Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (20): 3265-3272.doi: 10.12307/2022.631
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in burn wound repair and post-burn scar treatment
An Dong1, Liu Yang2, Yang Tongjiang1
- 1Xiushan Branch of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 409900, China; 2The First Clinical Medical College of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2021-04-30Accepted:2021-06-17Online:2022-07-18Published:2022-01-20 -
Contact:Liu Yang, The First Clinical Medical College of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:An Dong, Rehabilitation therapist in charge, Xiushan Branch of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 409900, China Liu Yang, MD, The First Clinical Medical College of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
An Dong, Liu Yang, Yang Tongjiang. Application of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in burn wound repair and post-burn scar treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3265-3272.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
2.1 烧伤修复及瘢痕的病理生理 烧伤后创面愈合是肉芽组织增生、瘢痕形成及表皮再生的复杂动态过程,各进程相辅相成,协同作用,直到瘢痕完成重塑完全成熟,此过程通常分为3个阶段:急性炎症期、细胞增殖期和瘢痕重塑期,且3个阶段相互重叠。 烧伤后,局部细胞坏死、蛋白基质变性或伴组织缺损,在血小板源性生长因子、转化生长因子等不同的细胞因子和趋化因子CXCL8和CCL2作用下,中性粒细胞、单核细胞、肥大细胞及损伤周边的巨噬细胞被招募,连同成纤维细胞等聚集于损伤区域,进入急性炎症期[9]。早期由于纤维蛋白凝块形成,作为支架附着于创面,有利于白细胞、巨噬细胞的黏附和成纤维细胞等附着增殖,为新生肉芽组织长入创造条件。随后,来自损伤周围和真皮深层等部位迁移的成纤维细胞和角质形成细胞增殖,分泌转化生长因子等细胞因子,合成透明质酸、蛋白多糖、弹性蛋白和前胶原蛋白。此外,部分纤维细胞从骨髓迁移到创面,分化为成纤维细胞,并增加转化生长因子的产生,进一步刺激成纤维细胞转化为肌成纤维细胞。这些肌成纤维细胞在细胞因子作用下收缩伤口,Ⅲ型胶原逐渐取代Ⅰ型胶原,细胞外基质重塑,逐步发展为瘢痕成熟期,此期时间可长达2年[10-11]。新生的健康肉芽组织分泌生长因子,并提供上皮再生的营养,同时伤口边缘的表皮基底增生,向伤口中心移动,覆盖肉芽组织表面形成单层上皮,逐渐增殖、分化成为鳞状上皮。在浅表伤口中,表皮通过来自基底层、毛囊和皮脂腺的角质形成细胞的迁移和增殖而再生[12],角质形成细胞沿创面边缘在肉芽组织内增殖和成熟,逐渐恢复上皮细胞的保护功能[13]。 生理性修复过程结束后,Ⅰ度、浅Ⅱ度烧伤创面可被新生皮肤完全修复,深Ⅱ度及Ⅲ度烧伤由新生结缔组织填补创面形成瘢痕。炎症反应在烧伤后修复中至关重要,但促炎介质的过度释放和抗炎介质的缺乏可导致修复过程失调,成纤维细胞、上皮细胞等增殖得不到及时调控,纤维结缔组织过度增生,胶原蛋白过度沉积,细胞外基质异常重塑,最终导致病理性瘢痕的形成,影响正常生理功能。 2.2 体外冲击波疗法对烧伤创面的作用 "

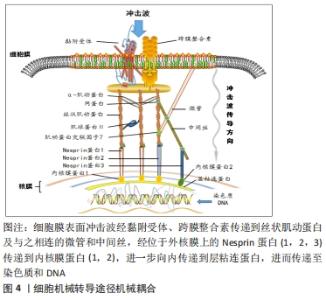
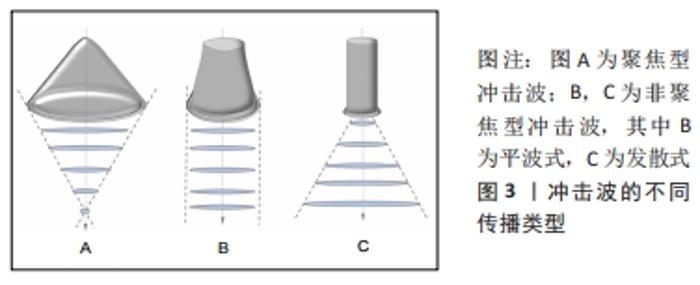
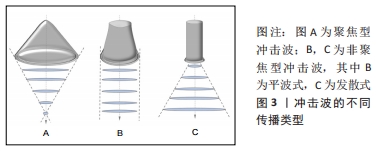
二者在冲击波的行程及能量的物理特性上不同[15]。聚焦型冲击波主要通过声透镜等装置将声波及能量聚焦于某一点发挥治疗作用,而非聚焦型冲击波通过声波的径向或发散传播作用于治疗部位的较大区域。聚焦型冲击波产生的脉冲压力可在10- 100 MPa范围内迅速增加,声能高强度聚集在固定的治疗部位,侵入深度约12 cm。非聚焦型冲击波通常能流密度较小,在轴向及横向传播过程中衰减快,因此作用较为浅表,最大侵入深度为皮下约3 cm [15],但覆盖的面积更大,较少的脉冲次数和脉冲压力和持续时间使患者的接受度提高,在软组织损伤康复中应用广泛。 2.2.1 体外冲击波疗法促进烧伤创面愈合的效应机制 在深Ⅱ-Ⅲ度烧伤后,皮肤屏障功能破坏,细胞坏死、炎性细胞因子大量释放,持续性炎症反应、水肿加重缺血缺氧和组织损伤,而后期细菌定植则进一步阻碍了创面的愈合。多项研究表明体外冲击波疗法对烧伤创面愈合具有促进作用。冲击波的机械刺激引起创面周围细胞微环境变化,涉及促炎抗炎反应、免疫调节、细胞因子改变的复杂动态过程,在细胞和分子水平对创面愈合进行优化调控。包括p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、丝裂原活化细胞外信号调节激酶1/2、细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2和转化生长因子β1/Smad在内的多种信号通路在创面的修复中发挥重要作用[16-17]。 细胞机械转导:冲击波振动作用于组织细胞后引起一系列生物化学变化,这种细胞将机械信号转化为生化反应及基因表达变化的机制被称为细胞机械转导,其关键是识别机械敏感分子及相对应的化学介质和细胞成分[18-19]。当体外冲击波能流密度达到0.5 mJ/mm2后,电镜下观察可发现包括细胞质和线粒体的超微结构发生改变。位于细胞膜表面的跨膜整合素、连接复合体、黏附受体如整合素和钙黏蛋白等向细胞内连接于丝状肌动蛋白,而丝状肌动蛋白链之间被α肌动蛋白相互绑定,同时被附着其上的肌球蛋白Ⅱ产生预应力而保持丝状肌动蛋白的紧张状态。丝状肌动蛋白一方面借肌动蛋白交联因子7连接微管,并以网蛋白连接中间丝,另一方面通过位于外核膜上的Nesprin蛋白1和2与内核膜蛋白1和2相连。同时,中间丝也通过网蛋白、Nesprin蛋白3和内核膜蛋白2相连。内核膜蛋白组进一步向内连接到形成膜和核支架的层粘连蛋白上,进而连接染色质和DNA。上述结构组成细胞外基质与细胞核的机械耦合,将细胞膜表面接收到冲击波的能量最终传递到核支架、染色质和核内DNA上,见图4[20]。传递到核支架的能量可能在毫秒内即可影响某些基因的激活,相较于生长因子通过化学级联反应改变核功能要迅速得多。"
