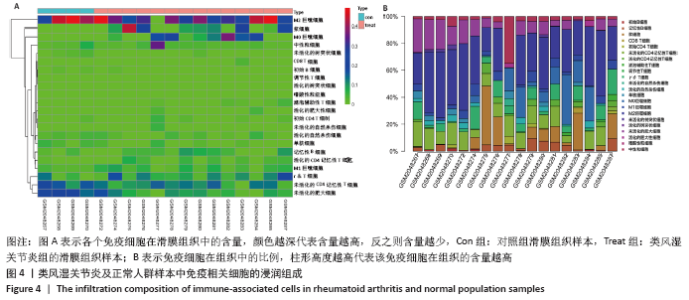
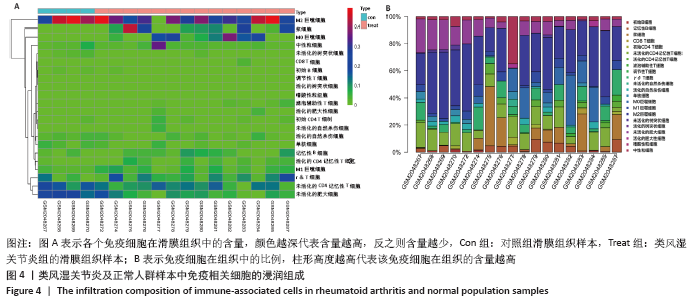
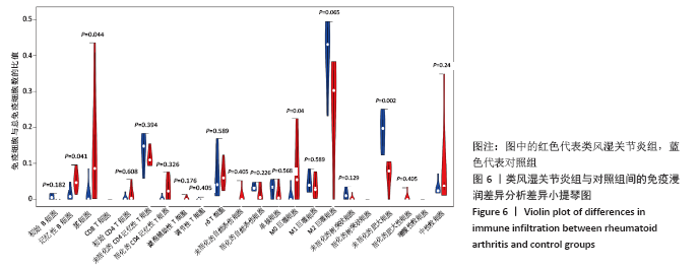
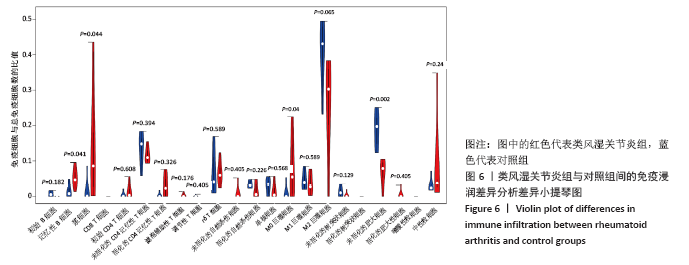
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (14): 2183-2191.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3797
Previous Articles Next Articles
Immune infiltration mechanism of differential expression genes in rheumatoid arthritis and potential therapeutic prediction of Chinese herbs
Shen Fu1, Kuang Gaoyan2, Yang Zhuo1, Wen Meng1, Zhu Kaimin1, Yu Guizhi1, Xu Wuji3, Deng Bo2
- 1Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410007, Hunan Province, China; 3Department of Spine, Second Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410005, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2020-06-10Revised:2020-06-13Accepted:2020-07-29Online:2021-05-18Published:2020-12-30 -
Contact:Xu Wuji, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Spine, Second Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410005, Hunan Province, China Deng Bo, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410007, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Shen Fu, Master candidate, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research & Development Program of China, No. 2018YFC2002500 (to KGY [project participant]); the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, No. 2019JJ50462 (to KGY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shen Fu, Kuang Gaoyan, Yang Zhuo, Wen Meng, Zhu Kaimin, Yu Guizhi, Xu Wuji, Deng Bo . Immune infiltration mechanism of differential expression genes in rheumatoid arthritis and potential therapeutic prediction of Chinese herbs[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2183-2191.
