Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (15): 2435-2442.doi: 10.12307/2023.612
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome transplantation for ischemic heart disease
Liu Dongyue1, 2, 3, Wang Xianyun2, 3, 4, Wang Le1, 2, 3, Zheng Mingqi1, 2, 3, Yin Yajuan1, 2, 3, Yang Jiawei1, 2, 3, Ding Lini1, 2, 3, Liu Gang1, 2, 3
- 1Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China; 2Hebei International Joint Research Center for Structural Heart Disease, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China; 3Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Heart and Metabolism, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China; 4Cell Therapy Laboratory, First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2022-05-10Accepted:2022-08-05Online:2023-05-28Published:2022-10-18 -
Contact:Liu Gang, MD, Chief physician, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China; Hebei International Joint Research Center for Structural Heart Disease, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China; Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Heart and Metabolism, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Liu Dongyue, Master candidate, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China; Hebei International Joint Research Center for Structural Heart Disease, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China; Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Heart and Metabolism, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Support Program of Hebei Province, No. 203777117D (to LG); Foreign Intelligence Project of Hebei Province, No. YZ202001 (to LG); Natural Science Youth Fund Project of Hebei Province, No. C2018206037 (to WXY); Key Project of Precision Medicine Joint Fund, No. H2021206399 (to ZMQ); Precision Medicine Joint Fund Cultivation Project, No. H2021206031 (to WL); Introduced Overseas Students Funding Project of Hebei Province, No. C20210347 (to WXY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Dongyue, Wang Xianyun, Wang Le, Zheng Mingqi, Yin Yajuan, Yang Jiawei, Ding Lini, Liu Gang. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome transplantation for ischemic heart disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2435-2442.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
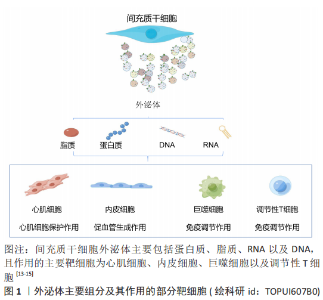
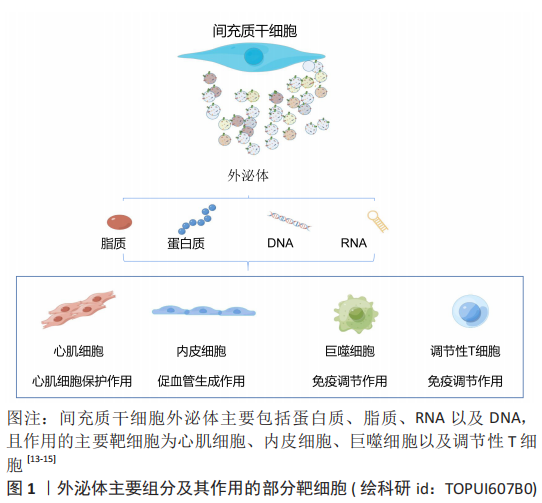
2.1 外泌体 2.1.1 外泌体基本特征 外泌体是指从细胞中释放出来的大小为30-150 nm的细胞外囊泡,主要通过细胞间通讯、抗原呈递及其携带因子的转移等途径发挥功能调节作用。干细胞外泌体的主要营养组分包括蛋白质、脂质、DNA和RNA,见图3。其中脂质包括白三烯、花生四烯酸、磷脂酸、前列腺素、溶血磷脂酰胆碱和二十二六烯酸;蛋白质包括典型的膜蛋白如GPI锚定蛋白、受体蛋白如肿瘤坏死因子受体1、抗原呈递蛋白和细胞黏附因子等[13-15];microRNA包括miRNA-21、miRNA-15a和miRNA-223等[15-16]。不同类型间充质干细胞在不同环境刺激下分泌的外泌体所含的生物组分比例不同,表明间充质干细胞外泌体的修复潜力可通过优化间充质干细胞而得到更好的优化[17]。此外,间充质干细胞外泌体具有的低免疫原性、较高的稳定性和良好的生物相容性,能够作为生物信息载体在缺血性心脏病的治疗中展现出更广泛的应用前景[18]。"
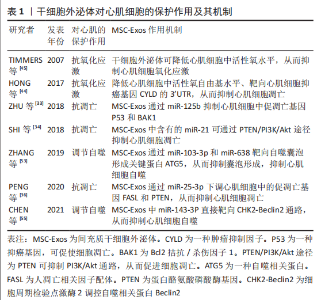
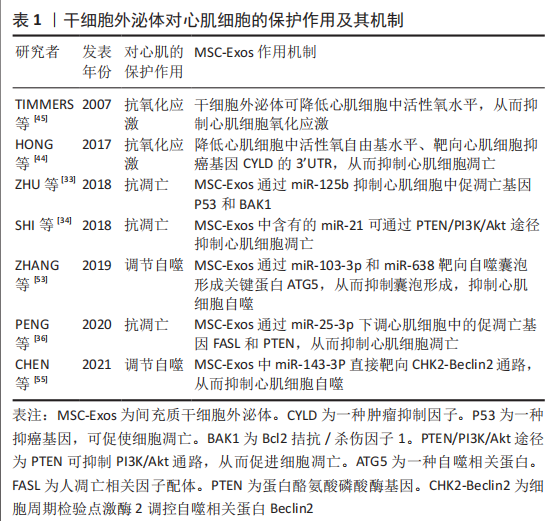
2.1.2 干细胞外泌体提取方法 目前,外泌体提取方法包括超滤法、超速离心法、免疫亲和捕获法、化学沉淀法和基于微流体的分离技术等,超速离心法是最常用的外泌体分离方法,该方法提取外泌体产量高,但纯度较差[19-22]。超滤法相较于超速离心法工作量小、耗时短及设备依赖性小[23-24],且高效液相层析法可提取高纯度外泌体,但超滤法容易发生过滤膜堵塞和囊泡截留问题[23]。免疫亲和捕获法、基于微流体的分离技术和化学沉淀法是基于外泌体特异性分离的方法,其中免疫亲和捕获法显著优点是选择性分离特定细胞亚群外泌体且外泌体富集程度较高,但样品预处理环节复杂[23]。总之,以上几种提取方法各有优缺点。 2.2 间充质干细胞源外泌体移植治疗缺血性心脏病的主要机制 2.2.1 促血管形成作用 心肌梗死后损伤区域的血管生成能力有限,严重的血管生成障碍导致心肌缺氧从而加重心肌损伤,因此,促血管生成研究成为治疗缺血性心脏病的主要机制之一[25]。研究表明,间充质干细胞外泌体能够发挥与间充质干细胞类似的促血管生成作用,但不同环境条件下间充质干细胞外泌体的作用机制不尽相同。据报道,间充质干细胞外泌体被血管内皮细胞摄取后可通过释放细胞外基质金属蛋白酶诱导剂(extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer,EMMPI)激活内皮细胞中Erk和Akt途径刺激血管的发芽长度、发芽数量和细胞浸润能力等从而促进血管生成[10]。EMMPI又可作为血管内皮生长因子2 (Vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGFR2)的共受体,通过EMMPI-VEGFR2途径刺激血管生成[26]。此外,间充质干细胞外泌体含有的半乳糖凝集素1、ezrin和p195是与内皮细胞增殖和血管生成相关的细胞黏附因子,提示外泌体可通过自身携带的细胞因子促进血管生成[9]。 微小核糖核酸(miRNA)是外泌体中另一重要的功能物质,其种类众多且功能复杂,但组分相对稳定,已被证明参与间充质干细胞外泌体介导的促血管形成作用。据报道,间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-125a可通过特异性结合DLL4(Angiogenic inhibitor delta-like 4,DLL4)的3’-UTR促进血管生成,miR-125a还可通过上调内皮细胞促血管生成因子Ang1和Flk1、下调抗血管生成因子Vash和TSP1来促进血管生成[27]。同时间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-125a诱导血管内皮细胞产生的纤维细胞生长因子β(fibroblast growth factor-β,FGF-β)和肝细胞生长因子也可显著促进血管生成[28]。