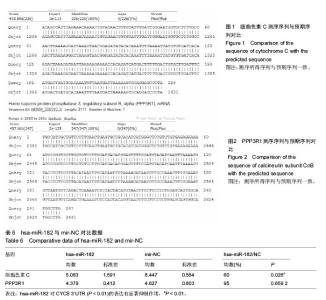
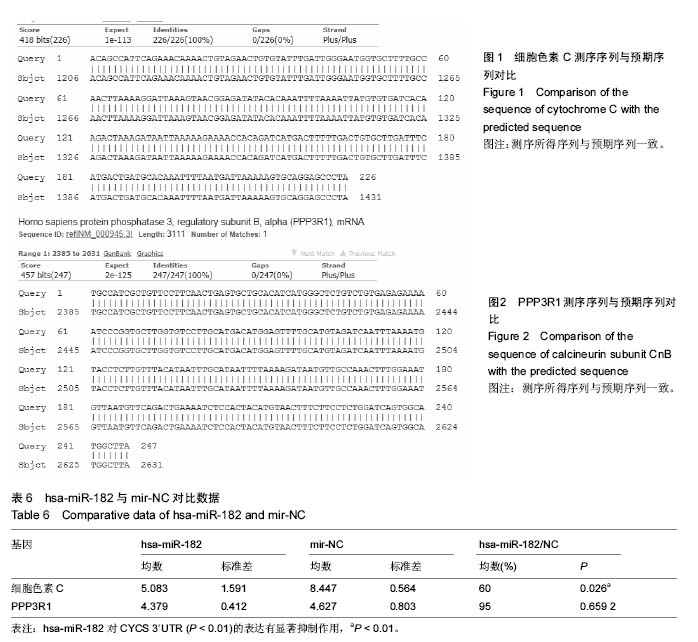
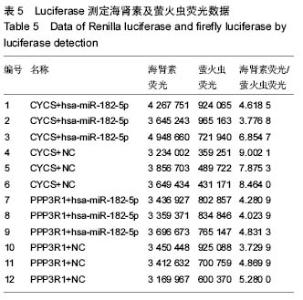
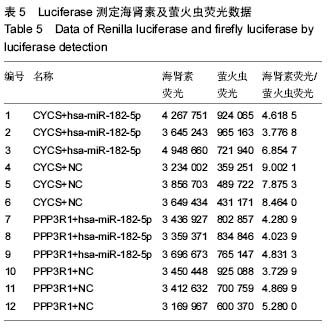
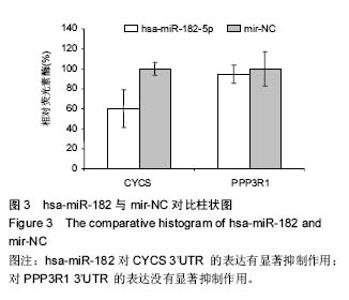
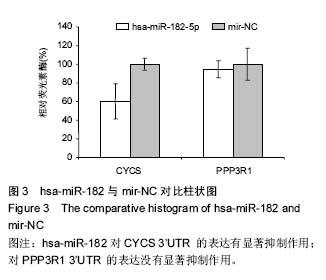
| [1] Wieser S,Horisberger B,Schmidhauser S,et al.Cost of low back pain in Switzerland in 2005.Eur J Health Econ. 2011;12(5):455-467.
[2] Jin K, Sorock GS, Courtney TK. Prevalence of low back pain in three occupational groups in Shanghai, People's Republic of China. J Safety Res.2004;35(1): 23-28.
[3] Takatalo J, Karppinen J, Niinimäki J, et al.Prevalence of Degenerative Imaging Findings in Lumbar Magnetic Resonance Imaging Among Young Adults.Spine.2009; 34(16):1716-1721.
[4] Ambros V.microRNAs: Tiny regulators with great potential. Cell.2001;107(7): 823-826.
[5] Zhao B, Yu Q, Li H, et al.Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in patients with intervertebral disc degeneration.Int J Mol Med.2014;33(1):43-50.
[6] Hüttemann M, Pecina P, Rainbolt M, et al.The multiple functions of cytochrome c and their regulation in life and death decisions of the mammalian cell: From respiration to apoptosis. Mitochondrion.2011;11(3): 369-381.
[7] Riedl SJ, Salvesen GS.The apoptosome: signalling platform of cell death.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(5): 405-413.
[8] Park JB, Kim KW, Han CW, et al.Expression of Fas receptor on disc cells in herniated lumbar disc tissue. Spine.2001;26(2):142-146.
[9] Wang D, Liu M, Song H, et al.Expression of Bax and Caspase-3 and apoptosis in human lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2008;22(4): 421-425.
[10] Haschtmann D, Stoyanov JV, Gédet P,et al.Vertebral endplate trauma induces disc cell apoptosis and promotes organ degeneration in vitro. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(2):289-299.
[11] Wang H, Liu H, Zheng ZM, et al.Role of death receptor, mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum pathways in different stages of degenerative human lumbar disc. Apoptosis. 2011;16(10): 990-1003.
[12] Su Z, Xin S, Xu L,et al.The calcineurin B subunit induces TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) expression via CD11b-NF-kappa B pathway in RAW264.7 macrophages. Biochemical And Biophysical Research Communications.2012; 417(2): 777-783.
[13] Wang HG, Pathan N, Ethell IM,et al.Ca2+-induced apoptosis through calcineurin dephosphorylation of BAD. Science.1999;284(5412): 339-343.
[14] Cho WC, Chow AS, Au JS.Restoration of tumour suppressor hsa-miR-145 inhibits cancer cell growth in lung adenocarcinoma patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Eur J Cancer.2009;45(12): 2197-206.
[15] Guan P, Yin Z, Li X, et al.Meta-analysis of human lung cancer microRNA expression profiling studies comparing cancer tissues with normal tissues. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012;31:54.
[16] Tan X, Qin W, Zhang L, et al.A 5-MicroRNA Signature for Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis and hsa-miR-31 for Prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17(21):6802-6811.
[17] Zheng D, Haddadin S, Wang Y, et al.Plasma microRNAs as novel biomarkers for early detection of lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011;4(6):575-586.
[18] Zhu W, Liu X, He J, et al.Overexpression of members of the microRNA-183 family is a risk factor for lung cancer: A case control study. BMC Cancer. 2011;11: 393.
[19] Zhang Y, Wang X, Wang Z, et al.miR-182 promotes cell growth and invasion by targeting forkhead box F2 transcription factor in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2015;33(5): 2592-2598. |