Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (32): 5123-5131.doi: 10.12307/2021.214
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cardiomyocyte direct reprogramming: a scientometric and visualization analysis based on the Web of Science
Hui Xiaoshan1, Zhang Jinsheng2, He Qingyong1, Wang Shiqi3, Yang Shuai4, Zhang Hui3, Wang Jie1
- 1Guang'anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China; 2Department of Encephalopathy, Third Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 3Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 4Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
-
Received:2020-08-15Revised:2020-08-18Accepted:2020-09-23Online:2021-11-18Published:2021-07-26 -
Contact:Wang Jie, MD, Doctoral supervisor, Guang'anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China -
About author:Hui Xiaoshan, MD candidate, Guang'anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hui Xiaoshan, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Wang Shiqi, Yang Shuai, Zhang Hui, Wang Jie. Cardiomyocyte direct reprogramming: a scientometric and visualization analysis based on the Web of Science[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5123-5131.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
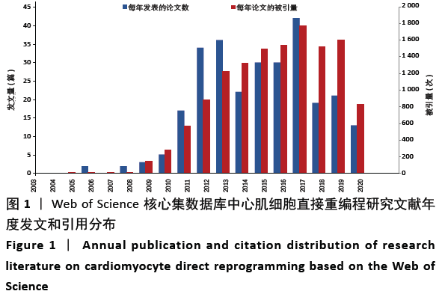
2.1 心肌细胞直接重编程研究文献发文量与引用情况 心肌细胞直接重编程研究文献年度发表量和引用情况见图1。共发表论文277篇,被引频次总计13 252次,每项平均引用47.84次。文献的发表量是一个专业领域研究发展情况的缩影,而文献的引用率是衡量论文学术影响力的关键指标,体现国家科研文献被其他国家或机构的接纳和认可。2003至2011年,年平均发文约3.75篇,提示该研究领域开始逐渐受到关注;2012至2017年,共发文194篇,约占发文总量的70%,提示该领域相关研究获得了快速发展;2017至2020年,文献的被引量高于发表量,说明心肌细胞直接重编程领域的研究被广泛接纳和认可,已形成一定程度的研究规模。 "

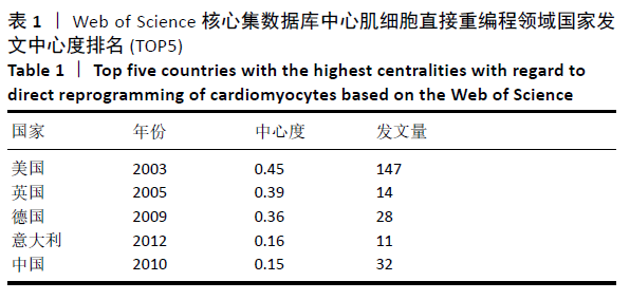
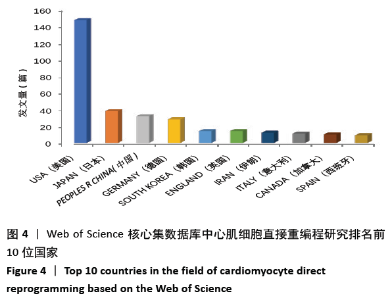
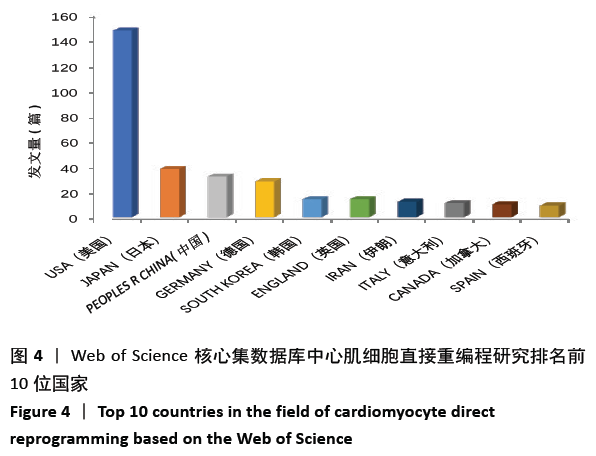
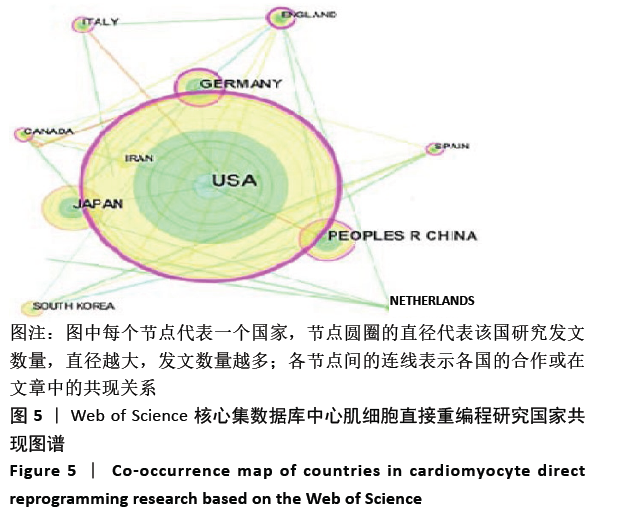
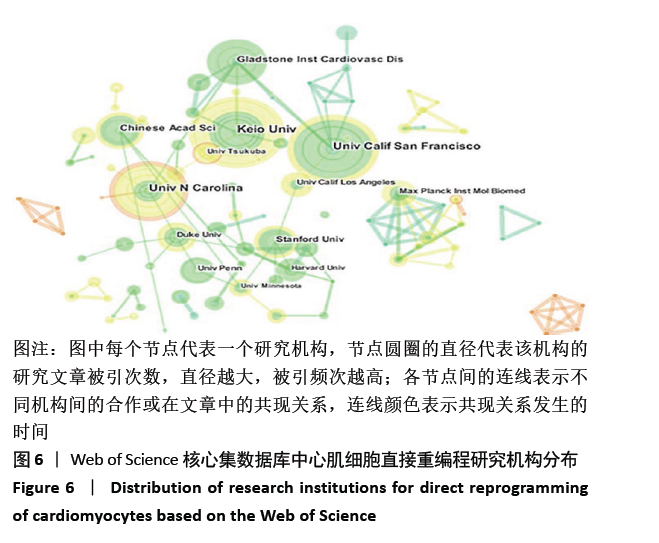
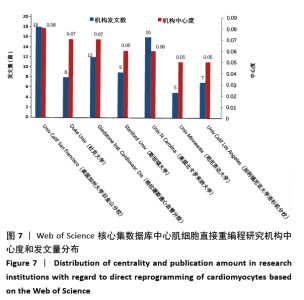
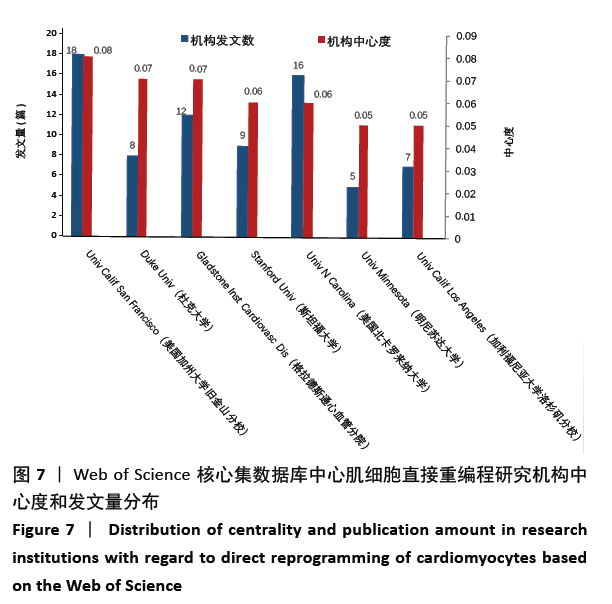
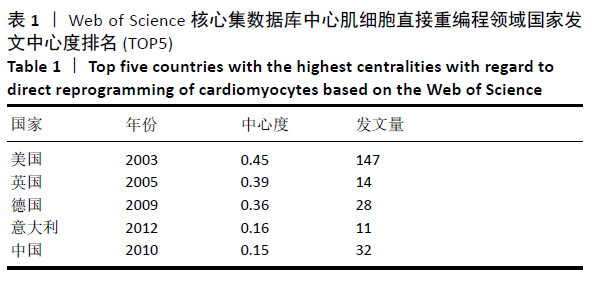