此外,间充质干细胞外泌体中的miR-291、miR-132、miR-17和miR-210也具有促血管生成作用[29-32]。由此可见,间充质干细胞外泌体携带丰富的miRNAs组分,在促血管形成方面发挥着非常重要的作用。 2.2.2 心肌细胞保护作用 心肌细胞耗氧量较大,因此对缺氧耐受能力极差。当发生缺血缺氧时,心肌细胞极易发生凋亡、氧化应激和自噬过度激活,最终导致心脏功能降低。越来越多研究发现间充质干细胞外泌体在抗凋亡、抗氧化应激及调节自噬方面发挥重要作用,下面就该3个方面进行详细阐述。 抗凋亡作用:心肌细胞极易受心肌缺血或氧化应激的影响而发生凋亡或坏死,如何有效抑制心肌细胞的凋亡将是间充质干细胞外泌体发挥心肌保护作用的重要方面。研究表明,间充质干细胞外泌体中富含的miRNAs组分具有显著的抗凋亡和抗氧化作用。例如:miR-125b可抑制心肌细胞中促凋亡基因P53和BAK1的表达而起到抗凋亡作用[33];miR-21可通过下调心肌细胞中促凋亡蛋白caspase3、细胞程序性死亡蛋白4(programmed cell death 4,PDCD4)等发挥抗凋亡作用;miR-21还可通过PTEN/PI3K/Akt途径抑制心肌细胞凋亡[34-35];miR-25-3p通过调节心肌细胞中促凋亡基因FASL和PTEN的表达发挥抗凋亡作用[36];间充质干细胞外泌体中的miR-19可下调心肌细胞中第10号染色体缺失的磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物基因和BIM基因的表达、激活Akt/ERKT通路来抑制心肌细胞凋亡[37]。另一项研究表明,间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-210可通过降低心肌细胞中凋亡诱导因子3(apoptosis-inducing factor, mitochondrion-associated 3,AIFM3)和磷酸化蛋白激酶B(phosphorylated Protein Kinase B,PKB)的表达从而抑制心肌细胞凋亡[38]。除此之外,间充质干细胞外泌体中的miR-23a-3p可通过抑制心肌细胞中二价金属转运蛋白1(divalentmetaltransporter 1,DMT1)的表达从而抑制心肌细胞铁死亡并减轻心肌缺血损伤[39]。另外,过表达GATA结合蛋白4(Recombinant GATA binding protein 4,GATA-4)的间充质干细胞外泌体可减少心肌细胞凋亡且保护线粒体功能和线粒体膜电位[40]。总之间充质干细胞外泌体在抗心肌细胞凋亡方面发挥巨大作用。 抗氧化应激作用:影响心肌细胞存活的主要因素是缺血再灌注产生的氧化应激损伤,它可引起脂质过氧化反应并降低细胞膜流动性,从而影响细胞膜离子通道的功能,造成细胞膜损伤[41]。还可造成DNA损伤,使DNA氢键断裂、碱基降解和主链解旋[42]。氧化应激还会导致线粒体损伤,造成线粒体肿胀、功能紊乱、数量减少甚或消失[43]。此外,氧化应激诱发的脂质过氧化反应生成的氧化型低密度脂蛋白(oxidized-Low density lipoprotein,ox-LDL)容易被巨噬细胞识别并吞噬形成泡沫细胞,形成粥样斑块诱发冠心病[43]。研究表明,间充质干细胞外泌体显示出较高的抗氧化应激能力,如miR-19a可靶向抑癌基因CYLD的3’UTR抑制心肌细胞氧化应激,还可通过降低细胞核中活性氧自由基来抑制心肌细胞氧化应激损伤[44]。其他研究结果显示,间充质干细胞外泌体还可通过激活心肌细胞中PI3K/Akt信号通路降低心肌细胞的氧化应激水平,进而恢复小鼠心脏的能量供应[44]。此外,在缺血和缺氧期间,间充质干细胞外泌体可通过降低心肌细胞活性氧自由基水平抑制心肌细胞损伤[45]。另外,间充质干细胞外泌体预处理可显著提高过氧化氢刺激H9C2细胞后的细胞活力和增殖能力[46]。间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-214还可降低心肌细胞活性氧生成水平来抑制氧化应激[40]。由此可见间充质干细胞外泌体可通过抑制心肌细胞氧化应激起到保护心脏的作用。 调节自噬:自噬是一种细胞器和蛋白质的降解过程,在维持细胞内外环境平衡中起重要作用。自噬在心血管病发病过程中具有双向作用,生理情况下,自噬可维持细胞代谢平衡,病理情况下,自噬被过度激活从而导致细胞凋亡[47]。因此抑制应激条件下自噬过度激活有利于心肌细胞存活。据报道,间充质干细胞外泌体中多种miRNAs已被证明可显著抑制过度自噬诱导的心肌损伤作用[48],如间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-34a和miR-101可分别靶向心肌细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α和重组DNA损伤诱导转录因子4(recombinant DNA damage inducible transcript 4,DDIT4)抑制自噬,从而减轻心肌缺氧/复氧损伤[49-50];间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-21可通过激活H9C2细胞中Akt/mTOR通路抑制自噬活性以减少缺氧/复氧诱导的细胞凋亡[51];间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-206和miR-216b可联合下调心肌细胞中的自噬基因ATG13表达从而抑制自噬活性[52];间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-103-3p和miR-638均通过靶向抑制自噬囊泡形成的关键蛋白ATG5而抑制心肌细胞凋亡[53-54];间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-143-3p可直接通过靶向CHK2-Beclin2通路抑制心肌细胞自噬,有效减少心肌细胞凋亡[55]。由此可见,间充质干细胞外泌体通过抑制心肌细胞过度自噬保护心肌免受缺血缺氧损伤。 文章汇总了干细胞外泌体对心肌细胞的保护作用及其机制的相关研究成果,详见表1。"
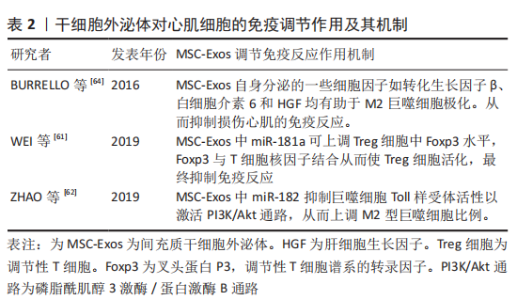
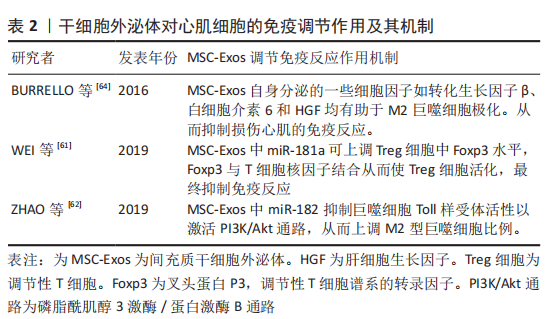
2.2.3 抗心肌纤维化 心肌梗死导致缺血性心肌细胞死亡会引起心脏多项修复反应,其中心肌纤维化是修复反应中重要过程,虽然最初纤维化过程对防止心室壁破裂至关重要,但过度纤维化会导致心脏功能进行性损害,并最终导致心力衰竭[56]。因此,抗心肌组织过度纤维化是改善心力衰竭的一个研究方向。 研究表明,间充质干细胞外泌体已被证明可减少心肌梗死模型中的梗死面积、纤维化面积和心肌细胞凋亡数量[57]。间充质干细胞外泌体预处理正常大鼠可改善预处理大鼠心梗后心脏炎症水平、纤维化水平和心脏功能。这种作用机制是间充质干细胞外泌体通过抑制转化生长因子β介导的成纤维细胞向肌成纤维细胞转化,从而抑制心肌纤维化[11]。此外间充质干细胞外泌体携带的miRNA可发挥重要抗纤维化作用。如缺血预处理的间充质干细胞外泌体可通过miR-22靶向成纤维细胞中甲基化CpG结合蛋白2(methyl-CpG-binding protein 2,MECP2)来改善心肌梗死导致的心脏纤维化,从而有效改善心功能[58]。另一项研究表明,间充质干细胞外泌体可通过miR-671抑制转化生长因子β信号传导从而抑制心肌梗死引起的心肌纤维化[59-60]。 2.2.4 调节免疫反应 间充质干细胞外泌体可通过免疫调节改善缺血性心肌病的治疗效果。研究表明,间充质干细胞外泌体可通过调节性T细胞(Treg细胞)抑制免疫反应[61]。间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-181a可通过c-fos(c-fos是一种关键的免疫激活剂)途径减少ox-LDL诱导的树突状细胞激活、炎症反应和Treg细胞活化,miR-181a还可在蛋白和DNA水平上调Treg细胞中FoxP3的表达,FoxP3可与T细胞核因子结合刺激Treg细胞活化以提高Treg细胞比例,从而抑制免疫反应[61]。另外,miR-181a可整合到心肌细胞siRNA中,整合了miR-181a的siRNA与c-fos结合形成c-fos-siRNA复合物,从而下调促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6、上调抗炎因子白细胞介素10和Treg细胞的比例[61]。 此外,miR-181a还可通过靶向抑制Smad7阻止Treg细胞中转化生长因子β信号从而促进Treg细胞的极化,以达到调控缺血性心脏病免疫修复的效果[61]。此外,间充质干细胞外泌体还可通过调节巨噬细胞极化来发挥抗炎作用。研究表明,间充质干细胞外泌体在体内外均可通过miR-182抑制巨噬细胞Toll样受体活性从而激活PI3K/Akt信号通路,进而起到减少M1型促炎巨噬细胞并增加M2型抗炎巨噬细胞数量的目的[62]。miR-182也可通过TLR4/Akt途径促进M2型巨噬细胞的极化[62]。此外,炎症因子γ干扰素(interferon-γ,IFN-γ)预处理间充质干细胞外泌体可促使M2型巨噬细胞极化[63]。间充质干细胞外泌体中的一些细胞因子和生长因子如转化生长因子β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素10和肝细胞生长因子均有助于M2巨噬细胞极化[64-65]。由此可见,间充质干细胞外泌体的免疫调节作用,可分别通过调节T细胞和巨噬细胞的极化调控免疫反应,进而起到调控心肌修复的作用,详见表2。"
