Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 445-451.doi: 10.12307/2023.876
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of bio-inks for 3D printing in tissue repair and regenerative medicine
Yang Jie1, Hu Haolei2, Li Shuo1, Yue Wei2, Xu Tao3, Li Yi2
- 1Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453003, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, 988 Hospital of the Joint Service Support Force of Chinese PLA, Zhengzhou 450042, Henan Province, China; 3Biological Manufacturing Center, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2022-11-11Accepted:2023-01-10Online:2024-01-28Published:2023-07-10 -
Contact:Li Yi, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, 988 Hospital of the Joint Service Support Force of Chinese PLA, Zhengzhou 450042, Henan Province, China -
About author:Yang Jie, Master candidate, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453003, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Jie, Hu Haolei, Li Shuo, Yue Wei, Xu Tao, Li Yi. Application of bio-inks for 3D printing in tissue repair and regenerative medicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 445-451.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
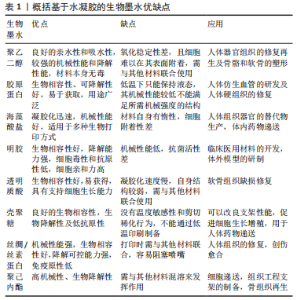
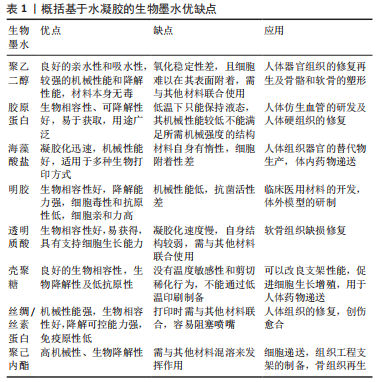
2.1 基于水凝胶的生物墨水 生物油墨最重要的作用是在印刷过程中保护细胞不受外界环境的影响,因此生物油墨必须具有生物相容性。水凝胶是3D打印中常用的支架材料,它提供了一个组织特异性的微环境,可以支持细胞的生长和成熟,同时还主导着生物墨水的物理和化学性质[5]。大多数水凝胶具有特定的细胞结合位点,是细胞附着、扩散、生长和分化所必须的[6]。 目前在科研人员长期的探索与论证下已经研究出几种常用的生物墨水,如合成水凝胶聚乙二醇、聚己内酯等以及天然水凝胶胶原蛋白(Ⅰ型)、海藻酸盐、透明质酸、明胶、壳聚糖、蚕丝等。这些水凝胶生物墨水的3D生物打印能力已经在几种受损组织的再生中得到证实,包括心脏、软骨、骨骼、肌肉、皮肤、肾脏、血管、脂肪组织、肝脏和其他工程生物组织。 由于目前生物打印技术的局限性,导致水凝胶在打印时只能以液体或糊状形存在,这对后续生物墨水形成用来支持细胞增殖的支架结构造成了很大限制。此外,水凝胶的厚度会影响凝胶内部信号分子、氧气及营养物质的扩散,这对水凝胶的设计也产生了挑战。各基于水凝胶的生物墨水的优缺点及应用见表1。"

2.1.1 聚乙二醇 聚乙二醇是3D生物打印中常用的生物墨水的组成成分,其化学结构式为H-(O-CH2-CH2)n-OH,是一种线性聚醚化合物,具有良好的亲水性和吸水性。该材料本身无毒且经FDA批准后可应用于医学临床,常用于对蛋白质、脂质体和其他生物分子的修饰,来作为赋形剂、支架的支撑材料以及借助3D生物打印的药物递送载体等[7]。经过静电纺丝方式制备的聚乙二醇/聚乳酸-共乙醇酸纳米纤维膜,可以充当盲肠和周围组织之间的屏障,从而有效防止腹腔粘连[8]。此外,为了解决喷墨生物打印法打印生物骨骼和软骨组织时打印单元的损坏和打印头的频繁堵塞这一常见情况,有学者将丙烯酰化肽与丙烯酰化聚乙二醇水凝胶共印,同时在支架制造过程中精确打印骨髓来源的人间充质干细胞,将多个步骤成功合成一个步骤,从而使打印出来的聚乙二醇肽支架和人间充质干细胞在堵塞最小化的情况下形成了坚固的骨骼和软骨[9]。在软骨损伤修复方面,BANDYOPADHYAY等[10]将含有不同浓度丝甲基丙烯酸酯和聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯的光交联生物墨水与软骨细胞进行混合,经过3D生物打印软骨构建体的生物加工,其印刷出的丝甲基丙烯酸酯-聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯水凝胶结构表现出可靠的流变性、印刷适性及良好的机械性和降解性,适用于软骨再生。 聚乙二醇具有很强的机械性能和降解性能,能够封装细胞,但其缺点是氧化稳定性差,在与紫外线交联过程中会导致细胞死亡。由于聚乙二醇是一种生物惰性材料,细胞很难附着于其表面,因此需要制备聚乙二醇与其他生物材料的复合材料,从而改善其性能。在预防腹腔粘连、血管再生以及骨骼和软骨的塑形方面,聚乙二醇这一材料有着很强的实用性。 2.1.2 胶原蛋白 人体内胶原蛋白的结构和重塑对于许多人体疾病的病理学研究以及正常的组织发育再生至关重要[11]。胶原蛋白基生物材料被公认为一种有前途的选择,是一种可以实现理想目的的生物墨水,其主要用于具有高细胞活化特性的几种组织的再生[12]。 胶原蛋白是人体内分布最广泛的一类蛋白质,也是最容易获得的一类蛋白质。目前胶原蛋白基生物材料在组织工程领域的应用日益广泛[13]。胶原蛋白具有生物可降解性、生物相容性好、易获得、用途广泛等优点,但其缺点是在不改变自身结构的情况下很难进行细菌灭活[11,13-14]。为支持细胞迁移和渗透,组织工程面临的挑战之一是开发可复制的3D支架[15],该支架由垂直的以及高度多孔的胶原链组成,层层排列,其结构主要由Ⅰ型胶原参与[15-16],这是因为Ⅰ型胶原有很好的细胞黏附特性,可用于细胞间或细胞材料的研究。在仿生血管组织工程结构的开发方面,由天然聚合物胶原蛋白和弹性蛋白中对微纤维和纳米纤维支架进行静电纺丝,该方法制造的血管替代物可以承受血液的高压和脉动环境,为随后血管置换术的体外开发创造了一个理想的条件[17]。为了实现对喷墨打印技术的精确控制和可重复性操作,提高这种新兴技术的进步,ROTH等[18]通过胶原蛋白的精确性高、自动沉积这些特性来控制细胞附着和增殖,从而应用于高通量喷墨打印技术。胶原蛋白基材料可以用于人体硬组织的修复,胶原纤维的矿化在确保硬组织(如骨骼和牙本质)的结构和机械功能方面起着至关重要的作用[19]。 然而,胶原蛋白在低温下只能保持液态,这是其局限性[12],更重要的是,其低机械性能不足以构建具有所需机械强度的多孔结构。因此,除了改变参数(如温度、浓度或pH值)外,研究人员还开发了一种新方法来改善胶原蛋白的性能。LEE等[20]使用低温打印工艺创建了一个3D多孔支架,该支架由胶原蛋白、脱细胞的组织和器官细胞外基质以及丝素蛋白组成,以诱导高细胞活性,从而获得适当的机械强度。在可预见的未来,胶原蛋白这一材料会有更多的发展空间。 2.1.3 海藻酸盐 海藻酸盐是一类非常重要的多糖家族,因为它们在温和的pH值和温度条件下在制备水凝胶方面具有实用性,适用于蛋白质和核酸等敏感生物分子,甚至适用于活细胞的制备[21]。海藻酸盐作为新型生物墨水,它适用于喷墨打印、激光辅助打印、微阀打印等打印技术,同时海藻酸盐具有凝胶化迅速、机械性能好等优点,但也有由于该生物材料的天然惰性,导致细胞附着性差等缺点。 海藻酸盐水凝胶被证明具有作为生物材料的广泛适用性,它们已被用作组织工程的支架、药物的递送载体及基础生物学研究的模型细胞外基质[22]。利用海藻酸盐凝胶和哺乳动物心肌细胞交替打印的收缩性心脏杂交体,可被替代为猫的功能性心脏假组织而使用[23]。由人胚胎干细胞衍生的肝细胞样细胞在使用海藻酸盐水凝胶进行3D打印后,经测试发现其活力以及白蛋白的分泌量与正常肝脏相近,这为日后利用患者特定细胞进行器官或组织的生产研究铺平了道路[24]。