Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (4): 594-601.doi: 10.12307/2023.849
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and application of early transient presence of M1 macrophages in bone tissue engineering
Yang Yuqing, Chen Zhiyu
- Department of Prosthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-25Accepted:2022-12-29Online:2024-02-08Published:2023-07-14 -
Contact:Chen Zhiyu, MD, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Prosthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Yang Yuqing, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:Hebei Provincial Talents Project, No. A202102010 (to CZY); Hebei Provincial Government Funded Clinical Medical Talents Training Project, No. 361029 (to CZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Yuqing, Chen Zhiyu. Role and application of early transient presence of M1 macrophages in bone tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 594-601.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

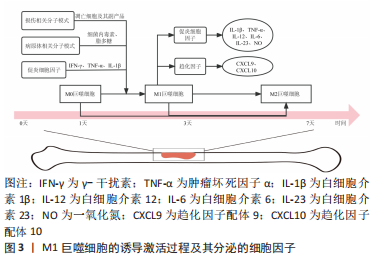
2.1 早期短暂M1巨噬细胞概述 巨噬细胞是一类可塑的固有免疫细胞,根据不同的骨局部微环境可极化为不同的表型。过去几十年以来,不同的术语被学者描述出来用于研究巨噬细胞的不同极化状态,目前最多以镜像“Th1/Th2”二分法的细胞命名方式[4],命名为“M1/M2型”巨噬细胞进行相关研究。 20世纪60年代,MACKANESS[5]提出“促炎M1表型巨噬细胞”的概念,用来描述巨噬细胞在抵抗微生物感染方面的重要作用。骨自然愈合环境时,M1巨噬细胞短暂存在于早期阶段,通常在骨损伤发生后的第一天,在损伤相关分子模式(例如凋亡细胞及其副产品)、病原体相关分子模式(如细菌内毒素、脂多糖)和促炎细胞因子(如γ-干扰素、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β)诱导下,由未极化的M0巨噬细胞极化而成,并在72 h内开始减少并逐渐消失,而后白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10等抗炎作用细胞因子对M2表型诱导,进入骨组织修复阶段[6]。早期短暂存在的M1巨噬细胞发挥着清除微生物、坏死组织和临时的纤维蛋白基质的宿主防御作用,并释放促炎细胞因子(白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素12、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素23、一氧化氮等)和趋化因子(趋化因子配体9、趋化因子配体10等)以启动早期的炎症反应[7]。图3总结了M1巨噬细胞的诱导激活过程及其分泌的细胞因子。以往研究表明,M1巨噬细胞介导的骨再生早期炎症反应的持续会减少骨组织生成。近年来,越来越多的研究发现M1巨噬细胞的早期短暂存在对骨再生过程具有启动作用,是必要条件。"

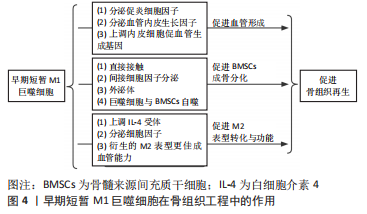
2.2 早期短暂M1巨噬细胞在骨组织工程中的作用 2.2.1 促进血管生成 血管生成对于细胞的氧气和营养供应、废物清除、内皮细胞及干细胞归巢、成骨因素的释放起着关键作用[8]。骨组织工程需要形成稳定的功能性血管网络。M1巨噬细胞可以通过分泌细胞因子刺激血管的初始形成,包括白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β、γ-干扰素、抑瘤素、肿瘤坏死因子α等促炎细胞因子以及血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF) [9-10]。其中γ-干扰素可以增强体内植入支架的血管化而被广泛研究。VEGF不仅可以促进内皮细胞尖端发芽和H型血管的发育,介导血管生成的启动,也直接调节着成骨过程[11]。 血管形成是一个极其复杂的过程,需要内皮细胞的迁移和增殖、周细胞维护血管稳定性等多个步骤。GRANEY等[12]利用单细胞RNA测序技术,发现M1巨噬细胞条件培养基培养的内皮细胞富含促进周细胞招募的标志物,并显著上调了内皮细胞的VEGF受体以及尖端细胞表面标志物VEGFR2(KDR)等在内的多个基因的表达。研究表明这些受体可以与相应配体结合,通过激活下游PI3K/AKT、MAPK、PLCγ/ERK/MERK等多种信号通路促进血管内皮细胞的增殖和血管生成[13-14]。同时发现,巨噬细胞超过3 d的持续存在将显著减少血管数量及总长度[12],表明血管生成是骨缺损愈合过程中顺序级联的结果,需要M1和M2巨噬细胞在有序的时间内共同参与,从而促进新生血管的成熟和吻合。目前M1巨噬细胞如何在基因组和转录组水平上同时调节血管重建和骨组织再生的理解仍然有限,需要进一步探索M1巨噬细胞、内皮细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞(bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells,BMSCs)之间的相互作用和涉及的信号通路,提供更佳的骨组织工程材料设计思路,以加强血管生成和骨再生。 2.2.2 促进BMSCs成骨分化 BMSCs作为主要的骨形成细胞,极大影响着骨再生。几项体外培养模型用于研究M1巨噬细胞对BMSCs的行为和功能的影响,包括二维直接共培养模型、巨噬细胞条件培养基间接共培养模型,表明了低炎症M1巨噬细胞状态可以通过直接接触和分泌肿瘤坏死因子α、抑瘤素、骨形态发生蛋白2和骨形态发生蛋白6等细胞因子促进BMSCs的迁移和成骨分化[15-16]。GOODMAN团队最近设计了新型体外三维培养模型,M1巨噬细胞在该模型中显著促进了BMSCs的成骨作用[17]。 除了直接接触和间接细胞因子分泌作用机制外,M1巨噬细胞也可以通过外泌体等旁分泌形式促进BMSCs成骨分化。外泌体是直径介于30-200 nm的细胞外囊泡,其内部富含微小RNA(microRNA,miR)和蛋白质等多种物质,作为巨噬细胞和成骨相关细胞间通信的新机制,巨噬细胞外泌体可释放至环境中并作用于远端的BMSCs,以调控其成骨作用[18]。 