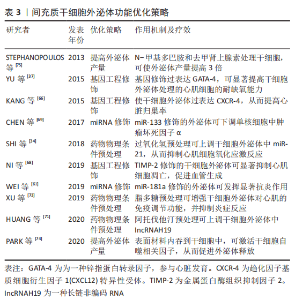
2.3 间充质干细胞外泌体的功能优化策略 间充质干细胞外泌体已被证明较间充质干细胞具有更好的修复和调控作用。为了进一步提高外泌体的产量、稳定性和高效靶向修复特性,越来越多的研究聚焦于一些基因或工程化的修饰策略,下面就这些优化策略分别予以阐述。 2.3.1 基因工程修饰策略 目前,利用基因工程修饰技术提高外泌体功能的研究越来越多,比如过表达4型趋化因子受体(CXC chemokine receptor 4,CXCR-4)的间充质干细胞外泌体在减轻左心室重塑和促进心功能恢复方面表现出良好性能[66],过表达GATA-4的间充质干细胞外泌体可显著增加心肌细胞耐缺氧能力,以促进损伤心肌的修复[37]。为进一步有效提高间充质干细胞外泌体的心脏归巢能力,心脏归巢肽(IMTP)修饰的间充质干细胞外泌体向缺血心肌组织的靶向归巢能力更强,并有效减少心肌梗死区炎症、细胞凋亡和心肌纤维化反应等[67]。金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂2(Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-2,TIMP-2)是基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂家族成员,它可抑制基质金属蛋白酶引起的心肌梗死后的心肌重构。 研究表明,过表达TIMP2的脐带间充质干细胞外泌体可显著抑制H2O2介导的H9C2细胞凋亡,促进内皮细胞增殖、迁移和管形成,并通过减少成纤维细胞中转化生长因子β诱导的基质金属蛋白酶2、基质金属蛋白酶9和α平滑肌蛋白抑制心肌纤维化过程,同时还可通过上调心肌细胞中谷胱甘肽和超氧化物歧化酶的表达,降低丙二醛的水平,从而抑制心肌细胞中氧化应激反应[68]。由此可见,经特定基因修饰的间充质干细胞外泌体具备某些与该基因相关的特定功能,能够为缺血性心脏病的治疗提供更多的治疗方法。 2.3.2 miRNA修饰策略 研究表明,过表达特定miRNA可增强间充质干细胞外泌体对损伤心肌修复作用。如过表达miR-181a的间充质干细胞外泌体可通过miRNA-181a靶向调控c-Fos基因表达、减弱ox-LDL诱导的树突状细胞的激活、下调心肌细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6、上调抗炎因子白细胞介素10和Treg细胞的比例,进而发挥抗炎调节作用[61]。此外,过表达miR-133的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体还可下调人外周血单核细胞中促炎细胞因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6以及上调抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10的表达[69]。过表达miR-133的间充质干细胞外泌体还能诱导Treg细胞的形成,显著改善心脏炎症水平、减小梗死面积并抑制心肌纤维化[69]。过表达miR-146的脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体可通过抑制生长因子1的表达并减弱Toll样受体核转录因子κB信号传导来抑制心梗大鼠心肌炎症反应和心肌纤维化[70]。总之,通过过表达特定miRNA可提高间充质干细胞外泌体对缺血性心脏病的治疗效果。 2.3.3 药物或物理条件预处理策略 许多研究表明,用药物或条件预处理干细胞可显著增强干细胞及其外泌体的心脏修复功能。如阿托伐他汀可通过上调间充质干细胞外泌体中的lncRNA H19促进内皮细胞迁移、管状结构形成和存活率,最终减少心肌细胞凋亡、缩小梗死面积并显著改善心功能[71]。H2O2处理间充质干细胞可通过提高其外泌体中miR-21含量抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌细胞损伤,保护心脏功能[34]。缺氧预处理间充质干细胞提高了其外泌体中miR-125b-5p含量从而抑制心肌细胞凋亡[72]。脂多糖预处理骨髓间充质干细胞可增强其产生的外泌体对心肌的免疫调节作用,限制巨噬细胞中促炎因子的产生并减轻心肌炎症,还可通过抗心肌细胞凋亡改善间充质干细胞外泌体移植后3个月梗死心脏的心功能[73]。由此可见,药物或条件预处理间充质干细胞方法简便,并可在一定程度上显著提高间充质干细胞外泌体在损伤心肌中的修复功能,具备很好的应用前景。 2.3.4 提高外泌体产量 外泌体产量低是限制外泌体临床转化的一个重要因素,因此有相关研究致力于提高外泌体产量。如表面材料可提高外泌体释放效率,有研究者发明的一种表面材料可通过网格蛋白介导的内吞作用被转运到间充质干细胞溶酶体中,从而刺激间充质干细胞自噬相关因子表达来促进间充质干细胞外泌体分泌,增加外泌体产量[74]。N-甲基多巴胺和去甲肾上腺素预处理间充质干细胞可促进其外泌体分泌,使外泌体产量提高3倍[75]。缺氧预处理间充质干细胞亦可促进其外泌体分泌[72]。因此条件预处理可提高间充质干细胞外泌体释放,从而在一定程度上解决了外泌体产量低的问题。 文章总结了间充质干细胞外泌体功能优化策略,详见表3。"

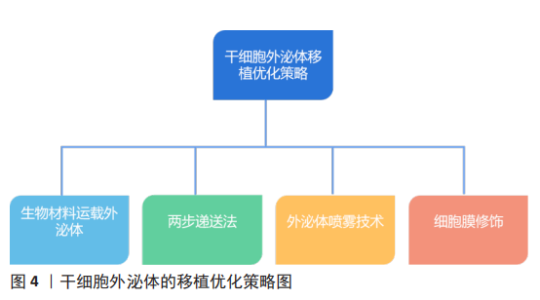
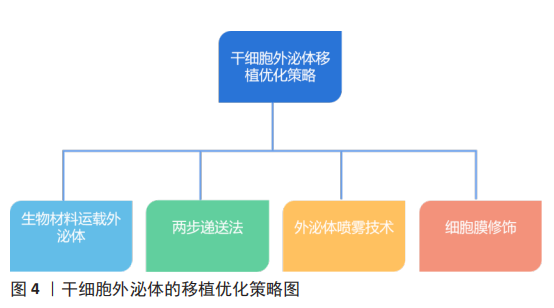
2.4 干细胞外泌体移植优化策略 干细胞外泌体移植优化可提高其对心脏的靶向性,并增强其对缺血性心脏病的治疗疗效,下面就以下几个方面分别进行阐述,见图4。 2.4.1 生物材料运载外泌体 间充质干细胞外泌体对损伤心肌的修复能力已被证实,但其低靶向性限制了其治疗疗效。因此一些研究人员设计出以生物材料为载体运载外泌体的治疗方案,且在实验中取得了较好结果。有研究表明水凝胶含水量大、类似细胞外基质,具有很好的生物相容性和良好延展性,且可通过改变水凝胶物理性质控制外泌体释放速率,并且还可维持外泌体完整性[76]。因此一些研究人员基于此设计出了一种剪切稀化凝胶(Shear-thinning gel,STG),这种凝胶可随剪切应力变化而改变自身物理状态,当剪切稀化凝胶包裹的外泌体(SGT-EVs)被注射入体时,随着剪切应力的增加,SGT-EVs变为液体状态,从而更易进入心肌组织,随着剪切应力的减小,SGT-EVs从液体状态变为凝胶状态,再通过扩散途径缓慢释放外泌体。研究表明,SGT-EVs可在21 d内稳定持续释放外泌体,并且减少了心肌纤维化、细胞凋亡和心肌炎症,还可改善血流动力学,如增加左室射血分数和心输出量,并增加梗死周围区的血管密度[77]。另一团队设计了一种以Fe3O4为核,以二氧化硅为壳的纳米颗粒,该纳米颗粒具有识别外泌体特异性标志物CD63和受损心肌细胞肌球蛋白轻链的能力,该纳米颗粒可通过CD63特异性结合间充质干细胞外泌体,并通过识别受损心肌细胞肌球蛋白轻链而被募集到受伤心肌组织并释放外泌体,从而提高外泌体对受损心肌的靶向性,最终发挥抗心肌细胞凋亡、改善左心室功能作用[78]。另一项研究开发了一个新型纳米颗粒,研究者们将肽NapFF和肽PA-GHRPS混合形成PGN水凝胶,用于装载外泌体。PA-GHRPS肽可保护H9C2细胞免受H2O2诱导的氧化应激,肽NapFF可增强PA-GHRPS的胶质化能力。该研究数据表明,PGN水凝胶能够有效地包裹外泌体,并确保外泌体稳定和持续释放。与单独外泌体治疗相比,PGN水凝胶包裹外泌体组的心肌细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α水平显著降低,促纤维化基因转化生长因子β1表达水平也显著降低,结果表明该混合物可通过更强大的抗炎、抗纤维化、抗心肌凋亡以及促进血管生成能力来改善心肌功能[46]。因此生物材料可提高间充质干细胞外泌体对损伤心肌的靶向修复能力。 2.4.2 两步递送法 外泌体疗法的低滞留率和巨噬细胞对外泌体的吞噬作用明显降低了其疗效,由此研究人员发明了两步递送法,又称“吃我/不吃我”策略。由于阳离子化甘露聚糖修饰的细胞外囊泡可提高被巨噬细胞吞噬的概率[79],且有研究发现来源于CD2.4细胞的胞外小泡主要被巨噬细胞吞噬[79],因此阳离子化甘露聚糖修饰CD2.4细胞的胞外小泡可显著提高被巨噬细胞吞噬的概率,从而使单核-巨噬系统饱和。CD47可与信号调节蛋白结合从而阻断单核-巨噬系统的吞噬过程。所以将富含CD47的外泌体与纳米颗粒融合可阻止被巨噬细胞吞噬[80]。因此先注射阳离子化甘露聚糖修饰的CD2.4细胞的胞外小泡使单核-巨噬达到饱和,再注射与纳米颗粒融合的富含CD47的外泌体从而降低外泌体被巨噬细胞清除的概率,从而提高了外泌体疗法的治疗功效[80]。由此可见,两步递送法可在一定程度上提高外泌体在心脏组织的滞留率。 2.4.3 外泌体喷雾技术 近年来,再生医学在心肌梗死治疗方面的研究有了一定进展,间充质干细胞外泌体已被确定为心肌梗死治疗的重要方法[9-10,81],然而,该疗法受到心脏输送效率低下的阻碍。因此该研究设计了一种基于生物材料和间充质干细胞外泌体相结合的微创外泌体喷雾技术。在心肌梗死小鼠模型中,外泌体喷雾可直接喷射到心肌表面,研究结果表明微创外泌体喷雾技术增加了心脏部位外泌体滞留率、减少了心肌纤维化、改善了心功能并促进了梗死后血管生成。该研究进一步测试了微创外泌体喷雾技术的安全性和可行性,结果表明,微创外泌体喷雾技术是一种具有可行性和安全性的混合物。因此该技术是一项具有前途的策略,可为冠心病治疗拓宽思路[82]。 2.4.4 细胞膜修饰改善外泌体靶向修复特性 为进一步提高外泌体的心肌靶向特性,细胞膜修饰技术的发展为外泌体疗法的优化提高新的思路。研究表明,单核细胞膜修饰外泌体可形成单核细胞膜-外泌体复合物,单核细胞膜-外泌体复合物显著提高了其向缺血心肌的靶向归巢率性和滞留率、降低了心肌细胞中的炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的含量、增加了M2型巨噬细胞的极化,从而起到免疫抑制作用。同时单核细胞膜-外泌体复合物还具有促进内皮细胞成管能力和抑制心肌细胞凋亡的作用[83]。此外,利用血小板膜修饰间充质干细胞外泌体提供了“不吃我”的信号蛋白CD47,进而阻止巨噬细胞摄取间充质干细胞外泌体,提高了其到达损伤心肌的靶向归巢率,有效促进心脏血管生成并抑制心肌氧化应激,进而提高了其对心肌梗死的修复作用[84-86]。由此可见,不同的细胞膜具有不同的生物学特性,利用其修饰的间充质干细胞外泌体具备细胞膜和外泌体的双重特性,可为间充质干细胞外泌体的功能优化提高非常重要的策略。"