美国居于心肌细胞直接重编程研究的核心地位,与大部分国家有着学术研究合作。中国合作较为紧密的国家有美国、韩国和英国等国家。将图中信息导出,形成心肌细胞直接重编程研究国家发文中心度排名表,见表1。中心度(centrality)亦称中介中心度(betweeness centrality)[6],是衡量某个节点在网络中重要性的指标。通过对中心度出现时间分析,中心度排名前5的除中国外均为发达国家。美国是探测出中心度最早也是中心度最高的国家,说明美国是在心肌细胞直接重编程研究领域最早开始探索并形成一定研究规模的国家;中国的发文量虽然居第3位,但其中心度值较英国、德国和意大利3国低,说明中国在心肌细胞直接重编程研究领域的影响力有待进一步提高。 "
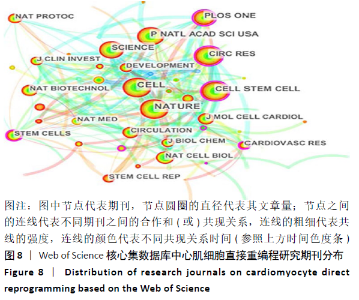
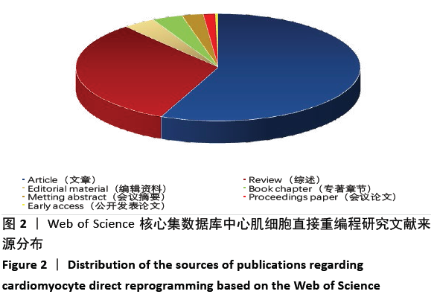
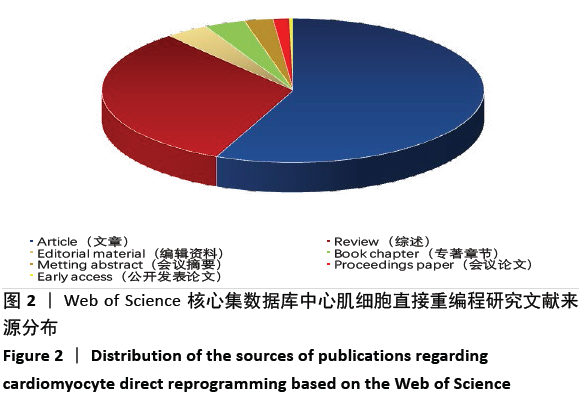
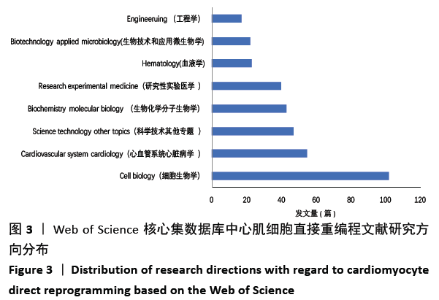
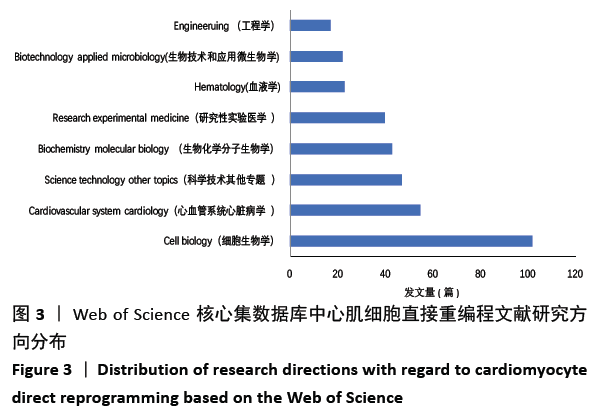
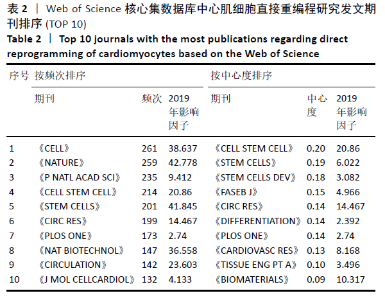
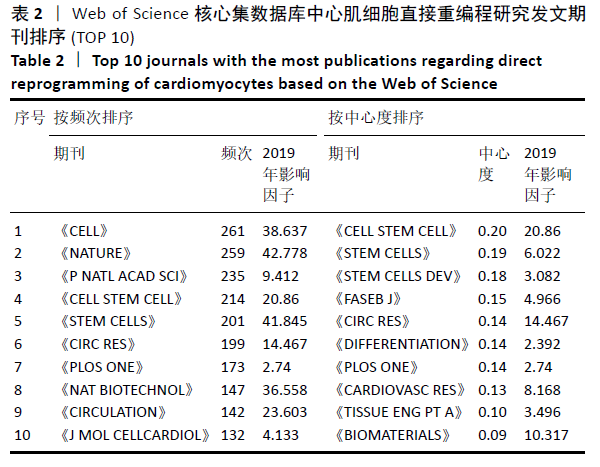
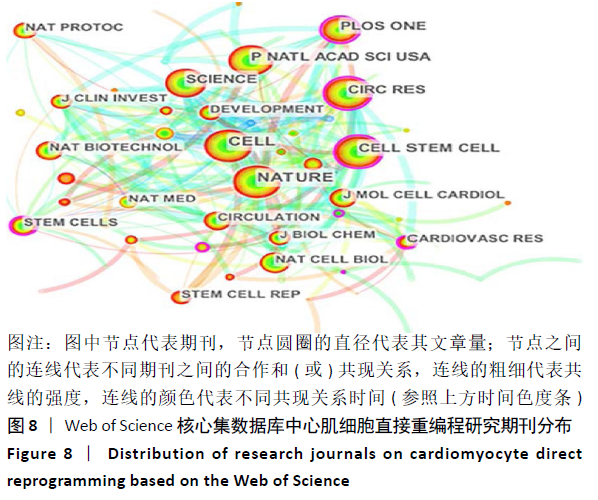
2.6 心肌细胞直接重编程研究领域核心期刊分析 对纳入文献的期刊进行分析可知,共被引期刊主要是《CELL》《NATURE》《CELL STEM CELL》和《SCIENCE》等,结果见图8,表2。期刊的研究多分布在细胞生物学、分子生物学等方向。通过期刊中心度可知,《CELL STEM CELL》《STEM CELLS》和《STEM CELLS DEV》的中心度较高,分别为0.2,0.19和0.18,此3个杂志属于细胞生物学子行业、生物工程与应用微生物子行业和血液学子行业的顶级或中等级别杂志,在一定程度上说明心肌细胞直接重编程研究发表的论文质量较高,此类期刊也在该领域的研究中起到较重要的作用。 "
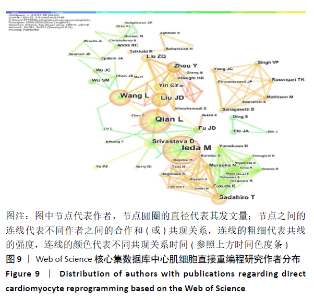
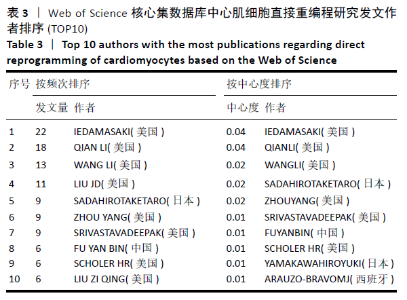
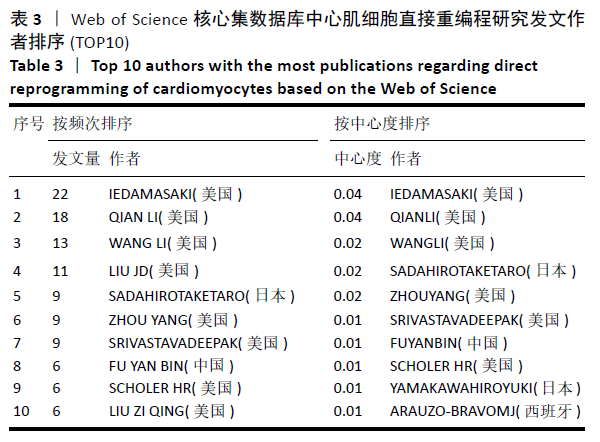
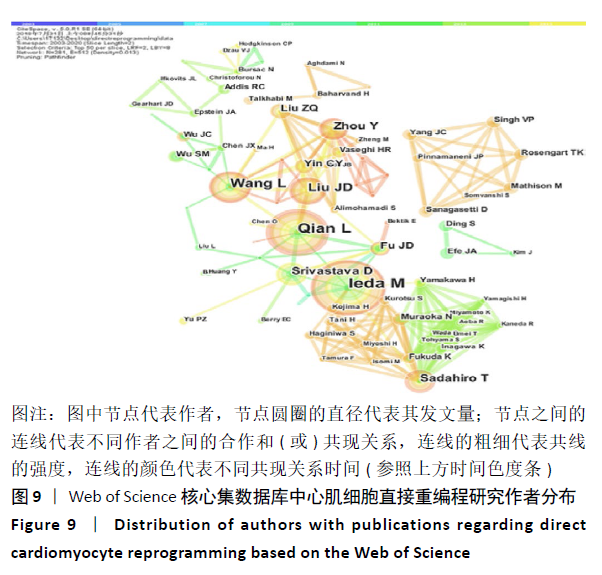
2.7 心肌细胞直接重编程领域作者分析 对研究领域内的文献作者进行可视化分析。各个合作团体相对固定,但其间作者合作并不密切。发文最多的作者是IEDA MASAKI(心血管疾病格拉斯通研究所,美国),发文量Npmax=22,QIAN LI(心血管疾病格拉斯通研究所,美国)、WANG LI(北卡罗来纳大学,美国)及SADAHIRO T(日本庆应大学医学院,日本)等发文数量也位居前列,结果见图9,表3。IEDA等[9]研究认为功能心肌细胞可以直接由分化的体细胞通过确定的因素重新编程,这可为心肌细胞再生提供来源;QIAN等[10]研究发现心脏成纤维细胞可以在其原生环境中被重新编程为类似心肌细胞的细胞,以实现再生;WANG等[11]研究证实Gata4,Mef2C和Tbx5蛋白表达的化学剂量会影响诱导心肌细胞重编程的效率和质量,明确其最佳表达条件对心肌细胞重编程十分重要。 "

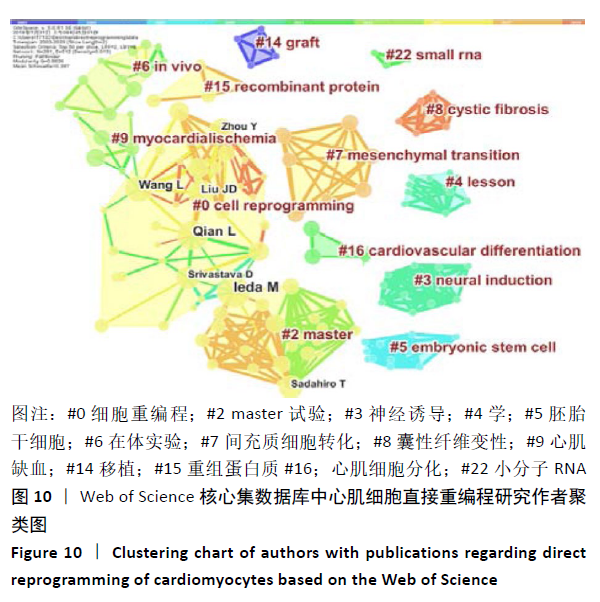
根据普赖斯公式[12],核心作者最小发文量 MP = 0.749 ( Npmax为同一主题中最高的发文量,此处 Npmax=22),MP≈4,核心作者共28位,共发文196篇,约占总发文量的70.76%。 图10为作者合作网络进行聚类分析,连线的颜色代表不同共现关系时间(参照上方时间色度条)可见该领域内有多个固定研究团队,各合作团队之间的合作并不紧密。较大的聚类为:#0 cell reprogramming(细胞重编程)、#2 master (master试验)、#3 neural induction (神经诱导)、#5 embryonic stem cell(胚胎干细胞)和#7 mesenchymal transition(间充质细胞转化)等。 "
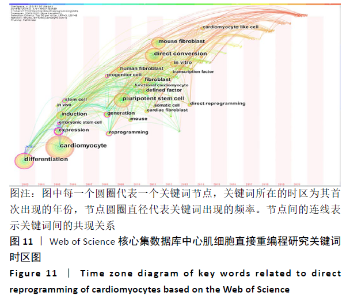
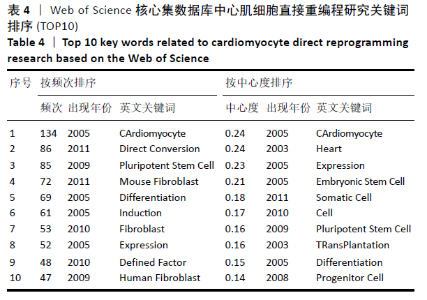
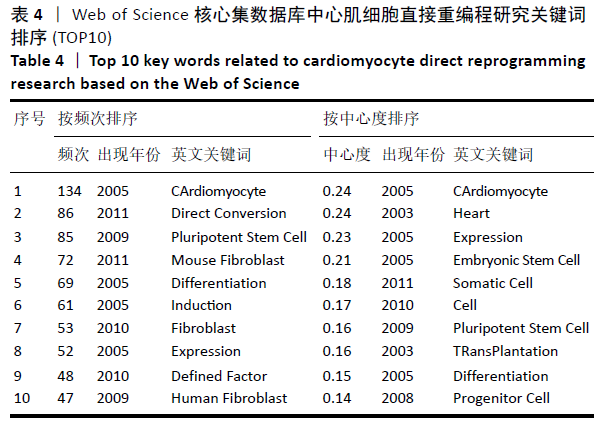
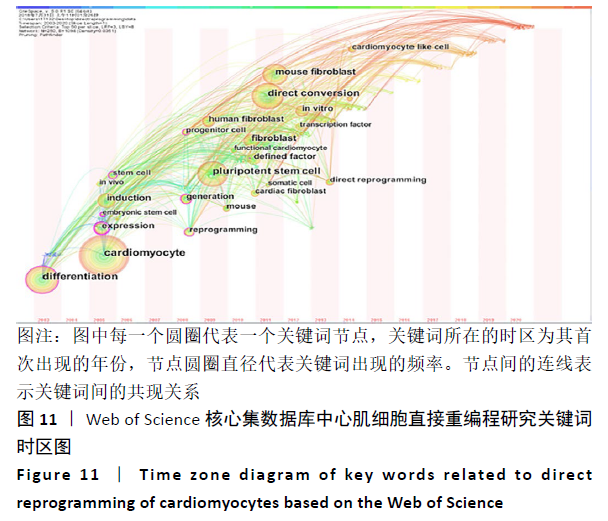
