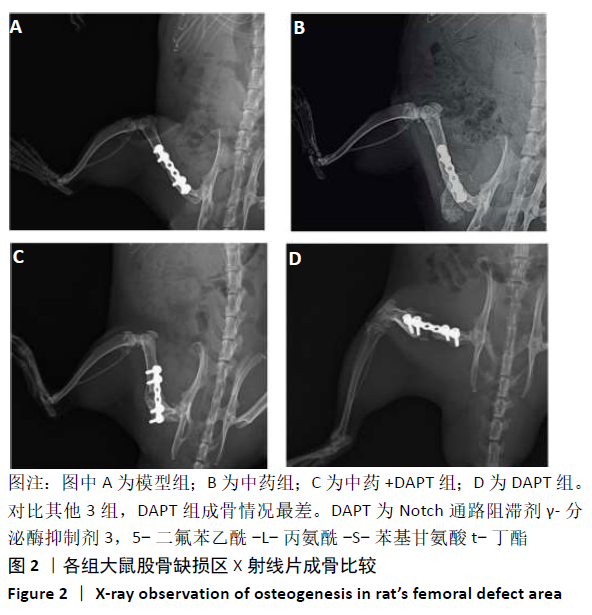
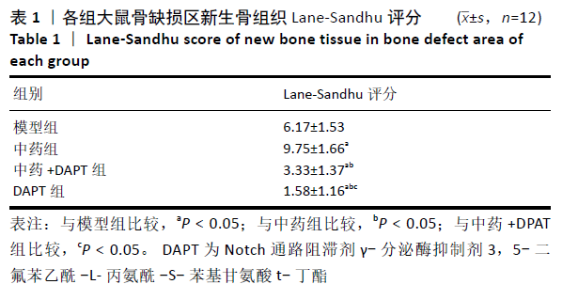
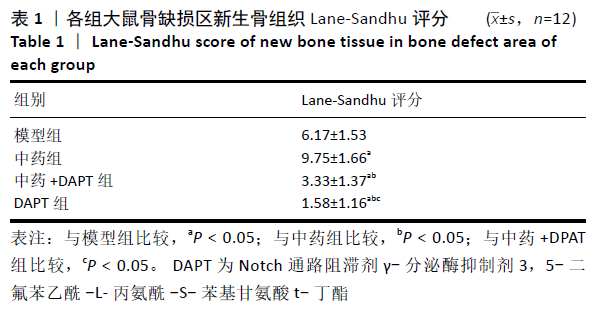
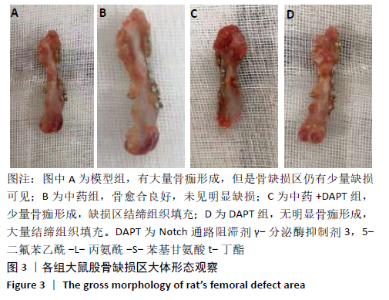
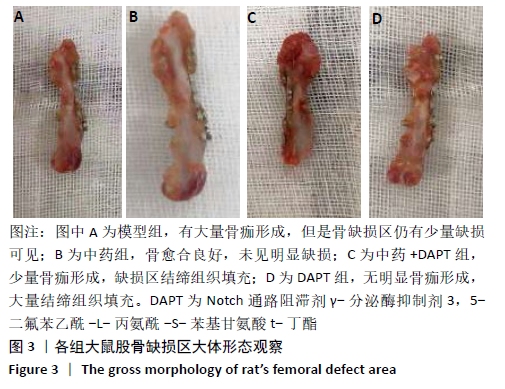
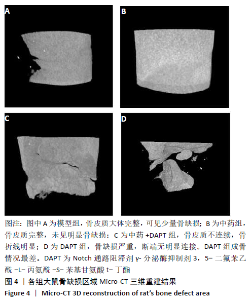
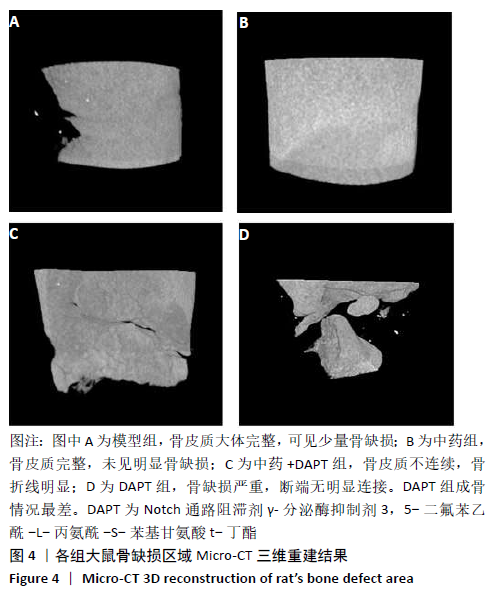
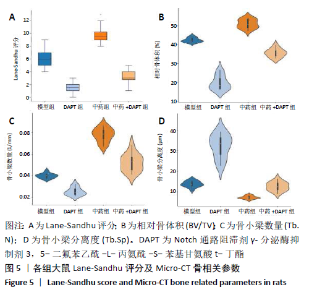
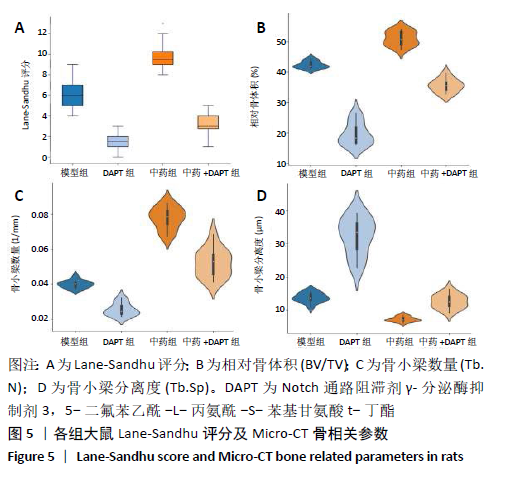
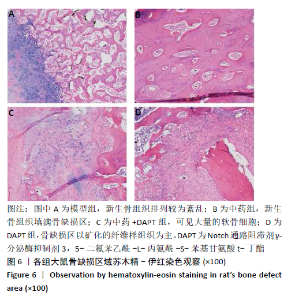
