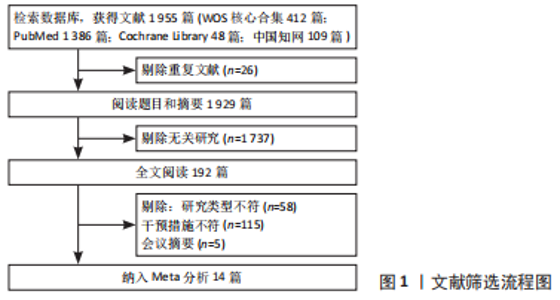
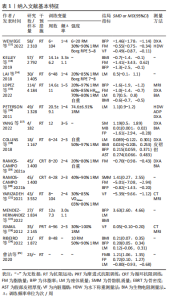
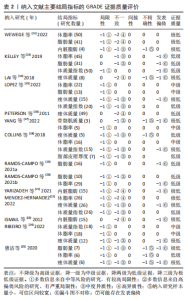
[1] 代米,邓仁丽,余杨文,等.成人睡眠时间与超重/肥胖的关系研究[J].护理研究, 2022,36(14):2471-2475.
[2] 张鑫,王文绢,张润,等.中国成人BMI和腹型肥胖与急性心肌梗死发病关系的前瞻性研究[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2022,26(7):750-755+789.
[3] 邹大进,张征,纪立农.缓解2型糖尿病中国专家共识[J].中国全科医学,2021, 24(32):4037-4048.
[4] 于洪军,任越.青少年力量训练:机制、方法与趋向[J].体育科学,2015, 35(8):76-85.
[5] FAIGENBAUM AD, MCFARLAND JE. Resistance Training for Kids Right from the Start. Acsms Health Fit J. 2016;20(5):16-22.
[6] KIM H, WRANN CD, JEDRYCHOWSKI M, et al. Irisin Mediates Effects on Bone and Fat via αV Integrin Receptors. Cell. 2018;175(7):1756-1768.
[7] KELLY LA, LOZA A, LIN X, et al. The effect of a home-based strength training program on type 2 diabetes risk in obese Latino boys. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2015;28(3-4):315-322.
[8] 梁果,王丽娟,陈欢,等.24 h活动时间分布及替代与儿童身体质量指数的关系研究:基于成分分析模型[J].体育科学,2022,42(3):77-84.
[9] 曾婕,卢旭,陈剑宇,等.四川省汉族中小学生超重肥胖现状及影响因素[J].中国学校卫生,2017,38(9):1299-1302.
[10] 孙重阳,张浩然,刘晓玉,等.伞形综述:选择与应用最佳综合证据的循证实践[J].中国循证医学杂志,2022,22(5):609-614.
[11] BRIGNARDELLO-PETERSEN R, BONNER A, ALEXANDER PE, et al. Advances in the GRADE approach to rate the certainty in estimates from a network meta-analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;98(36):162-162.
[12] WEWEGE MA, DESAI I, HONEY C, et al. The Effect of Resistance Training in Healthy Adults on Body Fat Percentage, Fat Mass and Visceral Fat: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2022;52(1):287-300.
[13] KELLEY GA, KELLEY KS, PATE RR. Exercise and adiposity in overweight and obese children and adolescents: a systematic review with network meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ Open. 2019;9(11):1-18.
[14] LAI CC, TU YK, WANG TG, et al. Effects of resistance training, endurance training and whole-body vibration on lean body mass, muscle strength and physical performance in older people: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2018;47(3): 367-373.
[15] LOPEZ P, TAAFFE DR, GALVÃO DA, et al. Resistance training effectiveness on body composition and body weight outcomes in individuals with overweight and obesity across the lifespan: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2022;23(5):1-25.
[16] PETERSON MD, SEN A, GORDON PM. Influence of resistance exercise on lean body mass in aging adults: a meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(2):249-258.
[17] YANG JM, YE H, ZHU Q, et al. Effects of resistance training on body composition and physical function in elderly patients with osteosarcopenic obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Osteoporos. 2022; 17(1):82-93.
