Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (27): 4083-4089.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.27.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of swimming on high-fat diet-induced obese and obese resistant rats
Wang Qing-fu1, 2, Gan Chun-long3, Yi Xue-jie1
- 1School of Human Sports Science, Shenyang Sport University, Shenyang 110102, Liaoning Province, China
2Qinhuangdao Training Base, General Administration of Sport of China, Qinhuangdao 066004, Hebei Province, China
3Guizhou Institute of Sport Science, Guiyang 550002, Guizhou Province, China
-
Revised:2016-04-05Online:2016-06-30Published:2016-06-30 -
Contact:Yi Xue-jie, M.D., Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Human Sports Science, Shenyang Sport University, Shenyang 110102, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Qing-fu, Master, Assistant researcher, School of Human Sports Science, Shenyang Sport University, Shenyang 110102, Liaoning Province, China; Qinhuangdao Training Base, General Administration of Sport of China, Qinhuangdao 066004, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Excellent Talent Support Program of Colleges and Universities of Liaoning Province, No. WR2013015; the Key Subject Construction Project of Shenyang Sport University, No. XKFX1511
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Qing-fu, Gan Chun-long, Yi Xue-jie. Effects of swimming on high-fat diet-induced obese and obese resistant rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(27): 4083-4089.
share this article
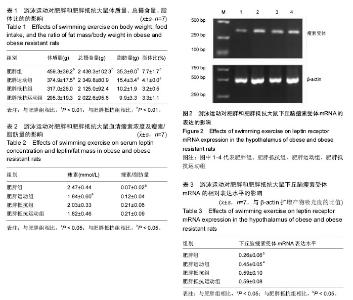
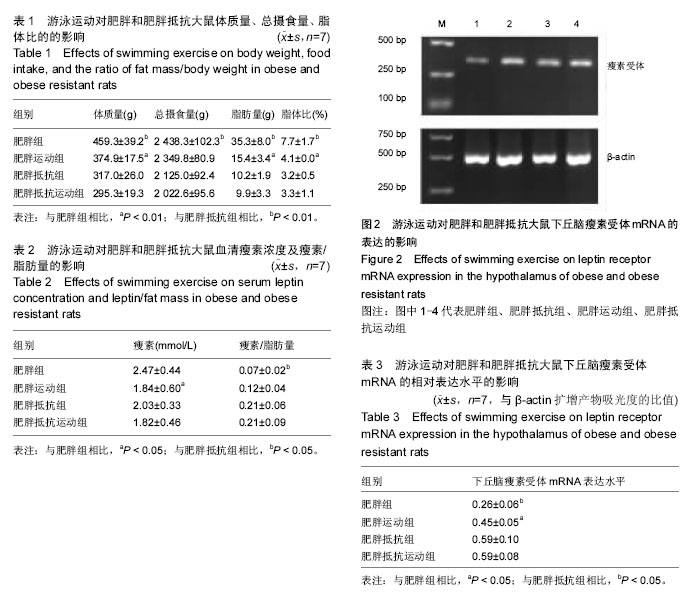
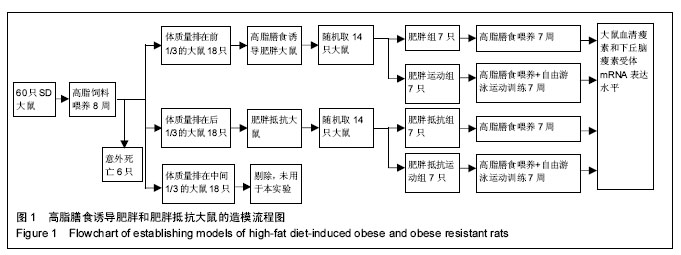
2.1 造模成功动物数量及过程 肥胖组、肥胖运动组、肥胖抵抗组和肥胖抵抗运动组大鼠均进入结果分析。实验流程见图1。 2.2 模型方法的改进及模型稳定性 通过8周高脂膳食喂养建立的肥胖大鼠模型更稳定,与人群中肥胖发生的异质性具有十分相似的特征,有利于肥胖症的研究。 2.3 主要观察结果和次要观察结果 2.3.1 总摄食量、体质量、脂肪量及脂体比 造模7周后,肥胖组大鼠体质量、总摄食量、脂肪量、脂体比显著高于肥胖抵抗组(P < 0.01);与肥胖组相比,肥胖运动组大鼠体质量、脂肪量、脂体比显著下降(P < 0.01);与肥胖抵抗组相比,肥胖抵抗运动组大鼠上述指标无显著变化(表1)。 2.3.2 血清瘦素浓度及瘦素/脂肪量 造模7周后,肥胖组大鼠瘦素/脂肪量比值显著低于肥胖抵抗组(P < 0.05);肥胖运动组大鼠血清瘦素浓度显著低于肥胖组 (P < 0.05);与肥胖抵抗组相比,肥胖抵抗运动组大鼠血清瘦素浓度和瘦素/脂肪量的差异无显著性意义(表2)。 2.3.3 下丘脑瘦素受体mRNA表达水平 与肥胖抵抗组比较,肥胖组大鼠下丘脑瘦素受体的基因表达水平显著下降(P < 0.05);与肥胖组相比,肥胖运动组大鼠下丘脑瘦素受体的基因表达水平显著升高(P < 0.05;图2,表3)。"
| [1] 刘健敏,郑龙,张焕铃,等.肥胖易感及肥胖抵抗动物模型的建立与评价[J].科学技术与工程,2012,12(28):7344- 7346. [2] 蔡滢.食源性肥胖大鼠和肥胖抵抗大鼠下丘脑的蛋白组学研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2011. [3] 张佳琪,王雪,林海青,等.不同健脾中药对饮食诱导肥胖大鼠肥胖程度及胰岛素抵抗的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志, 2015,22(6): 64-68. [4] 刘桂,殷亮,王晓慧,等.高脂饮食诱导的肥胖与肥胖抵抗大鼠肝FAS和ACAT-2的蛋白表达差异[J].上海体育学院学报, 2014,38(6):105-109. [5] 刘春阳,黄徐根.肥胖抵抗现象及其机制研究[J].南京体育学院学报(自然科学版),2014,13(4):20-22. [6] 王欢,李宛真,汪弋力,等.高脂饮食诱导的肥胖及肥胖抵抗小鼠肠道菌群元基因组的比较研究[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2014,35(2):240-244. [7] Wang X, Choi JW, Joo JI, et al. Differential expression of liver proteins between obesity-prone and obesity-resistant rats in response to a high-fat diet. Br J Nutr. 2011;106(4): 612-626. [8] Li J, Wang S, Zhang N, et al. Effects of changing dietary fat content on plasma gut hormone concentrations in diet-induced obese and diet-resistant rats. Br J Nutr. 2011;105(6):879-886. [9] Cottone P, Sabino V, Nagy TR, et al. Centrally administered urocortin 2 decreases gorging on high-fat diet in both diet-induced obesity-prone and -resistant rats. Int J Obes (Lond). 