海藻酸盐的本质是水溶性线性多糖,由1-4连接的α-L-古鲁酸和β-D-甘露糖残基的交替块组成。蛋白质掺入海藻酸盐这种基质可以在温和的环境下进行,从而有效避免了蛋白质的变性,同时交联海藻酸盐具有更强的保留药物的能力,与其他聚合物如中性树胶壳聚糖等混合还可以有效解决药物的浸出问题,因此在蛋白质药物的口服递送方面,海藻酸盐引起了越来越多的关注[25]。科研人员利用静电微滴法制备的可注射的混合RGD-海藻酸盐/青金石水凝胶微球并封装人牙髓干细胞,通过注射微球作为牙髓再生中的细胞载体,经观察发现这种微球显著提升了牙髓样组织的再生及新微血管的形成,具有巨大的科研潜力[26]。 研究发现,海藻酸盐等高黏度材料可以印刷成定义明确的长管和环形结构,用于激光辅助打印[27]。由海藻酸盐形成的凝胶,经过物理或化学修饰可以实现对生物材料特性的控制,并且已在许多体外和体内研究中得到证实[22]。海藻酸盐作为一种在科研领域使用逐渐增多的生物墨水,在人体组织器官的替代物生产以及药物递送方面有着良好的发展前景。 2.1.4 明胶 明胶是一种生物聚合物,具有优异的生物相容性、止血性、低细胞毒性和低抗原性,并能促进细胞附着和生长。然而,它具有较差的机械性能和抗菌活性,因此可以将它与其他聚合物交联以增强其机械性能[28]。壳聚糖是明胶最常用的化学交联剂,常用以制造电纺明胶/壳聚糖纳米纤维支架,其支架略呈纺锤状,拉伸性能较好,并且明胶/壳聚糖支架也具有较长时间(7 d)的保型性[29]。 明胶常用于半加工食品的制备、美容行业中的美容剂等[30],在伤口护理方面明胶也有着广泛的应用前景。目前临床常用的伤口敷料有着抗菌性差等局限性,而由明胶与纤维素、壳聚糖等合成的生物聚合物所配置的伤口敷料具有优异的生物相容性、止血性、低细胞毒性和低抗原性,并且可以促进细胞附着和生长[28]。甲基丙烯酸明胶和明胶交联可制备一系列电纺支架(纤维直径从200 nm到几微米),其弹性模量范围为1×105-1×107 Pa,这些电纺甲基丙烯酸明胶纤维可以用作平滑肌细胞培养以及体外模型开发的仿生支架,且可用作为体外药物筛选的工具[31]。YAN等[27]通过喷墨打印的方式来制备明胶/抗体层,因为当明胶/抗体层被加热至高于其溶胶-凝胶转变温度时就会快速溶解,其上附着的抗体就会彻底释放。因此,通过控制温度的变化,可以根据需要来控制明胶/抗体层上附着的免疫染色试剂的释放。 明胶可以在较低温度下以浓度依赖的方式形成水凝胶,并且其生物相容性强、细胞亲和力高、降解速度快、易于加工以及使用成本低,使得明胶在生物医学尤其是临床医用材料的制备中应用广泛。但明胶自身的机械性能和抗菌活性较差,需要与其他聚合物交联来完善自身的性能,这为明胶材料的研究带来了挑战。 2.1.5 透明质酸 透明质酸是一种免疫中性线性非硫酸化糖胺聚糖,在人体的结缔组织、皮肤组织中都有广泛存在。透明质酸直接影响着人体细胞和组织的生理功能,在临床上有着长达30年的运用历史[32]。透明质酸作为滑液和关节软骨的组成部分,具有生物相容性和支持细胞生长的能力以及包封干细胞的软骨分化能力,在治疗骨关节炎方面,透明质酸可以增强关节保留及控制药物释放,能有效提高骨关节炎的治疗效果[33]。SHIE等[34]使用数字光处理的方式制备由透明质酸参与构成的水性感光材料,用于软骨组织工程的应用。这类材料生物相容性好,机械性能与软骨关节相似,可以根据软骨的受损状况来进行定制,从而有效促进软骨组织的修复。相对于传统的由生物聚合物材料制备的支架,含有透明质酸的水性感光材料无毒且更加环保。 由于透明质酸具有一定的黏性且凝胶化速度较慢,故单纯的透明质酸很难制成生物墨水,但经加成/缩合化学或自由基聚合等化学改性后,透明质酸可转化为软性或硬性水凝胶、电纺纤维、各种网格和纳米材料等,可广泛应用于临床[32]。透明质酸可作为用喷墨生物打印技术制备亲水性药物的光固化生物墨水[35],也可作用在激光辅助打印平台中,用于研究细胞-细胞和细胞-环境相互作用[36]。用透明质酸构建多层水凝胶细胞激光打印平面结构,通过打印人脂肪来源的干细胞和内皮集落形成细胞的斑点,证明了这些细胞斑点可以在3D阵列中逐层排列并能发生细胞间的相互作用,并且细胞间的直接接触会触发稳定的血管样网络的发展[36]。 生物相容性好和易获得是透明质酸的优点,在人体组织的修复方面透明质酸这一材料前景广阔,但由于其本身结构较弱,无法单独支撑起生物墨水的结构,因此需要与其他材料结合使用。 2.1.6 壳聚糖 壳聚糖是一种线性多糖,它可从虾壳或甲壳动物中获得,其分子质量在10-1 000 kD之间,作为一种易获得的生物材料,壳聚糖有着巨大的开发潜力。壳聚糖具有固有的抑菌、抑真菌、止血和镇痛特性,是开发适用于外科应用的配方和设备的有前途的材料[37-38]。由于壳聚糖具有优异的生物相容性、生物降解性和低免疫原性,因此在组织工程中壳聚糖是一种优质支持材料。GRUENE等[36]制备的胶原蛋白/壳聚糖支架,为移植到支架上的细胞提供了一个良好的生长和迁移条件,能够满足组织工程中的不同应用。壳聚糖的加入使得支架的膨胀率显著降低,变得更为紧凑,同时降解速率也变得更慢。 壳聚糖水凝胶主要用于挤出型生物打印技术,用于喷墨打印的研究较少。GU等[39]通过在玻璃上喷墨打印制备壳聚糖微图案,与玻璃形成互相对照来观察巨噬细胞的生长情况以及清除效率,通过观察发现壳聚糖上的巨噬细胞对细菌的清除率更高,这是因为壳聚糖上的细胞不形成豆荚体,对巨噬细胞的发育不具有锚定作用,从而可以对细菌进行有效清除。这表明壳聚糖可作为生物医学植入物上的潜在涂层材料与巨噬细胞协同发挥杀菌作用[39]。壳聚糖制作纳米颗粒形式的药物载体目前研究比较广泛,它是以壳聚糖/乙酸溶液为原料,采用电喷雾法制备而成[40],通过降低乙酸浓度、壳聚糖浓度和流速从而获得更小的壳聚糖纳米颗粒,再通过加入乙醇使得电喷雾更加的有效和稳定。经过一系列的优化,可以使电喷雾法在生产用于口腔和肺部药物递送系统的固体微粒和纳米颗粒方面具有广阔的前景[40]。 由于壳聚糖自身并没有温度敏感性和剪切稀化行为,且不能通过低温印刷来进行制备,因此壳聚糖这一材料需要与其他生物材料交互来进行应用[37]。壳聚糖可以增强杂交支架的机械性能,提供更加稳定的结构,且对细胞的生长增殖无任何副作用。 2.1.7 丝绸/丝素蛋白 蚕丝是由蚕和蜘蛛纺制的天然纤维蛋白聚合物。科学家发现一种名为B.mori蚕的蚕茧可以提取丝素蛋白,再与其他生物材料协同后可以形成生物聚合物复合材料,可广泛应用于生物医学和技术领域的研究[41]。FDA已批准丝绸医疗器械用于缝合线和作为重建手术期间的支撑结构[41]。经人工开发的用于生产丝蛋白的重组方法,可以减少天然丝绸的差异性及快速降解的问题,并有效提高产量[42]。丝素蛋白作为一种具有突出机械性能、生物降解性、生物相容性和生物可吸收性的天然蛋白质,在组织工程中的应用十分广泛,包括骨骼、软骨、韧带、肌腱、皮肤、伤口愈合和鼓膜等方面[43]。 通过钙和磷酸盐交替浸泡法制备的静电纺丝素蛋白/纳米羟基磷灰石生物复合材料,作为一种新型组织工程支架材料可以在几分钟内在再生丝素蛋白纳米纤维上生产[44]。经过一系列实验表明,纳米羟基磷灰石这种生物复合材料在骨组织工程大有前途[44]。通过静电纺丝制备出的壳聚糖和丝素蛋白复合纳米纤维膜,具有良好的生物降解性和优异的抗菌性能,是应用于伤口愈合方面有希望的候选者[45]。使用喷墨打印法制造的生物相容性丝素蛋白巢微观阵列,能够为未来的生物传感器容纳细胞,为细胞的印刷、固定、封装和生长提供生物模板化的平台[46]。 丝绸的优点比较多,比如降解可控、免疫原性低等,但用在喷墨打印时需与其他聚合物混合,才能获得最佳流变性和顺应性;其缺点是在打印时容易堵塞喷嘴,需要更进一步的研究来进行改善。在人体组织的修复以及创伤愈合方面,通过3D生物打印方式制备的丝素蛋白制品有着广阔的应用前景。 2.1.8 聚己内酯 聚己内酯是一种重要的合成聚合物,它具有高机械性、与多种其他聚合物的混溶性及生物降解性[47]。目前,生物可吸收聚合物在生物医学和植入设备中的应用方面具有显著的优势,例如在细胞递送、组织工程支架以及水凝胶等领域[48]。 用3D打印技术制造的多孔聚己内酯血管支架,可以将阿司匹林和阿托伐他汀钙盐混合物浸渍于其表面,再使用药物包衣技术将支架表面的药物沉积,可有效减少血液中的低密度脂蛋白胆固醇和血管再狭窄[48]。聚己内作为可以进行静电纺丝的生物聚合物,在组织再生领域应用广泛。通过改变聚己内酯的官能团或与其他材料(如合成聚合物、金属材料等)结合来修饰,可以改善聚已内酯聚合物的物理、化学、机械和生物性能,使静电纺丝支架能够满足不同组织工程和再生医学中的要求[49]。通过挤出型生物打印方式制备的基于聚己内酯和非共价官能化少层石墨烯的复合支架,具有足够的形态学、热学、机械和生物学特性,可用于骨组织再生[50]。 