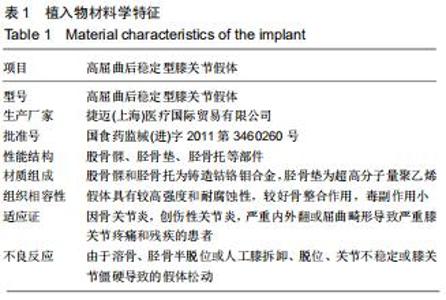
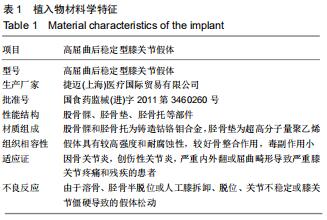
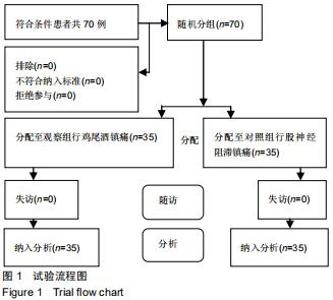
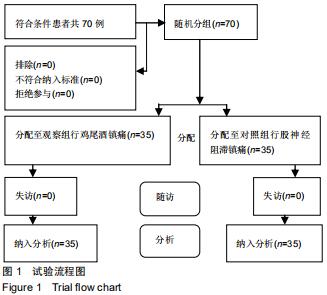
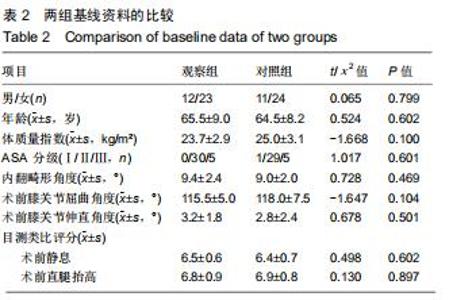
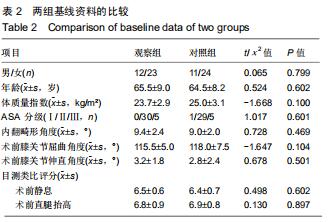
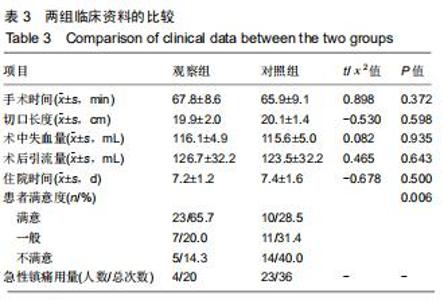
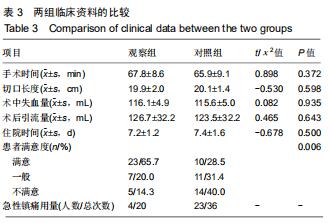
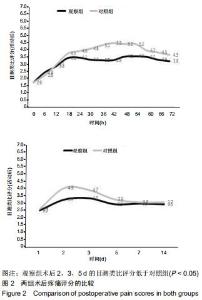
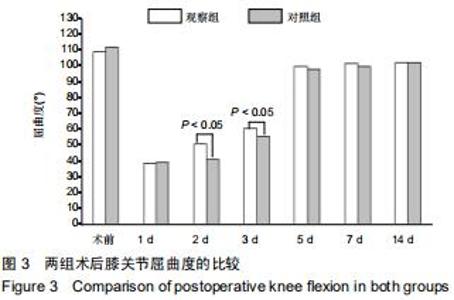
|
[1] LANE NE, BRANDT K, HAWKER G, et al. OARSI-FDA initiative:defining the disease state of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2011;19(5):478-482.
[2] HEIDARI B. Knee osteoarthritis prevalence,risk factors, pathogenesis and features:Part I.Caspian J Intern Med.2011; 2(2):205-212.
[3] ETHGEN O, BRUYERE O, RICHY F, et al. Health-related quality of life in total hip and total knee arthroplasty.A qualitative and systematic review of the literature.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2004;86(5):963-974.
[4] 吕厚山.人工膝关节置换术的进展和现状[J].中华外科杂志, 2004,42(1):30-33.
[5] DORR LD, CHAO L.The emotional state of the patient after total hip and knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2007; 463:7-12.
[6] DENG Z, LI Y, STORM GR, et al. The efficiency and safety of steroid addition to multimodal cocktail periarticular injection in knee joint arthroplasty:a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Sci Rep.2019;9(1):7031.
[7] KOH IJ, CHANG CB, SEO ES, et al. Pain management by periarticular multimodal drug injection after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction:a randomized, controlled study. Arthroscopy.2012;28(5):649-657.
[8] DUELLMAN TJ, GAFFIGAN C, MILBRANDT JC, et al. Multi-modal, pre-emptive analgesia decreases the length of hospital stay following total joint arthroplasty.Orthopedics. 2009;32(3):167.
[9] ILFELD BM, MARIANO ER, GIRARD PJ, et al. A multicenter,randomized,triple-masked,placebo-controlled trial of the effect of ambulatory continuous femoral nerve blocks on discharge-readiness following total knee arthroplasty in patients on general orthopaedic wards.Pain. 2010;150(3): 477-484.