2013;37(12):1515-1523. [10] Balasubramanian P, Jagannathan L, Mahaley RE, et al. High fat diet affects reproductive functions in female diet-induced obese and dietary resistant rats. J Neuroendocrinol. 2012; 24(5):748-755. [11] Thanos PK, Cho J, Kim R, et al. Bromocriptine increased operant responding for high fat food but decreased chow intake in both obesity-prone and resistant rats. Behav Brain Res. 2011;217(1):165-170. [12] Smith PM, Hindmarch CC, Murphy D, et al. AT1 receptor blockade alters nutritional and biometric development in obesity-resistant and obesity-prone rats submitted to a high fat diet. Front Psychol. 2014; 5:832. [13] Cifani C, Micioni Di Bonaventura MV, Pucci M, et al. Regulation of hypothalamic neuropeptides gene expression in diet induced obesity resistant rats: possible targets for obesity prediction? Front Neurosci. 2015;9:187. [14] Ma W, Yuan L, Yu H, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in the brain of diet-induced obese rats but not in diet-resistant rats. Life Sci. 2014; 110(2):53-60. [15] Wang B, Sun J, Ma Y, et al. Increased oxidative stress and the apoptosis of regulatory T cells in obese mice but not resistant mice in response to a high-fat diet. Cell Immunol. 2014;288(1-2):39-46. [16] Stoffel W, Hammels I, Jenke B, et al. Obesity resistance and deregulation of lipogenesis in Δ6-fatty acid desaturase (FADS2) deficiency. EMBO Rep. 2014; 15(1):110-120. [17] Tateishi K, Okada Y, Kallin EM, et al. Role of Jhdm2a in regulating metabolic gene expression and obesity resistance. Nature. 2009;458(7239):757-761. [18] Friedlander NJ, Burhans MS, Ade L, et al. Global deletion of lipocalin 2 does not reverse high-fat diet-induced obesity resistance in stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 skin-specific knockout mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;445(3):578-583. [19] Pierce WD, Diane A, Heth CD, et al. Evolution and obesity: resistance of obese-prone rats to a challenge of food restriction and wheel running. Int J Obes (Lond). 2010;34(3): 589-592. [20] Kus V, Prazak T, Brauner P, et al. Induction of muscle thermogenesis by high-fat diet in mice: association with obesity-resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008;295(2):E356-367. [21] Morita M, Oike Y, Nagashima T, et al. Obesity resistance and increased hepatic expression of catabolism-related mRNAs in Cnot3+/- mice. EMBO J. 2011;30(22):4678-4691. [22] Marcelin G, Liu SM, Schwartz GJ, et al. Identification of a loss-of-function mutation in Ube2l6 associated with obesity resistance. Diabetes. 2013;62(8):2784-2795. [23] Tucker K, Overton JM, Fadool DA. Diet-induced obesity resistance of Kv1.3-/- mice is olfactory bulb dependent. J Neuroendocrinol. 