share this article

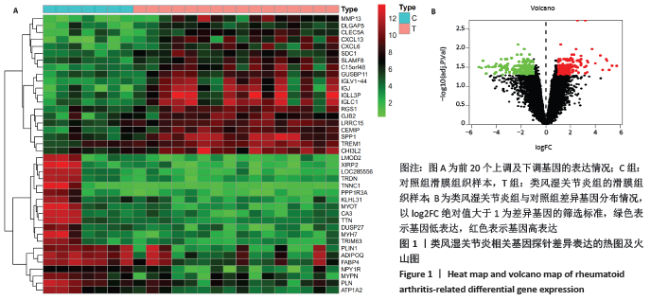
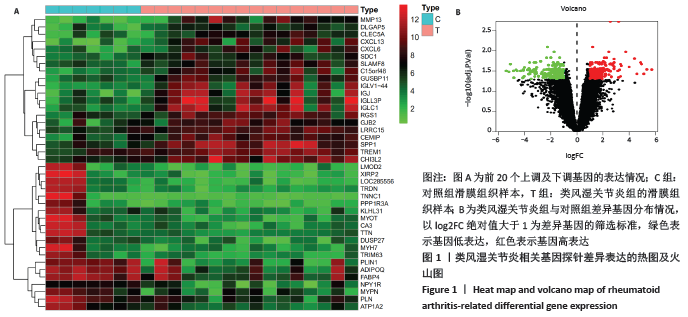
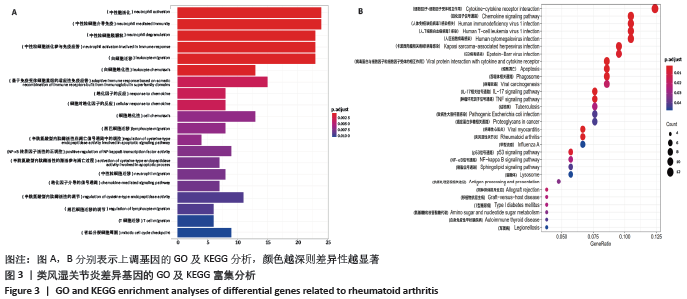
2.3 差异基因的GO及KEGG富集分析结果 运用R语言程序中的“clusterProfiler”插件包分析类风湿关节炎差异基因进行生物学功能及通路富集分析,上调基因的GO分析中共获取生物过程(biological process,BP)75条,下调基因共富集214条BP。在KEGG富集分析中,上调基因共富集34条通路,下调基因共富集31条信号通路。该课题组在数据分析时发现,上调基因的GO及KEGG富集分析与免疫炎症关系较为密切,如图3A所示,上调基因的GO主要涉及neutrophil activation (中性粒细胞活化)、neutrophil mediated immunity(中性粒细胞介导的免疫)、neutrophil degranulation(中性粒细胞脱颗粒)、neutrophil activation involved in immune response(中性粒细胞活化参与免疫应答)、leukocyte migration(白细胞迁移)、leukocyte chemotaxis(白细胞趋化性)、lymphocyte migration(淋巴细胞迁移)及T cell migration(T淋巴细胞迁移)。如图3B所示,对上调基因按照差异显著性进行气泡图展示,具体通路及富集基因信息如表3所示,在KEGG富集分析中,上调基因主要涉及多种病毒感染通路、趋化因子信号通路、白细胞介素17相关通路以及核转录因子κB通路。 "

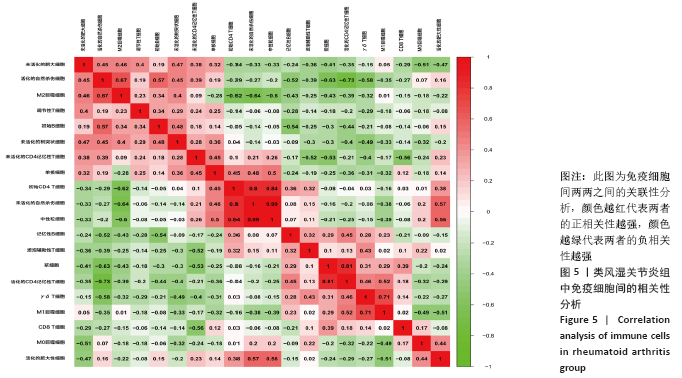
2.5 免疫细胞间相关性分析 如图5所示,未活化的自然杀伤细胞(NK cells resting)与中性粒细胞(Neutrophils)呈强烈正相关性(r=0.99),中性粒细胞(Neutrophils)与初始CD4+T细胞(T cells CD4 naive)呈强烈正相关性(r=0.84),未活化的自然杀伤细胞(NK cells resting)与初始CD4+T细胞(T cells CD4 naive)呈强烈正相关性(r=0.80),浆细胞(Plasma cells)与活化的CD4+记忆性T细胞(T cells CD4 memory activated)呈强烈正相关性(r=0.81)。并且,活化的CD4+记忆性T细胞(T cells CD4 memory activated)与活化的自然杀伤细胞(NK cells activated)呈强负相关性(r=-0.73),M2巨噬细胞(macrophages M2)与未活化的自然杀伤细胞(NK cells resting)呈现较强的负相关性(r=-0.64)。"
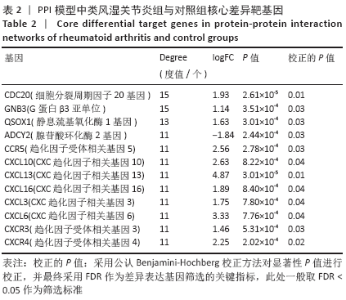
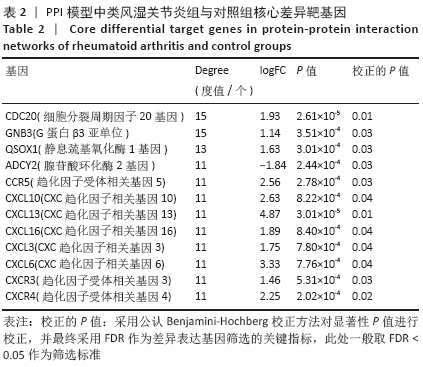
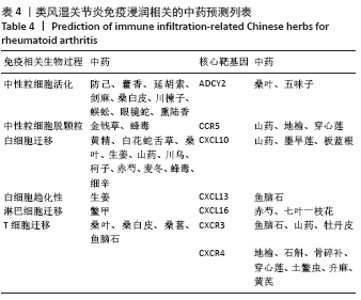
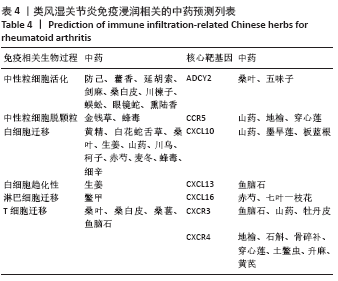
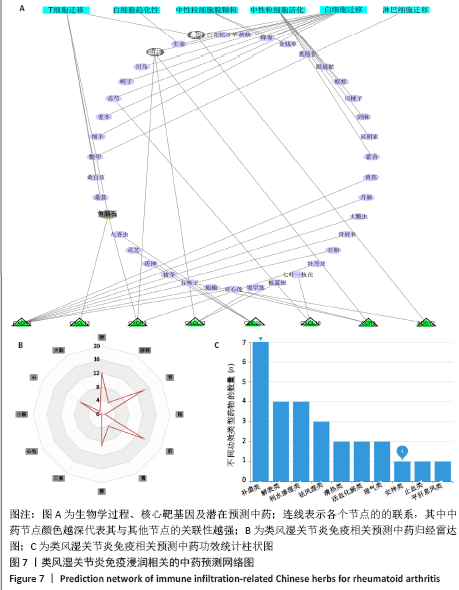
2.7 免疫浸润相关生物途径的中药预测 通过Coremine Medical预测具有潜在干预类风湿关节炎免疫浸润的中药,如表4所示,以P < 0.05作为筛选标准,预测得出39种中药与中性粒细胞活化、中性粒细胞脱颗粒、白细胞迁移、白细胞趋化性、淋巴细胞迁移、T细胞迁移相关等免疫生物过程及ADCY2,CCR5,CXCL10,CXCL13,CXCL16,CXCR3等核心靶基因相关,将结果导入Cytoscape软件中进行可视化展示,如图7A所示,该网络中共有节点53个,边51条,该网络中山药、鱼脑石、桑叶的度值较高,提示与类风湿关节炎相关免疫浸润的关系最密切,其干预类风湿关节炎免疫浸润的机制可能与通过作用于CCR5,CXCL10,CXCR3及CXCL13干预白细胞及T细胞迁移相关。对预测的中药进行归经分类,如图7B所示,与类风湿关节炎免疫浸润相关中药多归肝肾经,且与补虚、解表及利水渗湿相关,药物功效统计具体如图7C所示。"
| [1] FALCONER J, MURPHY AN, YOUNG SP, et al. Review: synovial cell metabolism and chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70(7):984-999. [2] MCINNES IB, SCHETT G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2017;389(10086):2328-2337. [3] SHI YQ, QI WF, KONG CY. Drug screening and identification of key candidate genes and pathways of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(2):986-996. [4] AREND WP, FIRESTEIN GS. Pre-rheumatoid arthritis: predisposition and transition to clinical synovitis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(10):573-586. [5] COUTANT F, MIOSSEC P. Evolving concepts of the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis with focus on the early and late stages. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2020; 32(1):57-63. [6] FANG Q, ZHOU C, NANDAKUMAR KS. Molecular and cellular pathways contributing to joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2020; 2020:3830212. [7] ORR C, VIEIRA-SOUSA E, BOYLE DL, et al. Corrigendum: synovial tissue research: a state-of-the-art review. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;14(1):60. [8] FANG Q, OU J, NANDAKUMAR KS. Autoantibodies as diagnostic markers and mediator of joint inflammation in arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019: 6363086. [9] YANG X, CHANG Y, WEI W. Emerging role of targeting macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis: Focus on polarization, metabolism and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(7): e12854. [10] ROBERTS CA, DICKINSON AK, TAAMS LS. The Interplay Between Monocytes/Macrophages and CD4(+) T Cell Subsets in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol 2015;6:571. [11] SMOLEN JS, LANDEWÉ R, BIJLSMA J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):685-699. [12] 逯卓卉,韦登明,张伊,等.组织工程方法修复类风湿性关节炎软骨缺损的研究进展[J].北京生物医学工程,2013,32(3):315-319. [13] CHATZIDIONYSIOU K, SFIKAKIS PP. Low rates of remission with methotrexate monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis: review of randomised controlled trials could point towards a paradigm shift. RMD Open. 2019;5(2):e000993. [14] XING Q, FU L, YU Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of integrated traditional chinese medicine and western medicine on the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:4348709. [15] 陈坤威,童亚林,姚咏明.组织工程支架材料对固有免疫反应的影响及调控效应[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2018,43(8):698-703. [16] GUO X, JI J, FENG Z, et al. A network pharmacology approach to explore the potential targets underlying the effect of sinomenine on rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;80:106201. [17] 池里群,周彬,高文远,等.治疗类风湿性关节炎常用药物的研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2014,39(15):2851-2858. [18] 王亚黎,刘健,叶文芳,等.