对心肌细胞直接重编程研究的关键词可视化分析时区图见图11。最大的节点为cardiomyocyte(心肌细胞),出现频率为134次,首次出现在2005年,同期出现的高频关键词embryonic stem cell(胚胎干细胞)、induction(诱导)和differentiation(分化)等,说明2005年前后这一阶段,诱导干细胞向心肌细胞分化是当时的一个研究热点,PASSIER等[13]于2005年在《Stem Cells》发表研究,该研究通过体积分数20%胎牛血清(FCS)与内脏内胚层样细胞系END-2共培养来诱导HES-2细胞系的心肌细胞分化,发现在HES-2-END-2共培养期间,心肌细胞分化和FCS浓度呈显著的反向关系;并且该研究提出从人胚胎干细胞中增加心肌细胞的形成对未来细胞替代治疗至关重要。Takahashi等[14]于2007年在《Cells》上提出,人诱导性多能干细胞在细胞形态、增殖、表面抗原、基因表达、多能细胞特异性基因的表观遗传状态和端粒酶活性方面与人胚胎干细胞相似。结合该研究前期成果此发现表明诱导性多能干细胞可以从成年人类成纤维细胞中产生,将分化的人类体细胞重编程为多能状态将允许创造出针对患者和疾病特异性的干细胞。随着细胞替代治疗和再生医学的研究不断深入,reprogramming(重编程)、pluripotent stem cell(多潜能干细胞)、fibroblast(成纤维细胞)及cardiomyocyte-like cell(心肌样细胞)等研究热点不断涌现:HUANG等[15]于2011年直接从小鼠尾尖成纤维细胞诱导功能性肝细胞样(iHep)细胞,研究发现iHep细胞表现出典型的上皮形态,表达肝脏基因并获得肝细胞功能,此成果为肝工程和再生医学的目的提供了一种产生功能性肝细胞样细胞的新策略,发表于《Cell》杂志;INAGAWA等[16]于2012年研究发现3种心脏转录因子Gata4、Mef2C和Tbx5(GMT)的组合可在体外将成纤维细胞直接重编程为功能性心肌细胞,GMT基因的转移可在梗死心脏中诱导心肌样细胞。细胞重编程技术经历发展,已广泛发展运用于各组织工程中,不仅只局限于心脏。 "
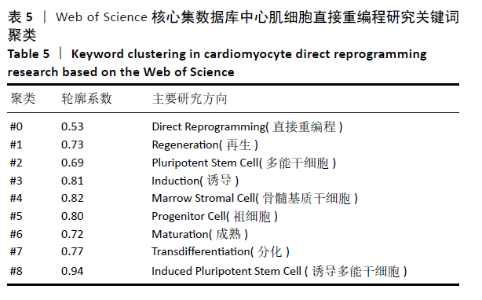
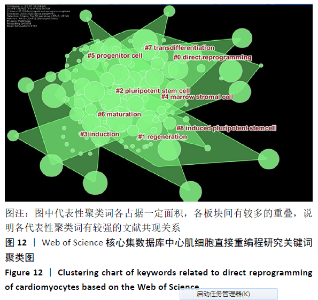
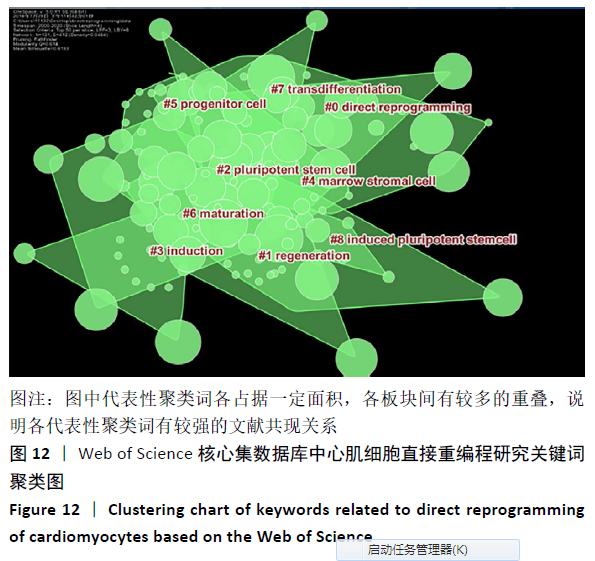
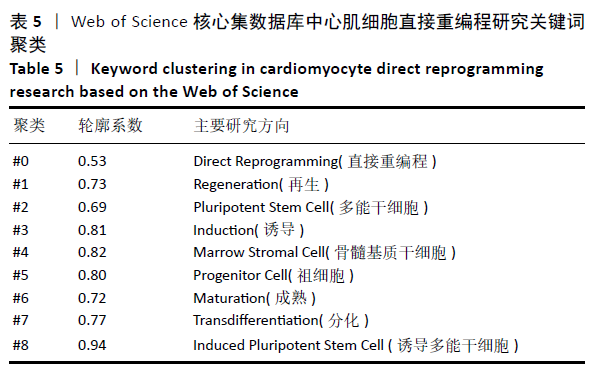
轮廓系数(Silhouette Coefficient)是对聚类结果有效性和合理性的解释和验证方法,轮廓系数取值为[-1,1],越接近1则说明样本的聚类合理、有效。各聚类的轮廓系数结果见表5,平均轮廓系数约为0.76,表明聚类合理,direct reprogramming(直接重编程)、Regeneration(再生)、pluripotent stem cell(多能干细胞)、Induction(诱导)、marrow stromal cell(骨髓基质干细胞)、progenitor cell(祖细胞)、Maturation(成熟)、transdifferentiation(分化)及induced pluripotent stem cell (诱导多能干细胞)9类关键词的聚类,基本可揽括心肌细胞重编程技术的发展进程。 "
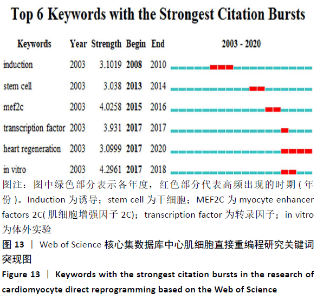
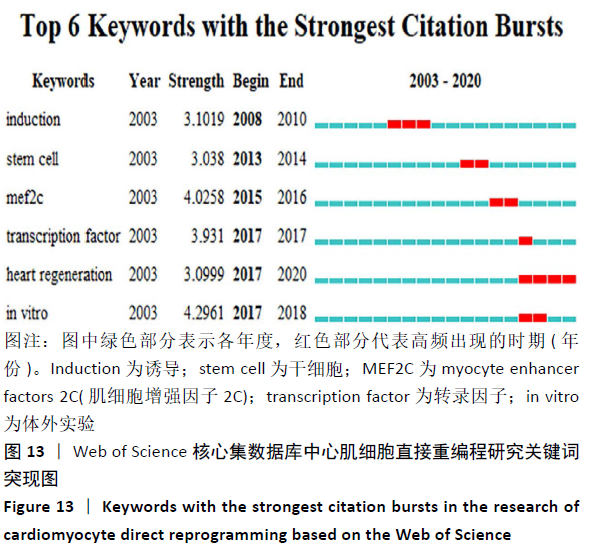
突现词为某一时期内高频出现、具有突现强度关键词,可反映所研究领域的演进态势和研究热点前沿。心肌细胞直接重编程研究的突现词见图13。据此推测转录因子(transcription factor)、肌细胞增强因子2C(myocyte enhancer factors 2C,MEF2C)及心脏再生(heart regeneration)等可能是该领域研究的前沿方向。近年转录因子在细胞重编程领域的研究逐渐深入,大多数重编程方法使用遗传物质和(或)潜在的诱变分子来生成诱导性神经元细胞,RYU等[17]使用30Kc19蛋白作为转录因子Ascl1的新型融合伴侣,诱导成纤维细胞直接重编程为诱导性神经元细胞,基于蛋白质的直接重编程系统可避免使用遗传材料带来的潜在风险,在神经发育、神经系统疾病建模和再生医学方面具有巨大发展潜力;XIAO等[18]研究证实非神经祖细胞转录因子Ptf1a可直接将小鼠和人成纤维细胞重编程为自身可再生的诱导性神经干细胞,且移植这种诱导性神经干细胞还可改善阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型的认知功能障碍;2020年WANG等[19]在《Cells》发表研究提出,心脏中存在2种主要的Mef2c同工型(isoform2,Mi2和isoform4,Mi4),该研究证实了在诱导型心肌细胞重编程过程中Mef2c的同工型特异作用,并提出实验室间将其分别用于诱导型心肌细胞重编程效率的差异可能会产生的后续影响。因心肌的增殖能力有限,再生疗法作为一种新的心脏治疗策略一直是领域的研究热点和前沿,前期研究证实GMT可以将成纤维细胞直接重编程为心肌细胞。有研究发现,表达GMT的仙台病毒(SeV)载体可以通过强大的转基因表达在体外有效且快速地将成纤维细胞重编程为无整合的心肌细胞,通过直接心脏重编程,可以产生新的心肌细胞并减少瘢痕组织以恢复心脏功能,为直接心脏重编程作为心脏再生的策略提供了有力支撑[20]。 "