LIU等[19]发现miR-21a-5p在M1巨噬细胞分泌的外泌体中高度富集,并且可以转移到BMSCs,在体外诱导了成骨分化。更多的研究开始探索其中的分子机制,发现M1巨噬细胞可以通过释放肿瘤坏死因子α、外泌体、白细胞介素1等抑制Notch通路,诱导Wnt信号通路,促进了早期BMSCs的成骨分化[20]。鉴于上述原理,外泌体结合于骨组织工程中的应用很有希望。但是也有研究显示M1巨噬细胞外泌体抑制骨修复,减少了BMSCs的成骨分化[21]。这些矛盾的结论可能是由于巨噬细胞来源、外泌体提取技术、共培养条件以及作用持续时间等差异所致。另外,体内的生理环境和极化刺激更加复杂,M1巨噬细胞衍生外泌体影响BMSCs成骨分化的机制仍需要更多体内动物实验建模的参考。 近年研究发现,自噬作为真核细胞中一种高度保守的利用溶酶体发生的自身降解过程,除了在维持细胞稳态方面发挥重要作用外,也参与了巨噬细胞和BMSCs的交叉串扰过程[22]。首先,促进BMSCs成骨作用依赖于M1巨噬细胞发生的自噬机制。LUO等[23]发现硅酸钙诱导M1巨噬细胞产生的早期短暂促炎环境促进了BMSCs的成骨分化,而该材料可以通过上调巨噬细胞内活性氧的产生和钙离子的过载诱导线粒体功能障碍,为了减少炎性体激活物如活性氧和受损线粒体的累积,巨噬细胞内自噬相关蛋白质Beclin 1和LC3-Ⅱ的表达发生了上调,同时线粒体功能障碍和自噬共同诱导了巨噬细胞炎症反应,促炎细胞因子包括肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6的表达增加,这种早期短暂促炎微环境赋予了硅酸钙的成骨潜能。另外,低炎症条件下M1巨噬细胞促BMSCs的迁移和成骨分化作用也依赖于BMSCs自噬相关基因ATG5、ATG7和Beclin 1以及LC3-Ⅱ蛋白表达[24]。以上研究表明,自噬与炎症和成骨之间有着错综复杂的关系,巨噬细胞和BMSCs的自噬发生,参与了二者的交叉串扰。目前,骨组织工程材料和药物诱导M1巨噬细胞内线粒体功能障碍和自噬的确切分子机制,以及如何将其应用于骨组织工程领域以达到诊断或治疗的目的,仍有待进一步研究。 2.2.3 促进巨噬细胞M2表型的转化和功能 巨噬细胞M2表型介导骨再生过程中的建设性重塑,M1巨噬细胞的早期激活对后续M2表型极化具有重要的调节作用。白细胞介素4是促进M0或M1表型向M2表型极化的关键细胞因子。O’BRIEN等[25]研究发现,M1巨噬细胞较M0未极化状态向上调节了白细胞介素4受体的表达,包括白细胞介素4受体复合物IL4Ra、IL13RA1、IL2RG及其相应Janus激酶JAK1、JAK2、JAK3,加速了受体STAT6磷酸化过程,表明M1巨噬细胞对白细胞介素4配体具有相对更高的敏感性。另外,研究表明M1巨噬细胞分泌细胞因子可诱导M2表型的分化,例如白细胞介素6可诱导M2表型中M2b和M2d亚群[26-27]。肿瘤坏死因子α是M1巨噬细胞分泌的主要产物,同时也是潜在的M2表型诱导剂。最近研究表明,肿瘤坏死因子α增加了CD73基因在牙龈组织源性间充质干细胞分泌外泌体的表达,介导间充质干细胞的免疫抑制作用,间接性地显著促进了M2极化[28]。 另外,M1衍生的M2巨噬细胞较直接从M0制备的M2巨噬细胞具有更高的成血管能力。一项RNA测序证实,二者互为不同的表型,有2 000多个基因表达差异[29]。两者的基因差异也使前者表现出M2相关蛋白质的分泌增加,特别是趋化因子配体和血小板生长因子,促进了人脐静脉血管内皮细胞的迁移和新生血管的稳定[25]。然而,许多研究只评估了少数M1和M2表型相关基因的表达,尽管研究证实了这些基因表达的结果具有意义,同时这些基因的差异是否表现为对其他骨组织细胞如BMSCs行为及功能的改变,仍需更深入关注骨组织工程材料的细胞和分子间的调控机制。但总体而言,M1表型的增强是促进M2巨噬细胞介导的血管生成和骨生成的潜在策略之一。 综上所述,早期短暂存在的M1巨噬细胞作为参与炎症反应的重要因素,促进了血管生成、BMSCs成骨分化和M2表型巨噬细胞的转化,在骨组织工程中发挥着重要作用,如图4所示。然而,M1巨噬细胞的持久激活将导致炎症的长期持续和纤维封装,不利于后续的骨再生过程。因此,早期短暂地诱导激活M1巨噬细胞并产生温和的炎症反应,成为了骨组织工程的关键方向。"

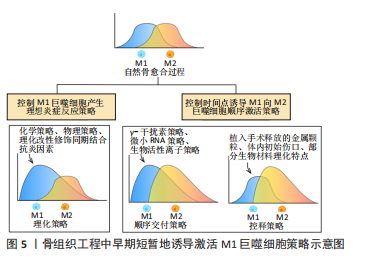
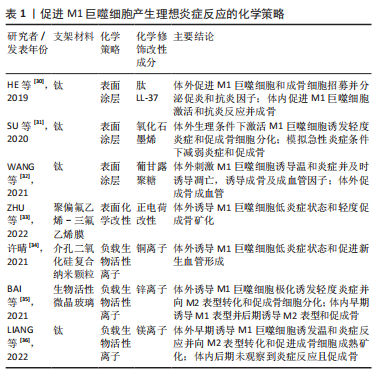
表面涂层:利用涂层技术对植入物表面进行化学成分修饰可以用于产生温和的炎症反应。例如,SU等[31]在钛表面建立氧化石墨烯涂层,生理条件下激活M1巨噬细胞,诱发了轻度炎症和促成骨环境,而在模拟急性炎症条件时减弱了炎症反应。研究表明多肽LL-37能够刺激和调节巨噬细胞分泌促炎因子,同时可以与微环境中其他细胞因子协同起到抗炎作用[37]。但是有关多肽活性的保持和持续释放问题依然是难点。HE等[30]在钛表面构建了肽LL-37负载的丝纤维蛋白纳米颗粒,早期促进了较高M1标记表达,后期协同发挥抗炎作用,最终促进了骨形成。WANG等[32]提出了诱导M1巨噬细胞的早期极化并及时凋亡的内部刺激响应创新涂层策略,该涂层能够招募和诱导巨噬细胞M1表型,诱导成骨细胞分化并产生碱性磷酸酶,对涂层化学键进行切割,实现了涂层在钛表面释放和巨噬细胞凋亡,导致炎症的消失。 表面化学改性:骨组织工程研究仍致力于通过对引导骨再生技术膜材料进行表面固有化学改性以调节局部免疫环境,增强骨再生效果。压电生物材料的表面电荷极性作为最近研究的热点,可以通过提供局部电刺激精确调节骨骼再生[38]。ZHU等[33]发现带负电荷和带正电荷的聚偏氟乙烯-三氟乙烯膜分别诱导了巨噬细胞的抗炎和促炎反应,其中正电荷极性诱导的是一种低炎症M1巨噬细胞状态,能轻度促进体外成骨矿化。尽管如此,目前研究仍存在许多空白:①专注于带电压活性材料对介导适度炎症反应的研究仍然较少;②压电荷物质通过影响巨噬细胞调节免疫成骨微环境的作用及确切机制并不十分明确;③鉴于体内微环境具有多样性,电荷极性的体内免疫效果仍有待深入研究。 生物活性离子:生物活性离子对炎症反应的调节程度及作用机制的研究仍不充分,但将其纳入生物材料的策略仍为介导理想炎症反应提供了新的努力方向。一些生物活性离子可以将巨噬细胞极化为M1表型。许晴[34]制作掺杂铜离子的介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒,在体外诱导M1表型并促进了新生血管的形成。但是这种策略要求纳米载体具有规避离子泄漏至超过生理浓度风险的性质,而极大限制了其临床应用。 另外一些生物活性离子对巨噬细胞的极化影响在很大程度上取决于环境的离子浓度和pH效应。BAI等[35]制作了含锌离子的生物活性微晶玻璃,早期低浓度锌离子造成急性应激反应诱导了M1巨噬细胞极化,介导了早期适度炎症反应,后期随着离子局部滞留,浓度增加的锌离子将巨噬细胞极化为M2表型。最近,LIANG等[36]制作了钛-镁合金,镁离子的释放导致了局部碱性微环境,由于短时间内pH值对M1表型的极化效应超过了镁离子的M2极化效应,诱导了早期一过性M1巨噬细胞增加,与后期镁离子长期释放诱导的抗炎反应联合促进了骨形成。然而,骨组织工程材料中生物活性离子的释放剂量、速率的控制以及生物材料的降解过程仍然是当前骨组织工程材料设计面临的主要难题。能否刺激M1巨噬细胞介导理想骨免疫微环境效果,需取决于这些因素协同作用的结果。 (2)物理策略:除了化学改性修饰外,骨组织工程材料不同物理特征也会对巨噬细胞的极化产生巨大影响。例如,与平坦表面相比,双相磷酸钙陶瓷微图案表面可以调控巨噬细胞向M1极化并促进了体外成骨分化[39]。