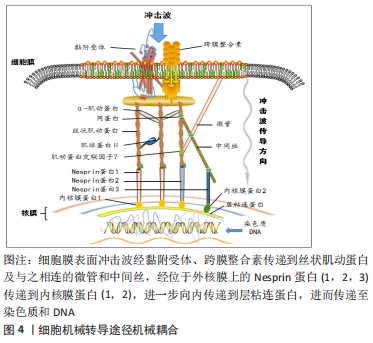
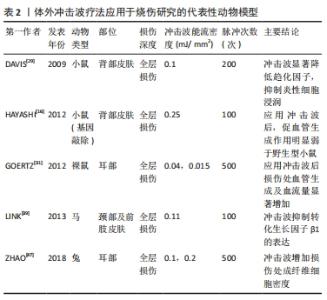
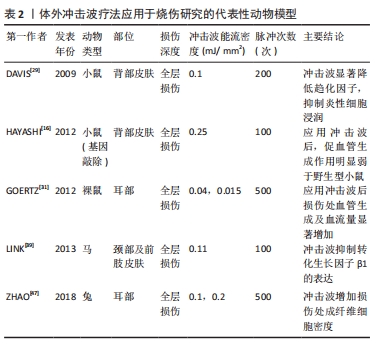
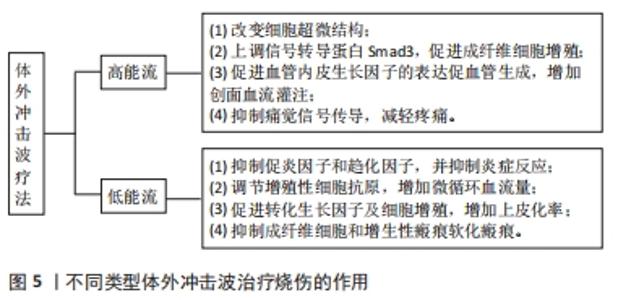
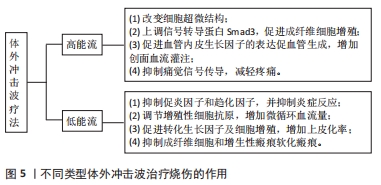
当冲击波传递到组织细胞膜后,膜受体接收到机械振动,可激活机械敏感离子通道、异三聚体G蛋白、蛋白激酶和其他膜相关信号转导分子并引起下游的级联反应,导致力依赖的生物信号表达改变,进而影响组织细胞功能[21]。冲击波的振动能量不仅能激活膜信号,传递到细胞核后还可能改变特定蛋白分子形态,影响其折叠、组装和动力学,促进细胞核的机械化学转化,影响基因的复制和转录,从而影响细胞行为[22]。有研究发现,体外冲击波可通过Toll样受体3通路实现细胞机械转导,介导细胞质RNA的释放,促进血管生成[23]。同时,随着体外冲击波疗法技术的推广,大量研究表明冲击波还可通过细胞机械转导调节成纤维细胞、角质细胞的增殖、分化和迁移,促进组织再生及上皮化过程而加速烧伤创面的愈合[24-26]。 抑菌及炎症反应调控:自烧伤开始,中性粒细胞、单核细胞浸润,炎性细胞因子分泌,炎症反应贯穿于整个损伤修复过程。局部皮肤屏障功能及免疫力的下降还可导致细菌定植,阻碍创面修复。冲击波作用可增加细菌细胞壁和细胞膜的通透性,影响细菌增殖及侵袭性或直接杀灭细菌。在生化反应方面,体外冲击波可能通过快速增强内皮型一氧化氮合酶的活性,调节一氧化氮水平,抑制核因子κB的活化而参与组织炎症调控[27]。HOLFELD等[28]利用冲击波(0.08 mJ/mm2,3 Hz,250脉冲)冲击人脐静脉内皮细胞,用实时定量PCR分析Toll样受体3、炎症基因和信号分子在不同时间点的基因表达,结果显示Toll样受体3、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素10表达量均增加,而血管内皮细胞黏附分子表达无明显变化,推测体外冲击波可能通过Toll样受体3通路调节炎症,Toll样受体3激活、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素10的相互作用可以被视为炎症的3阶段调节。除此之外,DAVIS等[29]对小鼠全身高度炎症性皮肤烧伤创面(15%体表面积)进行研究,实验组在伤后1 h行体外冲击波疗法(0.1 mJ/mm2,200脉冲)治疗,结果显示使用体外冲击波疗法可显著降低趋化因子CC和CXC以及急性促炎细胞因子的表达,明显减弱多形核中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞的浸润,还可减低创面周围细胞外基质蛋白水解酶的活性。由此推测体外冲击波疗法可能促进伤口生理性修复过程中炎性反应的自我调控过程。 促血管生成改善循环:烧伤后创面血管变性堵塞,血流中断,创缘细胞缺氧分泌细胞毒性介质,基质中前列环素和白三烯等刺激微循环扩张,血管通透性增加,组织水肿。体外冲击波的快速机械振动可形成局部湍流使部分闭合血管重新开放,部分高能冲击波还可产生空化效应疏通部分闭合的血管改善微循环[14]。同时,体外冲击波可上调促血管生成因子如增值性细胞核抗原、内皮型一氧化氮合酶、血管内皮生长因子等促进血管生成,改善局部血供[30]。HAYASHI等[16]利用体外冲击波(0.25 mJ/mm2,4 Hz,100脉冲)作用于野生型小鼠时发现可促进创面愈合,他们进一步利用内皮型一氧化氮合酶基因敲除鼠重复体外冲击波实验,结果显示无论血管内皮生长因子的表达、新生血管的增加还是创面愈合速度均明显弱于野生型小鼠(P < 0.05)。表明体外冲击波可通过诱导创面组织中的内皮型一氧化氮合酶表达,进而促进血管内皮生长因子表达和新生血管的形成来加速创面愈合,内皮型一氧化氮合酶在创面愈合过程中具有重要作用。 多项动物实验观察到应用体外冲击波疗法治疗后烧伤创面血流灌注增加、血管生成和创面愈合速度加快。GOERTZ等[31]对51例裸鼠行耳部全层烧伤后分别于第1,3,7天行体外冲击波疗法(1 Hz,500脉冲)治疗,利用活体荧光显微镜获取损伤区血管生成、血流量等微循环参数进行比较,发现体外冲击波治疗组在血管生成及血流量方面均优于无体外冲击波对照组(P < 0.05),且能流密度为0.04 mJ/mm2组优于能流密度 0.015 mJ/mm2组(P < 0.05)。另外,作者还观察到使用冲击波治疗增加了黏附和滚动白细胞的数量。该团队在进一步的研究中,控制体外冲击波的能流密度(0.03 mJ/mm2),实验组梯次增加冲击波治疗的次数,结果发现在第12天时,接受3次体外冲击波治疗组的创缘水肿面积约为接受2次体外冲击波的1.1倍,约为接受一次体外冲击波的1.2倍,同时,随着冲击波治疗次数的增多,非灌注区面积逐渐缩小,血管生成活性增强。在促进微循环方面,KISCH等[32]对大鼠后肢进行体外冲击波(10 J,1 000脉冲)冲击,利用激光多普勒成像和光谱学联合评估后肢远肢端微循环变化,结果显示,与无体外冲击波组相比,体外冲击波组在冲击结束10 min后远端皮肤毛细血管血流速度明显增加(152.8%,P < 0.01),皮肤氧饱和度也相应提高。 上述研究表明,体外冲击波疗法可通过物理机械刺激增加血流改善微循环,还可通过诱导内皮型一氧化氮合酶表达,增加血管内皮生长因子表达量促进新生血管的形成,增加创面修复需要的营养。在一定范围内,高能流密度体外冲击波的促血管生成和改善微循环作用优于低能流密度体外冲击波,且随着冲击波使用次数增加而效果增强。 