中医药对类风湿关节炎患者免疫球蛋白影响的研究进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2014,3(4):62-65. [19] MOROZ LA, TALAKO ТМ, POTAPNEV MP, et al. Dichotomy of Local Th1- and Systemic Th2/Th3-Dependent Types of Immune Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2019;167(1):69-73. [20] KOMATSU N, TAKAYANAGI H. Immune-bone interplay in the structural damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;194(1):1-8. [21] ALI HR, CHLON L, PHAROAH PD, et al. Patterns of immune infiltration in breast cancer and their clinical implications: a gene-expression-based retrospective study. PLoS Med. 2016;13(12):e1002194. [22] XIONG Y, WANG K, ZHOU H, et al. Profiles of immune infiltration in colorectal cancer and their clinical significant: a gene expression-based study. Cancer Med. 2018;7(9):4496-4508. [23] NEWMAN AM, LIU CL, GREEN MR, et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods. 2015;12(5):453-457. [24] LU G, CHEN L, WU S, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells and Relevant Therapeutic Strategy in Esophageal Cancer. Dis Markers. 2020; 2020:8974793. [25] 古龙,周牮,彭建华,等.颅内动脉瘤的相关信号通路基因集富集及免疫浸润分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2020,26(7):178-185. [26] LAN YY, WANG YQ, LIU Y. CCR5 silencing reduces inflammatory response, inhibits viability, and promotes apoptosis of synovial cells in rat models of rheumatoid arthritis through the MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10): 18748-18762. [27] GUO Q, ZHENG K, FAN D, et al. Wu-Tou Decoction in rheumatoid arthritis: integrating network pharmacology and in vivo pharmacological evaluation. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:230. [28] LEE JH, KIM B, JIN WJ, et al. Pathogenic roles of CXCL10 signaling through CXCR3 and TLR4 in macrophages and T cells: relevance for arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):163. [29] ARMAS-GONZÁLEZ E, DOMÍNGUEZ-LUIS MJ, DÍAZ-MARTÍN A, et al. Role of CXCL13 and CCL20 in the recruitment of B cells to inflammatory foci in chronic arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):114. [30] PANDYA JM, LUNDELL AC, ANDERSSON K, et al. Blood chemokine profile in untreated early rheumatoid arthritis: CXCL10 as a disease activity marker. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):20. [31] MIYABE Y, LIAN J, MIYABE C, et al. Chemokines in rheumatic diseases: pathogenic role and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(12):731-746. [32] TSUJIMURA S, ADACHI T, SAITO K, et al. Relevance of P-glycoprotein on CXCR4+ B cells to organ manifestation in highly active rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2018;28(2):276-286. [33] COSTANTINO AB, ACOSTA C, ONETTI L, et al. Follicular helper T cells in peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatol Clin. 2017;13(6):338-343. [34] ZHOU LF, ZENG W, SUN LC, et al. IKKε aggravates inflammatory response via activation of NF-κB in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018; 22(7):2126-2133. [35] LIU YR, YAN X, YU HX, et al. NLRC5 promotes cell proliferation via regulating the NF-κB signaling pathway in Rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Immunol. 