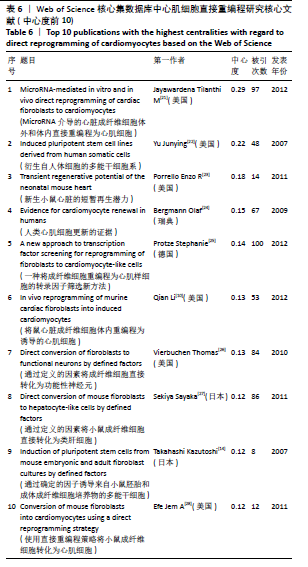
选取文献中心度位于前10的文献形成核心文献表,见表6。中心度最高的文章是JAYAWARDENA等[21]于2012年发表在《Circ Res》杂志上的文章,是体内直接进行心脏重编程的首次报道,共被引用97次,其研究证明miRNA具有在体外将成纤维细胞直接转化为心肌样表型的能力,对治疗性组织再生特别是心肌细胞的再生具有广泛而重要的意义。其次是2007年YU等[22]发表于《Science》杂志上的文章,该研究运用体细胞核转移将人体细胞重编程为多能干细胞,诱导得到的细胞有正常的核型,表达端粒酶活性,表达人类胚胎干细胞的细胞表面标记和基因特征,在移植医学领域前景广泛。排名第3位的是2011年Porrello等[23]在《Science》杂志上发表的研究,研究发现1日龄的新生小鼠部分心脏在手术切除后可以再生,遗传命运图谱显示再生组织中的大多数心肌细胞起源于先前存在的心肌细胞,但这种再生能力在小鼠7日龄时消失。故研究推测在出生后一段时间内,哺乳动物心脏可能具有再生的能力。同年BERGMANN等[24]在《Science》上发表文章提出人类的心肌细胞也可能存在更新,该团队研究利用冷战期间核弹试验产生的14C与DNA的结合,来确定人类心肌细胞的年龄,发现心肌细胞更新从25岁时每年1%的转化率逐渐下降到75岁时的0.45%,且在正常生命周期内,心肌细胞的转化率不到50%,由此推测激发成年人类心脏中产生心肌细胞的能力,可能会成为心脏病理学治疗、研究的发展方向。排名第5的是PROTZE等[25]发表在《J Mol Cell Cardiol》杂志上关于成纤维细胞重编程为心肌样细胞转录因子的替代筛选方法文章,该研究证明Tbx5,Mef2C和Gata4组合可诱导成纤维细胞重编程,通过运用新的筛选方法发现,Tbx5,Mef2C和Myocd的组合比Tbx5,Mef2C和Gata4(GMT)更能广泛上调心脏基因。这些研究从不同层面、不同维度丰富发展心肌细胞重编程研究,在该研究领域具有重要意义和导向性价值。 "
| [1] PAPANIKOLAOU P, ANTONOPOULOS AS, MASTORAKOU I, et al. Antithrombotic therapy in carotid artery disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(23):2725-2734 [2] LI W, ZHAO J, SONG L, et al. Combined effects of carotid plaques and hypertension on the risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality. ClinCardiol. 2020;43(7):715-722. [3] LEPILINA A, COON AN, KIKUCHI K, et al. A dynamic epicardial injury response supports progenitor cell activity during zebrafish heart regeneration. Cell. 2006;127(3):607-619. [4] TSENG CC, RAMJANKHAN FZ, DE JONGE N, et al. Advanced strategies for end-stage heart failure: combining regenerative approaches with LVAD, a new horizon? Front Surg. 2015;2:10. [5] SONG SY, KIM H, YOO J, et al. Prevascularized, multiple-layered cell sheets of direct cardiac reprogrammed cells for cardiac repair. Biomater Sci. 2020; 8(16):4508-4520. [6] 陈悦,陈超美,胡志刚,等.引文空间分析原理与应用CiteSpace实用指南[M].