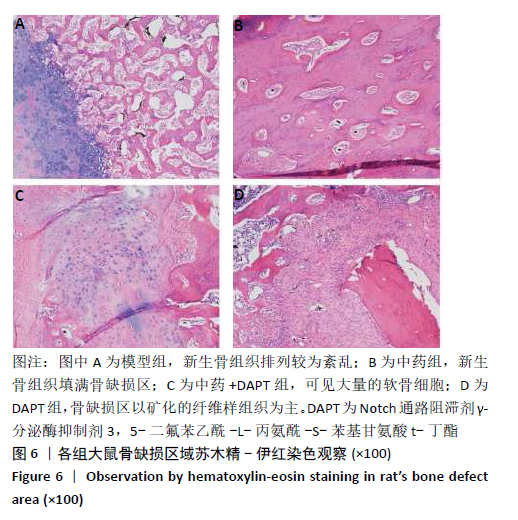
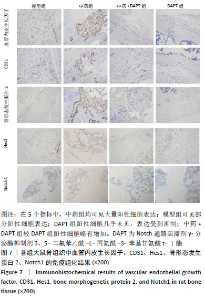
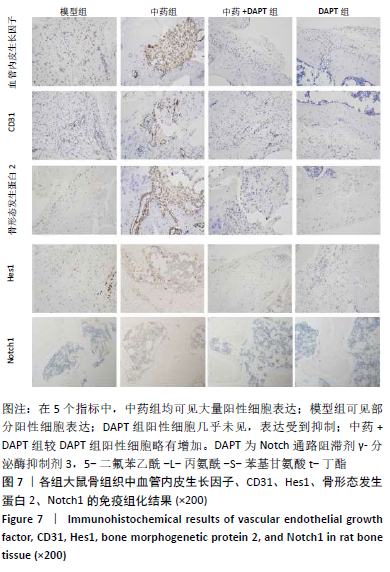
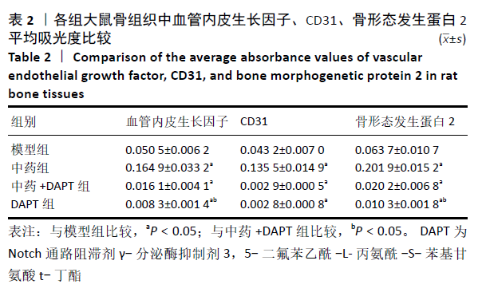
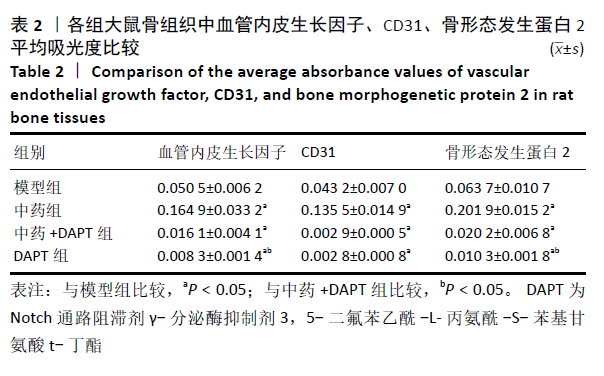
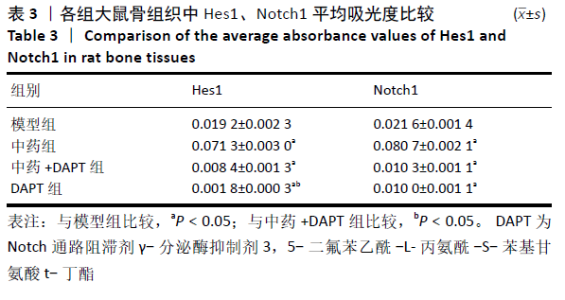
[1] DIMITRIOU R, MATALIOTAKIS GI, ANGOULES AG, et al. Complications following autologous bone graft harvesting from the iliac crest and using the RIA: a systematic review. Injury. 2011;42 Suppl 2:S3-15.
