Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (4): 587-593.doi: 10.12307/2023.864
Previous Articles Next Articles
The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine
Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo
- Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-11-11Accepted:2023-01-04Online:2024-02-08Published:2023-07-14 -
Contact:Lin Zonghan, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wei Yuanxun, Master candidate, Ruikang Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2021GXNSFAA220089 (to CF); Postgraduate Education Innovation Program of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. YCBZ2021075 (to ZC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
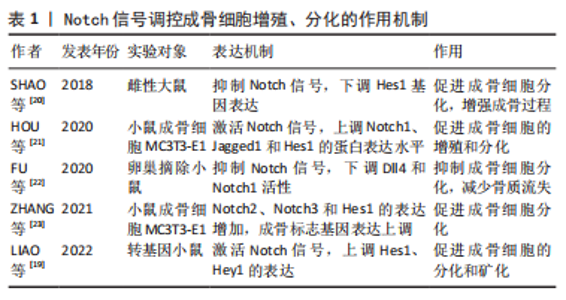
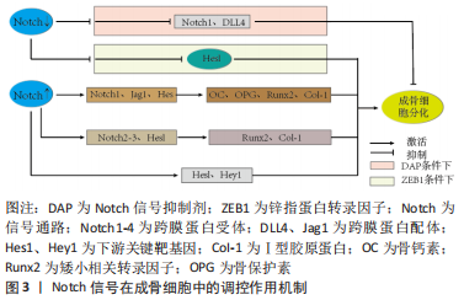
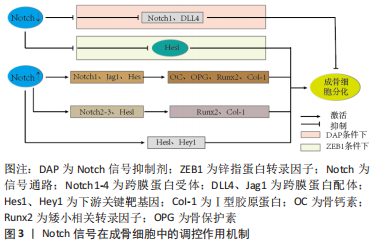
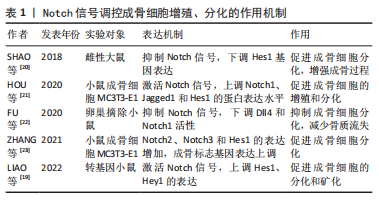
2.1 Notch信号通路与骨质疏松症的关系 国内外研究证实,成骨细胞及破骨细胞功能受损、间充质干细胞衰老、微环境失衡、免疫调节紊乱等是引起骨质疏松症的重要因素[15]。Notch信号在维持骨稳态和决定成骨细胞命运中起着重要作用,且骨形成研究反映了其在成骨细胞分化和破骨细胞分化中具有双向调节的作用[16]。此外还有研究表明,Notch信号在血管内皮细胞影响骨形成中也发挥着重要作用[17]。现文章根据检索结果,将Notch信号调控骨质疏松症分为成骨细胞、破骨细胞、间充干细胞、血管内皮细胞4个方面进行阐述。 2.1.1 Notch信号调控成骨细胞 成骨细胞通过合成细胞外基质来维持骨量,同时抑制或增加骨吸收,从而促进骨形成[18]。LIAO等[19]在小鼠体内实验中证实了Jagged1上调了多个Notch典型基因(Hes1、Hey1)的表达,进一步分析表明这些基因在γ分泌酶抑制剂存在下被下调,而早期成骨细胞增殖促进剂(Prl2c2、Smurf1和Esrra)和破骨细胞抑制剂(Id1)显著上调。因此,Jagged1通过刺激颅神经嵴中成骨细胞特异性基因的表达,促进成骨细胞的分化和矿化。同样有实验证明,使用Notch信号抑制剂γ分泌酶抑制剂,让骨细胞分化中Notch信号下游关键靶基因Hes1表达下调,矿化过程发生显著改变,从而增强成骨过程[20]。HOU等[21]观察在利拉鲁肽治疗20 min后,小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体中Notch1、Jagged1和Hes1的蛋白表达达到峰值,且Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、Runx2、骨钙素、骨保护素等成骨相关基因表达与对照组相比均明显升高,这些数据表明,利拉鲁肽可以通过激活Notch信号通路来促进成骨细胞的增殖和分化。相反,FU等[22]研究发现骨质疏松小鼠的骨血管生成受损,成骨细胞活性降低,在ZEB1-GFP阳离子脂质体系统处理后有效地恢复,该研究结果表明,促进血管生成依赖性成骨并改善骨质流失的关键是通过抑制Notch信号传导、降低Dll4和Notch1上的组蛋白乙酰化作用实现的。 ZHANG等[23]证实lnc-Evf2与成骨细胞的成熟和前体间充质干细胞的成骨分化有关,在成骨诱导后,Notch2、Notch3和Hes1的表达急剧增加,且成骨标志基因(碱性磷酸酶、Bglap、Runx2、Bsp、Sp7和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白)表达均上调,由此可知,lnc-Evf2通过在转录后水平调节Notch信号传导的成分来促进成骨细胞分化。 综上,Notch信号在成骨细胞增殖、分化方面影响骨形成与再吸收,但在调控骨质疏松症中双向调节的具体机制尚不完全清楚,缺少相关方面的临床试验研究及报道,因此后续研究者可将此作为研究重点。Notch信号调控成骨细胞增殖、分化的作用机制见表1,图3。"
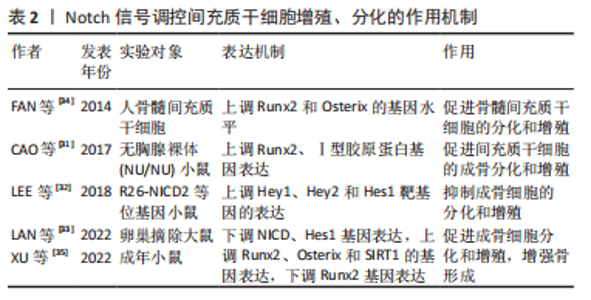
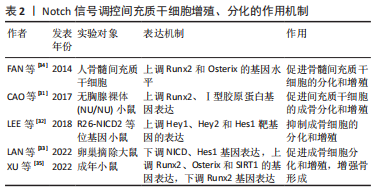
2.1.2 Notch信号调控破骨细胞 破骨细胞来源于造血谱系,是分化单核细胞和巨噬细胞的骨吸收细胞。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子对破骨细胞的增殖和分化至关重要,其中破骨细胞的分化是通过与核因子κB受体活化因子配体进行调节的。当前,Notch信号已被证明是破骨细胞生成和骨吸收的关键调节因子[24] 。ASHLEY等[25]通过用固定配体Jagged1或Delta-like1刺激破骨细胞分化过程中Notch信号的改变,结果显示,在巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和核因子κB受体活化因子配体刺激Notch信号的作用下,破骨细胞的细胞核数量、大小及骨矿物吸收均增加,破骨细胞的生成及再吸收活性明显增强,进一步证明了Notch信号在破骨细胞成熟中的重要性。HUANG等[26]利用体外实验研究发现,在核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导的破骨细胞形成过程中,用分泌酶抑制剂RO4929097进行骨髓巨噬细胞诱导裂解,结果表明,NFATc1、C-fos、Cath-K和抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶破骨基因表达在剂量依赖性和时间依赖性方面显著下调,Notch1、Hes1和NFATc1的蛋白表达下调,抑制了骨质流失和破骨细胞的增殖、分化。Hes1为Notch信号通路关键靶基因及决定破骨细胞命运的转录调节因子。YU等[27]通过小鼠实验对破骨细胞表型和RNA-Seq进一步分析,结果显示破骨融合标志物、整合素信号传导和用于密封区形成的结构蛋白的基因亚群在破骨细胞中显著上调,其结果进一步证实了Hes1介导Notch2信号表达对破骨细胞的生成有直接作用。破骨细胞的生成和发展主要取决于核因子κB受体活化因子配体和巨噬细胞刺激因子。