聚己内酯这一生物聚合物可塑性很强,以聚己内酯为原材料制造的支架在在未来的研究和临床应用中会有着很大的潜力。 2.2 基于DNA及细胞活性因子的生物墨水 DNA、细胞及细胞活性因子也可以混进生物墨水中,这类生物墨水可使用喷墨打印方式来进行制备,在喷射到相应的支架或组织上后即可发挥作用。目前由DNA以及细胞活性颗粒制备的生物墨水,在医学检测和再生医学以及细胞行为研究中有着很大的发挥空间。 使用细胞及细胞活性因子直接进行生物打印会增加操作的复杂性,并且由于多种细胞需要并行打印,因此需要使用多种生物墨水,这使得后续的生物打印过程中容易造成错误。针对这些问题,有学者使用干细胞代替普通细胞进行生物打印,这样做虽可减少生物墨水的使用,但同时会造成自身并发症的出现。 2.2.1 DNA DNA微阵列包括高密度微阵列(高通量筛查)和低密度微阵列(各种诊断)[51]。微阵列制作方法较多,包括各种喷墨和微喷射沉积或斑点技术等。微阵列技术目前多应用于蛋白质组学、基因组学和细胞分析的新领域,它是针对基因表达进行鉴别诊断的新技术[51-52]。通过单链DNA制造的电化学生物传感器,可以作为便携式生物传感设备用来鉴定和定量测定HPV病毒[52]。用长链DNA适配子组成的水性油墨,具有足够的节段迁移率进行结构切换和荧光信号传导,从而使打印出的图案化纸张传感器具有允许多通路复用检测的效果[53]。 基因转染是研究基因功能的新技术,目前常通过喷墨打印应用于细胞内递送和转染[54-56]。通过将编码绿色荧光蛋白(GFP)与猪动脉内皮细胞使用喷墨打印法共印,可以在将基因转染到细胞中的同时将这些细胞群精确地递送到靶位点上,并且这些质粒在打印后没有发现明显的结构改变和损伤,这为肿瘤的精准细胞疗法提供了可能[55]。用热敏喷墨打印技术打印的中国仓鼠卵巢细胞(CHO)在打印后观察到细胞活力达89%,凋亡率为3.5%,并且用绿色荧光蛋白(GFP)DNA质粒通过共印递送到CHO细胞上后发现转染率达到了30%。这些研究表明,有DNA分子参与热敏喷墨打印技术可用于精确的细胞接种,在基因和大颗粒递送方面有广泛的应用前景[54]。 基于DNA技术而研发的一系列生物打印技术有效提高了产品的使用效率,并为细胞疗法的研究提供了一条新的研究道路,在未来可进行广泛的应用。 2.2.2 生长因子 生长因子通常指一组蛋白质或类固醇激素,能够刺激细胞增殖、分化和组织再生。在体内,生长因子以可溶性和固相分子的形式存在,固定在细胞表面和细胞外基质内[57]。使用喷墨打印技术将生长因子的空间定义模式固定,可以完成对干细胞进行多谱系分化的空间控制[57]。PHILLIPPI等[57]将小鼠的原代肌肉来源干细胞在骨形态发生蛋白2模式的肌源条件下培养,普通模式下的细胞分化为成骨系,而肌源模式下的细胞则分化为肌源谱系。使用喷墨打印机制备亚微米聚苯乙烯纤维,再使用促进肌腱成纤维细胞生长因子2和骨形态发生蛋白2对这种纤维进行图案化,然后用小鼠C2C12成肌细胞接种,经实验发现成纤维细胞生长因子2和骨形态发生蛋白2控制了细胞的分化命运[58],这种方法在再生医学上有应用的潜力[57-58]。通过生长因子的固定模式可以实现对干细胞群体迁移的空间定向引导[59]。使用喷墨打印法制备的固定化成纤维细胞生长因子2墨水具有生物活性[60],并且可调控细胞增殖[61],从而引导C2C12细胞的分化走向[62]。 生长因子是人体内的一种重要的物质,同时是一种重要的生物墨水组成成分。由生长因子参与制备的生物墨水可以根据需求对目标细胞进行分化调控,从而满足科研的需求,在再生医学以及生物科研领域应用前景广阔。 2.2.3 细胞 随着3D生物打印技术的不断进步,目前细胞也作为生物墨水的一部分被广泛应用于3D生物打印的各个方面,尤其是应用于基于喷射的3D生物打印中的细胞打印,包括细胞喷墨打印、激光辅助细胞打印、细胞的微阀打印、细胞的声学打印、细胞的电流体动力喷射打印等。由于传统的细胞培养工作无法获得理想的细胞产物[63-64],科研人员运用细胞打印技术开发了水凝胶中的小型化3D细胞培养物,用于细胞的测定[63]。此外,生物功能化水凝胶在癌症和其他疾病的研究中有着很大的优势[64]。使用喷墨打印技术制备的含有人羊水来源的干细胞、犬平滑肌细胞和牛主动脉内皮细胞的多细胞异质构建体,在体内可以正常存活并成熟为具有足够血管化的功能组织[65]。SOLIS等[66]研究发现,经过热喷墨生物打印的人类微血管内皮细胞可以参与微血管的形成,在植入人体后会形成移植物-宿主吻合现象。这种基于喷射的细胞打印技术可以用于新生血管支架的开发和应用,在再生医学中有较大的发挥空间[65-66]。 细胞生物打印技术打印的生物材料可以减少实验动物的使用,并为移植器官的短缺问题带来希望[67]。ROVERSI等[67]使用背根神经节神经元作为生物墨水,使用激光辅助细胞生物打印技术进行打印,发现打印的神经元依然可以保持高活力和功能完整性,这为今后的生物打印神经元测定铺平了道路。细胞的声学打印是以非接触式的方法将生物材料图案化为3D构造,这是一种全新的生物制造技术,减少了细胞损伤,并且操作简单、打印速度快。到目前为止,声学细胞图案已被用于复制生物过程,例如血管生成[68]、神经分化等[69]。 目前细胞打印技术的应用面十分广泛,在药物的研发、器官移植以及再生医学等方面都有着实际的意义。目前仍需解决的问题就是寻找到可靠的细胞来源,来为细胞生物打印提供原材料。 2.3 功能性复合材料 复合材料分化学复合材料和物理复合材料,其合成方法分化学合成法和物理合成法。经过合成处理后的复合材料性能会发生相应的变化,从而适用于生物工程中的应用。人工合成的复合材料有着强大的机械性能,可以根据需求对材料进行搭配,从而满足人们在生物医学以及再生医学中的需求。 2.3.1 可打印聚合物水凝胶 生物工程中所需的可打印水凝胶对生物相容性和机械强度有极高的要求[70],而传统的生物聚合物水凝胶很多时候并不能满足打印时的要求,因此,使用多种有机物与无机物聚合后经物理方法或化学方法聚合的生物材料受到了人们的关注[71]。有学者研制出可打印聚合物水凝胶,该聚合物属于化学复合材料,它由甲基丙烯酸基团衍生的聚[N-(2-羟丙基)甲基丙烯酰胺乳酸]A-嵌段和分子质量为10 kD的亲水性聚(乙二醇)B-嵌段组成,该凝胶由热化处理并通过光聚合和化学交联来形成,具有很强的机械性能,可用于软骨细胞的培养[72]。GLUKHOVA等[71]基于钙离子交联的软藻酸盐网络中嵌入的刚性渗滤埃洛石纳米管网络研制的纳米复合水凝胶,具有明显的剪切变稀行为,对3D打印具有重要的流变学意义。由于这两种组分为天然来源,具有低毒性和良好的生物相容性,可用于生物医学目的。LAI等[73]使用阳离子纤维素纳米晶体和两性离子水凝胶在光聚合等一系列物理合成下设计的水凝胶,具有良好的机械强度、高透明度和3D可打印性等特点,可应用于可穿戴电子设备和制备人造肌肉。LIU等[70]对天然存在的小分子叶酸进行配位触发的分层自组装,在低于1%的浓度下制备具有与合成双网聚合物凝胶相当的强力学弹性模量的超分子水凝胶,具有剪切变稀和即时愈合能力,可注射和打印成各种三维结构,在各种生物工程技术应用中很有希望。 可打印聚合物水凝胶是一种新颖的生物墨水,可以克服单独一种材料的局限性,结合它们的优点进行生产制造,其在人体组织再生以及器官修复方面十分有前景。 2.3.2 多肽-DNA水凝胶 由化学复合材料制备的多肽-DNA水凝胶,是一种愈合性能强、机械强度高的生物材料。研究者利用超分子多肽-DNA水凝胶首次实现了原位多层3D生物打印,其原理是通过交替沉积两种互补的生物油墨打印出符合设计的、保形效果良好的3D结构[74],可以达到毫米级的结构且不塌陷,并保留了细胞生物活性作用。多肽-DNA水凝胶在生物医学领域的真正潜力仍有待探索。HIVARE等[75]使用化学交联剂将DNA水凝胶与IKVAV肽耦合,经实验发现神经母细胞瘤的干细胞种植于这种材料包被的支架上后神经元分化增强,神经突起长度延长,这为神经科学与神经再生领域的研究带来了一种新的思路。 相比常见的生物工程材料,多肽-DNA水凝胶具有更致密的结构以及更强的弹性,在制药和生物医学方面有着巨大的潜力。 2.3.3 合成材料 物理合成法在医学生物工程方面应用也比较普遍,物理复合材料最大的特点是不改变每个材料各自的特性,而组合后又能获得个体材料无法获得的特殊功能。YAO等[76]通过热诱导纳米纤维自团聚技术制备的3D静电纺丝聚己内酯/聚乳酸混合物(质量比:4/1)纳米纤维支架,具有相比传统纯聚己内酯-3D支架更高的机械性能和体外生物活性,可有效促进实验动物新骨的形成,在骨缺损修复领域有很高的运用价值。DENG团队[77]研制出一种由左旋聚乳酸和明胶组成的新型物理性质的聚合物,与胶原相比,这种新型聚合物表面性质更接近细胞外基质,能促进细胞相容、组织生长和新生血管的形成,并具有良好的修复效果,这为硬脑膜的修复提供了很好的生物材料。 通过静电纺丝制备的生物材料具有一定的临床意义。由甲基丙烯酸化明胶/左旋聚乳酸制造的杂化纳米纤维垫,具有显著的亲水性能,表现出很好的生物相容性,可用作临床敷料[78]。为了预防外科手术后出现的腹腔粘连问题,LI等[78]通过静电纺丝方式制备了复合聚乙二醇/聚乳酸-共乙醇酸纳米纤维膜,该材料具有良好的力学性能、热稳定性和适度的亲水性,可以充当盲肠和周围组织之间的屏障,而不会中断传质和盲肠愈合,从而有效预防腹腔粘连的出现。 合成材料的机械性能强且无细胞毒性和免疫原性,可根据需求对个体材料进行搭配,并发挥作用。由于合成材料拥有细胞惰性,导致细胞无法轻易附着,因此需要与其他生物活性水凝胶相结合,从而发挥作用。在人体器官修复以及组织再生领域,合成材料潜力巨大。合成材料的运用,见图3。"


