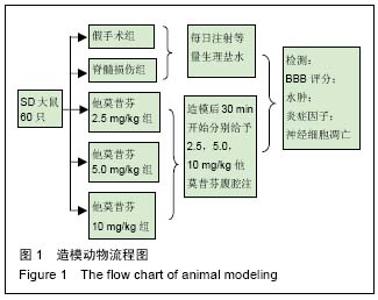
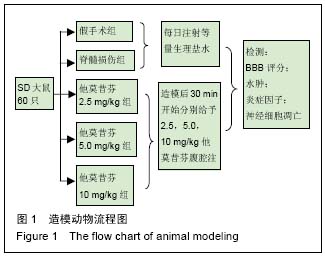
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (51): 7710-7716.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.51.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Neuroprotective effect of tamoxifen in a model rat with aucte spinal cord injury
Huang Wei
- Renhe Hospital of China Three Gorges University, Yichang 443001, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2016-11-08Online:2016-12-09Published:2016-12-09 -
About author:Huang Wei, Master, Associate chief physician, Renhe Hospital of China Three Gorges University, Yichang 443001, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Wei. Neuroprotective effect of tamoxifen in a model rat with aucte spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(51): 7710-7716.
share this article
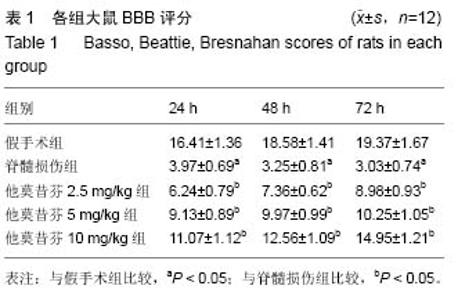
2.2 模型更接近人类 Allen在1911年创造了垂直打击脊髓用于建立脊髓损伤模型的方法。由于此法很接近于人类脊髓损伤发生过程,临床相关性好。模型的特点是:模拟人类脊髓受损的过程,临床相似度高;可以人为调整致伤的部位和范围。硬膜具有完整性,保证无外源性成分侵入,防止脑脊液外漏。可以说此模型是当前与临床脊髓损伤相关性最好的造模方式[14]。 2.3 他莫昔芬对大鼠后肢运动功能的影响 见表1。与假手术组比较,脊髓损伤组大鼠下肢运动功能明显下降,评分降低。然而,经他莫昔芬2.5,5.0,10 mg/kg治疗后,下肢运动功能得到明显提升,且随着治疗时间的延长,药物浓度的加大,评分升高,呈现剂量-时间依赖关系。提示他莫昔芬可有效提高脊髓损伤大鼠下肢运动功能。"
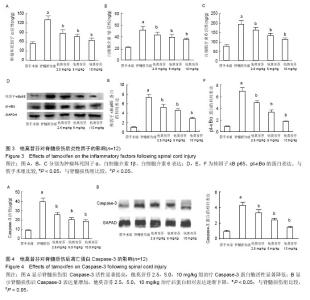
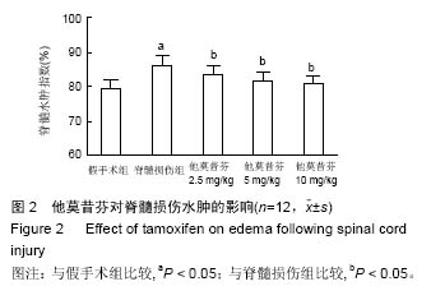
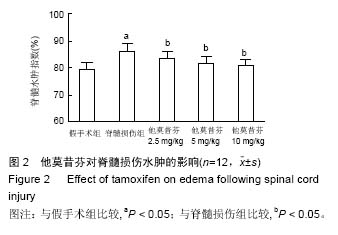
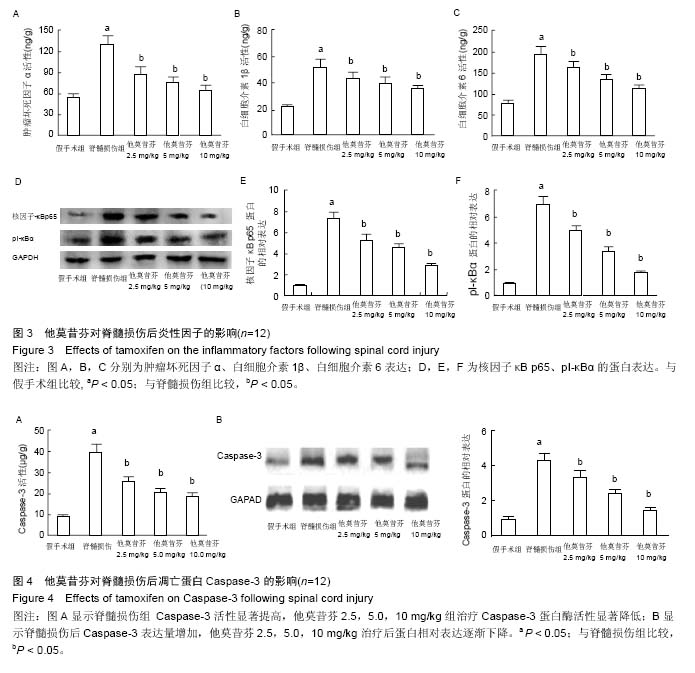
2.5 他莫昔芬对脊髓损伤中炎症因子的影响 术后72 h,损伤脊髓中炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6活性明显提高(P < 0.05),而经过他莫昔芬2.5,5.0,10 mg/kg治疗后,损伤脊髓中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6活性得到抑制,与假手术组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),他莫昔芬对肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6活性抑制作用呈剂量依赖关系,见图3A。从Western-blot法检测可知,核因子κB p65、pI-κBα的蛋白表达在脊髓损伤后条带明显加深,通过灰度值软件分析,核因子κB p65、pI-κBα的蛋白相对表达得到明显提高(P < 0.05),经过他莫昔芬2.5,5.0,10 mg/kg治疗后,核因子κB p65、pI-κBα的蛋白条带逐渐变浅,蛋白相对表达得到明显抑制(P < 0.05),并呈剂量依赖关系,见图3B。可知他莫昔芬可明显抑制脊髓损伤中的炎症因子的表达,从而发挥神经保护作用。 2.6 他莫昔芬对脊髓损伤中神经细胞凋亡的影响 术后72 h,与假手术组相比,Caspase-3活性在脊髓损伤模型中得到明显提高(P < 0.05),而经过他莫昔芬2.5,5.0,10 mg/kg可明显抑制损伤脊髓中Caspase-3蛋白酶活性(P < 0.05),见图4A。Western-blot法检测结果显示,术后72 h,与假手术组相比,Caspase-3条带灰度加深,提示脊髓损伤后Caspase-3表达量增加,而经过他莫昔芬2.5,5.0,10 mg/kg治疗后Caspase-3条带灰度逐渐变浅,蛋白相对表达逐渐下降(P < 0.05),见图4B。可知他莫昔芬可抑制脊髓损伤中凋亡蛋白的表达,抑制神经细胞凋亡从而发挥神经保护作用。"
| [1] Hausmann ON.Post-traumatic inflammation following spinal cord injury.Spinal Cord.2003;41(7):369-378.[2] Tettenborn B,Hägele-Link S.Spinal Cord Disorders.Eur Neurol.2015,74(3-4):141-146.[3] Kimelberg HK,Feustel PJ,Jin Y,et al.Acute treatment with tamoxifen reduces ischemic damage following middle cerebral artery occlusion.Neuroreport. 2000;11(12):2675-2679.[4] Kimelberg HK,Jin Y,Charniga C,et al.Neuroprotective activity of tamoxifen in permanent focal ischemia.J Neurosurg.2003;99(1):138-142.[5] 韦竑宇,梁立.他莫昔芬对大鼠脊髓损伤后炎性反应及细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国医药导报,2014,11(34):23-26.[6] Lan WB,Lin JH,Chen XW,et al.Overexpressing neuroglobin improves functional recovery by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury.Brain Res. 2014;1562:100-108.