YANG等[28]在小鼠细胞实验中通过qRT-PCR对破骨细胞进行检测分析,发现破骨细胞相关基因(抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、NFATc1和C-Fos)高表达且呈正相关,进一步探索发现,Notch2信号可以诱导(抑制)核因子κB受体活化因子配体在成骨细胞中的表达,刺激破骨细胞活性,从而促进破骨细胞的分化。 总之,破骨细胞分化各个阶段的Notch信号活性,通过细胞自主和非细胞自主机制由特定的配体-受体相互作用控制。关于受体-配体组合在多个细胞分化阶段中作用的研究,有利于阐明Notch信号在破骨细胞中的作用,并有助于确定骨质疏松的其他靶点。此外,非标准Notch信号是否在破骨细胞增值、分化过程中起作用尚待确定。 2.1.3 Notch信号调控间充质干细胞 间充质干细胞作为多能干细胞,具有较高的多功能性,可分化为多能骨、软骨和脂肪组织细胞,这些细胞已经成为干细胞基础治疗最合适的来源[29]。目前已证实,间充质干细胞可调节成骨细胞分化,增加骨密度,阻止骨质疏松症的恶化,是一种有效的、新颖的治疗方法[30]。CAO等[31]利用小鼠实验证实,Notch信号增强了基质金属蛋白酶9诱导的骨形态发生蛋白/Smad信号传导的活性,并增加成骨因子的基因表达,促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化和增殖。LEE等[32]使用携带R26-NICD2等位基因的成年小鼠进行实验,结果表明小鼠细胞内Notch2结构域上调Hey1、Hey2和Hes1靶基因的表达,激活Notch信号传导,并显著抑制了骨髓间充质干细胞中成骨细胞标记物Alpl、Bsp、Bglap和Sp7的蛋白表达,进一步证实了Notch信号传导抑制间充质干细胞的葡萄糖代谢,以限制成骨细胞的分化和增殖。LAN 等[33]发现,雌激素活性的环肽化合物(SB)通过下调NICD、乙酰基NICD和Hes1的基因表达,上调Runx2、Osterix和SIRT1的蛋白表达,促进卵巢摘除大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的矿化,提高骨钙素。此外,SB还能显著降低卵巢摘除大鼠体内骨丢失,抑制钙、磷损失,提高碱性磷酸酶活性,进而促进成骨细胞分化和增殖,对骨质疏松症起到重要作用。FAN等[34]通过17β-雌二醇干预绝经后骨质疏松症患者,蛋白印迹检测显示,成骨标志物Runx2、碱性磷酸酶和Osterix的基因水平显著上升,且随着时间的推移Osterix基因表达不断增加,提示Notch信号通路在雌激素的激活下调节骨髓间充质干细胞的分化和增殖,并有效改善绝经后骨质疏松症的骨量。XU等[35]研究表明,Dll4(E12)可用于激活骨间充质基质细胞中的Notch信号传导,降低Runx2基因表达,从而增强骨形成、减少骨骼脆弱性和骨折发生率。 因此,相关Notch信号通路通过自身表达的差异性,调控间充质干细胞对成骨细胞增殖与分化,从而产生不同程度的影响,其作用主要取决于相关Notch信号对间充质干细胞起到促进或者抑制的作用。但作者通过检索结果发现,对于Notch信号通过调控间充质干细胞干预骨质疏松症的研究仅停留在某种靶基因或某些化合物上,其具体的应用途径、时间或浓度依赖性及机体免疫原性等方面尚未进行系统阐明,这可能是未来研究治疗骨质疏松症的新的突破点。Notch信号调控间充质干细胞增殖、分化的作用机制,见表2。总体而言,Notch信号主要通过Notch1、Jagged1、巨噬细胞刺激因子、核因子κB受体活化因子配体、Hes等关键因子进行综合调控,增强成骨细胞、破骨细胞、间充干细胞的增殖、分化,进而调整骨骼发育和体内平衡。"
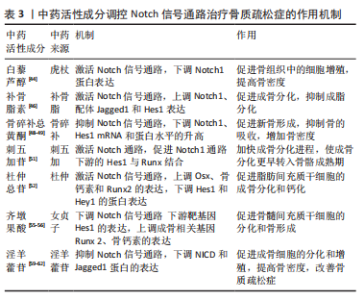
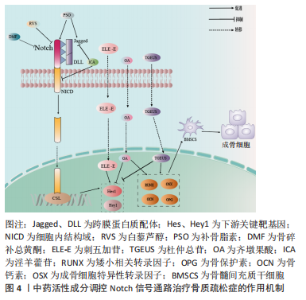
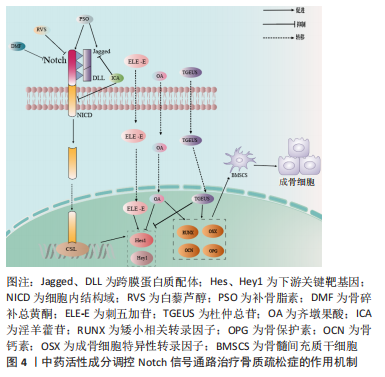
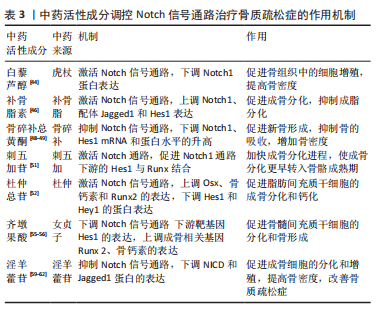
2.1.4 Notch信号调控血管内皮细胞 血管内皮生长因子A是骨骼发育过程中血管生成与软骨内和膜性骨形成有效介质,其通过将内皮细胞吸引到骨组织,调节成骨细胞和破骨细胞的分化和功能,进而参与骨形成[36]。LIU等[37]实验证实,血管内皮生长因子通过调节Notch信号中转录因子Runx2和过氧化物酶增殖物激活受体γ2以及通过与核包膜蛋白层粘连蛋白a/C的相互作用来控制间充质干细胞的分化。此外,间充质干细胞中血管内皮生长因子表达减少导致成骨细胞减少和脂肪细胞分化增加。CHEN等[38]利用人参皂苷Rg1进行体外实验,结果表明,Rg1不仅增加了骨祖细胞的数量,还可促进骨祖细胞分泌血管内皮生长因子,加速成骨与血管生成耦合。进一步研究表明,Rg1还可以促进高糖培养的人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖,增强内皮细胞的血管生成能力,激活Notch通路促进内皮细胞分泌成骨相关因子Noggin调节成骨作用,为血管生成和成骨提供进一步耦合。 综上,Notch信号调控血管内皮细胞有望成为骨质疏松症新的干预措施,但目前关于此方面的相关文献研究相对缺乏,仍需深入研究,进而为防治骨质疏松症方面提供血管新生层面的应用参考。 2.2 中医对骨质疏松症的认识 中医对骨质疏松症的认识有着悠久的历史,虽没有明确记载骨质疏松症病名,但根据其临床症状、发病机制、治则治法等,将其归属于“骨枯”“骨痿”“骨痹”等范畴,《素问·痿论》记载:“肾者水脏也,今水不胜火,则骨枯而髓虚,故足不任身,发为骨痿”“脾健则四肢强劲……脾运化精微……下归于肾。”中医认为肾虚为骨质疏松症的根本原因,肾为先天之本,肾藏精,主骨生髓。脾虚是骨质疏松发病的重要病机,脾为后天之本,气血生化之源,脾气虚则四肢不用。血瘀则是病理产物,血液运行依赖元气的推动,元气为肾精所化,肾精不足,无源化气,必致血瘀[39]。中医药经过长期实践确立了“肾主骨,生髓”的理论,并以“治未病”“辨证施治”等整体治疗观为指导思想,树立了补肾壮骨、健脾益气及活血通络的三大治法。目前,中医药通过干预Notch信号防治骨质疏松症研究仅从某种中药或中药活性成分进行,缺乏深入全面性的阐述。因此,有必要对中医药干预Notch信号通路对中医药防治骨质疏松症的作用机制做更深入的分析与总结。 2.3 中医药调控Notch信号通路防治骨质疏松症 2.3.1 中药活性成分 基于中医药具有辨证论治整体宏观调控人体防治疾病作用,以其具有多角度、多层次和不良反应小的优势,在缓解骨质疏松疼痛等方面具有显著作用,因此,运用中药或活性成分治疗骨质疏松症已成为研究热点之一[40]。Notch信号通路能够促进骨质疏松患者成骨细胞与破骨细胞的增殖与分化,是研究骨质疏松症发生进展的一条重要通路[41],目前研究显示多种中药活性成分及提取物对该通路起到调控作用[42]。 虎杖具有利湿退黄、清热解毒、散瘀止痛、止咳化痰的功效。白藜芦醇是从虎杖中提取出具有生物活性的多羟基二苯乙烯类化合物,还具有抗炎、抗氧化和基因修饰等作用[43]。邹庆峰等[44]研究发现,白藜芦醇通过激活雌激素受体调控Notch信号通路,降低Notch1蛋白的表达,促进骨内组织中的细胞增殖,提高骨质疏松大鼠骨密度,从而发挥抗骨质疏松症的作用。 