2017;91:24-34. [36] ONISHI RM, PARK SJ, HANEL W, et al. SEF/IL-17R (SEFIR) is not enough: an extended SEFIR domain is required for IL-17RA-mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(43):32751-32759. [37] 郭江燕,高梓珊,姜姝姝,等.IL-17和NF-κB通路与类风湿性关节炎的相关性研究[J].长春中医药大学学报,2015,31(1):192-194. [38] 董甜甜,王金龄,李世刚,等.肥大细胞在小鼠佐剂性关节炎疼痛中的作用及其机制研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2020,36(4):693-699. [39] OKAMURA Y, MISHIMA S, KASHIWAKURA JI, et al. The dual regulation of substance P-mediated inflammation via human synovial mast cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Allergol Int. 2017;66S:S9-9S20. [40] KUNG CC, DAI SP, CHIANG H, et al. Temporal expression patterns of distinct cytokines and M1/M2 macrophage polarization regulate rheumatoid arthritis progression. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(5):3423-3437. [41] 阮静瑶,陈必成,张喜乐,等.巨噬细胞M1/M2极化的信号通路研究进展[J].免疫学杂志,2015,31(10):911-917. [42] 王艳霞.类风湿性关节炎滑膜淋巴细胞CD3、CD4、CD8的表达及意义[D].天津:天津医科大学,2012:1-60. [43] 田杰祥,陶永明,王钢,等.中医药治疗类风湿关节炎滑膜炎的机理研究进展[J].中医药学报,2019,47(3):122-124. [44] 张佳琪.基于焦树德教授治疗类风湿关节炎辨证分型的用药规律探讨[J].风湿病与关节炎,2017,6(12):33-37. [45] 卜祥伟,张红红,张建萍,等.基于数据挖掘探讨孟凤仙教授治疗类风湿关节炎用药规律[J].中华中医药学刊,2018,36(7):1573-1576. [46] 蔡辉,陆乐,赵智明.“以毒攻毒”在类风湿关节炎治疗中的运用[J].中医学报,2015,30(11):1664-1666. [47] NIU X, HE Z, LI W, et al. Immunomodulatory Activity of the Glycoprotein Isolated from the Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb). Phytother Res. 2017;31(10): 1557-1563. [48] JEONG JW, LEE HH, LEE KW, et al. Mori folium inhibits interleukin-1β-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators by suppressing the activation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK in SW1353 human chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(2):452-460. [49] 侯瑞宏,廖森泰,刘凡,等.桑叶多糖对小鼠免疫调节作用的影响[J].食品科学,2011,32(13):280-283. [50] 赵婷,高昂,巩江,等.鱼脑石药学研究概况[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2011, 13(9):82-84. [51] 匡红,解葵,孙晨,等.512例类风湿关节炎患者血清5种微量元素含量分析[J].国际检验医学杂志,2013,34(10):1214-1215,1218. [52] 吴文英,张如峰,马凤英,等.不同药物治疗对类风湿关节炎患者血清铜、硒及锌水平的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(6):1555-1556. |