加速修复性细胞增殖及上皮化:烧伤创面修复中后期,成纤维细胞、角质形成细胞、表皮细胞的增殖、迁移和基质重塑最终使创面愈合。此过程中促生长因子如成纤维细胞生长因子7、转化生长因子β等发挥了重要作用,在人脐血间充质干细胞及急慢性损伤等多项研究中证实冲击波能促进转化生长因子β的产生,增加创面上皮化率加速和改善伤口修复过程[33-35]。体外冲击波疗法可增加分泌促炎细胞因子的角质形成细胞的迁移,诱导成纤维细胞中细胞周期调控基因的上调,促进成纤维细胞增殖[36]。另一方面,冲击波刺激可触发细胞ATP的释放,随后激活嘌呤能受体,最终通过下游ERK1/2信号通路增强促进细胞增殖。在体外,上述过程可促进包括间充质干细胞在内的多种细胞增殖[17],并且在细胞实验中,冲击波的机械刺激可提高人骨髓基质细胞的生长、增殖和迁移速率,同时降低细胞凋亡速率,从而加速创面愈合[37]。然而,也有部分研究发现在瘢痕后期经过体外冲击波疗法干预后人真皮成纤维细胞转化生长因子β的表达受到抑制[38]。LINK等[39]发现经体外冲击波干预后,不同时间段(体外冲击波治疗前1,2,6,12,24,36 h)预损伤的马颈部和前肢组织标本中转化生长因子β1表达量降低,而未行预损伤的皮肤中转化生长因子β1表达量无显著变化,作者认为抑制转化生长因子β1可能会减少肉芽组织的产生,改善马肢体远端伤口的愈合。 2.2.2 体外冲击波治疗烧伤创面的临床应用 自2005年体外冲击波疗法用于烧伤创面的治疗以来,该技术在烧伤领域发展推广十分迅速,在多项临床研究中显示体外冲击波疗法缩可短创面上皮化时间,增加上皮化率[40],促进创面愈合,改善疼痛及减少病理性瘢痕。MEIRER等[5]在2005年首次报告使用体外冲击波疗法治疗右前臂热油烧伤创面(Ⅰ-Ⅲ度,2%体表面积),在伤后第3,7天运用低能流体外冲击波疗法(0.11 mJ/mm2,1 500脉冲)治疗,创面在第15天时基本完成了上皮化,冲击波治疗加速了愈合进程,并且在伤后6个月未观察到病理性瘢痕的形成。此后冲击波被更多的用于烧伤创面的修复,对不同烧伤深度,冲击波能量、频率、脉冲次数等参数设置进行了更广泛的探索。OTTOMANN等[35]进行的一项前瞻性随机对照试验中,对44例急性Ⅱ度烧伤患者随机分为基础治疗加体外冲击波疗法 (0.1 mJ/mm2,100脉冲/cm2,1次)组和基础治疗组。冲击波应用类型为非聚焦型,对比发现,加体外冲击波疗法组的创面完成上皮化率(95%)时间明显优于基础治疗组(P < 0.05),表明体外冲击波疗法可显著加速表皮形成。 相较于治疗烧伤后的病理性瘢痕,目前体外冲击波疗法直接用于促进烧伤创面愈合的临床应用较少,可能与治疗者顾虑冲击波探头及凝胶引起创面感染相关,而无菌操作显著减低了冲击波治疗的便捷性。 综合以上研究,体外冲击波对烧伤创面的促进作用主要通过机械力实现。一方面,经细胞机械转导途径将机械波从膜受体最终传递至染色质、DNA,引起力依赖性生物信号变化,促进细胞核机械化学转化,影响基因蛋白表达和细胞生物学行为。另一方面,体外冲击波刺激生物活性酶类、炎性因子、生长因子表达改变,调节内皮型一氧化氮合酶等增值性细胞抗原促血管生成,改善血供,通过影响Toll样受体3信号通路、抑制核因子κB的活化等方式调控炎症反应。同时,通过上调转化生长因子β等促生长因子的表达加速修复性细胞的增殖和上皮化。体外冲击波疗法在临床应用中加速了烧伤创面的愈合进程。 2.3 体外冲击波疗法对烧伤后瘢痕的作用 "
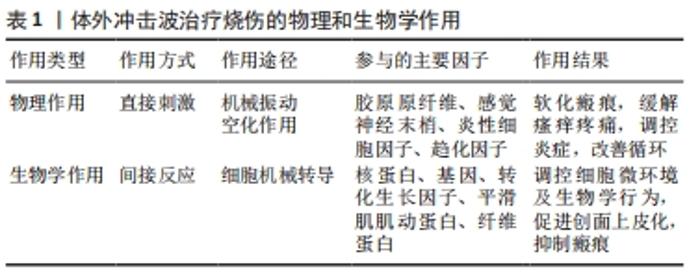
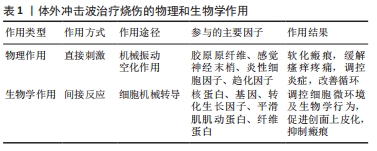
烧伤后增生性瘢痕的发生率高达70%,瘢痕挛缩的发生率为38%-54% [41],在瘢痕形成过程中常伴有创面及周缘的疼痛和瘙痒,在严重烧伤6个月后疼痛和瘙痒程度与病理性瘢痕具有相关性[42]。相较于切割和挫擦等创伤,烧伤后形成的病理性瘢痕面积更大,也更易挛缩。临床对于病理性瘢痕的治疗通常包括局部加压、润肤霜剂、硅酮类制剂、糖皮质激素瘢痕注射、激光、超声波和拉伸功能训练、手术切除、疼痛和瘙痒控制等,但疗效并不十分理想,难以恢复正常的皮肤功能和改善精细动作。近年来,将体外冲击波疗法用于瘢痕治疗的研究逐渐增多,多项研究表明体外冲击波疗法治疗可以显著改善增生性瘢痕的症状、外观和功能。 2.3.1 体外冲击波疗法对瘢痕纤维的物理作用 冲击波的机械振动可能抑制原胶原的共价交联,阻碍胶原原纤维的形成及排列结合为胶原纤维。已形成的纤维瘢痕在冲击波不同方向的综合振动作用下来回拉伸、挤压和剪切,部分胶原原纤维交联破坏、纤维间隙增大,原胶原共价交联破坏后被逐步代谢,同时,冲击波在局部产生的空化效应可在100 μs内使组织间微气泡膨胀和破溃,释放能量使纤维崩解破坏,产生一定强度的组织裂解,宏观表现为纤维瘢痕组织的软化[43-44]。 2.3.2 对瘢痕的分子生物学调控 细胞机械转导不仅在烧伤创面修复中至关重要,在冲击波改善烧伤瘢痕的过程中也具有重要作用。冲击波可通过细胞机械转导途径调节核蛋白、基因的表达,下调转化生长因子β1、上调抗纤维化蛋白基质金属蛋白酶2[45],调控局部瘢痕微环境及修复性细胞代谢,从而对瘢痕增生挛缩产生治疗作用,但其具体分子机制仍有待研究[18]。 CUI等[38]对人真皮成纤维细胞原代提取分离培养后进行不同能流密度的冲击波照射(0.03,0.1,0.3 mJ/mm2,1 000脉冲),分别在第24和72 小时后检测,发现经体外冲击波干预后α平滑肌肌动蛋白、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、纤维连接蛋白和转录因子1表达均显著降低,成纤维细胞的迁移减少,同时,DNA结合抑制蛋白1和2的表达均增加。由此推测体外冲击波可能通过抑制上皮-间充质细胞的转化来减少瘢痕形成。但也有研究表明冲击波作用后皮肤成纤维细胞和Ⅰ型胶原浓度增加[46]。在另一项动物实验中,ZHAO等[47]构建了兔耳增生性瘢痕模型,分别设立低能流体外冲击波(0.1 mJ/mm2)组、高能流(0.2 mJ/mm2)组和空白组,结果发现冲击波治疗组的瘢痕抬高指数、成纤维细胞密度均明显优于空白组;而低能流体外冲击波组的α平滑肌肌动蛋白表达量显著降低,推测低能流冲击波可通过抑制瘢痕抬高指数、减低成纤维细胞密度以及下调α平滑肌肌动蛋白的表达来抑制增生性瘢痕。该作者在另一项兔耳瘢痕实验中,发现相对于无体外冲击波组,信号转导蛋白Smad3的mRNA表达量在低能流体外冲击波(0.1 mJ/mm2)组中明显降低,而当体外冲击波能流密度提高到0.18 mJ/mm2时其表达量增高[48]。由此推测低能流冲击波还可通过调控转化生长因子β1/信号转导蛋白Smad通路影响瘢痕增生。 由此可知,冲击波对烧伤的作用体现为物理和生物学双重影响,对瘢痕抑制的分子生物调控主要通过调节平滑肌肌动蛋白、胶原蛋白、纤维蛋白、成纤维细胞以及以细胞机械转导途径影响核蛋白和基因的表达来实现,见表1。"