SRIDHARAN等[40]制作了包含不同大小和形状羟基磷灰石颗粒的胶原支架,5 μm针状羟基磷灰石胶原支架同时促进了M1和M2型巨噬细胞促炎和抗炎因子的分泌和基因表达并促进了体外成骨。 以上研究表明,巨噬细胞的极化状态可以通过改善材料的物理特征进行调节,开发具有一定物理特征的材料-骨界面微环境,进而诱导适度的炎症反应的新型材料可能有利于增强骨再生和早期血管形成潜力,但是仅仅考虑这种单向M1极化调节可能产生不足的巨噬细胞极化水平,或者持续激活M1巨噬细胞而产生潜在促炎作用,难以实现抗炎表型的及时转换以及M1和M2二者之间的平衡协调,甚至不利于骨组织再生。因此,物理策略需要全面分析生物材料的免疫调节能力,特别是对M1表型极化的持续时间及强度的评价。目前物理特性对巨噬细胞极化的影响的基础研究和材料设计方面的发现仍处于起步阶段,需要进行更多的实验研究。 (3)理化改性修饰同期结合抗炎因素:尽管上述研究证明了对材料进行物理化学改性修饰可以作为促进体内成骨的潜在策略,但是这些研究往往着眼于材料的固有属性而非仿生设计,导致了M1巨噬细胞的非生理性诱导而产生较低的巨噬细胞极化强度和效率,不利于理想的成骨修复。生物材料同期结合其他抗炎因素是最常见的优化材料骨免疫调节性能的策略之一。例如,ZHENG等[41]在氧化石墨烯涂层中负载了富含镁离子的纳米颗粒,与单一氧化石墨烯涂层通过诱导激活低极化水平的M1巨噬细胞所产生的成骨作用相比,由于镁离子的释放促进了后期M2表型转变,更促进了大鼠颅骨缺损的血管化骨再生,保持氧化石墨烯促炎作用的同时提高了成骨效果。 另外,材料的物理固有属性容易导致M1巨噬细胞的持续激活而无法及时向M2表型转化,需要同期结合其他抗炎因素以减轻慢性炎症反应的风险。例如临床上用于引导骨再生的BioGide?胶原屏障膜的粗糙表面可以促进巨噬细胞M1表型极化以及成骨因子表达,但具有潜在促炎作用,将纳米生物活性玻璃Ca2ZnSi2O7修饰胶原膜后调节了局部炎症并显著促进了成骨矿化[42]。类似的,研究表明高基质刚度的物理特性倾向于长期诱导M1表型[43]。HE等[44]在高刚度水凝胶中加入白细胞介素4和基质细胞衍生因子,通过综合产生了更理想的炎症反应,促进了大鼠牙周骨再生。 一些生物活性离子可以通过促进巨噬细胞极化为M1表型而引发强烈甚至过度的炎症反应,结合具有抗炎作用的表面改性可以引发温和的炎症反应以促进成骨。例如,黄千里[45]制作含铜的微/纳米形生物陶瓷表面,相对比直接外源性铜离子所引发的强烈M1表型极化刺激,由于该改性表面的抗炎作用,最终引发了较低的炎症反应,促进了良好的骨形成。以上这些理化改性修饰同期结合抗炎因素策略为生物材料的设计提供了一定的指导意义。 2.3.2 控制时间点诱导M1向M2巨噬细胞顺序激活策略 (1)顺序交付策略:M1和M2巨噬细胞在骨再生过程中按时间进程介导着炎症反应向修复状态的切换,顺序和协同发挥着许多功能。与单独早期诱导激活M1巨噬细胞产生理想炎症反应相比,依次促进M1和M2表型的激活将是促进骨再生另一有希望的策略。已经探索了一些顺序交付技术,以调节巨噬细胞表型的顺序极化。在此,以激活早期M1巨噬细胞极化的材料为分类依据,讨论诱导M1和M2型巨噬细胞依次极化的顺序交付策略的最新研究进展,包括γ-干扰素策略、微小RNA策略和生物活性离子策略。总结见表 2。"
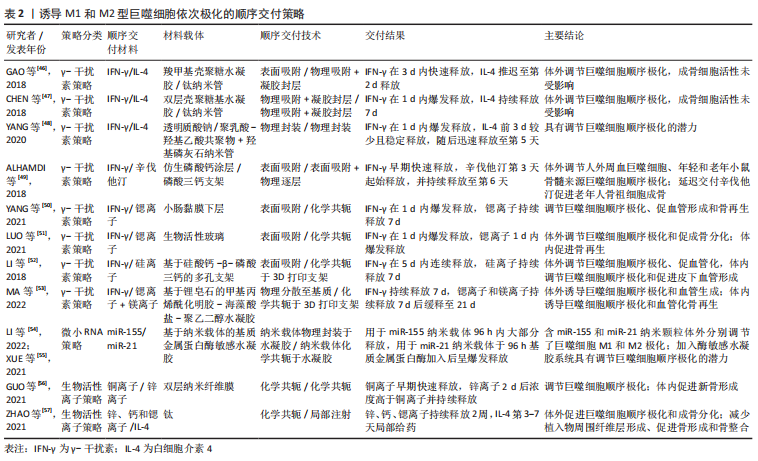

γ-干扰素策略:鉴于促炎细胞因子γ-干扰素出色地诱导巨噬细胞向M1表型极化的能力,研究最多的是γ-干扰素和其他抗炎物质的顺序递送,并表现了相当的骨再生以及血管形成潜力。为了诱导激活初期短暂的M1巨噬细胞,早期交付γ-干扰素的常用方法包括物理吸附至材料表面并通过扩散驱使初始的爆发释放,以及物理封装至水凝胶中或分散到3D打印支架基质中,通过物理扩散结合基质的膨胀或降解实现快速释放。 最近许多研究关注受控于纳米管特定空间分布的γ-干扰素和抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素4的顺序交付策略。CHEN等[47]通过在钛纳米管表面构建双壳聚糖基水凝胶涂层,实现γ-干扰素和吸附于纳米管内部的白细胞介素4分隔交付,体外调节了巨噬细胞顺序极化。YANG等[48]提出了基于双层基质封装细胞因子的羟基磷灰石纳米管控释技术,将封装γ-干扰素的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物和封装白细胞介素4的透明质酸分别加载到纳米管底部和顶部,介导因子的顺序递送,是促进成骨修复的可行方法。但释放动力学是一个复杂的过程,需要在大量的体内实验中评估该策略的免疫调节和骨再生效果。 除了白细胞介素4,γ-干扰素与其他抗炎物质的双递送策略也被引入研究:γ-干扰素与辛伐他汀、γ-干扰素与促进巨噬细胞M2表型极化的生物活性离子,如锶离子、硅离子。ALHAMDI等[49]设计了仿生磷酸钙涂层,实现了γ-干扰素的早期释放和辛伐他汀的延迟交付,促进了老年人骨祖细胞的成骨分化。另外,γ-干扰素与化学共轭在支架材料中的金属活性离子的双重交付,作为最近研究的一种简便策略,避免了多种物质理化性质相似时的递送难题。虽然体内实验证明了良好的骨再生以及血管形成,但是该策略往往伴随着特别是3D打印材料中的金属活性离子的过早释放[50-51],与γ-干扰素的释放时间极大重叠,这对初始M1巨噬细胞活性可能产生某些适得其反的作用[52-53]。因此,仍需要探索组合优化的交付方式,控制并分离生物活性离子的释放时间,以实现更优的顺序极化和骨再生效果。 微小RNA策略:虽然细胞因子对巨噬细胞表型的调节有良好的影响,但它们的应用仍面临着易失活、价格昂贵、释放剂量难以控制导致不良反应等多种挑战。微小RNA已被证明通过调节巨噬细胞极化促进成骨和血管形成,可以作为一种替代策略。其中,miR-155诱导M1巨噬细胞极化的作用已得到了广泛研究。LI等[54]开发了负载miR-155和miR-21的纳米颗粒,体外分别调节了巨噬细胞M1和M2极化。XUE等[55]以牛血清白蛋白为模型蛋白,将能够负载miR-155和miR-21的纳米颗粒分别通过物理嵌入和化学键合在基质金属蛋白酶敏感水凝胶中,实现了二者的顺序递送,表明在精确的时间点上控制巨噬细胞M1和M2表型极化的潜能。但是微小RNA策略的顺序递送研究目前仍处于起步阶段,需要体内成骨实验的验证。另外,由于暴露在循环系统中的微小RNA会被迅速酶解的特性,基因治疗仍需要探索合适的基因载体,特别是关于载体的颗粒尺寸和电化学性能考虑,尽可能高效转移至巨噬细胞内部以实现预期的疗效。 生物活性离子策略:鉴于一些生物活性离子可以诱导巨噬细胞向M1表型极化,最近研究了这些生物活性离子和其他抗炎物质的顺序交付策略。GUO等[56]构建了双层纳米纤维膜,铜离子早期快速释放及后期锌离子的持续释放,诱导了巨噬细胞由M1向M2表型转化,加速了体内新骨形成。ZHAO等[57]在钛种植体表面制备了新型钙锶锌磷酸盐涂层,诱导了巨噬细胞M1极化,3 d后白细胞介素4以注射方式的局部输送引发了更多促愈合的M2表型,在大鼠股骨缺损模型中促进了骨再生和骨整合。但是,生物活性离子往往以化学共轭形式存在于生物材料中,导致在局部环境中持续释放,巨噬细胞M1表型极化诱导时间被延长,与M2表型重叠而无法匹配骨组织的自然愈合过程,因此生物活性离子在骨组织工程顺序极化策略的应用仍需探索。 (2)控释策略:顺序激活策略中递送的各组分之间的复杂代谢动力学和生物学分布特点使其协同骨免疫调节效应复杂化。除了主动递送促炎物质外,植入手术过程中释放的金属颗粒可以促进巨噬细胞向M1表型极化,释放肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β等促炎细胞因子诱发炎症反应[58]。体内初始伤口以及部分生物材料理化特点,也可以直接引发中度的炎症反应。由于炎症细胞因子水平开始下降的时间是在骨组织工程材料植入后3 d,因此提出了植入3 d内单独交付抗炎物质的免疫调节策略。白细胞介素4是促进M2表型极化的关键细胞因子之一,单独控制白细胞介素4的交付与释放时间,可以维持部分生物材料植入后早期适度炎症反应,而后及时调节M2表型转换改变局部免疫微环境,促进成血管反应和骨再生。表3总结了近年控制白细胞介素4释放的骨组织工程策略。"
