Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (26): 4106-4112.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.26.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
In vitro experimental research of basic fibroblast growth factor/chitosan/polylactic acid scaffolds in periodontal tissue regeneration
- 1Department of Stomatology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Prosthodontics, Tianjin Stomatological Hospital, Tianjin 300000, China; 3Department of Prosthodontics, Stomatological Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2017-07-23Online:2017-09-18Published:2017-09-28 -
Contact:Lei Zhi-min, Associate chief physician, Department of Stomatology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Chen Li-hong, Studying for master’s degree, Physician, Department of Stomatology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the Innovation Training Project for Undergraduate Students in Liaoning Province, No. 201510160000045; the Science Plan Project of Liaoning Province, No. 2014022003
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Li-hong, Lei Zhi-min, Wang Li-li.
share this article
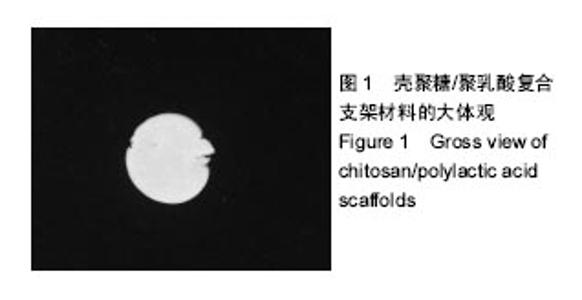
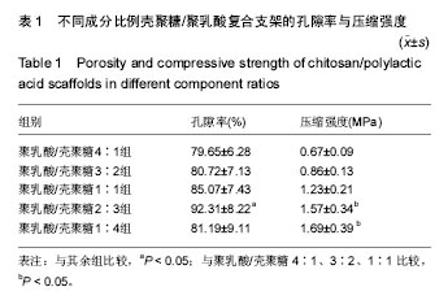
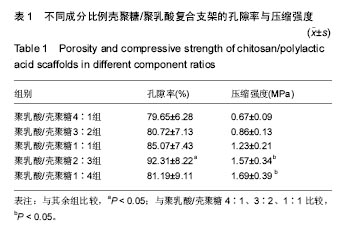
2.1 复合材料的理化性能检测 复合材料的大体观:通过冷冻干燥法制备的复合支架呈乳黄色,海绵样,多孔结构,孔分布较均匀,孔径大小不等,可见有的孔与孔之间相通,质地硬脆,材料可被修剪成任意形态、大小,可塑性较理想(图1)。扫描电镜下,可见复合材料有较好的相互贯通的窝洞结构,孔径在100-300 μm之间,形态不规则(图2)。 复合材料的孔隙率:不同比例壳聚糖、聚乳酸所制备的复合支架材料中,聚乳酸/壳聚糖2∶3组孔隙率最高,其次为聚乳酸/壳聚糖1∶1组,再次为聚乳酸/壳聚糖1:4组和聚乳酸/壳聚糖3∶2组,聚乳酸/壳聚糖4∶1组孔隙率最低,聚乳酸/壳聚糖2∶3组孔隙率高于其余各组(P < 0.05),见表1。 复合材料的机械强度:聚乳酸/壳聚糖4∶1组压缩强度最低,聚乳酸/壳聚糖1∶4组压缩强度最高,聚乳酸/壳聚糖2∶3组次之,两者均高于其余各组(P < 0.05),但聚乳 酸/壳聚糖2∶3组与聚乳酸/壳聚糖1∶4组压缩强度无差异(P > 0.05),其余各组间比较亦无差异(P > 0.05),见表1。 聚乳酸/壳聚糖2∶3组及聚乳酸/壳聚糖1∶4组的机械强度优于其余各组,此外,聚乳酸/壳聚糖2∶3组的孔隙率亦优于其余各组,因此,综合考虑,将聚乳酸/壳聚糖2∶3组选为最优配比组,作为支架材料用于后续实验中。"
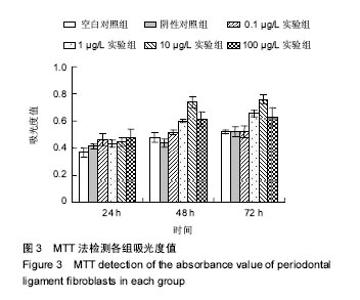
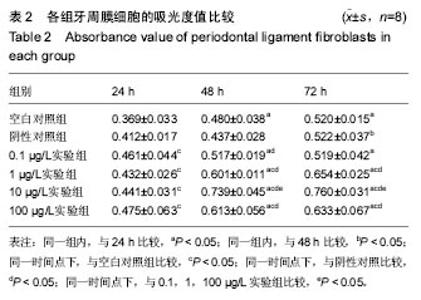
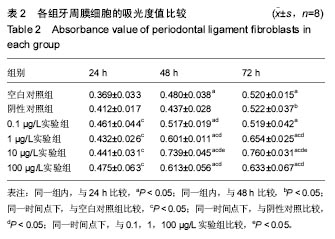
2.2 含bFGF复合支架的毒性实验 MTT比色法检测吸光度值:不同浸提液作用不同时间后的MTT检测结果见图3。结果表明,随着培养时间的增长,各组A值逐渐增高:①组内比较:各实验组组内48 h与72 h A值比较无差异(P > 0.05),其余时间点两两比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);阴性对照组组内24 h与48 hA值比较无差异(P > 0.05),其余时间点两两比较差异有显著性意义;空白对照组组内48 h与72 h的A值比较无差异(P > 0.05),其余时间点两两比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②组间比较:培养24 h时,各实验组A值均高于空白对照组(P < 0.05),阴性对照组与空白对照组A值比较无差异(P > 0.05),各实验组A值与阴性对照组无差异(P > 0.05);培养48,72 h时,阴性对照组、0.1 µg/L实验组A值与空白对照组无差异(P > 0.05),其余各组A值均高于空白对照组(P < 0.05);培养48 h时,各实验组A值高于阴性对照组(P < 0.05);培养72 h时,0.1 µg/L实验组A值与阴性对照组无差异,其余实验组A值高于阴性对照组(P < 0.05);10 µg/L实验组培养48,72 h的A值高于0.1,1,100 µg/L实验组 (P < 0.05),见表2。"