[7] Seo JY,Kim YH,Kim JW,et al.Effects of therapeutic hypothermia on apoptosis and autophagy after spinal cord injury in rats.Spine.2015,40(12):883-890.[8] Hagg T,Oudega M.Degenerative and spontaneous regenerative processes after spinal cord injury.J Neurotrauma.2006;23(3-4):264-280.[9] Jiang S,Bendjelloul F,Ballerini P,et al.Guanosine reduces apoptosis and inflammation associated with restoration of function in rats with acute spinal cord injury.Purinergic Signal.2007;3(4):411-421.[10] Choudhary GS,Al-Harbi S,Almasan A.Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis.Methods Mol Biol.2015;1219:1-9.[11] Zhao J,Wang J,Wu J.Roles of cytochrome c,caspase-9, and caspase-3 in pentavalent vanadium-induced neuronalapoptosis.Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi.2014;32(9):664-667.[12] Ravikumar R,Fugaccia I,Scheff SW,et al.Nicotine attenuates morphological deficits in a contusion model of spinal cord injury.J Neurotrauma.2005;22(2): 240-251.[13] Basso DM,Beattie MS,Bresnahan JC,et al.MASCIS evaluation of open field locomotor scores:effects of experience and teamwork on reliability.J Neurotrauma.1996;13(7):343-359.[14] 熊春翔,宗少晖,曾高峰,等.大鼠Allen’s脊髓损伤模型的建立及评价[J].广西医科大学学报,2011,28(2):215-217.[15] Osuka K,Feustel PJ,Mongin AA,et al.Tamoxifen inhibits nitrotyrosine formation after reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat.J Neurochem. 2001; 76(6):1842-1850.[16] Suuronen T,Nuutinen T, Huuskonen J,et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) in microglial cells.Inflamm Res. 2005;54(5):194-203.[17] Salgado IK,Torrado AI,Santiago JM,et al.Tamoxifen and Src kinase inhibitors as neuroprotective/neuroregenerative drugs after spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res.2015;10(3):385-390.[18] Yang T,Wu L,Wang H,et al.Inflammation level after decompression surgery for a rat model of chronic severe spinal cord compression and effects on ischemia-reperfusion injury.Neurol Med Chir.2015; 55(7):578-586.[19] Zhang N,Fang MR,Chen HH,et al.Evaluation of spinal cord injury animal models. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9 (22): 2008-2012.[20] Zhang Z,Zhang YP,Shields LB,et al.Technical comments on rodent spinal cord injuries models. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9 (5): 453-455.[21] Sun X,Ji C,Hu T,et al.Tamoxifen as an effective neuroprotectant against early brain injury and learning deficits induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage: possible involvement of inflammatory signaling.J Neuroinflammation.2013;10:157.[22] Campagnolo DI,Bartlett JA,Keller SE.Influence of neurological level on immune function following spinal cord injure:a review.J Spinal Cord Med.2000; 23(2): 121-128.[23] Cao XJ,Feng SQ,Fu CF,et al.Repair, protection and regeneration of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(12): 1953-1975.[24] Xie JB,Zhang X,Li QH,et al.Inhibition of inflammatory cytokines after early decompression may mediate recovery of neurological function in rats with spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(2): 219-224.