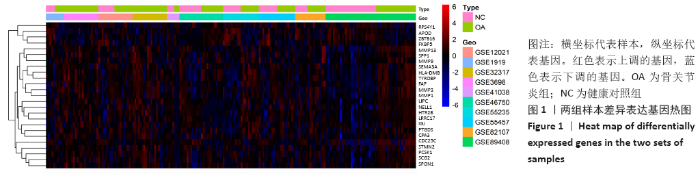
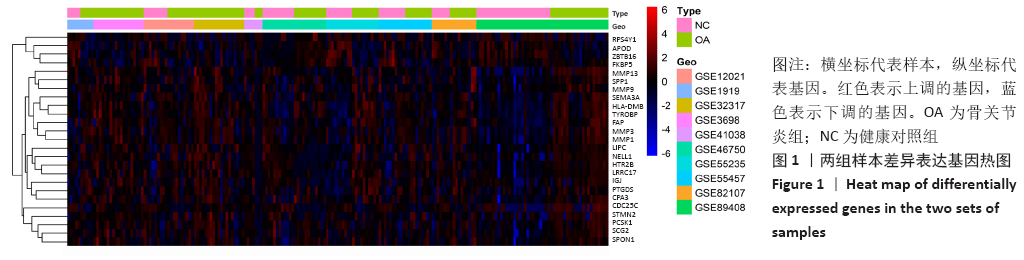
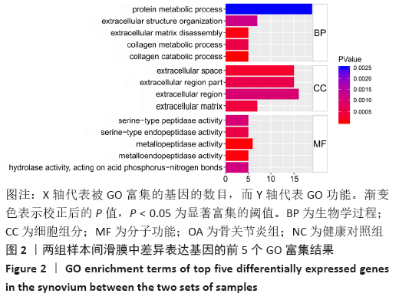
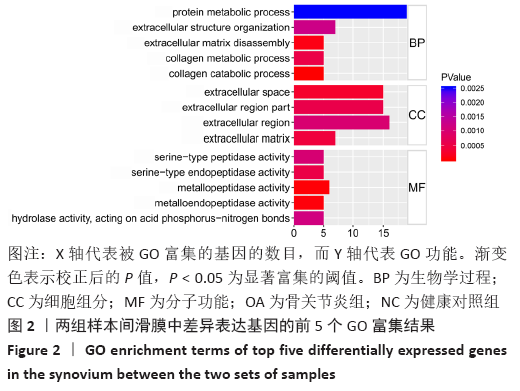
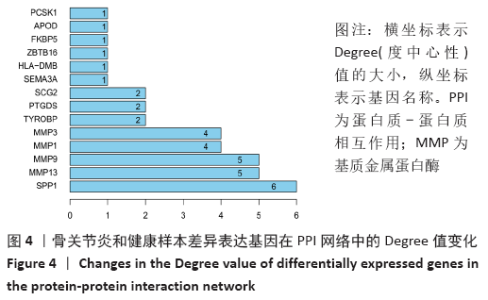
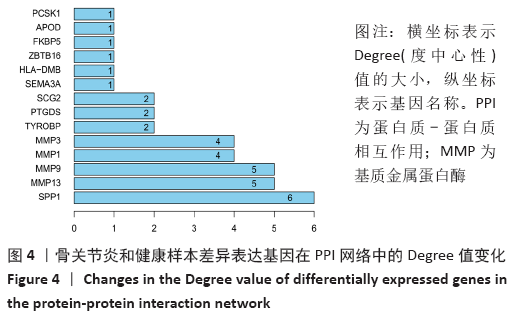
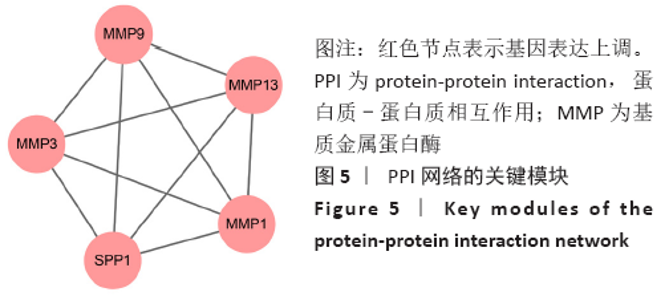
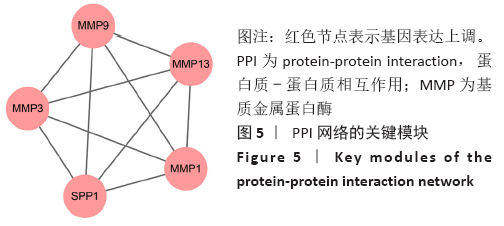
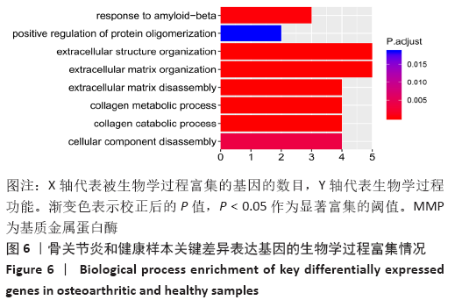
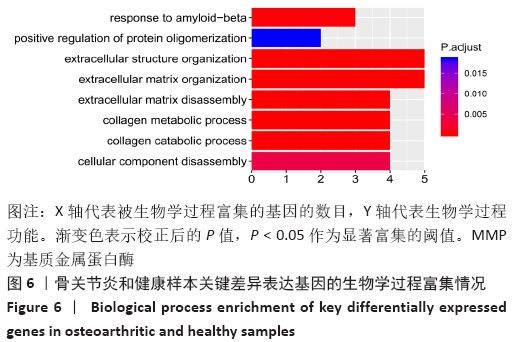
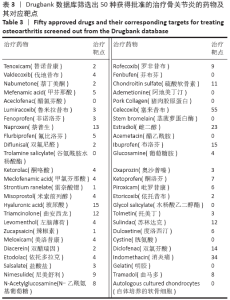
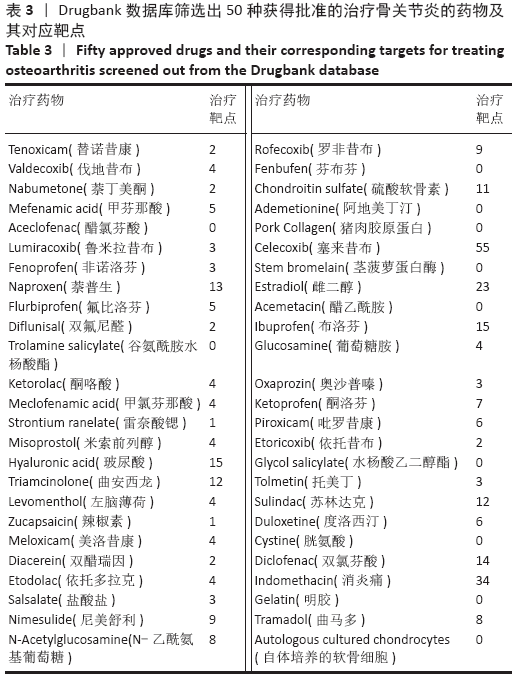
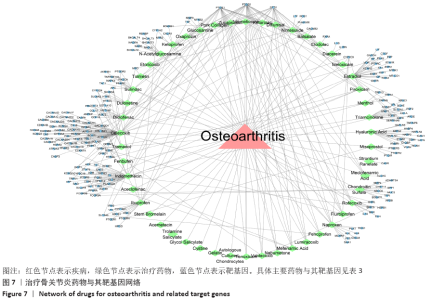
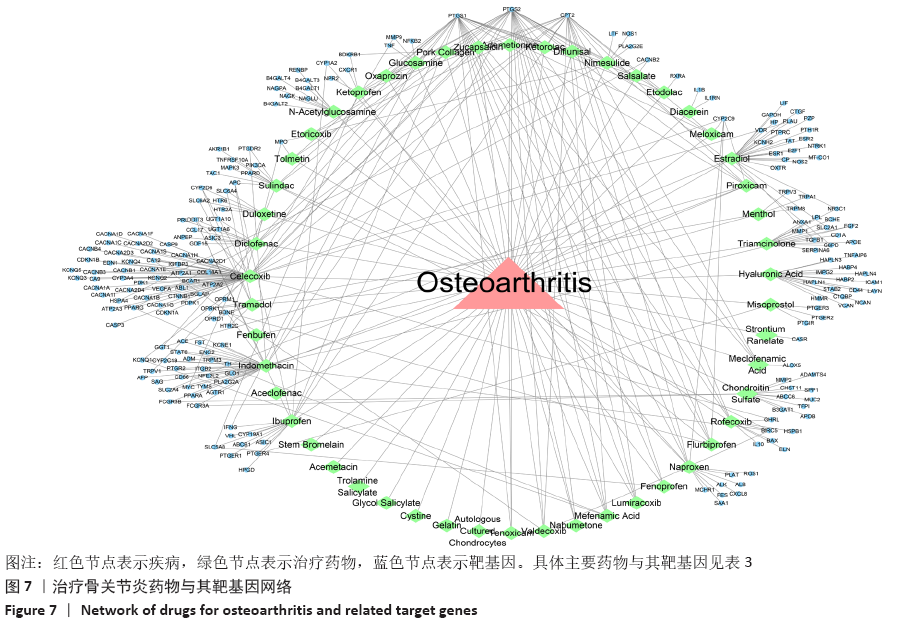
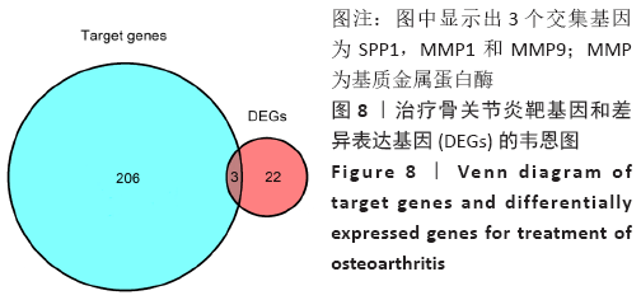
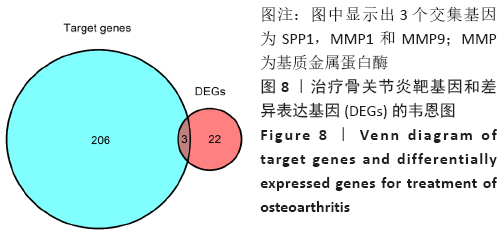
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (23): 3690-3696.doi: 10.12307/2021.041
Previous Articles Next Articles
Integrative analysis of biomarkers and therapeutic targets in synovium of patients with osteoarthritis by multiple microarrays
Liu Jinfu1, Zeng Ping2, Nong Jiao2, Fan Siqi2, Feng Chengqin1, Huang Jiaxing1
- 1Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530299, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2020-07-20Revised:2020-07-22Accepted:2020-08-13Online:2021-08-18Published:2021-02-24 -
Contact:Zeng Ping, MD, Professor, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liu Jinfu, Master candidate, Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530299, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960876 (to ZP); Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2017GXNSFAA198296 (to ZP); First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2017ZD002 (to ZP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Jinfu, Zeng Ping, Nong Jiao, Fan Siqi, Feng Chengqin, Huang Jiaxing. Integrative analysis of biomarkers and therapeutic targets in synovium of patients with osteoarthritis by multiple microarrays[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3690-3696.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
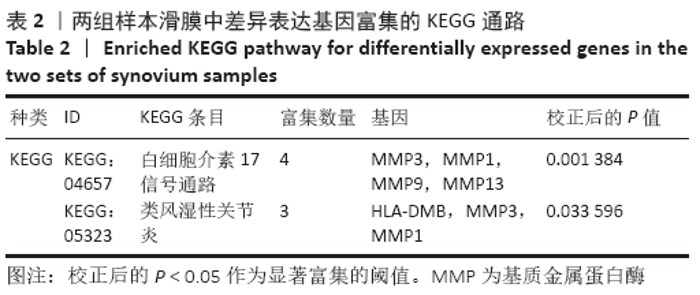
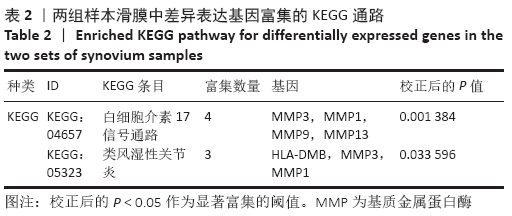
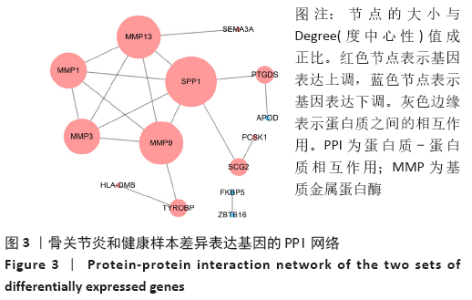
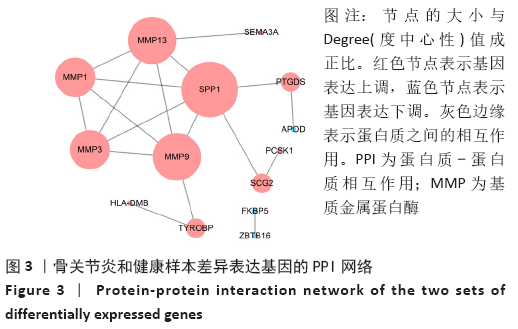
