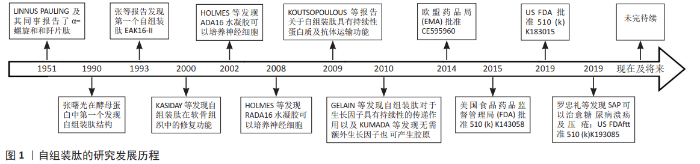
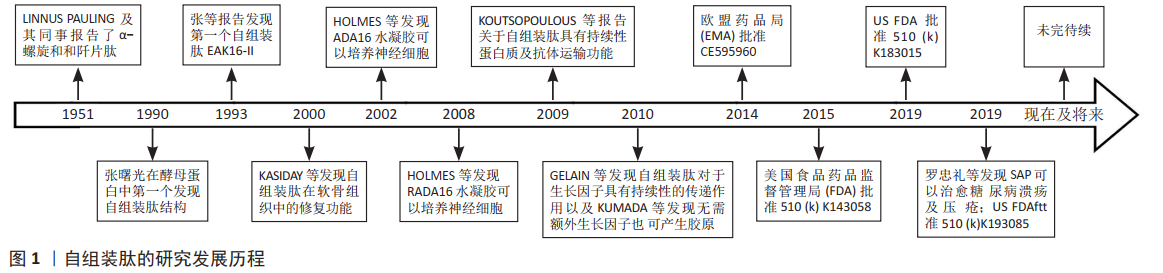
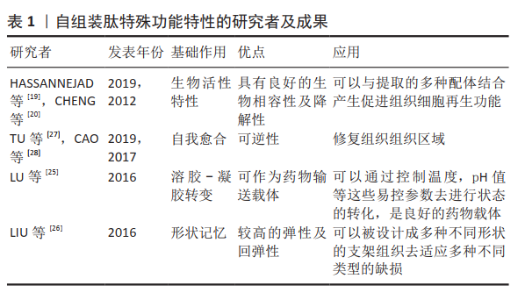
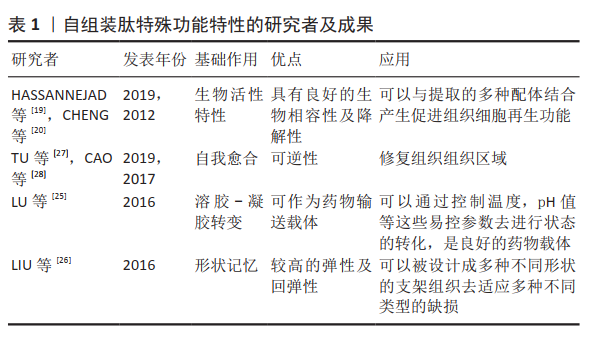
| [1] |
Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu.
Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444.
|
| [2] |
Zhang Haobo, Zhao Yunan, Yang Xuejun.
Role and therapeutic implications of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451.
|
| [3] |
Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan.
Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458.
|
| [4] |
Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian.
Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466.
|
| [5] |
Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin.
Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265.
|
| [6] |
Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming.
Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277.
|
| [7] |
Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide.
Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019.
|
| [8] |
Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian.
Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079.
|
| [9] |
Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu.
Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101.
|
| [10] |
Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun.
Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106.
|
| [11] |
Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi.
Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112.
|
| [12] |
Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong.
Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118.
|
| [13] |
Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing.
Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124.
|
| [14] |
Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei.
Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129.
|
| [15] |
An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu.
Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136.
|