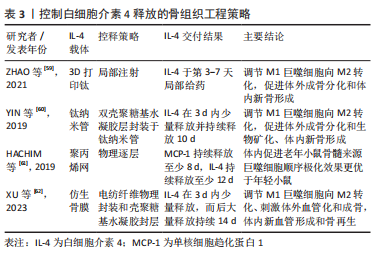

粗糙的表面特征可以在植入早期诱发持续的M1表型极化,ZHAO等[59]通过3D打印技术制作了钛植入物,3 d后在大鼠皮下植入物周围组织人为主动注射白细胞介素4,促进了巨噬细胞的表型转换和新骨形成。此外,白细胞介素4可以沉积在钛纳米管内,并通过在表面建立了海藻酸钠与壳聚糖复合膜实现被动控释,体内外实验均表明了早期温和炎症反应的保持以及良好的骨生成效果[60]。近期,将白细胞介素4引入仿生人工骨膜的研究正在展开。XU等[62]建立电纺纤维膜封装白细胞介素4,并在表面附着混合水凝胶层以实现早期控释,维持了早期M1巨噬细胞成骨和成血管作用,而后白细胞介素4随着凝胶降解发生大量释放,促进了M2表型极化。 此外,HACHIM等[61]利用逐层技术在聚丙烯网上加载了单核细胞趋化蛋白1和白细胞介素4,二者顺序释放实现了对M1巨噬细胞向M2表型极化的调节。但是单核细胞趋化蛋白1只促进了老龄小鼠体内巨噬细胞招募行为,M1巨噬细胞的极化增强主要由于生物材料的植入过程引发的炎症反应,而老年因素也将促进局部炎症环境形成[63]。同时体内实验表明年轻小鼠顺序递送细胞因子在极化为促愈合M2表型方面不如单独递送白细胞介素4有效,说明骨组织工程材料的设计需要正确理解局部环境依赖性的生物反应和适用场景。关于老龄和年轻骨髓源性巨噬细胞和成骨相关细胞之间相互作用的机制和区别比较,仍需要进行更全面的研究。"

| [1] RANALLETTA M, TANOIRA I, BERTONA A, et al. Autologous Tricortical Iliac Bone Graft for Failed Latarjet Procedures. Arthrosc Tech. 2019;8(3): e283-e289. [2] JAMALPOOR Z, ASGARI A, LASHKARI MH, et al. Modulation of Macrophage Polarization for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;17(5):398-408. [3] HOZAIN S, COTTRELL J. CDllb+ targeted depletion of macrophages negatively affects bone fracture healing. Bone. 2020;138:115479. [4] MICHALSKI MN, MCCAULEY LK. Macrophages and skeletal health. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;174:43-54. [5] MACKANESS GB. The immunological basis of acquired cellular resistance. J Exp Med. 1964;120(1):105-120. [6] ALHAMDI JR, PENG T, AL-NAGGAR IM, et al. Controlled M1-to-M2 transition of aged macrophages by calcium phosphate coatings. Biomaterials. 2019; 196:90-99. [7] CHEN M, ZHANG Y, ZHOU P, et al. Substrate stiffness modulates bone marrow-derived macrophage polarization through NF-κB signaling pathway. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(4):880-890. [8] HE S, HOU T, ZHOU J, et al. Endothelial Cells Promote Migration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells via PDGF-BB/PDGFRβ-Src-Akt in the Context of Inflammatory Microenvironment upon Bone Defect. Stem Cells Int. 2022; 2022:1-15. [9] SPILLER KL, NASSIRI S, WITHEREL CE, et al. Sequential delivery of immunomodulatory cytokines to facilitate the M1-to-M2 transition of macrophages and enhance vascularization of bone scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2015;37:194-207. [10] XUE D, CHEN E, ZHONG H, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of graphene oxide for osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Int J Nanomed. 2018;Volume 13: 5799-5810. [11] TANG W, YU Y, WANG J, et al. Enhancement and orchestration of osteogenesis and angiogenesis by a dual-modular design of growth factors delivery scaffolds and 26SCS decoration. Biomaterials. 2020;232:119645. [12] GRANEY PL, BEN-SHAUL S, LANDAU S, et al. Macrophages of diverse phenotypes drive vascularization of engineered tissues. Sci Adv. 2020;6(18):eaay6391. [13] LIU C, HE L, WANG J, et al. Anti-angiogenic effect of Shikonin in rheumatoid arthritis by downregulating PI3K/AKT and MAPKs signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;260:113039. [14] CHENG WX, LIU YZ, MENG XB, et al. PLGA/β-TCP composite scaffold incorporating cucurbitacin B promotes bone regeneration by inducing angiogenesis. J Orthop Transl. 