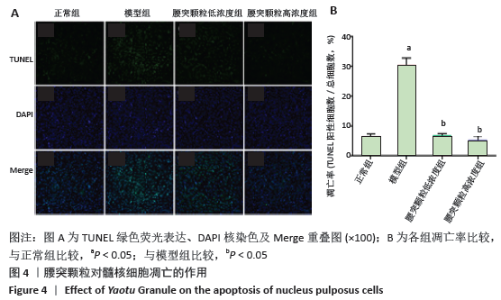
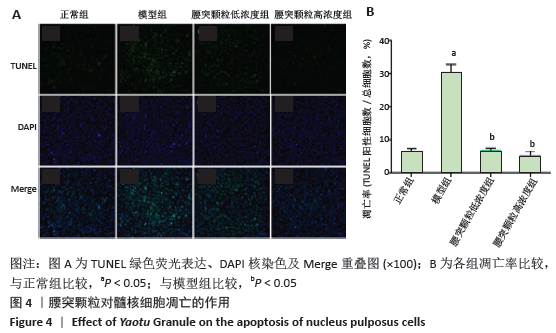
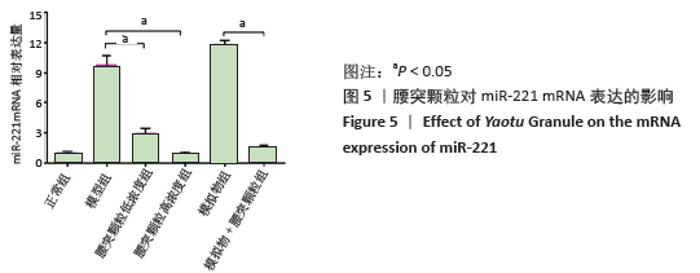
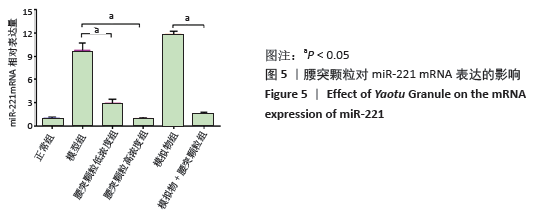
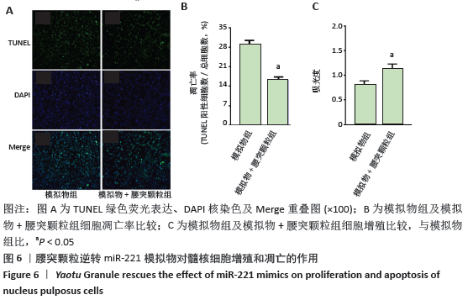
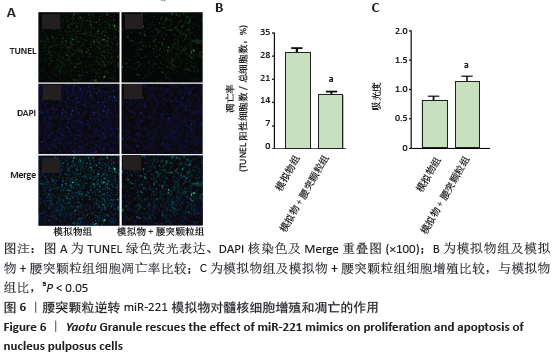
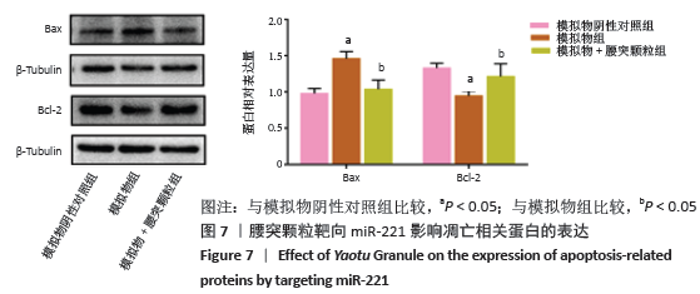
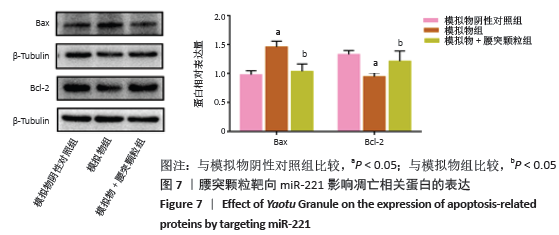
[1] HARTVIGSEN J, HANCOCK MJ, KONGSTED A, et al. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet. 2018;391(10137):2356-2367.
[2] LIU H, KANG H, SONG C, et al. Urolithin A Inhibits the Catabolic Effect of TNFalpha on Nucleus Pulposus Cell and Alleviates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in vivo. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1043.
[3] BOWLES RD, SETTON LA. Biomaterials for intervertebral disc regeneration and repair. Biomaterials. 2017;129:54-67.
[4] ADAMS MA, ROUGHLEY PJ. What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it?. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(18):2151-2161.
[5] VERGROESEN PP, KINGMA I, EMANUEL KS, et al. Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: a vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(7):1057-1070.