补骨脂具有补肾壮阳、温脾止泻、纳气平喘的功效,是从补骨脂内提取的有效成分,为天然酚类香豆素,具有多种药理活性,包括抗氧化、抗菌、抗炎、抗抑郁等。有研究表明,补骨脂素在多种疾病中起着有益的作用,特别是癌症和骨质疏松症[45]。有研究证实,补骨脂素能够上调干细胞内已降低的Notch信号通路活性,使Notch1、配体Jagged1和Hes1的蛋白表达升高,增强成骨细胞活性,对成脂细胞的分化起到一定的抑制作用,进而促进成骨[46]。 骨碎补具有补肾强骨、疗伤止痛的作用,是骨质疏松症常用药之一。黄酮类化合物骨碎补总黄酮是骨碎补的重要提取成分,经现代药理药实验研究证实,骨碎补总黄酮能够增强骨的钙化,保持骨的吸收,调节骨代谢,从而达到改善骨生物力学指标的功效,同时还具有抗炎和改善微循坏的作用[47]。韩亚力等[48]利用体外实验证明,骨碎补总黄酮能降低大鼠骨髓间充质细胞Notch1、Hes1 mRNA基因表达程度,增强成骨细胞的活性,提高骨质疏松大鼠骨密度,促进骨形成并抑制体内骨吸收。同样的,黄翔宇等[49]实验表明,骨碎补总黄酮有效改善了小鼠股骨的骨微结构,调节了骨代谢相关蛋白的表达,通过下调Notch1、Hes1 mRNA基因表达促进新骨形成,同时抑制骨的吸收,增加骨密度。 刺五加具有益气健脾、补肾安神的功效,木脂素类化合物刺五加苷是刺五加的主要活性成分。现代研究表明,刺五加苷具有广泛的药理活性,包括改善外周血循环、抗缺血再灌注损伤、预防和延缓神经元凋亡、免疫调节、促进伤口愈合、防止骨质流失等[50]。有研究表明,1×10-8 mol/L浓度的刺五加苷可缩短骨髓间充质干细胞诱导时间,加速成骨进程,通过激活Notch通路上调成骨细胞特异性转录因子、骨涎蛋白、骨钙素mRNA表达水平,下调Runx表达量,促进Notch1通路下游的Hes1与Runx结合,从而加快了成骨分化的进程,使成骨分化更早转入骨骼成熟期,缓解骨质疏松[51]。 杜仲具有补益肝肾、强筋壮骨的功效,常用于骨质疏松症的治疗。杜仲总苷作为杜仲的主要成分之一,具有抗炎、镇痛、抗骨质疏松、提高免疫力等作用。ZHOU等[52]一项实验表明,使用杜仲总苷后,大鼠的骨小梁明显增加,连接增厚,通过激活Notch信号通路传导,上调Osx、骨钙素和Runx2因子表达程度,下调Hes和Hey1的蛋白表达,并显著增强细胞、碱性磷酸酶活性和钙沉积,促进脂肪间充质干细胞的成骨分化和钙化,这表明杜仲总苷是一种潜在的抗骨质疏松症治疗药物。由此可见,杜仲提取物促进脂肪间充质干细胞的成骨分化和钙化可能是通过激活Notch信号通路实现的。 女贞子具有滋补肝肾、乌发明目的功效。五环三萜类化合物齐墩果酸是女贞子中含量较高的成分之一[53],经证明其在代谢紊乱、糖尿病、肝炎和各种癌症等疾病中也具有广泛治疗作用[54]。程韶等[55]研究表明,齐墩果酸局部给药可以促进去卵巢小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的分化和骨形成,下调Notch信号通路下游靶基因 Hes1的表达,上调成骨相关基因Runx2、骨钙素的表达,促进骨质疏松性骨折愈合,改善骨折后肢体的功能活动受限或疼痛感,加速骨折肢体的功能恢复。有研究者指出,齐墩果酸在卵巢摘除诱导的骨质疏松大鼠中发挥骨保护作用,并在体外刺激骨间充质干细胞的成骨分化,齐墩果酸及其糖苷可通过上调骨钙素和矮小相关蛋白2蛋白水平抑制破骨细胞的形成来防止骨质流失,这种效应的分子机制可能与Notch信号通路有关[56]。 淫羊藿具有补肾壮阳、强筋壮骨的功效。黄酮类化合物淫羊藿苷是补肾中药淫羊藿的主要活性成分之一,具有许多药理作用,包括抗血管生成、抗自噬、抗细胞凋亡及保护神经等[57]。另有研究证实,淫羊藿苷不仅可以促进骨髓间充干细胞和成骨细胞的分化,还可以调节骨代谢、减缓骨丢失速度,预防骨质疏松的发展[58]。李永贤等[59]采用高浓度淫羊藿苷治疗骨质疏松大鼠,结果显示大鼠骨小梁结构紧密,骨量恢复明显,同时血浆碱性磷酸酶和NP水平明显下降,骨钙素、雌二醇和骨形态发生蛋白2水平显著升高,主要机制是通过降低碱性磷酸酶和抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶活性,提高骨钙素、雌二醇、骨形态发生蛋白2含量,提高Notch1和骨保护素的表达水平,降低骨质的吸收,促进骨形成。同时,孙杰等[60]研究表明,与骨质疏松骨折组相比,淫羊藿组能通过调控Notch信号通路提高Notch1、骨保护素表达,抑制血清碱性磷酸酶的活性和核因子κB受体活化因子配体基因表达,随着治疗时间的推移,大鼠骨密度、骨体积、骨小梁显著增加。LIU等[61]观察淫羊藿苷干预治疗去卵巢大鼠的研究显示,淫羊藿苷通过下调NICD和Jagged1蛋白的表达抑制Notch信号通路,增加骨小梁的数量和厚度,促进成骨分化和钙化。此外,淫羊藿苷通过降低脂肪生成相关因子mRNA的表达,抑制间充质干细胞向脂肪细胞的分化,从而对骨质疏松症产生有益的影响。汪小飞等[62]实验免疫组化染色结果显示,试验组(淫羊藿提取物)、阳性对照组中骨密度、股骨抗弯力、骨保护素和25羟维生素D均高于模型对照组,表明淫羊藿提取物增加骨质疏松大鼠骨密度、调节骨代谢平衡。综上所述,淫羊藿苷通过调控Notch信号通路传导,进一步拓展了中医药多效点防治骨质疏松症的途径,具有重要意义,详见表3,图4"

2.3.2 中药复方及制剂 中药成分的多样性和药物机制的多元性是中药复方的独特优势,与西药单一成分相比具有明显优势。周灵通[63]在固本增骨方干预大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的实验中,通过蛋白免疫印迹法检测结果发现,成骨因子中Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、骨钙素、Runx2蛋白表达水平显著性升高,提示固本增骨方调控Notch信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,减缓骨质疏松症的发生发展。许日明等[64]认识到温肾固疏方是由淫羊藿、骨碎补、补骨脂等具有补肾强骨的药物组成,在以往研究基础上得出温肾固疏方能更好地提高肾阳虚患者的骨密度,促进骨形成,该实验表明,治疗组中肾阳虚患者骨密度和Notch通路关键分子表达比对照组均上升(P < 0.05),并通过上调雌激素受体蛋白表达水平恢复骨髓间充质干细胞功能,诱导成骨细胞增值、分化,促进骨形成。王洁芳[65]为明确益骨胶囊治疗大鼠骨质疏松症的作用机制,拟用益骨胶囊干预大鼠骨质疏松症模型,观察益骨胶囊对大鼠骨组织基因的表达的影响,结果显示益骨胶囊下调Noch1、Noch2、Jagged1、Jagged2的基因表达,同时抑制转录因子过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ mRNA分化,促进了Runx2 mRNA表达,增加骨形成指标雌二醇、骨钙素、骨保护素水平,提升椎骨最大负荷,增加骨小梁数量和厚度,降低骨小梁的分离性和形态因素,最终起到防治骨质疏松症的效果。