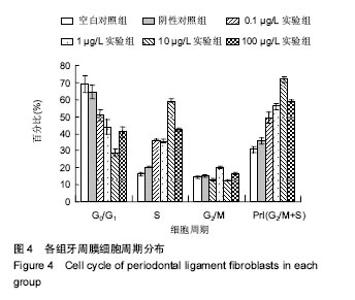
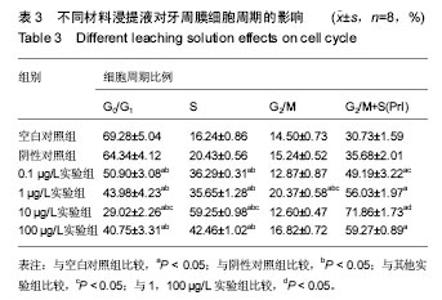
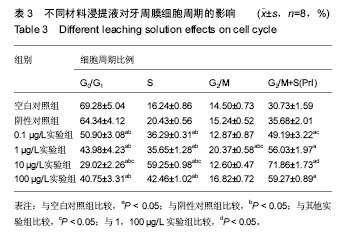
流式细胞仪检测细胞周期:牙周膜细胞在不同浸提液中培养后,细胞周期结果见图4。统计结果表明:①G0/G1期所占百分比:各实验组均低于空白对照组、阴性对照组(P < 0.05),阴性对照组与空白对照组比较无差异(P > 0.05);②S期所占百分比:随着bFGF质量浓度的增加,各实验组S期所占百分比也随之提高,高于空白对照组、阴性对照组(P < 0.05),其中10 µg/L实验组高于其余实验组(P < 0.05),空白对照组与阴性对照组比较无差异(P > 0.05),0.1,1,100 µg/L实验组间两两比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③G2/M期所占百分比:1 µg/L实验组高于其余各组(P < 0.05),其余组间两两比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④能够反映细胞增殖活力的PrI指数(G2/M+S):各实验组明显高于空白对照组、阴性对照组(P < 0.05),阴性对照组与空白对照组比较无差异(P > 0.05),1,10,100 µg/L实验组高于0.1 µg/L实验组(P < 0.05),10 µg/L实验组高于1,100 µg/L实验组(P < 0.05),1,100 µg/L实验组比较无差异,见表3。"

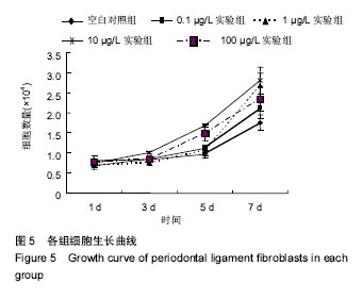
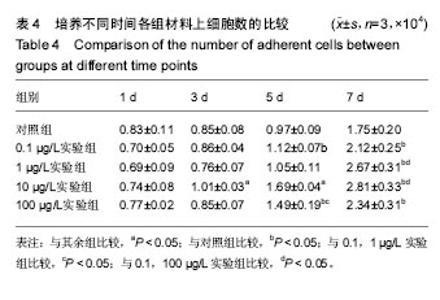
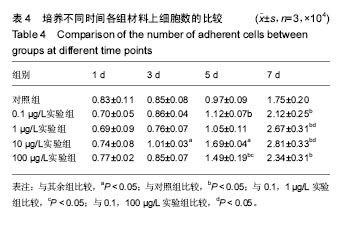
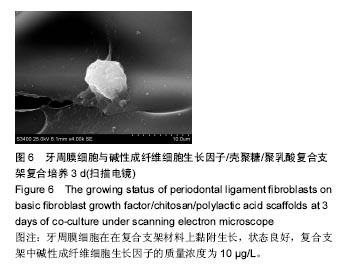
2.3 含bFGF复合材料的生物相容性 细胞生长曲线:各组细胞-材料的生长曲线见图5。培养1 d时,各组之间细胞数量比较无差异(P > 0.05);培养 3 d时,各组细胞数量较1 d时都有增长,10 µg/L实验组高于其余各组(P < 0.05),其余组间两两比较差异无显著性意义;培养5 d时,各组细胞生长状态依然良好,数量均有增长,10 µg/L实验组细胞数量仍高于其余各组(P < 0.05),0.1,100 µg/L实验组细胞数量高于对照组(P < 0.05),100 µg/L实验组高于0.1,1 µg/L实验组(P < 0.05),其余组间两两比较差异无显著性意义;培养7 d时,各实验组细胞数量较1 d时已基本翻至4倍,各实验组细胞数量高于对照组(P < 0.05),1,10 µg/L实验组高于0.1,100 µg/L实验组(P < 0.05),其余组间两两比较差异无显著性意义,见表4。 细胞-材料复合培养的扫描电镜观察:经以上实验, 10 µg/L实验组更有利于牙周膜细胞的生长。牙周膜细胞在10 µg/L实验组支架上培养3 d后,扫描电镜下观察见细胞在支架材料上已黏附生长,状态良好(图6)。"

| [1]涂小丽,刘宏伟.骨髓基质细胞-牙根-珊瑚羟基磷灰石复合体体内再植的初步观察[J].实用口腔学杂志,2006, 22(1):45-47.[2]Zhang Y,Cheng X,Wang J et al.Novel chitosan/collagen scaffold conta-ining transforming growth factor-beta1 DNA for periodontal tissue engineering.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2006;344(1):362-369.[3]El-Sherbiny IM,Yacoub MH.Hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering: Progress and challenges.Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2013;2013(3):316-342.[4]安世昌.复合壳聚糖纳米微球PLGA/nHA缓释载体系统的制备及其对蛋白类药物缓释作用的实验研究[D].青岛大学,2011.[5]姚子昂,吴海歌,韩宝芹,等.不同脱乙酰度对壳聚糖膜与角膜基质细胞相容性的影响[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2006,23(4):800-804.