| [1] MOBASHERI A, BATT M. An update on the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59(5-6):333-339. [2] 章晓云,张驰,宋世雷,等.基于网络药理学和蛋白模块分析淫羊藿治疗骨关节炎的作用与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(17): 2660-2666. [3] KUBOSCH EJ, LANG G, FURST D, et al. The Potential for Synovium-derived Stem Cells in Cartilage Repair. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018; 13(3):174-184. [4] MATHIESSEN A, CONAGHAN PG. Synovitis in osteoarthritis: current understanding with therapeutic implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017; 19(1):18. [5] LI Z, ZHONG L, DU Z, et al. Network analyses of differentially expressed genes in osteoarthritis to identify hub genes. BioMed Res Int. 2019; 2019:8340573. [6] LI M, ZHI L, ZHANG Z, et al. Identification of potential target genes associated with the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis using microarray based analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(3):2799-806. [7] UNGETHUEM U, HAEUPL T, WITT H, et al. Molecular signatures and new candidates to target the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Physiol Genomics. 2010;42a(4):267-282. [8] FINIS K, SÜLTMANN H, RUSCHHAUPT M, et al. Analysis of pigmented villonodular synovitis with genome-wide complementary DNA microarray and tissue array technology reveals insight into potential novel therapeutic approaches. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(3):1009-1019. [9] HUBER R, HUMMERT C, GAUSMANN U, et al. Identification of intra-group, inter-individual, and gene-specific variances in mRNA expression profiles in the rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):R98. [10] WANG Q, ROZELLE AL, LEPUS CM, et al. Identification of a central role for complement in osteoarthritis. Nat Med. 2011;17(12):1674-1679. [11] THOMAS GP, DUAN R, PETTIT AR, et al. Expression profiling in spondyloarthropathy synovial biopsies highlights changes in expression of inflammatory genes in conjunction with tissue remodelling genes. BMC Musculoskelet Disorders. 2013;14:354. [12] LAMBERT C, DUBUC JE, MONTELL E, et al. Gene expression pattern of cells from inflamed and normal areas of osteoarthritis synovial membrane. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(4):960-968. [13] WOETZEL D, HUBER R, KUPFER P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R84. [14] BROEREN MG, DE VRIES M, BENNINK MB, et al. Functional tissue analysis reveals successful cryopreservation of human osteoarthritic synovium. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0167076. [15] GUO Y, WALSH AM, FEARON U, et al. CD40L-dependent pathway is active at various stages of rheumatoid arthritis disease progression. J Immunol. 