[6] CHENG X, ZHANG G, ZHANG L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-21 via exosomes to inhibit nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and reduce intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(1):261-276.
[7] LIU S, YANG SD, HUO XW, et al. 17beta-Estradiol inhibits intervertebral disc degeneration by down-regulating MMP-3 and MMP-13 and up-regulating type II collagen in a rat model. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup2):182-191.
[8] BARTEL DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281-297.
[9] YANG S, YANG Y. Downregulation of microRNA221 decreases migration and invasion in fibroblastlike synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(2):2395-2401.
[10] HU XH, ZHAO ZX, DAi J, et al. MicroRNA-221 regulates osteosarcoma cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion by targeting CDKN1B/p27. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(3):4665-4674.
[11] GONG W, LI J, WANG Y, et al. miR-221 promotes lens epithelial cells apoptosis through interacting with SIRT1 and E2F3. Chem Biol Interact. 2019;306:39-46.
[12] PENOLAZZI L, LAMBERTINI E, BERGAMIN LS, et al. MicroRNA-221 silencing attenuates the degenerated phenotype of intervertebral disc cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2018;10(8):2001-2015.
[13] 周文明,林一峰,张震,等.补肾壮督方对大鼠退变椎间盘细胞线粒体凋亡通路的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(19):25-31.
[14] 佟德民,孙凤杰,冯福盈,等.身痛逐瘀汤对大鼠中重度退变腰椎间盘髓核内TNF-α、IL-1β的影响[J].中国中医急症,2019,28(4): 603-606.
[15] 王乐,徐无忌. 灌胃给予六味地黄丸后椎间盘退变组织蛋白多糖成分的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(42):6271-6277.
[16] 何升华,赖居易,王业广,等.腰突颗粒调节腰椎间盘退变模型兔Fas/FasL基因的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(32):5140-5145.
[17] 何升华,赖居易,孙志涛,等.基于RNA-seq技术分析腰突颗粒防治腰椎间盘退变的转录组学特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(24):3778-3783.
[18] 嵇丽娜,刘丹,邓贤,等.解毒祛瘀滋阴方冻干粉和含药血清对小鼠单核巨噬细胞的影响[J].中草药,2018,49(16):3868-3874.
[19] ITSUJI T, TONOMURA H, ISHIBASHI H, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor regulates HIF-1alpha-induced nucleus pulposus cell proliferation through MAPK-, PI3K/Akt-, and STAT3-mediated signaling. J Orthop Res. 2020 Apr 3. doi: 10.1002/jor.24679.
[20] ZHOU X, HONG Y, ZHAN Y. Karacoline, identified by network pharmacology, reduces degradation of the extracellular matrix in intervertebral disc degeneration via the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J Pharm Anal. 2020;10(1):13-22.
[21] CHENG X, ZHANG G, ZHANG L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-21 via exosomes to inhibit nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and reduce intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(1):261-276.
[22] LI N, GAO Q, ZHOU W, et al. MicroRNA-129-5p affects immune privilege and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells via regulating FADD in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(8):933-948.
[23] SUN JC, ZHENG B, SUN RX, et al. MiR-499a-5p suppresses apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells and degradation of their extracellular matrix by targeting SOX4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;113:108652.
[24] WANG R, WEN B, SUN D. miR-573 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting Bax in nucleus pulposus cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019;24:2.
[25] WANG X, LV G, LI J, et al. LncRNA-RP11-296A18.3/miR-138/HIF1A Pathway Regulates the Proliferation ECM Synthesis of Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells (HNPCs). J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(12):4862-4871.
[26] LIN X, LIN Q. MiRNA-495-3p Attenuates TNF-α Induced Apoptosis and Inflammation in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells by Targeting IL5RA. Inflammation. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01254-5.
[27] 陈江,肖辉灯,孙旗,等.人椎间盘髓核细胞增殖活性与益肾活血通络方的干预调控[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(8):1200-1206.
[28] 陈国铭,汤顺莉,冯家明,等.岭南骨科中药治疗腰椎间盘退变研究进展[J].中华中医药杂志,2018, 33(1):201-205.
[29] 滕金艳,丁德光,黄国付,等.补肾壮腰膏联合补肾祛瘀针法治疗腰椎间盘突出症急性发作的疗效观察[J].中华全科医学,2020, 18(4):654-656.
[30] 杨杰科,王嘉伟,周科望,等.独活寄生汤结合推拿对腰椎间盘突出疗效及TXB-2、 TNF-α、IL-1β变化研究[J].中华中医药学刊, 2020,38(2):44-46.
[31] 莫伟,许金海,叶洁,等.腰椎间盘突出症中医治疗方法的研究进展[J].中国中医急症,2016,25(3):474-476.
[32] 何升华,谭伟伟,孙志涛,等.腰突颗粒对人髓核细胞核因子κB信号通路的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(33):4933-4939.
[33] 赖居易.腰突颗粒治疗肝肾亏虚型腰椎间盘突出症临床研究[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2017.
[34] ZHU H, SUN B, SHEN Q. TNF-α induces apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells via activating the TRIM14/NF-κB signalling pathway. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):3004-3012.
|