[6]徐晓龙.精氨酸-壳聚糖/DNA纳米粒控释PELA微球的制备及其成骨诱导效能的实验研究[D].南方医科大学,2016.[7]涂浩.聚乳酸/壳聚糖复合膜的制备及神经营养因子检测方法研究[D].武汉理工大学,2006.[8]王建华,李学敏,陶晓军,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子/双层胶原基复合材料制备及其生物安全性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(47):8801-8804.[9]Sonmez AB,Castelnuovo J.Applications of basic fibroblastic growth factor (FGF-2, bFGF) in dentistry.Dent Traumatol. 2014; 30(2):107-111.[10]徐文峰,廖晓玲.碳纤维/聚乳酸/壳聚糖三元多孔复合支架材料的制备及评价[J].材料导报:研究篇,2010,24(12):114-117.[11]Zhang R,Ma PX.Poly ( alpha- hydroxyl acids )/ hydroxyapatite porous composites for bone – tissue engineering I Preparation and morphology.J Biomed Mater Res.1999;44(4):446-455.[12]Guilak F,Butler DL,Goldstein SA,et al.Biomechanics and mechanobiology in functional tissue engineering.J Biomech. 2014;47(9):1933-1940.[13]Iwata T,Yamato M,Ishikawa I,et al.Tissue engineering in periodontal tissue.Anat Rec (Hoboken).2014; 297(1):16-25.[14]Ivanovski S,Vaquette C,Gronthos S,et al.Multiphasic scaffolds for periodontal tissue engineering.J Dent Res. 2014;93(12): 1212-1221.[15]苗雷英,孙卫斌.牙周组织工程研究进展[J].医学研究生学报, 2016, 29(1):3-9.[16]Betz MW,Yeatts AB,Richbourg WJ,et al.Macroporous hydrogels upregulate osteogenic signal expression and promote bone regeneration.Biomacromolecules. 2010;11(5):1160-1168.[17]Dutta RC,Dey M,Dutta AK,et al.Competent processing techniques for scaffolds in tissue engineering.Biotechnol Adv. 2017;35(2):240-250.[18]郭睿,农晓琳.复合支架材料在口腔骨组织工程领域的研究与进展[J].口腔生物医学,2012,3(3):155-159.[19]史晨楠,刘佳,王峰,等.同轴静电纺丝法制备OPG-PLA /壳聚糖纳米纤维膜及相关性能研究[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2017,27(3): 141-144.[20]Magalhães J,Lebourg M,Deplaine H,et al.Effect of the physicochemical properties of pure or chitosan-coated poly(L-lactic acid)scaffolds on the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from osteoarthritic patients.Tissue Eng Part A.2015;21(3-4):716-728.[21]Ji Y,Wang M, Liu W,et al.Chitosan/nHAC/PLGA microsphere vehicle for sustained release of rhBMP-2 and its derived synthetic oligopeptide for bone regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A.2017;105(6):1593-1606.[22]许尧祥,李亚莉,陈立强,等.壳聚糖微球/纳米羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸复合支架制备及其蛋白缓释效果:与单纯纳米羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸支架、壳聚糖微球的比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2010,14(3):452-456.