刘蔚楠等[66]研究表明,在高剂量益肾健骨膏对骨质疏松大鼠骨的干预作用下,血清中骨保护素、Ⅰ型原胶原N-端前肽水平和骨组织中Notch1、Notch2、Jagged1、Jagged2的mRNA表达均上升,而血清抗酒石酸盐酸性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白交联羧基末端肽水平及骨组织RANKL、RANK、TRAF6的mRNA蛋白表达显著降低,其作用机制可能与Notch通路及骨保护素/ RANKL/RANK系统有关。因此,高剂量的益肾健骨膏可以显著提高骨质疏松模型大鼠的骨密度、骨强度及骨形成指标,降低骨吸收指标水平。周强等[67]观察左归丸对骨质疏松大鼠治疗的研究中,利用免疫吸附测定法检测大鼠股骨组织中Notch1和骨形态发生蛋白9蛋白表达水平,发现左归丸能够上调Notch1和骨形态发生蛋白9蛋白表达水平,进而改善骨代谢异常,维持骨内平衡。同时临床试验发现,左归丸还具有保护神经、抗炎等作用[68-69]。孙鑫[70]通过左、右归丸干预绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠的研究中得出,左、右归丸均可激活Notch信号通路的活性提高大鼠骨密度、碱性磷酸酶含量,降低抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶含量,改善骨代谢情况,对骨质疏松症有一定的防治作用。王军等[71]在骨松益骨方联合芦丁对骨质疏松症患者的研究中,发现骨松益骨方、芦丁单独使用或联合用药均能刺激Notch信号通路传导,上调Notch1、Jagged1、Hes1基因表达水平,促进成骨分化、抑制成脂分化。同时,实验研究发现,骨松益骨方具有益气活血、补肾健脾、促进骨细胞增殖分化的功效,可帮助抑制骨质疏松病情进展,改善临床疗效。综上,中药复方及制剂可以综合调控Notch信号通路多角度、多效应干预骨质疏松症的发生与进展,详见表4。"

| [1] LI H, XIAO Z, QUARLES LD, et al. Osteoporosis: Mechanism, Molecular Target and Current Status on Drug Development. Curr Med Chem. 2021; 28(8):1489-1507. [2] ROSEN CJ. The Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis//FEINGOLD KR, ANAWALT B, BOYCE A, et al. Endotext. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc., 2020. [3] NOH JY, YANG Y, JUNG H. Molecular Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutics for Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7623. [4] SALARI N, DARVISHI N, BARTINA Y, et al. Global prevalence of osteoporosis among the world older adults: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):669. [5] LEBOFF MS, GREENSPAN SL, INSOGNA KL, et al. The clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(10): 2049-2102. [6] LU J, HU D, MA C, et al. Advances in Our Understanding of the Mechanism of Action of Drugs (including Traditional Chinese Medicines) for the Intervention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:938447. [7] AIBAR-ALMAZÁN A, VOLTES-MARTÍNEZ A, CASTELLOTE-CABALLERO Y, et al. Current Status of the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(16):9465. [8] JOHNSTON CB, DAGAR M. Osteoporosis in Older Adults. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(5):873-884. [9] MCINTYRE B, ASAHARA T, ALEV C. Overview of Basic Mechanisms of Notch Signaling in Development and Disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1227:9-27. [10] MATSUNO K. Notch signaling. Dev Growth Differ. 2020;62(1):3. [11] REICHRATH J, REICHRATH S. A Snapshot of the Molecular Biology of Notch Signaling: Challenges and Promises. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1227:1-7. [12] ZHOU B, LIN W, LONG Y, et al. Notch signaling pathway: architecture, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):95. [13] SPRINZAK D, BLACKLOW SC. Biophysics of Notch Signaling. Annu Rev Biophys. 2021;50:157-189. [14] YU J, CANALIS E. Notch and the regulation of osteoclast differentiation and function. Bone. 2020;138:115474. [15] SONG S, GUO Y, YANG Y, et al. Advances in pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;237:108168. [16] CANALIS E, ZANOTTI S, SCHILLING L, et al. Activation of Notch3 in osteoblasts/osteocytes causes compartment-specific changes in bone remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100583. [17] WATSON EC, ADAMS RH. Biology of Bone: The Vasculature of the Skeletal System. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(7):a031559. [18] HOU X, TIAN F. STAT3-mediated osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis in osteoporosis. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):112. [19] LIAO J, HUANG Y, WANG Q, et al. Gene regulatory network from cranial neural crest cells to osteoblast differentiation and calvarial bone development. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(3):1-15. [20] SHAO J, ZHOU Y, LIN J, et al. Notch expressed by osteocytes plays a critical role in mineralisation. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018;96(3-4):333-347. [21] HOU HW, XUE P, WANG Y, et al. Liraglutide regulates proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of preosteoblasts through a signaling network of Notch/Wnt/Hedgehog signaling pathways. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(23):12408-12422. [22] FU R, LV WC, XU Y, et al. Endothelial ZEB1 promotes angiogenesis-dependent bone formation and reverses osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):460. [23] ZHANG Z, QI H, XIA H, et al. Preosteoblast-enriched lnc-Evf2 facilitates osteogenic differentiation by targeting Notch. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021;53(2):179-188. [24] GAO J, WU P, CHI Y, et al. LY450139 Inhibited Ti-Particle-Induced Bone Dissolution via Suppressing Notch and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022;111(2):211-223. [25] Ashley JW, Ahn J, Hankenson KD. Notch signaling promotes osteoclast maturation and resorptive activity. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(11):2598-2609. [26] HUANG T, ZHAO C, ZHAO Y, et al. RO4929097 regulates RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and LPS-mediated bone resorption. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(9): 12526-12536. [27] YU J, SCHILLING L, ELLER T, et al. Hairy and enhancer of split 1 is a primary effector of NOTCH2 signaling and induces osteoclast differentiation and function. J Biol Chem. 2021;297(6):101376. [28] YANG B, FU C, WU Y, et al. γ-Secretase inhibitors suppress IL-20-mediated osteoclastogenesis via Notch signalling and are affected by Notch2 in vitro. Scand J Immunol. 2022;96(2):e13169. [29] JIANG Y, ZHANG P, ZHANG X, et al. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of osteoporosis. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(1): e12956. [30] Chen T, Yang T, Zhang W, et al. The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in treating osteoporosis. Biol Res. 2021;54(1):42. [31] CAO J, WEI Y, LIAN J, et al. Notch signaling pathway promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing BMP9/Smad signaling. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(2):378-388. [32] LEE SY, LONG F. Notch signaling suppresses glucose metabolism in mesenchymal progenitors to restrict osteoblast differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2018;128(12):5573-5586. [33] LAN X, MA H, CHENG Q, et al. SIRT1/Notch1 signal axis involves in the promoting effect of Segetalin B on bone formation. Drug Dev Res. 2022; 83(8):1845-1857. [34] FAN JZ, YANG L, MENG GL, et al. Estrogen improves the proliferation and differentiation of hBMSCs derived from postmenopausal osteoporosis through notch signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;392(1-2):85-93. [35] XU C, DINH VV, KRUSE K, et al. Induction of osteogenesis by bone-targeted Notch activation. Elife. 2022;11:e60183. [36] RAMASAMY SK, KUSUMBE AP, SCHILLER M, et al. Blood flow controls bone vascular function and osteogenesis. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13601. [37] LIU Y, BERENDSEN AD, JIA S, et al. Intracellular VEGF regulates the balance between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(9): 3101-3113. [38] CHEN W, JIN X, WANG T, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 interferes with the progression of diabetic osteoporosis by promoting type H angiogenesis modulating vasculogenic and osteogenic coupling. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13:1010937. [39] 石敏,赵继荣,薛旭,等.从“肾”论治激素性骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].时珍国医国药,2021,32(1):174-176. [40] 赵继荣,蒋鹏,陈文,等.Nrf2/HO-1信号通路在骨质疏松症中的作用及中药干预研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(20):241-249. [41] 胡芳科,张银光.LncRNA在骨质疏松中对破骨细胞作用的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2022,42(19):4899-4903. [42] LIN J, ZHU J, WANG Y, et al. Chinese single herbs and active ingredients for postmenopausal osteoporosis: From preclinical evidence to action mechanism. Biosci Trends. 2017;11(5):496-506. [43] AMEEN O, YASSIEN RI, NAGUIB YM. Activation of FoxO1/SIRT1/RANKL/OPG pathway may underlie the therapeutic effects of resveratrol on aging-dependent male osteoporosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):375. [44] 邹庆峰,李守民,舒隆钧,等.白藜芦醇对绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠的促细胞增殖作用[J].实用临床医药杂志,2020,24(19):86-89. [45] XIN Z, WU X, YU Z, et al. Mechanisms explaining the efficacy of psoralidin in cancer and osteoporosis, a review. Pharmacol Res. 2019;147:104334. [46] 邢贞武.补骨脂素对绝经后骨质疏松患者骨髓间充质干细胞Notch信号通路的影响[J].中医学报,2017,32(11):2181-2184. [47] JIN H, JIANG N, XU W, et al. Effect of flavonoids from Rhizoma Drynariae on osteoporosis rats and osteocytes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113379. [48] 韩亚力,罗奕,曾佳学.骨碎补总黄酮基于Notch信号通路改善骨质疏松的作用及机制研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2018,34(2):261-266. [49] 黄翔宇,林立垚,郝敏,等.骨碎补总黄酮基于Notch信号通路改善骨质疏松的作用及机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(19):4361-4363. [50] YANG X, LIU T, QI S, et al. Tea saponin additive to extract eleutheroside B and E from Eleutherococcus senticosus by ultrasonic mediation and its application in a semi-pilot scale. Ultrason Sonochem. 2022;86:106039. [51] 黄月,颜亮,崔向荣,等.刺五加苷诱导大鼠间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J].解放军医学杂志,2019,44(3):215-221. [52] ZHOU YH, XIE Q. Total glycosides from Eucommia ulmoides seed promoted osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and bone formation in ovariectomized rats through regulating Notch signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):660. [53] 刘美红,邹峥嵘.