2.4 刺激响应性生物材料 刺激响应性生物材料是生物3D打印的生物墨水,该生物墨水包括单组分墨水、多组分墨水、动态墨水、纳米复合墨水等[79]。响应性聚合物材料指可以响应外部环境的变化,例如热量、pH值、离子、电场、磁场和紫外线/可见光、葡萄糖[80]、酶、氧化还原反应等,并导致其物理和化学性质发生变化的一种材料[81]。该生物墨水的理化性质在外界理化刺激和生物学刺激下能产生一定的可控响应,它包括理/化交联、键裂、流变性改变、形态改变等[79],从而成为提供细胞的黏附、增殖和分化的理想材料[80]。常见的刺激响应材料有聚乙二醇[79]、聚沙胞苷、基质金属蛋白酶13[79]、聚丙烯酰胺[82]、N-异丙基丙烯酰胺等[83],它们大多是由天然聚合物或合成聚合物等高分子材料复合而成。 刺激响应材料作为一种新兴材料有着很强的可塑性,在今后的再生医学以及组织工程方面有着广泛的发展空间。"

| [1] MANDRYCKY C, WANG Z, KIM K, et al. 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Biotechnol Adv. 2016;34(4):422-434. [2] DEY M, OZBOLAT IT. 3D bioprinting of cells, tissues and organs. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14023. [3] ZHANG J, WEHRLE E, RUBERT M, et al. 3D Bioprinting of Human Tissues: Biofabrication, Bioinks, and Bioreactors. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(8):3971. [4] GUNGOR-OZKERIM PS, INCI I, ZHANG YS, et al. Bioinks for 3D bioprinting: an overview. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(5):915-946. [5] ZHANG YS, DUCHAMP M, OKLU R, et al. Bioprinting the Cancer Microenvironment. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2016;2(10):1710-1721. [6] GU Z, FU J, LIN H, et al. Development of 3D bioprinting: From printing methods to biomedical applications. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2020;15(5): 529-557. [7] RAIJADA D, GENINA N, FORS D, et al. A Step toward Development of Printable Dosage Forms for Poorly Soluble Drugs. J Pharm Sci. 2013; 102(10):3694-3704. [8] LI J, ZHU J, HE T, et al. Prevention of intra-abdominal adhesion using electrospun PEG/PLGA nanofibrous membranes. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol. 2017;78:988-997. [9] GAO G, YONEZAWA T, HUBBELL K, et al. Inkjet-bioprinted acrylated peptides and PEG hydrogel with human mesenchymal stem cells promote robust bone and cartilage formation with minimal printhead clogging. Biotechnol J. 2015;10(10):1568-4577. [10] BANDYOPADHYAY A, MANDAL BB, BHARDWAJ N. 3D bioprinting of photo-crosslinkable silk methacrylate (SilMA)-polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) bioink for cartilage tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2022;110(4):884-898. [11] ABRAHAM LC, ZUENA E, PEREZ-RAMIREZ B, et al. Guide to collagen characterization for biomaterial studies. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;87(1):264-285. [12] MARQUES CF, DIOGO GS, PINA S, et al. Collagen-based bioinks for hard tissue engineering applications: a comprehensive review. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(3):32. [13] PARENTEAU-BAREIL R, GAUVIN R, BERTHOD F. Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue engineering applications. Materials. 2010;3(3):1863-1887. [14] GLOWACKI J, MIZUNO S. Collagen scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biopolymers. 2008;89(5):338-344. [15] AHN S, YOON H, KIM G, et al. Designed three-dimensional collagen scaffolds for skin tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010; 16(5):813-820. [16] PARK JY, CHOI JC, SHIM JH, et al. A comparative study on collagen type I and hyaluronic acid dependent cell behavior for osteochondral tissue bioprinting. Biofabrication. 2014;6(3):035004. [17] BOLAND ED, MATTHEWS JA, PAWLOWSKI KJ, et al. Electrospinning collagen and elastin: preliminary vascular tissue engineering. Front Biosci. 2004;9:1422-1432. [18] Roth EA, Xu T, Das M, et al. Inkjet printing for high-throughput cell patterning. Biomaterials. 