| [1] | Li Jiacheng, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Differential mRNA expression profile and competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [2] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [3] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [4] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [5] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [6] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [7] | Wang Qiufei, Gu Ye, Peng Yuqin, Xue Feng, Ju Rong, Zhu Feng, Wang Yijun, Geng Dechun, Xu Yaozeng. Effect of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway on osteoblasts under the action of wear particles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3894-3901. |
| [8] | Fan Junchao, Chen Yong, Song Junjie. Sevoflurance combined with xenon pretreatment protects against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3660-3665. |
| [9] | Liu Jinfu, Zeng Ping, Nong Jiao, Fan Siqi, Feng Chengqin, Huang Jiaxing. Integrative analysis of biomarkers and therapeutic targets in synovium of patients with osteoarthritis by multiple microarrays [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3690-3696. |
| [10] | Chen Feng, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Liao Jianzhao, Li Jiajun, Song Shilei, Lai Yu. Molecular mechanism of anhydroicaritin in the treatment of osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology and bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3704-3710. |
| [11] | Zhong Yuanming, He Bingkun, Wu Zhuotan, Wu Sixian, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng. An exploration on the mechanism of Shaoyao Gancao Decoction in treating early pain of lumbar disc herniation based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3194-3201. |
| [12] | Chen Xinling, Wang Shenglan. Cell autophagy, pathway, regulation and its multiple correlations with pulmonary hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 311-316. |
| [13] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [14] | Yan Xiurui, Tao Jin, Liang Xueyun. Mechanism by which exosomes from human fetal placental mesenchymal stem cells protect lung epithelial cells against oxidative stress injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2994-2999. |
| [15] | Su Mingzhu, Ma Yuewen. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy regulates the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells in the hippocampus via Notch1/Hes1 pathway after cerebral ischemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3009-3015. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||