| [1] ADAMS RH, ALITALO K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(6):464-478. [2] ARSLAN F, LAI RC, SMEETS MB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;10(3):301-312. [3] NOORT WA, OERLEMANS MI, ROZEMULLER H, et al. Human versus porcine mesenchymal stromal cells: phenotype, differentiation potential, immunomodulation and cardiac improvement after transplantation. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16(8):1827-1839. [4] VAN DER SPOEL TI, JANSEN OLS, AGOSTONI P, et al. Human relevance of pre-clinical studies in stem cell therapy: systematic review and meta-analysis of large animal models of ischaemic heart disease. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;91(4):649-658. [5] JEEVANANTHAM V, BUTLER M, SAAD A, et al. Adult bone marrow cell therapy improves survival and induces long-term improvement in cardiac parameters: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2012; 126(5):551-568. [6] WANG X, ZHANG J, ZHANG F, et al. The clinical status of stem cell therapy for ischemic cardiomyopathy. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:135023. [7] CHENG L, ZHANG K, WU S, et al. Focus on mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: opportunities and challenges in cell-free therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:6305295. [8] LAI RC, YEO RW, TAN KH, et al. Exosomes for drug delivery -a novel application for the mesenchymal stem cell. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(5):543-551. [9] LIANG X, ZHANG L, WANG S, et al. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J Cell Sci. 2016;129(11):2182-2189. [10] VRIJSEN KR, MARING JA, CHAMULEAU SA, et al. Exosomes from cardiomyocyte progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells stimulate angiogenesis via EMMPRIN. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(19):2555-2565. [11] SHAO L, ZHANG Y, LAN B, et al. MiRNA-sequence indicates that mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes have similar mechanism to enhance cardiac repair. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4150705. [12] FISCHER UM, HARTING MT, JIMENEZ F, et al. Pulmonary passage is a major obstacle for intravenous stem cell delivery: the pulmonary first-pass effect. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18(5):683-692. [13] FITZNER D, SCHNAARS M, VAN ROSSUM D, et al. Selective transfer of exosomes from oligodendrocytes to microglia by macropinocytosis. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(Pt 3):447-458. [14] VAN DER POL E, BOING AN, GOOL EL, et al. Recent developments in the nomenclature, presence, isolation, detection and clinical impact of extracellular vesicles. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14(1):48-56. [15] DENG H, SUN C, SUN Y, et al. Lipid, protein, and microRNA composition within mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Cell Reprogram. 2018; 20(3):178-186. [16] POWELL S, MCDOUGALL C. Clinical recognition of leprosy: some factors leading to delays in diagnosis. Br Med J. 1974;1(5908):612-613. [17] SLUIJTER JP, VERHAGE V, DEDDENS JC, et al. Microvesicles and exosomes for intracardiac communication. Cardiovasc Res. 2014;102(2):302-311. [18] WANG X, TANG Y, LIU Z, et al. The application potential and advance of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in myocardial infarction. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:5579904. [19] PACHLER K, LENER T, STREIF D, et al. A Good Manufacturing Practice-grade standard protocol for exclusively human mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(4):458-472. [20] ANDRIOLO G, PROVASI E, LO CV, et al. Exosomes from human cardiac progenitor cells for therapeutic applications: development of a GMP-grade manufacturing method. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1169. [21] ESCUDIER B, DORVAL T, CHAPUT N, et al. Vaccination of metastatic melanoma patients with autologous dendritic cell (DC) derived-exosomes: results of thefirst phase I clinical trial. J Transl Med. 2005;3(1):10. [22] LAMPARSKI HG, METHA-DAMANI A, YAO JY, et al. Production and characterization of clinical grade exosomes derived from dendritic cells. J Immunol Methods. 2002;270(2):211-226. [23] ZERINGER E, BARTA T, LI M, et al. Strategies for isolation of exosomes. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2015;2015(4):319-323. [24] BATRAKOVA EV, KIM MS. Using exosomes, naturally-equipped nanocarriers, for drug delivery. J Control Release. 2015;219:396-405. [25] SASAKI H, RAY PS, ZHU L, et al. Hypoxia/reoxygenation promotes myocardial angiogenesis via an NF kappa B-dependent mechanism in a rat model of chronic myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001;33(2):283-294. [26] KHAYATI F, PEREZ-CANO L, MAOUCHE K, et al. EMMPRIN/CD147 is a novel coreceptor of VEGFR-2 mediating its activation by VEGF. Oncotarget. 2015;6(12):9766-9780. [27] LIANG X, ZHANG L, WANG S, et al. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J Cell Sci. 2016;129(11):2182-2189. [28] XU H, WANG Z, LIU L, et al. Exosomes derived from adipose tissue, bone marrow, and umbilicalcord blood for cardioprotection after myocardial infarction. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(3):2089-2102. [29] KHAN M, NICKOLOFF E, ABRAMOVA T, et al. Embryonic stem cell-derived exosomes promote endogenous repair mechanisms and enhance cardiac function following myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 2015;117(1):52-64. [30] BARILE L, LIONETTI V, CERVIO E, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human cardiac progenitor cells inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2014;103(4):530-541. [31] GRAY WD, FRENCH KM, GHOSH-CHOUDHARY S, et al. Identification of therapeutic covariant microRNA clusters in hypoxia-treated cardiac progenitor cell exosomes using systems biology. Circ Res. 2015;116(2): 255-263. [32] KIM H S, CHOI D Y, YUN S J, et al. Proteomic analysis of microvesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells. J Proteome Res. 2012;11(2):839-849. [33] ZHU LP, TIAN T, WANG J Y, et al. Hypoxia-elicited mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitates cardiac repair through miR-125b-mediated prevention of cell death in myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 2018;8(22): 6163-6177. [34] SHI B, WANG Y, ZHAO R, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21 protects C-kit+ cardiac stem cells from oxidative injury through the PTEN/PI3K/Akt axis. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e191616. [35] CHEN CH, HSU SY, CHIU CC, et al. MicroRNA-21 mediates the protective effect of cardiomyocyte-derived conditioned medium on ameliorating myocardial infarction in rats. Cells. 2019. doi: 10.3390/cells8080935. [36] PENG Y, ZHAO JL, PENG ZY, et al. Exosomal miR-25-3p from mesenchymal stem cells alleviates myocardial infarction by targeting pro-apoptotic proteins and EZH2. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(5):317. [37] YU B, KIM HW, GONG M, et al. Exosomes secreted from GATA-4 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells serve as a reservoir of anti-apoptotic microRNAs for cardioprotection. Int J Cardiol. 2015;182:349-360. [38] CHENG H, CHANG S, XU R, et al. Hypoxia-challenged MSC-derived exosomes deliver miR-210 to attenuate post-infarction cardiac apoptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):224. [39] SONG Y, WANG B, ZHU X, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived MSCs exosome attenuate myocardial injury by inhibiting ferroptosis in acute myocardial infarction mice. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021;37(1):51-64. [40] WANG Y, ZHAO R, LIU D, et al. Exosomes derived from mir-214-enriched bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells regulate oxidative damage in cardiac stem cells by targeting CaMKII. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:4971261. [41] FERGUSON SW, WANG J, LEE CJ, et al. The microRNA regulatory landscape of MSC-derived exosomes: a systems view. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1419. [42] HEFLICH RH, MITTELSTAEDT RA, MANJANATHA MG, et al. DNA sequence analysis of hprt mutations in lymphocytes from Sprague-Dawley rats treated with7, 12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1996;28(1):5-12. [43] PHILLIPS EN, XIA F, KELSEY KT, et al. Spectra of spontaneous and X-ray-induced mutations at the hprt locus in related human lymphoblast cell lines that express wild-type or mutant p53. Radiat Res. 1995;143(3):255-262. [44] HONG J, WANG Y, HU BC, et al. Transcriptional downregulation of microRNA-19a by ROS production and NF-kappaB deactivation governs resistance to oxidative stress-initiated apoptosis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(41):70967-70981. [45] TIMMERS L, LIM SK, ARSLAN F, et al. Reduction of myocardial infarct size by human mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium. Stem Cell Res. 2007;1(2):129-137. [46] HAN C, ZHOU J, LIANG C, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes encapsulated in functional peptide hydrogels promote cardiac repair. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(7):2920-2933. [47] GU X, LI Y, CHEN K, et al. Exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate viral myocarditis through activating AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy flux pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(13):7515-7530. [48] GAO J, CHEN X, SHAN C, et al. Autophagy in cardiovascular diseases: role of noncoding RNAs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;23:101-118. [49] SHAO H, YANG L, WANG L, et al. MicroRNA-34a protects myocardial cells against ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibiting autophagy via regulating TNFalpha expression. Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;96(3):349-354. [50] LI Q, GAO Y, ZHU J, et al. MiR-101 Attenuates myocardial infarction-induced injury by targeting DDIT4 to regulate autophagy. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2020; 17(2):123-130. [51] HUANG Z, WU S, KONG F, et al. MicroRNA-21 protects against cardiac hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting excessive autophagy in H9c2 cells via the Akt/mTOR pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(3):467-474. [52] DING S, ABUDUPATAER M, ZHOU Z, et al. Histamine deficiency aggravates cardiac injury through miR-206/216b-Atg13 axis-mediated autophagic-dependant apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(6):694. [53] ZHANG C, ZHANG C, WANG H, et al. Effects of miR103a3p on the autophagy and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes by regulating Atg5. Int J Mol Med. 2019; 43(5):1951-1960. [54] ZHAO P, ZHANG B L, LIU K, et al. Overexpression of miR-638 attenuated the effects of hypoxia/reoxygenation treatment on cell viability, cell apoptosis and autophagy by targeting ATG5 in the human cardiomyocytes. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(23):8462-8471. [55] CHEN G, WANG M, RUAN Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-143-3p suppresses myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating autophagy. Life Sci. 2021;280:119742. [56] TALMAN V, RUSKOAHO H. Cardiac fibrosis in myocardial infarction-from repair and remodeling to regeneration. Cell Tissue Res. 2016;365(3):563-581. [57] LUTHER KM, HAAR L, MCGUINNESS M, et al. Exosomal miR-21a-5p mediates cardioprotection by mesenchymal stem cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018;119: 125-137. [58] FENG Y, HUANG W, WANI M, et al. Ischemic preconditioning potentiates the protective effect of stem cells through secretion of exosomes by targeting Mecp2 via miR-22. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88685. [59] WANG X, ZHU Y, WU C, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes carry microRNA-671 to alleviate myocardial infarction through inactivating the TGFBR2/Smad2 axis. Inflammation. 2021;44(5): 1815-1830. [60] MALGULWAR PB, PATHAK P, SINGH M, et al. Downregulation of SMARCB1/INI1 expression in pediatric chordomas correlates with upregulation of miR-671-5p and miR-193a-5p expressions. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2017;34(4):155-159. [61] WEI Z, QIAO S, ZHAO J, et al. miRNA-181a over-expression in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes influenced inflammatory response after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Life Sci. 2019;232:116632. [62] ZHAO J, LI X, HU J, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury through miR-182-regulated macrophage polarization. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115(7):1205-1216. [63] DOMENIS R, CIFU A, QUAGLIA S, et al. Pro inflammatory stimuli enhance the immunosuppressive functions of adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13325. [64] BURRELLO J, MONTICONE S, GAI C, et al. Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles and immune-modulation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016;4:83. [65] LAI RC, TAN SS, TEH BJ, et al. Proteolytic potential of the MSC exosome proteome: implications for an exosome-mediated delivery of therapeutic proteasome. Int J Proteomics. 2012;2012:971907. [66] KANG K, MA R, CAI W, et al. Exosomes secreted from CXCR4 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells promote cardioprotection via akt signaling pathway following myocardial infarction. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:659890. [67] WANG X, CHEN Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Engineered exosomes with ischemic myocardium-targeting peptide for targeted therapy in myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(15):e8737. [68] NI J, LIU X, YIN Y, et al. Exosomes derived from timp2-modified human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance the repair effect in rat model with myocardial infarction possibly by the Akt/Sfrp2 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:1958941. [69] CHEN Y, ZHAO Y, CHEN W, et al. MicroRNA-133 overexpression promotes the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells on acute myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):268. [70] SEO HH, LEE SY, LEE CY, et al. Exogenous miRNA-146a enhances the therapeutic efficacy of human mesenchymal stem cells by increasing vascular endothelial growth factor secretion in the ischemia/reperfusion-injured heart. J Vasc Res. 2017;54(2):100-108. [71] HUANG P, WANG L, LI Q, et al. Atorvastatin enhances the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes in acute myocardial infarction via up-regulating long non-coding RNA H19. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(2):353-367. [72] ZHU LP, TIAN T, WANG JY, et al. Hypoxia-elicited mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitates cardiac repair through miR-125b-mediated prevention of cell death in myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 2018;8(22):6163-6177. [73] XU R, ZHANG F, CHAI R, et al. Exosomes derived from pro-inflammatory bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce inflammation and myocardial injury via mediating macrophage polarization. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(11):7617-7631. [74] PARK DJ, YUN WS, KIM WC, et al. Improvement of stem cell-derived exosome release efficiency by surface-modified nanoparticles. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):178. [75] STEPHANOPOULOS N, ORTONY JH, STUPP SI. Self-Assembly for the Synthesis of Functional Biomaterials. Acta Mater. 2013;61(3):912-930. [76] WANG J, BONACQUISTI EE, BROWN AD, et al. Boosting the Biogenesis and Secretion of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Cells. 