2004;25(17):3707-3715. [19] YU L, WEI M. Biomineralization of Collagen-Based Materials for Hard Tissue Repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):944. [20] LEE H, YANG GH, KIM M, et al. Fabrication of micro/nanoporous collagen/dECM/silk-fibroin biocomposite scaffolds using a low temperature 3D printing process for bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;84:140-147. [21] PAWAR SN, EDGAR KJ. ALGINATE derivatization: a review of chemistry, properties and applications. Biomaterials. 2012;33(11):3279-3305. [22] AUGST AD, KONG HJ, MOONEY DJ. Alginate hydrogels as biomaterials. Macromol Biosci. 2006;6(8):623-633. [23] XU T, BAICU C, AHO M, et al. Fabrication and characterization of bio-engineered cardiac pseudo tissues. Biofabrication. 2009;1(3):035001. [24] FAULKNER-JONES A, FYFE C, CORNELISSEN DJ, et al. Bioprinting of human pluripotent stem cells and their directed differentiation into hepatocyte-like cells for the generation of mini-livers in 3D. Biofabrication. 2015;7(4):044102. [25] GEORGE M, ABRAHAM TE. Polyionic hydrocolloids for the intestinal delivery of protein drugs: alginate and chitosan--a review. J Control Release. 2006;114(1):1-14. [26] ZHANG R, XIE L, WU H, et al. Alginate/laponite hydrogel microspheres co-encapsulating dental pulp stem cells and VEGF for endodontic regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:305-316. [27] YAN J, HUANG Y, CHRISEY DB. Laser-assisted printing of alginate long tubes and annular constructs. Biofabrication. 2013;5(1):015002. [28] NDLOVU SP, NGECE K, ALVEN S, et al. Gelatin-Based Hybrid Scaffolds: Promising Wound Dressings. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(17):2959. [29] PEZESHKI-MODARESS M, ZANDI M, RAJABI S. Tailoring the gelatin/chitosan electrospun scaffold for application in skin tissue engineering: an in vitro study. Prog Biomater. 2018;7(3):207-218. [30] COOLEY P, HINSON D, TROST HJ, et al. Ink-jet-deposited microspot arrays of DNA and other bioactive molecules. Methods Mol Biol. 2001; 170:117-129. [31] BRIDGE JC, AMER M, MORRIS GE, et al. Electrospun gelatin-based scaffolds as a novel 3D platform to study the function of contractile smooth muscle cells in vitro. Biomed Phys Eng Expr. 2018;4(4). doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/aace8f. [32] BURDICK JA, PRESTWICH GD. Hyaluronic acid hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv Mater. 2011;23(12):H41-56. [33] KIM YS, GUILAK F. Engineering Hyaluronic Acid for the Development of New Treatment Strategies for Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(15):8662. [34] SHIE MY, CHANG WC, WEI LJ, et al. 3D Printing of Cytocompatible Water-Based Light-Cured Polyurethane with Hyaluronic Acid for Cartilage Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(2):136. [35] ACOSTA-VELEZ GF, LINSLY CS, CRAIG MC, et al. Photocurable Bioink for the Inkjet 3D Pharming of Hydrophilic Drugs. Bioengineering (Basel). 2017;4(1):11. [36] GRUENE M, PFLAUM M, HESS C, et al. Laser printing of three-dimensional multicellular arrays for studies of cell-cell and cell-environment interactions. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17(10):973-982. [37] SUO H, ZHANG J, XU M, et al. Low-temperature 3D printing of collagen and chitosan composite for tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;123:111963. [38] NOTARIO-PEREZ F, MARTIN-ILLANA A, CAZORLA-LUNA R, et al. Applications of Chitosan in Surgical and Post-Surgical Materials. Mar Drugs. 2022;20(6):396. [39] GU Y, ZHANG W, WANG H, et al. Chitosan surface enhances the mobility, cytoplasm spreading, and phagocytosis of macrophages. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;117:42-50. [40] ZHANG S, KAWAKAMI K. ONE-STEP preparation of chitosan solid nanoparticles by electrospray deposition. Int J Pharm. 2010;397(1-2):211-217. [41] HUANG W, LING S, LI C, et al. Silkworm silk-based materials and devices generated using bio-nanotechnology. Chem Soc Rev. 2018;47(17):6486-6504. [42] AIGNER TB, DESIMONE E, SCHEIBEL T. Biomedical Applications of Recombinant Silk-Based Materials. Adv Mater. 2018;30(19):e1704636. [43] SUN W, GREGORY DA, TOMEH MA, et al. Silk Fibroin as a Functional Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1499. [44] WEI K, LI Y, KIM KO, et al. Fabrication of nano-hydroxyapatite on electrospun silk fibroin nanofiber and their effects in osteoblastic behavior. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011;97(3):272-280. [45] CAI ZX, MO XM, ZHANG KH, et al. Fabrication of chitosan/silk fibroin composite nanofibers for wound-dressing applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2010;11(9):3529-3539. [46] SUNTIVICH R, DRACHUK I, CALABRESE R, et al. Inkjet printing of silk nest arrays for cell hosting. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(4):1428-1435. [47] LABET M, THIELEMANS W. Synthesis of polycaprolactone: a review. Chem Soc Rev. 2009;38(12):3484-3504. [48] KIM J, PARK SA, KIM J, et al. Fabrication and Characterization of Bioresorbable Drug-coated Porous Scaffolds for Vascular Tissue Engineering. Materials (Basel). 2019;12(9):1438. [49] ZHANG W, WENG T, LI Q, et al. Applications of Poly(caprolactone)-based Nanofibre Electrospun Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;16(4):414-442. [50] DIAS D, VALE AC, CUNHA EPF, et al. 3D-printed cryomilled poly(ε-caprolactone)/graphene composite scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(7):961-972. [51] HELLER MJ. DNA microarray technology: devices, systems, and applications. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2002;4:129-153. [52] RASOULI E, SHAHNAVAZ Z, BASIRUN WJ, et al. Advancements in electrochemical DNA sensor for detection of human papilloma virus - A review. Anal Biochem. 2018;556:136-144. [53] CARRASQUILLA C, LITTLE JR, LI Y, et al. Patterned paper sensors printed with long-chain DNA aptamers. Chemistry. 2015;21(20):7369-7373. [54] CUI X, DEAN D, RUGGERI ZM, et al. Cell damage evaluation of thermal inkjet printed Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2010; 106(6):963-969. [55] XU T, ROHOZINSKI J, ZHAO W, et al. Inkjet-mediated gene transfection into living cells combined with targeted delivery. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(1):95-101. [56] OWCZARCZAK AB, SHUFORD SO, WOOD ST, et al. Creating transient cell membrane pores using a standard inkjet printer. J Vis Exp. 2012; (61):3681. [57] PHILLIPPI JA, MILLER E, WEISS L, et al. Microenvironments engineered by inkjet bioprinting spatially direct adult stem cells toward muscle- and bone-like subpopulations. Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):127-134. [58] KER ED, NAIN AS, WEISS LE, et al. Bioprinting of growth factors onto aligned sub-micron fibrous scaffolds for simultaneous control of cell differentiation and alignment. Biomaterials. 2011;32(32):8097-8107. [59] MILLER ED, LI K, KANADE T, et al. Spatially directed guidance of stem cell population migration by immobilized patterns of growth factors. Biomaterials. 2011;32(11):2775-2785. [60] CAMPBELL PG, MILLER ED, FISHER GW, et al. Engineered spatial patterns of FGF-2 immobilized on fibrin direct cell organization. Biomaterials. 2005;26(33):6762-6770. [61] MILLER ED, FISHER GW, WEISS LE, et al. Dose-dependent cell growth in response to concentration modulated patterns of FGF-2 printed on fibrin. Biomaterials. 2006;27(10):2213-2221. [62] MILLER ED, PHILLIPPI JA, FISHER GW, et al. Inkjet printing of growth factor concentration gradients and combinatorial arrays immobilized on biologically-relevant substrates. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2009;12(6):604-618. [63] DATAR A, JOSHI P, LEE MY. Biocompatible Hydrogels for Microarray Cell Printing and Encapsulation. Biosensors (Basel). 2015;5(4):647-663. [64] SONG K, WANG Z, LIU R, et al. Microfabrication-Based Three-Dimensional (3-D) Extracellular Matrix Microenvironments for Cancer and Other Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):935. [65] XU T, ZHAO W, ZHU JM, et al. Complex heterogeneous tissue constructs containing multiple cell types prepared by inkjet printing technology. Biomaterials. 2013;34(1):130-139. [66] SOLIS LH, AYALA Y, PORTILLO S, et al. Thermal inkjet bioprinting triggers the activation of the VEGF pathway in human microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. Biofabrication. 2019;11(4):045005. [67] ROVERSI K, EBRAHIMI ORIMI H, FALCHETTI M, et al. Bioprinting of Adult Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) Neurons Using Laser-Induced Side Transfer (LIST). Micromachines (Basel). 2021;12(8):865. [68] KANG B, SHIN J, PARK HJ, et al. High-resolution acoustophoretic 3D cell patterning to construct functional collateral cylindroids for ischemia therapy. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):5402. [69] BOUYER C, CHEN P, GUVEN S, et al. A Bio-Acoustic Levitational (BAL) Assembly Method for Engineering of Multilayered, 3D Brain-Like Constructs, Using Human Embryonic Stem Cell Derived Neuro-Progenitors. Adv Mater. 2016;28(1):161-167. [70] LIU K, ZANG S, XUE R, et al. Coordination-Triggered Hierarchical Folate/Zinc Supramolecular Hydrogels Leading to Printable Biomaterials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(5):4530-4539. [71] GLUKHOVA SA, MOLCHANOV VS, LOKSHIN BV, et al. Printable Alginate Hydrogels with Embedded Network of Halloysite Nanotubes: Effect of Polymer Cross-Linking on Rheological Properties and Microstructure. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(23):4130. [72] CENSI R, SCHUURMAN W, MALDA J, et al. A printable photopolymerizable thermosensitive p(HPMAm-lactate)-PEG hydrogel for tissue engineering. Adv Funct Mater. 2011;21(10):1833-1842. [73] LAI PC, YU SS. Cationic Cellulose Nanocrystals-Based Nanocomposite Hydrogels: Achieving 3D Printable Capacitive Sensors with High Transparency and Mechanical Strength. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(5): 688. [74] LI C, FAULKNER-JONES A, DUN AR, et al. Rapid formation of a supramolecular polypeptide-DNA hydrogel for in situ three-dimensional multilayer bioprinting. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015;54(13):3957-3961. [75] HIVARE P, GANGRADE A, SWARUP G, et al. Peptide functionalized DNA hydrogel enhances neuroblastoma cell growth and differentiation. Nanoscale. 2022;14(24):8611-8620. [76] YAO Q, COSME JG, XU T, et al. Three dimensional electrospun PCL/PLA blend nanofibrous scaffolds with significantly improved stem cells osteogenic differentiation and cranial bone formation. Biomaterials. 2017;115:115-127. [77] DENG K, YANG Y, KE Y, et al. A novel biomimetic composite substitute of PLLA/gelatin nanofiber membrane for dura repairing. Neurol Res. 2017;39(9):819-829. [78] LI J, ZHU J, HE T, et al. Prevention of intra-abdominal adhesion using electrospun PEG/PLGA nanofibrous membranes. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;78:988-997. [79] FU Z, OUYANG L, XU R, et al. Responsive biomaterials for 3D bioprinting: A review. J Materials Today. 2022;52(1):112-132. [80] CHANG S, WANG S, LIU Z, et al. Advances of Stimulus-Responsive Hydrogels for Bone Defects Repair in Tissue Engineering. Gels. 2022; 8(6):389. [81] FANG R, PI J, WEI T, et al. Stimulus-Responsive Polymers Based on Polypeptoid Skeletons. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(13):2089. [82] LAN Q, LU R, CHEN H, et al. MMP-13 enzyme and pH responsive theranostic nanoplatform for osteoarthritis. J Nanobiotechnol. 2020; 18(1):117. [83] LI K, ZANG X, CHENG M, et al. Stimuli-responsive nanoparticles based on poly acrylic derivatives for tumor therapy. Int J Pharm. 2021;601: 120506. |