北京:科学出版社,2014:27-69. [7] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. [8] RANGAPPA S, ENTWISTLE JWC, WECHSLER AS, et al. Cardiomyocyte-mediated contact programs human mesenchymal stem cells to express cardiogenic phenotype. J Thor Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;126(1):124-132. [9] IEDA M, FU JD, DELGADO-OLGUIN P, et al. Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into functional cardiomyocytes by defined factors. Cell. 2010;142(3):375-386. [10] QIAN L, HUANG Y, SPENCER CI, et al. In vivo reprogramming of murine cardiac fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes. Nature. 2012;485 (7400):593-598. [11] WANG L, LIU Z, YIN C, et al. Stoichiometry of Gata4, Mef2C, and Tbx5 influences the efficiency and quality of induced cardiac myocyte reprogramming. Circ Res. 2015;116(2):237-244. [12] 邱均平.信息计量学[M].武汉:武汉大学出版社,2007:91. [13] PASSIER R, OOSTWAARD DW, SNAPPER J, et al.Increased cardiomyocyte differentiation from human embryonic stem cells in serum-free cultures. Stem Cells. 2005;23(6):772-780. [14] TAKAHASHI K, TANABE K, OHNUKI M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007; 131(5):861-872. [15] HUANG P, HE Z, JI S, et al. Induction of functional hepatocyte-like cells from mouse fibroblasts by defined factors. Nature. 2011;475 (7356):386-389. [16] INAGAWA K, MIYAMOTO K, YAMAKAWA H, et al. Induction of cardiomyocyte-like cells in infarct hearts by gene transfer of Gata4, Mef2c, and Tbx5. Circ Res. 2012;111(9):1147-1156. [17] RYU J, HWANG NS, PARK HH, et al. Protein-based direct reprogramming of fibroblasts to neuronal cells using 30Kc19 protein and transcription factor Ascl1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020;121:105717. [18] XIAO D, LIU X, ZHANG M, et al. Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into neural stem cells by single non-neural progenitor transcription factor Ptf1a. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):2865. [19] WANG L, HUANG P, NEAR D, et al. Isoform specific effects of mef2c during direct cardiac reprogramming. Cells. 