女贞子化学成分、药理作用及药动学研究进展[J].热带亚热带植物学报,2022,30(3):446-460. [54] Sen A. Prophylactic and therapeutic roles of oleanolic acid and its derivatives in several diseases. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8(10):1767-1792. [55] 程韶,杨骏杰,王晶,等.齐墩果酸局部给药对去卵巢小鼠骨折愈合的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(12):1717-1725. [56] BIAN Q, LIU SF, HUANG JH, et al. Oleanolic acid exerts an osteoprotective effect in ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic rats and stimulates the osteoblastic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Menopause. 2012;19(2): 225-233. [57] LI LR, SETHI G, ZHANG X, et al. The neuroprotective effects of icariin on ageing, various neurological, neuropsychiatric disorders, and brain injury induced by radiation exposure. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(3):1562-1588. [58] 李时斌,夏天,章晓云,等.淫羊藿活性单体成分调控骨质疏松症相关信号通路影响骨吸收与骨形成的稳态[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(11):1772-1779. [59] 李永贤,张顺聪,梁德,等.补肾中药通过调控Notch1蛋白的表达治疗大鼠骨质疏松性骨折的作用研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(11): 1425-1430. [60] 孙杰,宋鑫,王健.淫羊藿提取物对骨质疏松骨折大鼠愈合过程Notch信号通路的影响[J].中国中医急症,2019,28(4):611-614. [61] LIU H, XIONG Y, ZHU X, et al. Icariin improves osteoporosis, inhibits the expression of PPARγ, C/EBPα, FABP4 mRNA, N1ICD and jagged1 proteins, and increases Notch2 mRNA in ovariectomized rats. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(4):1360-1368. [62] 汪小飞,李晶晶.淫羊藿总黄酮对老年骨质疏松大鼠Notch和Smads通路蛋白表达的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(2):1-5. [63] 周灵通.固本增骨方含药血清调节Notch通路干预大鼠BMSCs成骨分化的机制研究[D].兰州:甘肃中医药大学,2018. [64] 许日明,陈美雄,林业武,等.温肾固疏方对绝经后骨质疏松症肾阳虚型患者类固醇激素受体辅激活子3、转录元件辅激活蛋白、B细胞淋巴瘤基因-2的蛋白表达及骨髓间充质干细胞Notch信号通路的影响[J].河北中医,2019,41(10):1470-1474. [65] 王洁芳.益骨胶囊对去卵巢大鼠骨组织Notch信号通路的影响[D].广州:暨南大学,2015. [66] 刘蔚楠,周晓霞,朱玮,等.益肾健骨膏对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(6):857-862. [67] 周强,孙鑫,邓洋洋,等.左归丸对去卵巢致绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠骨组织中Notch1、BMP9表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2016,31(7): 2782-2784. [68] 刘家峰,舒庆,张颖.左归丸含药血清对大鼠海马神经元和胶质细胞氧糖剥夺损伤的保护作用及机制研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2022,51(1):15-19. [69] 麦聪英,谭峰,李星,等.左归丸对绝经后骨质疏松症合并骨关节炎模型大鼠下丘脑神经肽P物质及其受体的影响[J].中医杂志,2021,62(14): 1259-1265. [70] 孙鑫.左、右归丸对绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠Notch信号通路调节机制的比较研究[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2015. [71] 王军,高峰,范涛,等.骨松益骨方联合芦丁对绝经后骨质疏松患者骨髓间充质干细胞Notch信号通路的影响[J/OL].中华中医药学刊:1-8[2022-10-22] |
| [1] | Zhang Min, Peng Jing, Zhang Qiang, Chen Dewang. Mechanical properties of L3/4 laminar decompression and intervertebral fusion in elderly osteoporosis patients analyzed by finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 847-851. |
| [2] | Xue Xiaofeng, Wei Yongkang, Qiao Xiaohong, Du Yuyong, Niu Jianjun, Ren Lixin, Yang Huifeng, Zhang Zhimin, Guo Yuan, Chen Weiyi. Finite element analysis of osteoporosis in proximal femur after cannulated screw fixation for femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 862-867. |