[25] Duo Z, He XJ.Advances in mechanisms of treatment for spinal cord injury with lithium.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28(7):679-682.[26] Cooney SJ,Zhao Y,Byrnes KR.Characterization of the expression and inflammatory activity of NADPH oxidase after spinal cord injury.Free Radic Res.2014; 48(8):929-939.[27] Khayrullina G,Bermudez S,Byrnes KR.Inhibition of NOX2 reduces locomotor impairment,inflammation, and oxidative stress after spinal cord injury.J Neuroinflammation.2015;12(1):172.[28] Kesani AK,Urquhart JC,Bedard N,et al.Systemic inflammatory response syndrome in patients with spinal cord injury: does its presence at admission affect patient outcomes?Clinical article.J Neurosurg Spine.2014;21(2):296-302.[29] Rathore KI,Redensek A,David S.Iron homeostasis in astrocytes and microglia is differentially regulated by TNF-αand TNF-β1.Glia.2012;60(5):738-750.[30] Jaworska A,Jamieson LE,Malek K,et al.SERS-based monitoring of the intracellular pH in endothelial cells: the influence of the extracellular environment and tumour necrosis factor-α.Analyst.2015;140(7):2321-9.[31] Lu M,Wang S,Han X,et al.Butein inhibits NF-κB activation and reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells and apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats.Neurosci Lett.2013;542:87-91.[32] Han X,Lu M,Wang S,et al.Targeting IKK/NF-κB pathway reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells and apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2012;511(1):28-32.[33] Henn IH,Bouman L,Schlehe JS,et al.Parkin mediates neuroprotection through activation of IkappaB kinase/nuclear factor-kappaB signaling.J Neurosci. 2007;27(8):1868-1878.[34] Wei HY,Ma X.Tamoxifen reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells,apoptosis and inhibits IKK/NF-κB pathway after spinal cord injury in rats.Neurol Sci.2014; 35(11):1763-1768. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [3] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [6] | Xu Yinqin, Shi Hongmei, Wang Guangyi. Effects of Tongbi prescription hot compress combined with acupuncture on mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, in degenerative intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 713-718. |
| [7] | Zhang Wenwen, Jin Songfeng, Zhao Guoliang, Gong Lihong. Mechanism by which Wenban Decoction reduces homocysteine-induced apoptosis of myocardial microvascular endothelial cells in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 723-728. |
| [8] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [9] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [10] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [11] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [12] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [13] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [14] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [15] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||