2021;31:41-51. [15] NATHAN K, LU LY, LIN T, et al. Precise immunomodulation of the M1 to M2 macrophage transition enhances mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis and differs by sex. Bone Joint Res. 2019;8(10):481-488. [16] VALLÉS G, BENSIAMAR F, MAESTRO-PARAMIO L, et al. Influence of inflammatory conditions provided by macrophages on osteogenic ability of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):57. [17] ROMERO-LÓPEZ M, LI Z, RHEE C, et al. Macrophage Effects on Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenesis in a Three-Dimensional In Vitro Bone Model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2020;26(19-20):1099-1111. [18] XIA Y, HE XT, XU XY, et al. Exosomes derived from M0, M1 and M2 macrophages exert distinct influences on the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. PeerJ. 2020;8:e8970. [19] LIU K, LUO X, LV ZY, et al. Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Promote Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Towards Osteoblastic Fate Through microRNA-21a-5p. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;9:801432. [20] WANG S, XIAO L, PRASADAM I, et al. Inflammatory macrophages interrupt osteocyte maturation and mineralization via regulating the Notch signaling pathway. Mol Med. 2022;28(1):102. [21] KANG M, HUANG CC, LU Y, et al. Bone regeneration is mediated by macrophage extracellular vesicles. Bone. 2020;141:115627. [22] WU MY, LU JH. Autophagy and Macrophage Functions: Inflammatory Response and Phagocytosis. Cells. 2019;9(1):70. [23] LUO Q, LI X, ZHONG W, et al. Dicalcium silicate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and autophagy-mediated macrophagic inflammation promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. Regen Biomater. 2022;9:rbab075. [24] YANG L, XIAO L, GAO W, et al. Macrophages at Low-Inflammatory Status Improved Osteogenesis via Autophagy Regulation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2021.0015. [25] O’BRIEN EM, SPILLER KL. Pro-inflammatory polarization primes macrophages to transition into a distinct M2-like phenotype in response to IL-4. J Leukoc Biol. 2022;111(5):989-1000. [26] PHILIPP D, SUHR L, WAHLERS T, et al. Preconditioning of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells highly strengthens their potential to promote IL-6-dependent M2b polarization. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018; 9(1):286. [27] RŐSZER T. Understanding the Mysterious M2 Macrophage through Activation Markers and Effector Mechanisms. Mediators Inflamm. 2015; 2015:1-16. [28] NAKAO Y, FUKUDA T, ZHANG Q, et al. Exosomes from TNF-α-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta Biomater. 2021;122:306-324. [29] LIU SX, GUSTAFSON HH, JACKSON DL, et al. Trajectory analysis quantifies transcriptional plasticity during macrophage polarization. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):1-9. [30] HE Y, YANG X, YUAN Z, et al. Regulation of MSC and macrophage functions in bone healing by peptide LL-37-loaded silk fibroin nanoparticles on a titanium surface. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(12):5492-5505. [31] SU J, DU Z, XIAO L, et al. Graphene oxide coated Titanium Surfaces with Osteoimmunomodulatory Role to Enhance Osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;113:110983. [32] WANG Z, NIU Y, TIAN X, et al. Switching on and off macrophages by a “bridge‐burning” coating improves bone‐implant integration under osteoporosis. Adv Funct Mater. 2021; 31(7):2007408. [33] ZHU P, LAI C, CHENG M, et al. Differently charged P (VDF-TrFE) membranes influence osteogenesis through differential immunomodulatory function of macrophages. Front Mater. 2022;8:790753. [34] 许晴.生物活性陶瓷复合材料制备及其抗菌和再生修复研究[D].上海:中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所),2021. [35] BAI X, LIU W, XU L, et al. Sequential macrophage transition facilitates endogenous bone regeneration induced by Zn-doped porous microcrystalline bioactive glass. J Mat Chem B. 2021;9(12):2885-2898. [36] LIANG L, SONG D, WU K, et al. Sequential activation of M1 and M2 phenotypes in macrophages by Mg degradation from Ti-Mg alloy for enhanced osteogenesis. Biomater Res. 2022;26(1):17. [37] CHINIPARDAZ Z, ZHONG JM, YANG S. Regulation of LL-37 in Bone and Periodontium Regeneration. Life (Basel). 2022;12(10):1533. [38] 何逸恒,程鸣威,朱培君,等.电活性生物膜促进大鼠的体内成骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(28):4446-4451. [39] CHE H, SELIG M, ROLAUFFS B. Micro-patterned cell populations as advanced pharmaceutical drugs with precise functional control. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;184:114169. [40] SRIDHARAN R, GENOUD KJ, KELLY DJ, et al. Hydroxyapatite Particle Shape and Size Influence MSC Osteogenesis by Directing the Macrophage Phenotype in Collagen-Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020;3(11):7562-7574. [41] ZHENG Z, CHEN Y, HONG H, et al. The The “Yin and Yang” of Immunomodulatory Magnesium-Enriched Graphene Oxide Nanoscrolls Decorated Biomimetic Scaffolds in Promoting Bone Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(2):2000631. [42] CHEN Z, CHEN L, LIU R, et al. The osteoimmunomodulatory property of a barrier collagen membrane and its manipulation via coating nanometer-sized bioactive glass to improve guided bone regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(5):1007-1019. [43] 刘真真.仿生基质的两种物理性质对巨噬细胞表型的影响及机制的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2021. [44] HE XT, LI X, XIA Y, et al. Building capacity for macrophage modulation and stem cell recruitment in high-stiffness hydrogels for complex periodontal regeneration: Experimental studies in vitro and in rats. Acta Biomater. 2019;88:162-180. [45] 黄千里.医用钛合金的选择性激光熔化成型与钛表面电化学改性[D].北京:清华大学,2017. [46] GAO L, LI M, YIN L, et al. Dual-inflammatory cytokines on TiO2 nanotube-coated surfaces used for regulating macrophage polarization in bone implants. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(7):1878-1886. [47] CHEN J, LI M, YANG C, et al. Macrophage phenotype switch by sequential action of immunomodulatory cytokines from hydrogel layers on titania nanotubes. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;163:336-345. [48] YANG PM, MU HZ, ZHANG YS, et al. Sequential release of immunomodulatory cytokines binding on nano-hydroxyapatite coated titanium surface for regulating macrophage polarization and bone regeneration. Med Hypotheses. 