2020. doi: 10.3390/cells9030660. [77] CHEN CW, WANG LL, ZAMAN S, et al. Sustained release of endothelial progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles from shear-thinning hydrogels improves angiogenesis and promotes function after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2018;114(7):1029-1040. [78] LIU S, CHEN X, BAO L, et al. Treatment of infarcted heart tissue via the capture and local delivery of circulating exosomes through antibody-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles. Nat Biomed Eng. 2020;4(11):1063-1075. [79] WEI G, JIE Y, HAIBO L, et al. Dendritic cells derived exosomes migration to spleen and induction of inflammation are regulated by CCR7. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42996. [80] RODRIGUEZ PL, HARADA T, CHRISTIAN DA, et al. Minimal “Self” peptides that inhibit phagocytic clearance and enhance delivery of nanoparticles. Science. 2013;339(6122):971-975. [81] VRIJSEN KR, MARING JA, CHAMULEAU SA, et al. Exosomes from cardiomyocyte progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells stimulate angiogenesis via EMMPRIN. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(19):2555-2565. [82] YAO J, HUANG K, ZHU D, et al. A minimally invasive exosome spray repairs heart after myocardial infarction. ACS Nano. 2021. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c00628. [83] ZHANG N, SONG Y, HUANG Z, et al. Monocyte mimics improve mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle homing in a mouse MI/RI model. Biomaterials. 2020;255:120168. [84] NIESWANDT B, WATSON SP. Platelet-collagen interaction: is GPVI the central receptor? Blood. 2003;102(2):449-461. [85] BUTLER LM, METSON-SCOTT T, FELIX J, et al. Sequential adhesion of platelets and leukocytes from flowing whole blood onto a collagen-coated surface: requirement for a GpVI-binding site in collagen. Thromb Haemost. 2007;97(5):814-821. [86] HU CM, FANG RH, WANG KC, et al. Nanoparticle biointerfacing by platelet membrane cloaking. Nature. 2015;526(7571):118-121. [87] ANDERSON JD, JOHANSSON HJ, GRAHAM CS, et al. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes reveals modulation of angiogenesis via nuclear factor-kappab signaling. Stem Cells. 2016;34(3):601-613. [88] LENER T, GIMONA M, AIGNER L, et al. Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials - an ISEV position paper. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:30087. |
| [1] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [4] | Xu Yan, Li Ping, Lai Chunhua, Zhu Peijun, Yang Shuo, Xu Shulan. Piezoelectric materials for vascularized bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [5] | Xue Ting, Zhang Xinri, Kong Xiaomei. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for pneumoconiosis using nanomaterials combined with multi-modal molecular imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1133-1140. |
| [6] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [7] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [8] | Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Lu Dahong, Xu Junrong, Liu Xiaocui, Wang Bingyun. Clinical-grade human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells affect the improvement of neurological function in rats with traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 835-839. |
| [9] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [10] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [11] | Zhang Houjun, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid exosomes derived from cerebral palsy children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 903-908. |
| [12] | Gao Ting, Ma Xiaohong, Li Xiaorong. Extraction and identification of exosomes from three different sources of ovarian granulosa cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 860-865. |
| [13] | Huang Guijiang, Ji Yuwei, Zhao Xin, Yang Yi, Zhao Yulan, Wang Peijin, Tang Wei, Jiao Jianlin. Effect and mechanism of different administration routes of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of tree shrews with osteoporotic fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 909-914. |
| [14] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| [15] | Yuan Bo, Xie Lide, Fu Xiumei. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote the repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||