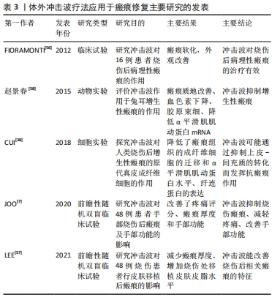
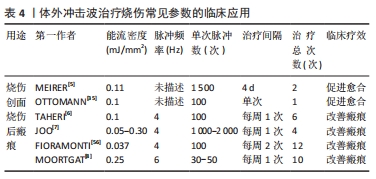
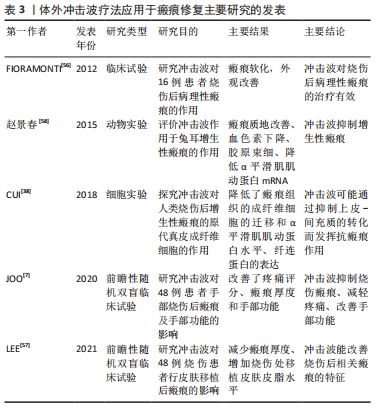
不同实验动物的皮肤存在损伤后修复速度、生化调节的差异,实验结果可能不同,不能直接比较,更多更接近人类损伤修复过程的动物模型需要被建立用于实验研究。 2.3.3 体外冲击波疗法改善瘢痕瘙痒疼痛 冲击波的机械振动可封闭局部神经末梢而产生镇痛效应[49],通过应力刺激神经末梢痛觉感受器C纤维和Aδ神经纤维的轴突,降低神经敏感性,抑制疼痛信号传导而缓解疼痛[50]。同时体外冲击波疗法可以通过对P物质及降钙素基因相关肽的调节修复微小无髓神经纤维,降低瘙痒及疼痛感[51],在烧伤瘢痕的治疗过程中降低了瘙痒和疼痛对疗效的影响[52]。在一项前瞻性随机双盲对照试验中,接受体外冲击波疗法(0.05-0.15 mJ/mm2,3周,每周1次)的治疗组在疗程结束时,相对于假性刺激对照组,其痛阈、痛觉阶段评价和疼痛评分均得到显著改善(P < 0.05),而与治疗前相比疼痛减轻有效率达到85%,结果表明体外冲击波疗法能明显减轻烧伤后的瘢痕疼痛[53]。此外,黎景波等[54]针对92例下肢烧伤后瘢痕患者的研究也得出了相似的结果。他们对实验组应用体外冲击波疗法(2 000脉冲,15 Hz)治疗8周,每周1次,治疗结束时其疼痛目测类比评分显著优于无体外冲击波组,且双下肢屈、伸膝肌的峰值扭矩值均高于无体外冲击波组。廖曼霞等[55]的研究也支持经体外冲击波治疗后烧伤患者目测类比评分可以得到显著改善这一结论。上述研究均表明体外冲击波对缓解烧伤后的瘢痕疼痛有益。 除缓解疼痛外,体外冲击波疗法还可控制瘙痒、抑制瘢痕增殖、改善瘢痕处精细运动功能,提高生活质量。在体外冲击波疗法治疗四肢烧伤瘢痕的研究中,作者进行连续6周,每周1次的冲击波治疗(100脉冲/cm2,0.1 J/mm2,4 Hz),治疗结束及之后的1,3个月分别进行疼痛、瘙痒目测类比评分,温哥华瘢痕量表评价,在所有时段评分均较治疗前改善(P < 0.05),且在随访的第3个月时改善率分别达到90%,78%,64%[6]。JOO等[7]进行的一项针对48例右手烧伤后瘢痕体外冲击波 (1 000-2 000脉冲,0.05-0.30 mJ/mm2,4次)治疗的前瞻性随机双盲研究显示,相较于传统治疗,体外冲击波可以改善瘢痕红斑和增殖厚度,显著抑制瘢痕增生,减轻疼痛,改善手部精细活动能力。该作者在此之前的研究中,已经发现体外冲击波疗法可以显著减少烧伤相关的瘙痒症状。 以上临床研究证实体外冲击波疗法可以有效改善烧伤后瘢痕增生引起的瘙痒和疼痛感,抑制病理性瘢痕形成,改善精细运动功能。 2.3.4 体外冲击波疗法改善瘢痕处皮肤功能 烧伤后因烧伤深度和面积范围的不同可形成不同大小和挛缩程度的病理性瘢痕,连同周边菲薄新生表皮一起呈现出淡红至深红色,皮肤弹性减弱,分泌及屏障功能降低。体外冲击波疗法在应用过程中显示出可淡化瘢痕处颜色、改善皮肤弹性等特性。FIORAMONTI等[56]对16例烧伤后病理性瘢痕患者进行连续6周(每周2次)的体外冲击波治疗(0.037 mJ/mm2,4 Hz),治疗结束后,与冲击波作用前相比所有的瘢痕均获得了明显的软化和颜色改善(P < 0.05)。 创面瘢痕处的弹性是评价预后的重要指标,但目前报道的结果并不一致。LEE等[57]进行的一项瘢痕双盲随机对照试验中,利用皮肤弹性测定仪(Cutometer)评价经体外冲击波疗法(0.05-0.30 mJ/mm2)治疗6周后的皮肤弹性,结果显示相较于标准治疗组,瘢痕体积和皮肤红斑有较大改善,但皮肤生物弹性无明显提升,同时黑色素水平、水分蒸发量均无明显差异。而MOORTGAT等[8]进行了一项更长时间的随机对照试验,所有患者均行常规基础治疗,实验组给予体外冲击波疗法(0.25 mJ/mm2,6 Hz)每周1次共10次治疗,对照组给予假性刺激,利用同品牌弹性测定仪(Cutometer)在治疗第1,3,6个月时分别测定皮肤弹性,结果均优于对照组(P < 0.05),且随着体外冲击波疗法治疗的持续,弹性逐渐改善,由此作者认为体外冲击波疗法能够提高愈合部位的皮肤弹性。 相较于在烧伤创面中的应用,体外冲击波治疗烧伤后瘢痕仅历经9年时间。FIORAMONTI等[56]于2012年根据体外冲击波治疗下肢慢性溃疡的经验首次将其应用于烧伤瘢痕,获得了良好的瘢痕软化和外观改善。赵景春[58]于2015年利用兔耳进行动物实验表明冲击波可抑制增生性瘢痕。此后更多学者从烧伤瘢痕处的真皮成纤维细胞实验以及更大样本量的前瞻性随机双盲临床试验验证了体外冲击波疗法对烧伤瘢痕的抑制和外观改善作用,研究时间脉络见表3。"
| [1] CHAUSSY C, BRENDEL W, SCHMIEDT E. Extracorporeally induced destruction of kidney stones by shock waves. Lancet. 1980;2(8207):1265-1268. [2] SAUERBRUCH T, DELIUS M, PAUMGARTNER G, et al. Fragmentation of gallstones by extracorporeal shock waves. N Engl J Med. 1986;314(13): 818-822. [3] XU ZH, JIANG Q, CHEN DY, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave treatment in nonunions of long bone fractures. Int Orthop. 2009;33(3):789-793. [4] SUN J, GAO F, WANG Y, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy is effective in treating chronic plantar fasciitis: a meta-analysis of RCTs. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(15):e6621. [5] MEIRER R, KAMELGER FS, PIZA-KATZER H. Shock wave therapy: an innovative treatment method for partial thickness burns. Burns. 2005; 31(7):921-922. [6] TAHERI P, KHOSRAWI S, MAZAHERI M, et al. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on improving burn scar in patients with burnt extremities in Isfahan, Iran. J Res Med Sci. 2018;23:81. [7] JOO SY, LEE SY, CHO YS, et al. Clinical utility of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on hypertrophic scars of the hand caused by burn injury: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. J Clin Med. 2020;9(5):1376. [8] MOORTGAT P, ANTHONISSEN M, VAN DAELE U, et al. The effects of shock wave therapy applied on hypertrophic burn scars: a randomised controlled trial. Scars Burn Heal. 2020;6:1006867704. [9] TARNUZZER RW, SCHULTZ GS. Biochemical analysis of acute and chronic wound environments. Wound Repair Regen. 1996;4(3):321-325. [10] FINNERTY CC, JESCHKE MG, BRANSKI LK, et al. Hypertrophic scarring: the greatest unmet challenge after burn injury. Lancet. 2016;388 (10052):1427-1436. [11] WOLFRAM D, TZANKOV A, PULZL P, et al. Hypertrophic scars and keloids-a review of their pathophysiology, risk factors, and therapeutic management. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(2):171-181. [12] COTSARELIS G. Epithelial stem cells: a folliculocentric view. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126(7):1459-1468. [13] SPIEKSTRA SW, BREETVELD M, RUSTEMEYER T, et al. Wound-healing factors secreted by epidermal keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts in skin substitutes. Wound Repair Regen. 2007;15(5):708-717. [14] 邢更彦,张浩冲,刘水涛,等.中国骨肌疾病体外冲击波疗法指南(2019年版)[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2019,11(4):1-10. [15] DYMAREK R, HALSKI T, PTASZKOWSKI K, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy as an adjunct wound treatment: a systematic review of the literature. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2014;60(7):26-39. [16] HAYASHI D, KAWAKAMI K, ITO K, et al. Low-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy enhances skin wound healing in diabetic mice: a critical role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Wound Repair Regen. 2012;20(6):887-895. [17] WEIHS AM, FUCHS C, TEUSCHL AH, et al. Shock wave treatment enhances cell proliferation and improves wound healing by ATP release-coupled extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(39):27090-27104. [18] INGBER DE. Cellular mechanotransduction: putting all the pieces together again. Faseb J. 2006;20(7):811-827. [19] 盛炜,张丽,李美蓉,等.体外冲击波疗法促进组织修复及再生的机制综述[J].解放军医学院学报,2020,41(6):638-643. [20] WANG N, TYTELL JD, INGBER DE. Mechanotransduction at a distance: mechanically coupling the extracellular matrix with the nucleus. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(1):75-82. [21] CHIEN S. Mechanotransduction and endothelial cell homeostasis: the wisdom of the cell. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292(3): H1209-H1224. [22] INGBER DE. The riddle of morphogenesis: a question of solution chemistry or molecular cell engineering? Cell. 1993;75(7):1249-1252. [23] HOLFELD J, TEPEKOYLU C, REISSIG C, et al. Toll-like receptor 3 signalling mediates angiogenic response upon shock wave treatment of ischaemic muscle. Cardiovasc Res. 2016;109(2):331-343. [24] KIM IG, LEE JY, LEE DS, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy combined with vascular endothelial growth factor-C hydrogel for lymphangiogenesis. J Vasc Res. 2013;50(2):124-133. [25] ZINS SR, AMARE MF, TADAKI DK, et al. Comparative analysis of angiogenic gene expression in normal and impaired wound healing in diabetic mice: effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Angiogenesis. 2010;13(4):293-304. [26] 赵景春,咸春静,于家傲,等.体外冲击波疗法对促进创面血管生成及愈合作用的研究进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版), 2014,9(1):71-75. [27] MARIOTTO S, DE PRATI AC, CAVALIERI E, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in inflammatory diseases: molecular mechanism that triggers anti-inflammatory action. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(19):2366-2372. [28] HOLFELD J, TEPEKOYLU C, KOZARYN R, et al. Shockwave therapy differentially stimulates endothelial cells: implications on the control of inflammation via toll-Like receptor 3. Inflammation. 2014;37(1):65-70. [29] DAVIS TA, STOJADINOVIC A, ANAM K, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy suppresses the early proinflammatory immune response to a severe cutaneous burn injury. Int Wound J. 2009;6(1):11-21. [30] WANG CJ, WANG FS, YANG KD, et al. Shock wave therapy induces neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction. A study in rabbits. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(6):984-989. [31] GOERTZ O, LAUER H, HIRSCH T, et al. Extracorporeal shock waves improve angiogenesis after full thickness burn. Burns. 2012;38(7): 1010-1018. [32] KISCH T, SORG H, FORSTMEIER V, et al. Remote effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on cutaneous microcirculation. J Tissue Viability. 2015;24(4):140-145. [33] SCHADEN W, THIELE R, KOLPL C, et al. Shock wave therapy for acute and chronic soft tissue wounds: a feasibility study. J Surg Res. 2007; 143(1):1-12. [34] WANG FS, YANG KD, WANG CJ, et al. Shockwave stimulates oxygen radical-mediated osteogenesis of the mesenchymal cells from human umbilical cord blood. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(6):973-982. [35] OTTOMANN C, STOJADINOVIC A, LAVIN PT, et al. Prospective randomized phase II trial of accelerated reepithelialization of superficial second-degree burn wounds using extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Ann Surg. 2012;255(1):23-29. [36] ASCHERMANN I, NOOR S, VENTURELLI S, et al. Extracorporal shock waves activate migration, proliferation and inflammatory pathways in fibroblasts and keratinocytes, and improve wound healing in an open-label, single-arm study in patients with therapy-refractory chronic leg ulcers. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(3):890-906. [37] SUHR F, DELHASSE Y, BUNGARTZ G, et al. Cell biological effects of mechanical stimulations generated by focused extracorporeal shock wave applications on cultured human bone marrow stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(2):951-964. [38] CUI HS, HONG AR, KIM JB, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy alters the expression of fibrosis-related molecules in fibroblast derived from human hypertrophic scar. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(1):124. [39] LINK KA, KOENIG JB, SILVEIRA A, et al. Effect of unfocused extracorporeal shock wave therapy on growth factor gene expression in wounds and intact skin of horses. Am J Vet Res. 2013;74(2):324-332. [40] DJEDOVIC G, KAMELGER FS, JESCHKE J, et al. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave treatment on deep partial-thickness burn injury in rats: a pilot study. Plast Surg Int. 2014;2014:495967. [41] FINNERTY CC, JESCHKE MG, BRANSKI LK, et al. Hypertrophic scarring: the greatest unmet challenge after burn injury. Lancet. 2016;388 (10052):1427-1436. [42] MAUCK MC, SHUPP JW, WILLIAMS F, et al. Hypertrophic scar severity at autograft sites is associated with increased pain and itch after major thermal burn injury. J Burn Care Res. 2018;39(4):536-544. [43] GERDESMEYER L, MAIER M, HAAKE M, et al. Physical-technical principles of extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT). Orthopade. 2002;31(7):610-617. [44] SPEED CA. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy in the management of chronic soft-tissue conditions. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(2):165-171. [45] KIM DH, HAN SH, SUH HS, et al. Benefits of extracorporeal shock waves for keloid treatment: a pilot study. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33(4):e13653. [46] SAGGINI R, SAGGINI A, SPAGNOLI AM, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy: an emerging treatment modality for retracting scars of the hands. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016;42(1):185-195. [47] ZHAO JC, ZHANG BR, HONG L, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy with low-energy flux density inhibits hypertrophic scar formation in an animal model. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(4):1931-1938. [48] ZHAO JC, ZHANG BR, SHI K, et al. Lower energy radial shock wave therapy improves characteristics of hypertrophic scar in a rabbit ear model. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(1):933-939. [49] TAKAHASHI N, OHTORI S, SAISU T, et al. Second application of low-energy shock waves has a cumulative effect on free nerve endings. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;443:315-319. [50] FRICOVA J, ROKYTA R. The effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on pain patients. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2015;36(2):161-164. [51] D’AGOSTINO MC, CRAIG K, TIBALT E, et al. Shock wave as biological therapeutic tool: from mechanical stimulation to recovery and healing, through mechanotransduction. Int J Surg. 2015;24(Pt B):147-153. [52] 赵胜超,陈永亮,吴博,等.体外冲击波治疗增生性瘢痕的研究进展及机制探讨[J].中国烧伤创疡杂志,2019,31(2):149-152. [53] CHO YS, JOO SY, CUI H, et al. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on scar pain in burn patients: a prospective, randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(32):e4575. [54] 黎景波,曹海燕,肖啸,等.综合康复结合冲击波治疗对下肢烧伤后增生性瘢痕患者疼痛程度及下肢功能的影响[J].中国实用医药, 2019,14(24):184-185. [55] 廖曼霞,曹海燕,易先锋,等.冲击波联合综合康复治疗对下肢烧伤后增生性瘢痕的疗效观察[J].中国康复,2016,31(2):141-143. [56] FIORAMONTI P, CIGNA E, ONESTI MG, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the management of burn scars. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38(5): 778-782. [57] LEE SY, JOO SY, CHO YS, et al. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for burn scar regeneration: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Burns. 2021;47(4):821-827. [58] 赵景春.体外冲击波抑制兔耳增生性瘢痕的实验研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2015. [59] SHI L, LI Z, WANG P, et al. Irritant contact dermatitis following extracorporeal shockwave therapy: a case report. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1830. |
| [1] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [2] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [3] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [4] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [5] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [6] | Kan Houming, Fan Lijun, Chen Xuetai, Shen Wen. Application of platelet-rich plasma in neuropathic pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1286-1292. |
| [7] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [8] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [9] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [10] | Zhang Yujie, Yang Jiandong, Cai Jun, Zhu Shoulei, Tian Yuan. Mechanism by which allicin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of rat vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1080-1084. |
| [11] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [12] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [13] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [14] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [15] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||