[10] HANNON CP, KEATING TC, LANGE JK, et al.Anesthesia and Analgesia Practices in Total Joint Arthroplasty:A Survey of the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons Membership. J Arthroplasty.2019;34(12):2872-2877
[11] GAN TJ. Poorly controlled postoperative pain: prevalence, consequences,and prevention. J Pain Res.2017;10: 2287-2298.
[12] AYAD S, KHANNA AK, IQBAL SU, et al. Characterisation and monitoring of postoperative respiratory depression:current approaches and future considerations.Br J Anaesth. 2019; 123(3):378-391.
[13] CHAUMERON A, AUDY D, DROLET P, et al. Periarticular injection in knee arthroplasty improves quadriceps function. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2013;471(7):2284-2295.
[14] KOH HJ, KOH IJ, KIM MS, et al. Does Patient Perception Differ Following Adductor Canal Block and Femoral Nerve Block in Total Knee Arthroplasty? A Simultaneous Bilateral Randomized Study.J Arthroplasty.2017;32(6):1856-1861.
[15] FREDRICKSON MJ, KILFOYLE DH. Neurological complication analysis of 1000 ultrasound guided peripheral nerve blocks for elective orthopaedic surgery:a prospective study.Anaesthesia.2009;64(8):836-844.
[16] WANG D, YANG Y, LI Q, et al. Adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block for total knee arthroplasty:a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Sci Rep.2017; 7:40721.
[17] MOGHTADAEI M, FARAHINI H, FAIZ SH, et al. Pain Management for Total Knee Arthroplasty:Single-Injection Femoral Nerve Block versus Local Infiltration Analgesia.Iran Red Crescent Med J.2014;16(1):e13247.
[18] JOHNSON RL, KOPP SL, HEBL JR, et al. Falls and major orthopaedic surgery with peripheral nerve blockade:a systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Anaesth. 2013; 110(4):518-528.
[19] 冯硕,吴居泰,查国春,等.关节腔内注射氨甲环酸对单髁置换术围手术期失血量的影响[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(5): 402-406.
[20] ODERDA GM, GAN TJ, JOHNSON BH, et al. Effect of opioid-related adverse events on outcomes in selected surgical patients.J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother.2013; 27(1):62-70.
[21] BEAUPRE LA, JOHNSTON DB, DIELEMAN S, et al. Impact of a preemptive multimodal analgesia plus femoral nerve blockade protocol on rehabilitation, hospital length of stay, and postoperative analgesia after primary total knee arthroplasty: a controlled clinical pilot study. ScientificWorldJournal.2012;2012:273821.
[22] UESUGI K, KITANO N, KIKUCHI T, et al. Comparison of peripheral nerve block with periarticular injection analgesia after total knee arthroplasty:a randomized,controlled study. Knee.2014;21(4):848-852.
[23] SANDHU S, ZADZILKA JD, NAGEEB E, et al. A Comparison of Pain Management Protocols Following Total Knee Arthroplasty:Femoral Nerve Block versus Periarticular Injection of Liposomal Bupivacaine with an Adductor Canal Block.Surg Technol Int.2019;34:403-408.
[24] KAMPITAK W, TANAVALEE A, NGARMUKOS S, et al. Opioid-Sparing Analgesia and Enhanced Recovery After Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Combined Triple Nerve Blocks With Local Infiltration Analgesia.J Arthroplasty.2019;34(2):295-302.
[25] TALMO CT, KENT SE, FREDETTE AN, et al. Prospective Randomized Trial Comparing Femoral Nerve Block With Intraoperative Local Anesthetic Injection of Liposomal Bupivacaine in Total Knee Arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2018; 33(11):3474-3478.
[26] 贾东林,郭向阳.膝关节置换术后镇痛研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2012,18(4):245-248.
[27] NG FY, NG JK, CHIU KY, et al. Multimodal periarticular injection vs continuous femoral nerve block after total knee arthroplasty:a prospective, crossover, randomized clinical trial.J Arthroplasty.2012;27(6):1234-1238.
[28] 王鹏,李凯,万伟伟,等.胃肠道微创手术后局部浸润麻醉联合氟比洛芬酯静脉镇痛效果的观察[J].腹部外科,2018,31(3):210-213.
[29] KNUDSEN K, BECKMAN SUURKULA M, BLOMBERG S, et al. Central nervous and cardiovascular effects of i.v.infusions of ropivacaine, bupivacaine and placebo in volunteers.Br J Anaesth.1997;78(5):507-514.
[30] MA J, ZHANG W, YAO S. Liposomal bupivacaine infiltration versus femoral nerve block for pain control in total knee arthroplasty:A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg.2016;36(Pt A):44-55.
[31] TOFTDAHL K, NIKOLAJSEN L, HARALDSTED V, et al. Comparison of peri- and intraarticular analgesia with femoral nerve block after total knee arthroplasty:a randomized clinical trial.Acta Orthop.2007;78(2):172-179.
[32] BARRINGTON JW, LOVALD ST, ONG KL, et al. Postoperative Pain After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: Comparison of Local Injection Analgesic Cocktails and the Role of Demographic and Surgical Factors.J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(9 Suppl):288-292.
|