[23]Mas N,Galiana I,Hurtado S,et al.Enhanced antifungal efficacy of tebuconazole using gated p H-driven mesoporous nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine.2014;9:2597-2606.[24]Fortino VR,Chen RS,Pelaez D,et al.Neurogenesis of neural crest-derived periodontal ligament stem cells by EGF and bFGF.J Cell Physiol.2014;229(4):479-488.[25]Wodewotzky TI,Lima-Neto JF,Pereira-Júnior OC,et al.In vitro cultivation of canine multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells on collagen membranes treated with hyaluronic acid for cell therapy and tissue regeneration.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012;45(12): 1157-1162.[26]VandeVord PJ,Matthew HW,DeSilva SP,et al.Evaluation of the biocompatibility of a chitosan scaffold in mice.J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;59(3):585-590.[27]曹宇,王莉莉.血管内皮细胞生长因子与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子联合应用对鼠牙周膜成纤维细胞增殖与碱性磷酸酶活性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(4):580-585. |
| [1] | Le Guoping, Zhang Ming, Xi Licheng, Luo Hanwen. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of vancomycin hydrochloride@polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer-chitosan-hyaluronic acid composite sustained-release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 528-534. |
| [2] | Ye Xiangling, Xia Yuanjun, Wang Boqun, Kang Zhengyang, Wu Bin. Function on 3D printing poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/calcium sulfate hemihydrate scaffold integrated chitosan hydrogel coating [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1574-1581. |
| [3] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [4] | Zhang Zhiwen, Huang Yuliang, Zhang Lixuan, Wang Xiaofeng, Chen Ruixiong. Acellular bone matrix/chitosan scaffold combined with basic fibroblast growth factor for repairing bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5439-5444. |
| [5] | Li Rui. Biological characteristics of hydroxyapatite/chitosan combined with metformin for bone defect in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(28): 4460-4464. |
| [6] | Yang Menglu, Zhang Na, Wang Fangyuan, Liu Jianguo. Application of chitosan in nano drug delivery system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(28): 4546-4552. |