[18] COLLINS H, FAWKNER S, BOOTH JN, et al. The effect of resistance training interventions on weight status in youth: a meta-analysis. Sports Med Open. 2018;4(1):41-57.
[19] RAMOS-CAMPO DJ, ANDREU-CARAVACA L, CARRASCO-POYATOS M, et al. Effects of Circuit Resistance Training on Body Composition, Strength, and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Middle-Aged and Older Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Aging Phys Act. 2021;30(4):725-738.
[20] RAMOS-CAMPO DJ, ANDREU CARAVACA L, MARTÍNEZ-RODRÍGUEZ A, et al. Effects of Resistance Circuit-Based Training on Body Composition, Strength and Cardiorespiratory Fitness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(5):377-399.
[21] YARIZADEH H, EFTEKHAR R, ANJOM-SHOAE J, et al. The Effect of Aerobic and Resistance Training and Combined Exercise Modalities on Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Adv Nutr. 2021;12(1):179-196.
[22] MENDEZ-HERNANDEZ LD, RAMIREZ-MORENO E, BARRERA-GALVEZ R, et al. Effects of Strength Training on Body Fat in Children and Adolescents with Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Children-Basel. 2022; 9(1):995-1009.
[23] ISMAIL I, KEATING SE, BAKER MK, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of aerobic vs. resistance exercise training on visceral fat. Obes Rev. 2012;13(1):68-91.
[24] RIBEIRO B, FORTE P, VINHAS R, et al. The Benefits of Resistance Training in Obese Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med Open. 2022;8(1):109-121.
[25] 曾洁,彭莉.抗阻力训练对不同女性群体身体成影响的Meta分析[J].湖北体育科技,2020,39(5):426-433+461.
[26] 闫纪红,吴文平,代新语.“双减”背景下中小学体育教师专业发展的生态化路径研究[J].体育学研究,2022,36(2):1-18.
[27] 杨蓓,李文芳,陈丹,等.湖北省某高校青年超重/肥胖人群不同减重方法的效果评价[J].中国健康教育,2019,35(6):557-560.
[28] 余卫军,刘峥,徐英,等.深圳市宝安区不同代谢类型体重正常、超重或肥胖的流行现状及影响因素分析[J].中国慢性病预防与控制,2022, 30(8):597-601+605.
[29] 吴天晨,梁艳,杨卉,等.脂蛋白磷脂酶A2联合临床相关指标预测缺血性脑卒中模型的建立与验证[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2022, 24(10):1013-1018.
[30] 杨星雅,李鹏飞,房国梁,等.有氧和抗阻运动对大鼠白色脂肪棕色化的作用[J].体育科学,2017,37(6):69-74+97.
[31] 杨星雅,田野,冯葆欣,等.有氧运动和抗阻运动对大鼠棕色脂肪组织形态及活性的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(1):43-48+65.
[32] 金银哲.抗阻运动对2型糖尿病大鼠模型血脂代谢和胰岛素抵抗的影响[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(9):4235-4242.
[33] 张英平,郑晓鸿,毕学翠,等.不同水平赛艇运动员男子单人艇关键技术指标比较及其优化研究[J].体育科学,2021,41(9):46-56.
[34] 陈泽恺,朱琳,李展权.肥胖儿童青少年每日步数与减脂效果的剂量效应关系[J].中国学校卫生,2022,43(9):1329-1332.
[35] 杨莎,邱林.抗阻训练对烧伤患儿康复效果影响的研究进展[J].中华烧伤杂志,2021,37(9):895-899.
[36] 刘伊依,邱俊强,衣龙燕,等.接受抗阻训练中老年人白细胞介素6与C-反应蛋白变化的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(5):804-812.
[37] 周园,张婧,陈建刚,等.抗阻训练在骨骼肌减少症中应用效果的Meta分析[J].护理研究,2021,35(22):3960-3967.
[38] JORGE ML, DE OLIVEIRA VN, RESENDE NM, et al. The effects of aerobic, resistance, and combined exercise on metabolic control,inflammatory markers, adipocytokines, and muscle insulin signaling in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2011;60(9):1244-1252. |