2017;198(11):4490-4501. [16] GREEN GH, DIGGLE PJ. On the operational characteristics of the Benjamini and Hochberg False Discovery Rate procedure. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 2007;6:Article27. [17] RAUDVERE U, KOLBERG L, KUZMIN I, et al. g:Profiler: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W191-W198. [18] SZKLARCZYK D, FRANCESCHINI A, WYDER S, et al. STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic acids res. 2015;43(Database issue):D447-D452. [19] WISHART DS, FEUNANG YD, GUO AC, et al. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018; 46(D1):D1074-D1082. [20] RHODES DR, CHINNAIYAN AM. Bioinformatics strategies for translating genome-wide expression analyses into clinically useful cancer markers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1020:32-40. [21] ZHANG H, LIEW CC, MARSHALL KW. Microarray analysis reveals the involvement of beta-2 microglobulin (B2M) in human osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10(12):950-960. [22] DEL REY MJ, USATEGUI A, IZQUIERDO E, et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals specific changes in osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(2):275-280. [23] BIRCH HL. Extracellular Matrix and Ageing. Sub-cellular biochemistry. 2018;90:169-190. [24] SHI Y, HU X, CHENG J, et al. A small molecule promotes cartilage extracellular matrix generation and inhibits osteoarthritis development. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1914. [25] VAN DER KRAAN PM, VAN DEN BERG WB. Chondrocyte hypertrophy and osteoarthritis: role in initiation and progression of cartilage degeneration? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(3):223-232. [26] FAVERO M, BELLUZZI E, TRISOLINO G, et al. Inflammatory molecules produced by meniscus and synovium in early and end-stage osteoarthritis: a coculture study. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(7): 11176-11187. [27] PASTOUREAU PC, CHOMEL AC, BONNET J. Evidence of early subchondral bone changes in the meniscectomized guinea pig. A densitometric study using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry subregional analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1999;7(5):466-473. [28] YAMADA K, HEALEY R, AMIEL D, et al. Subchondral bone of the human knee joint in aging and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10(5):360-369. [29] IWAKURA Y, ISHIGAME H, SAIJO S, et al. Functional specialization of interleukin-17 family members. Immunity. 