| [7] | Li Xinping, Cui Qiuju, Zeng Shuguang, Ran Gaoying, Zhang Zhaoqiang, Liu Xianwen, Fang Wei, Xu Shuaimei. Effect of modification of β-tricalcium phosphate/chitosan hydrogel on growth and mineralization of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3493-3499. |
| [8] | Chen Siyu, Li Yannan, Xie Liying, Liu Siqi, Fan Yurong, Fang Changxing, Zhang Xin, Quan Jiayu, Zuo Lin. Thermosensitive chitosan-collagen composite hydrogel loaded with basic fibroblast growth factor retards ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2472-2478. |
| [9] | Liu Feng, Zhang Yu, Wang Yanli, Luo Wei, Han Chaoshan, Li Yangxin. Application of temperature-sensitive chitosan hydrogel encapsulated exosomes in ischemic diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2479-2487. |
| [10] | Li Jie, Xu Jianzhen, Hu Ping, Lei Qiqi, Zhang Wenning, Ao Ningjian . Preparation and performance evaluation of carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized glucomannan/Panax notoginseng compound sponge dressing for chronic wound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2528-2534. |
| [11] | Feng Xiaoxia, Hou Weiwei, Jin Xiaoting, Wang Xinhua. Construction of periodontal biomimetic membrane with electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibers and electrosprayed chitosan microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 511-516. |
| [12] | Li Li, Ma Li, Li He. Preparation and characterization of magnetic chitosan microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 577-582. |
| [13] | Liu Haiyan, Hu Yang, Wu Xiuping, Pan Haobo, Jing Xuan. Chitosan-based polysaccharide biomaterial for prevention and treatment of oral diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 631-636. |
| [14] | Liao Jian, Huang Xiaolin, Huo Hua, Zhou Qian, Cheng Yuting, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Yang Tongjing, Liao Yunmao, Liang Xing. Effects of calcined bone/chitosan composite materials on proliferation and adhesion in osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5447-5453. |
| [15] | Fang Yulu, Yi Bingcheng, Shen Yanbing, Tang Han, Zhang Yanzhong. Potential of corn husk fibers reinforced chitosan-based hydrogels in cartilage tissue engineering scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5493-5501. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||