2020;9(2):268. [20] TANI H, SADAHIRO T, IEDA M. Direct cardiac reprogramming: a novel approach for heart regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(9):2629. [21] JAYAWARDENA TM, EGEMNAZAROV B, FINCH EA, et al. MicroRNA-mediated in vitro and in vivo direct reprogramming of cardiac fibroblasts to cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 2012;110(11):1465-1473. [22] YU J, VODYANIK MA, SMUGA-OTTO K, et al.Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007;318 (5858):1917-1920. [23] PORRELLO ER, MAHMOUD AI, SIMPSON E, et al. Transient regenerative potential of the neonatal mouse heart. Science. 2011;331(6020): 1078-1080. [24] BERGMANN O, BHARDWAJ RD, BERNARD S, et al. Evidence for cardiomyocyte renewal in humans. Science. 2009;324(5923):98-102. [25] PROTZE S, KHATTAK S, POULET C, et al. A new approach to transcription factor screening for reprogramming of fibroblasts to cardiomyocyte-like cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012;53(3):323-332. [26] VIERBUCHEN T, OSTERMEIER A, PANG ZP, et al. Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors. Nature. 2010; 463(7284):1035-1041. [27] SEKIYA S, SUZUKI A. Direct conversion of mouse fibroblasts to hepatocyte-like cells by defined factors. Nature. 2011;475(7356):390-393. [28] EFE JA, HILCOVE S, KIM J, et al. Conversion of mouse fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes using a direct reprogramming strategy. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(3):215-222. [29] CHEN JX, KRANE M, DEUTSCH MA, et al. Inefficient reprogramming of fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes using Gata4, Mef2c, and Tbx5. Circ Res. 2012;111(1):50-55. [30] MURAOKA N, YAMAKAWA H, MIYAMOTO K, et al. MiR-133 promotes cardiac reprogramming by directly repressing Snai1 and silencing fibroblast signatures. EMBO J. 2014;33(14):1565-1581. [31] ZHAO Y, LONDONO P, CAO Y, et al. High-efficiency reprogramming of fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes requires suppression of pro-fibrotic signalling. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8243. [32] YAMAKAWA H, MURAOKA N, MIYAMOTO K, et al. Fibroblast growth factors and vascular endothelial growth factor promote cardiac reprogramming under defined conditions. Stem Cell Rep. 2015;5(6):1128-1142. [33] MATHISON M, GERSCH RP, NASSER A, et al. In vivo cardiac cellular reprogramming efficacy is enhanced by angiogenic preconditioning of the infarcted myocardium with vascular endothelial growth factor. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012;1(6):e005652. |
| [1] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [2] | Long Guiyue, Li Dongdong, Liao Hongbing. Calcium phosphate cement/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) degradation products promote osteoclast differentiation of mouse monocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1193-1198. |
| [3] | Yin Shuoxin, Zhang Tao, Wang Shuping, Lu Xin, Huang Xuping, Yin Mengying, Yang Yuwei, Yuan Bingmao, Mao Zhihua, Chen Yuanneng. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of researches on gastric cancer stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 941-947. |
| [4] | Zhang Qing, Gao Chunlan, Yu Feifei, Zhang Zhenghao, Ma Fang, Gao Yuan, Li Guizhong, Jiang Yideng, Ma Shengchao. Ephrin A receptor 2 DNA methylation increases in pancreatic beta cell apoptosis induced by homocysteine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 714-719. |
| [5] | Song Jian, Zhao Lei, Liu Aishi. Construction and application of myocardial ischemia model in miniature pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 772-778. |
| [6] | Li Rui, Liu Zhen, Guo Zige, Lu Ruijie, Wang Chen. Aspirin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and polydopamine modified titanium sheets improve osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 374-379. |
| [7] | Ou Hangjun, Zhao Guangjian, Pan Yujia, Gong Caiwei, Zhao Quanwei, Liu Danan. Construction of a lentiviral vector overexpressing fibronectin type III domain containing 5 to inhibit apoptosis of endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 216-222. |