| [3] | Kaiyisaier•Abudukelimu, Maimaitimin•Abulimiti, Li Lei, Yang Xiaokai, Zhang Yukun, Liu Shuai. Effect of lumbar CT values in the diagnosis of osteoporosis in women patients with lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 945-949. |
| [4] | Wang Liping, Lian Tianxing, Hu Yongrong, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Liu Hao, Qu Bo. HU value of chest CT vertebral body in the opportunistic screening of type 2 diabetes mellitus osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 950-954. |
| [5] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [6] | Liu Luxing, Di Mingyuan, Yang Qiang. Signaling pathways in the mechanism underlying active ingredients of Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 609-614. |
| [7] | Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Maimaitimin·Abulimiti, Tuerhongjiang·Abudurexiti. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of terlipatide and bisphosphate in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 639-645. |
| [8] | Lin Feng, Cheng Ling, Gao Yong, Zhou Jianye, Shang Qingqing. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel-encapsulated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote cardiac function in myocardial infarction rats (III) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 355-359. |
| [9] | Zhu Zhiqi, Yuan Sijie, Zhang Zilin, Ji Shijie, Meng Mingsong, Yan Anming, Han Jing. Mechanism underlying the effect of Liuwei Dihuang Pill on osteolysis and osteogenesis induced by titanium particles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 392-397. |
| [10] | Bi Yujie, Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Zhou Ziqiong, Zhao Jing, Zhu Houjun, Zhong Qiuhui, Yang Yuxin. Strategy and significance of Chinese medicine combined with medical hydrogel for disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 419-425. |
| [11] | Liu Baofang, Xu Bin, Chen Lei. Pueraria decoction in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 193-199. |
| [12] | Yin Linwei, Huang Xiarong, Qu Mengjian, Yang Lu, Wang Jinling, Jia Feiyang, Liao Yang, Zhou Jun. Effects of treadmill exercise on osteoporosis and wnt/beta-catenin signal pathway in aged rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 231-236. |
| [13] | Ying Chunmiao, Pan Xiaolong, Liu Feixiang, Chen Na, Fan Feiyan, Zhang Yunke. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine and compounds for supplementing qi and activating blood circulation and inducing resuscitation on regulating stem cells to promote nerve repair of acute ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 121-130. |
| [14] | Yang Ting, Ding Zhibin, Jiang Nan, Han Hongxia, Hou Miaomiao, Ma Cungen, Song Lijuan, Li Xinyi. Astrocytes regulate glial scar formation in cerebral ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 131-138. |
| [15] | Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Liu Tao, Li Yan, He Yuanxu, He Bo, Wang Weiwei, Wei Xiaotao. Traditional Chinese medicine monomer in the prevention and treatment of flap necrosis by regulating “autophagy” [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 153-158. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||