediated autophagy, exercise and skeletal muscle aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 295-301. |
| [10] | Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Liu Tao, Li Yan, He Yuanxu, He Bo, Wang Weiwei, Wei Xiaotao. Traditional Chinese medicine monomer in the prevention and treatment of flap necrosis by regulating “autophagy” [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 153-158. |
| [11] | Deng Rui, Huang Keming, Luo Jian, Chen Gong, Feng Jian, Huang Weiyi, Wei Gang. Effect of heme oxygenase-1-mediated atorvastatin on macrophage polarization and cholesterol accumulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 62-67. |
| [12] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [13] | Zhang Qing, Gao Chunlan, Yu Feifei, Zhang Zhenghao, Ma Fang, Gao Yuan, Li Guizhong, Jiang Yideng, Ma Shengchao. Ephrin A receptor 2 DNA methylation increases in pancreatic beta cell apoptosis induced by homocysteine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 714-719. |
| [14] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [15] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||