| [8] | Fan Qinghua, Qi Jie, Zhang Jun. The regulatory role of Hippo-YAP signaling pathway in exercise-induced cardiac hypertrophy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2708-2715. |
| [9] | Liu Dongyue, Wang Xianyun, Wang Le, Zheng Mingqi, Yin Yajuan, Yang Jiawei, Ding Lini, Liu Gang. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome transplantation for ischemic heart disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2435-2442. |
| [10] | Wang Jiajia, Xie Jianshan, Li Hairong, Jing Yixin, Yang Yanping. Notch2 contributes to the development of aortic and pulmonary valves in mouse embryonic heart [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2176-2181. |
| [11] | Zhu Biwen, Wang Dongzhi, Wu Di, Gong Tiancheng, Pan Haopeng, Lu Yuhua, Guo Yibing, Wang Zhiwei, Huang Yan. Biomimetic microenvironment constructed from gelatin methacrylamide/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes the function of insulinoma cell line MIN6 in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1824-1831. |
| [12] | Su Meng, Wang Xin, Zhang Jin, Bei Ying, Huang Yu, Zhu Yanzhao, Li Jiali, Wu Yan. Nanocellular vesicles loaded with curcumin promote wound healing in diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1877-1883. |
| [13] | Diao Xiaojuan, Shi Chaoqun, Li Dong, Wang Shuai, Xiao Chun, Liu Guojun, Qu Tingyu, Yang Weijuan, Jia Xiaopeng. Efficient expansion of natural killer cells from cryopreserved umbilical cord blood by pure cytokine method without animal ingredients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1572-1577. |
| [14] | Zhou Jingjing, Sun Yixin, Sheng Yang, Zhang Rong. Effects of chiral polyethyleneimine/graphene oxide/phenylalanine interface on adhesion and proliferation of multilineage-differentiating stress enduring cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1547-1552. |
| [15] | Ma Munan, Xie Jun, Sang Yuchao, Huang Lei, Zhang Guodong, Yang Xiaoli, Fu Songtao. Electroacupuncture combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian insufficiency in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 1-7. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||