[2] YONG KW, CHOI JR, CHOI JY, et al. Recent Advances in Mechanically Loaded Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5816.
[3] 孙丙银.骨碎补总黄酮促进股骨缺损牵张成骨新骨形成的实验研究[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2013.
[4] 姜自伟,曾景奇,黄枫,等.骨碎补总黄酮对大鼠胫骨牵张成骨效能的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2018,33(2):661-663.
[5] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):426-436.
[6] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014; 507(7492):323-328.
[7] WANG C, INZANA JA, MIRANDO AJ, et al. NOTCH signaling in skeletal progenitors is critical for fracture repair. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(4): 1471-1481.
[8] LUO X, JIANG Y, BI R, et al. Inhibition of notch signaling pathway temporally postpones the cartilage degradation progress of temporomandibular joint arthritis in mice. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;46(7):1132-1138.
[9] LEIBLEIN M, KOCH E, WINKENBACH A, et al. Size matters: Effect of granule size of the bone graft substitute (Herafill®) on bone healing using Masquelet’s induced membrane in a critical size defect model in the rat’s femur. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(4): 1469-1482.
[10] SHEN Z, LIN H, CHEN G, et al. Comparison between the induced membrane technique and distraction osteogenesis in treating segmental bone defects: An experimental study in a rat model. PLoS One. 2019;14(12):e0226839.
[11] DAI Z, LI Y, YAN Y, et al. Evaluation of the internal fixation effect of nano-calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite/poly-amino acid composite screws for intraarticular fractures in rabbits. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13: 6625-6636.
[12] SCHWARTZ AM, SCHENKER ML, AHN J, et al. Building better bone: The weaving of biologic and engineering strategies for managing bone loss. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(9):1855-1864.
[13] XIE H, CUI Z, WANG L, et al. PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis. Nat Med. 2014;20(11):1270-1278.
[14] WANG J, GAO Y, CHENG P, et al. CD31hiEmcnhi Vessels Support New Trabecular Bone Formation at the Frontier Growth Area in the Bone Defect Repair Process. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):4990.
[15] KOPAN R, ILAGAN MX. The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell. 2009;137(2):216-233.
[16] GALE NW, DOMINGUEZ MG, NOGUERA I, et al. Haploinsufficiency of delta-like 4 ligand results in embryonic lethality due to major defects in arterial and vascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(45):15949-15954.
[17] DONG Y, JESSE AM, KOHN A, et al. RBPjkappa-dependent Notch signaling regulates mesenchymal progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation during skeletal development. Development. 2010;137(9):1461-1471.
[18] CUI J, ZHANG W, HUANG E, et al. BMP9-induced osteoblastic differentiation requires functional Notch signaling in mesenchymal stem cells. Lab Invest. 2019;99(1):58-71.
[19] GERBER HP, VU TH, RYAN AM, et al. VEGF couples hypertrophic cartilage remodeling, ossification and angiogenesis during endochondral bone formation. Nat Med. 1999;5(6):623-628.
[20] CARLEVARO MF, CERMELLI S, CANCEDDA R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in cartilage neovascularization and chondrocyte differentiation: auto-paracrine role during endochondral bone formation. J Cell Sci. 2000;113 ( Pt 1):59-69.
[21] JIANG YC, WANG XF, XU YY, et al. Polycaprolactone Nanofibers Containing Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Encapsulated Gelatin Particles Enhance Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation and Angiogenesis of Endothelial Cells. Biomacromolecules. 2018; 19(9):3747-3753.
[22] KIM BS, YANG SS, YOU HK, et al. Fucoidan-induced osteogenic differentiation promotes angiogenesis by inducing vascular endothelial growth factor secretion and accelerates bone repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(3):e1311-e1324.
[23] 江丽霞, 袁瑞娟.骨碎补总黄酮促进骨膜细胞增殖及对兔骨不连的治疗作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(19):2953-2958.
[24] SONG N, ZHAO Z, MA X, et al. Naringin promotes fracture healing through stimulation of angiogenesis by regulating the VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling pathway in osteoporotic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2017;261:11-17.
[25] 高怡加,黄培镇,李悦,等.骨碎补总黄酮对牵张成骨过程中骨形态发生蛋白-2和转化生长因子-β1表达的影响[J].广州中医药大学学报,2016,33(5):679-683.
|