2011;34(2):149-162. [30] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42. [31] CAI L, YIN JP, STAROVASNIK MA, et al. Pathways by which interleukin 17 induces articular cartilage breakdown in vitro and in vivo. Cytokine. 2001;16(1):10-21. [32] LUBBERTS E, JOOSTEN LA, VAN DE LOO FA, et al. Reduction of interleukin-17-induced inhibition of chondrocyte proteoglycan synthesis in intact murine articular cartilage by interleukin-4. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(6):1300-1306. [33] DE LANGE-BROKAAR BJ, IOAN-FACSINAY A, VAN OSCH GJ, et al. Synovial inflammation, immune cells and their cytokines in osteoarthritis: a review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1484-99. [34] BROUWERS H, VON HEGEDUS J, TOES R, et al. Lipid mediators of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2015;29(6):741-755. [35] MALEMUD CJ. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Synovial Joint Pathology. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2017;148:305-325. [36] YAMAGA M, TSUJI K, MIYATAKE K, et al. Osteopontin level in synovial fluid is associated with the severity of joint pain and cartilage degradation after anterior cruciate ligament rupture. PLoS One. 2012; 7(11):e49014. [37] HONSAWEK S, TANAVALEE A, SAKDINAKIATTIKOON M, et al. Correlation of plasma and synovial fluid osteopontin with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis. Clin Biochem. 2009;42(9):808-812. [38] WANG Q, WANG W, ZHANG F, et al. NEAT1/miR-181c Regulates Osteopontin (OPN)-Mediated Synoviocyte Proliferation in Osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(11):3775-3784. [39] XU G, NIE H, LI N, et al. Role of osteopontin in amplification and perpetuation of rheumatoid synovitis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(4): 1060-1067. [40] CHENG C, GAO S, LEI G. Association of osteopontin with osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2014;34(12):1627-1631. [41] THORSON C, GALICIA K, BURLESON A, et al. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors and Proteoglycan 4 in Patients Undergoing Total Joint Arthroplasty. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2019;25: 1076029619828113. [42] Eo SH, Choi SY, Kim SJ. PEP-1-SIRT2-induced matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -13 modulates type II collagen expression via ERK signaling in rabbit articular chondrocytes. Exp Cell Res. 2016; 348(2):201-208. [43] PELLETIER JP, RAYNAULD JP, CARON J, et al. Decrease in serum level of matrix metalloproteinases is predictive of the disease-modifying effect of osteoarthritis drugs assessed by quantitative MRI in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dise. 2010;69(12):2095-2101. [44] WYATT LA, NWOSU LN, WILSON D, et al. Molecular expression patterns in the synovium and their association with advanced symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(4):667-675. [45] BURRAGE PS, MIX KS, BRINCKERHOFF CE. Matrix metalloproteinases: role in arthritis. Front Biosci. 2006;11:529-543. [46] NAGASE H, WOESSNER JF JR. Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(31):21491-21494. [47] FLANNERY CR. MMPs and ADAMTSs: functional studies. Front Biosci. 2006;11:544-569. [48] LI H, WANG D, YUAN Y, et al. New insights on the MMP-13 regulatory network in the pathogenesis of early osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):248. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [4] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [5] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [6] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [7] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [8] | Liu Zhichao, Zhang Fan, Sun Qi, Kang Xiaole, Yuan Qiaomei, Liu Genzhe, Chen Jiang. Morphology and activity of human nucleus pulposus cells under different hydrostatic pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1172-1176. |
| [9] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [10] | Li Jiacheng, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Differential mRNA expression profile and competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [11] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [12] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [13] | Tan Jingyu, Liu Haiwen. Genome-wide identification, classification and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciclin gene family for osteoblast specific factor 2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1243-1248. |
| [14] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [15] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||