2020;144:110241. [49] ALHAMDI J. Modulating Aged Macrophages and Osteoprogenitors with a Calcium Phosphate Drug Delivery System. University of Connecticut. 2018. [50] YANG L, ZHOU J, YU K, et al. Surface modified small intestinal submucosa membrane manipulates sequential immunomodulation coupled with enhanced angio- and osteogenesis towards ameliorative guided bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;119:111641. [51] LUO M, ZHAO F, LIU L, et al. IFN-γ/SrBG composite scaffolds promote osteogenesis by sequential regulation of macrophages from M1 to M2. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(7):1867-1876. [52] LI T, PENG M, YANG Z, et al. 3D-printed IFN-γ-loading calcium silicate-β-tricalcium phosphate scaffold sequentially activates M1 and M2 polarization of macrophages to promote vascularization of tissue engineering bone. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:96-107. [53] MA Z, HE H, DENG C, et al. 3D bioprinting of proangiogenic constructs with induced immunomodulatory microenvironments through a dual cross-linking procedure using laponite incorporated bioink. Compos B Eng. 2022; 229:109399. [54] LI X, XUE S, ZHAN Q, et al. Sequential Delivery of Different MicroRNA Nanocarriers Facilitates the M1-to-M2 Transition of Macrophages. ACS Omega. 2022;7(9):8174-8183. [55] XUE S, LI X, LI S, et al. Bone fracture microenvironment responsive hydrogel for timing sequential release of cargoes. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2021;629:127413. [56] GUO G, XU Q, ZHU C, et al. Dual-temporal bidirectional immunomodulation of Cu-Zn Bi-layer nanofibrous membranes for sequentially enhancing antibacterial activity and osteogenesis. Appl Mater Today. 2021;22:100888. [57] ZHAO DW, ZUO KQ, WANG K, et al. Interleukin-4 assisted calcium-strontium-zinc-phosphate coating induces controllable macrophage polarization and promotes osseointegration on titanium implant. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111512. [58] TOLEDANO-SERRABONA J, BOSCH BM, DÍEZ-TERCERO L, et al. Evaluation of the inflammatory and osteogenic response induced by titanium particles released during implantoplasty of dental implants. Sci Rep. 2022; 12(1):15790. [59] ZHAO DW, REN B, WANG HW, et al. 3D-printed titanium implant combined with interleukin 4 regulates ordered macrophage polarization to promote bone regeneration and angiogenesis. Bone Joint Res. 2021;10(7):411-424. [60] YIN X, LI Y, YANG C, et al. Alginate/chitosan multilayer films coated on IL-4-loaded TiO2 nanotubes for modulation of macrophage phenotype. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019; 133:503-513. [61] HACHIM D, IFTIKHAR A, LOPRESTI ST, et al. Distinct release strategies are required to modulate macrophage phenotype in young versus aged animals. J Control Release. 2019;305:65-74. [62] XU Z, WU L, TANG Y, et al. Spatiotemporal Regulation of the Bone Immune Microenvironment via Dam-Like Biphasic Bionic Periosteum for Bone Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(1):e2201661. [63] BARRETT JP, COSTELLO DA, O’SULLIVAN J, et al. Bone marrow-derived macrophages from aged rats are more responsive to inflammatory stimuli. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12(1):67. |