| [1] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Changcheng, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Guo Lin. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of a three-dimensional porous cartilage scaffold made of silk fibroin/gelatin/chitosan [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 366-372. |
| [2] | Xu Xiaodong, Zhou Jiping, Zhang Qi, Feng Chen, Zhu Mianshun, Shi Hongcan. 3D printing process of gelatin/oxidized nanocellulose skin scaffold with high elastic modulus and high porosity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 398-403. |
| [3] | Wang Xinmin, Yan Wenkai, Song Yahui, Liu Fei. Leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin with autologous hamstring tendon for traumatic patella dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 404-410. |
| [4] | Bi Yujie, Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Zhou Ziqiong, Zhao Jing, Zhu Houjun, Zhong Qiuhui, Yang Yuxin. Strategy and significance of Chinese medicine combined with medical hydrogel for disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 419-425. |
| [5] | Wang Xinyi, Xie Xianrui, Chen Yujie, Wang Xiaoyu, Xu Xiaoqing, Shen Yihong, Mo Xiumei. Electrospun nanofiber scaffolds for soft and hard tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 426-432. |
| [6] | Long Jundong, Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Effects of different freezing techniques on the rejection of allogeneic vascular transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 433-438. |
| [7] | Gao Xueyu, Zhang Wentao, Sun Tianze, Zhang Jing, Li Zhonghai. Application of metal ions in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 439-444. |
| [8] | Chen Pinrui, Pei Xibo, Xue Yiyuan. Function and advantages of magnetically responsive hydrogel in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 452-457. |
| [9] | Chen Junyan, Meng Qingqi, Li Siming. Cartilage targeting function in the drug delivery system by intra-articular injection for the treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 458-463. |
| [10] | Long Zhirui, Huang Lei, Xiao Fang, Wang Lin, Wang Xiaobei. Characteristics of hydrogel microspheres in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 472-478. |
| [11] | Kong Xiangyu, Wang Xing, Pei Zhiwei, Chang Jiale, Li Siqin, Hao Ting, He Wanxiong, Zhang Baoxin, Jia Yanfei. Biological scaffold materials and printing technology for repairing bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 479-485. |
| [12] | Xu Jing, Lyu Huixin, Bao Xin, Zhang Yi, Wang Yihan, Zhou Yanmin. Application of near infrared responsive hydrogels in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 486-492. |
| [13] | Dai Xinyu, Yan Jihong, Hua Lingjun, Zheng Xiaohong. Resistance exercise improves body composition in overweight and obese people: an umbrella review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 267-271. |
| [14] | Meng Zhicheng, Qiao Weiping, Zhao Yang, Liu Hongfei, Li Kaijie, Ma Bo. Effects of immune cells and related cytokines in the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 280-287. |
| [15] | Long Yi, Yang Jiaming, Ye Hua, Zhong Yanbiao, Wang Maoyuan. Extracellular vesicles in sarcopenic obesity: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 315-320. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||