| [1] | Zhou Shibo, Guan Jianbin, Yu Xing, Zhao He, Yang Yongdong, Liu Tao. Animal models of femoral bone defects: preparation status and characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 633-638. |
| [2] | Dai Jing, Liu Shasha, Shen Mingjing. Exosome-loaded injectable hydrogel for repairing bone defects around implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 347-354. |
| [3] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Changcheng, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Guo Lin. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of a three-dimensional porous cartilage scaffold made of silk fibroin/gelatin/chitosan [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 366-372. |
| [4] | Wang Xinmin, Yan Wenkai, Song Yahui, Liu Fei. Leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin with autologous hamstring tendon for traumatic patella dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 404-410. |
| [5] | Bi Yujie, Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Zhou Ziqiong, Zhao Jing, Zhu Houjun, Zhong Qiuhui, Yang Yuxin. Strategy and significance of Chinese medicine combined with medical hydrogel for disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 419-425. |
| [6] | Wang Xinyi, Xie Xianrui, Chen Yujie, Wang Xiaoyu, Xu Xiaoqing, Shen Yihong, Mo Xiumei. Electrospun nanofiber scaffolds for soft and hard tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 426-432. |
| [7] | Gao Xueyu, Zhang Wentao, Sun Tianze, Zhang Jing, Li Zhonghai. Application of metal ions in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 439-444. |
| [8] | Yang Jie, Hu Haolei, Li Shuo, Yue Wei, Xu Tao, Li Yi. Application of bio-inks for 3D printing in tissue repair and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 445-451. |
| [9] | Chen Pinrui, Pei Xibo, Xue Yiyuan. Function and advantages of magnetically responsive hydrogel in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 452-457. |
| [10] | Long Zhirui, Huang Lei, Xiao Fang, Wang Lin, Wang Xiaobei. Characteristics of hydrogel microspheres in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 472-478. |
| [11] | Kong Xiangyu, Wang Xing, Pei Zhiwei, Chang Jiale, Li Siqin, Hao Ting, He Wanxiong, Zhang Baoxin, Jia Yanfei. Biological scaffold materials and printing technology for repairing bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 479-485. |
| [12] | Xu Jing, Lyu Huixin, Bao Xin, Zhang Yi, Wang Yihan, Zhou Yanmin. Application of near infrared responsive hydrogels in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 486-492. |
| [13] | Liu Baofang, Xu Bin, Chen Lei. Pueraria decoction in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 193-199. |
| [14] | Guo Xiangying, Peng Zifu, He Yimin, Fang Hongbo, Jiang Ning. MiRNA-122 contributes to the effect of exercise on non-alcoholic fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 272-279. |
| [15] | Meng Zhicheng, Qiao Weiping, Zhao Yang, Liu Hongfei, Li Kaijie, Ma Bo. Effects of immune cells and related cytokines in the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 280-287. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||