2012;24(8):1087-1095. [24] Kotz C, Nixon J, Butterick T, et al. Brain orexin promotes obesity resistance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012; 1264:72-86. [25] Lou MF, Shen W, Fu RS, et al. Maternal dietary protein supplement confers long-term sex-specific beneficial consequences of obesity resistance and glucose tolerance to the offspring in Brandt's voles. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2015;182:38-44. [26] Butterick TA, Billington CJ, Kotz CM, et al. Orexin: pathways to obesity resistance? Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2013;14(4):357-364. [27] Teske JA, Billington CJ, Kotz CM. Mechanisms underlying obesity resistance associated with high spontaneous physical activity. Neuroscience. 2014; 256:91-100. [28] 徐凯旋,郁婷燕,管磊剑,等.下丘脑中瘦素/瘦素受体的促发育作用被干扰引起成年期肥胖:肥胖新机制[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2015,19(9):949-954. [29] 李红辉,唐宁,曾婷,等.瘦素受体基因多态性与壮族儿童单纯性肥胖的相关性研究[J].中国儿童保健杂志, 2013,21 (11):1148-1150. [30] 薛琨,郭红卫,万文涛,等.中国学龄儿童瘦素受体基因SNP rs1137101多态分布与肥胖相关性研究[J].营养学报, 2012, 34(6):536-539. [31] 姜萍,姜月华.运脾与化湿祛痰药物对饮食诱导肥胖大鼠肥胖程度及脂肪激素、瘦素抵抗的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2014,34(8):997-1001. [32] 姜萍,宋钦兰.升清中药对饮食诱导肥胖大鼠瘦素抵抗的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2014,21(8):60-62. [33] 田雷,陈钢.运动对高脂饮食大鼠下丘脑SOCS-3和BDNF以及瘦素抵抗的影响[J].广州体育学院学报,2013,33(6): 85-89. [34] 张琛琛,司虎克.营养和运动综合治疗对单纯性肥胖儿童血脂水平、瘦素抵抗以及炎症反应的影响[J].海南医学院学报,2014,20(12):1696-1698. [35] 甘春龙,王庆福,赵大林,等.有氧运动对高脂膳食肥胖和肥胖抵抗大鼠胰腺神经肽Y受体mRNA表达的影响[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2012,31(5):68-72. [36] Levin BE. Arcuate NPY neurons and energy homeostasis in diet-induced obese and resistant rats. Am J Physiol. 1999;276(2 Pt 2):R382-387. [37] 杜晓平,衣雪洁,曹师承.长期有氧训练对高脂膳食肥胖和肥胖抵抗大鼠骨骼肌胰岛素受体mRNA表达的影响[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2010,29(5):53-56. [38] 刘倩倩,肖国强.游泳运动对肥胖及肥胖抵抗型NAFLD大鼠干预效果的对比研究[J].体育学刊,2013,20(1):129-134. [39] Watson PM, Commins SP, Beiler RJ, et al. Differential regulation of leptin expression and function in A/J vs. C57BL/6J mice during diet-induced obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000;279(2):E356-365. [40] 甄静,张蕴琨.运动与瘦素的研究进展[J].南京体育学院学报(自然科学版),2014,13(2):46-51. [41] 王红霞,王茹,娄淑杰.调节性T细胞与瘦素在运动抗炎机制中的作用研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2013,32(9): 840-843. [42] Kohara K, Uemura K, Takata Y, et al. Postprandial hypotension: evaluation by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Am J Hypertens. 1998;11(11 Pt 1):1358- 1363. [43] 汪毅,周琨,李松波,等.限制饮食对大鼠血清瘦素和可溶性瘦素受体影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2012,35(2):46-49. [44] 李玉莲,战新梅,王德华.瘦素与运动的关系及其在运动训练监测中的应用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2006,25(3): 327-331. [45] 刘文学.有氧运动对老年肥胖女性血清瘦素、脂联素水平的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,(12):3431-3432. [46] 刘琳.不同音乐节奏的健美操对超重女大学生血清瘦素、瘦素蛋白表达的影响[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2014,33(4): 77-80. [47] Lepercq J, Cauzac M, Lahlou N, et al. Overexpression of placental leptin in diabetic pregnancy: a critical role for insulin. Diabetes. 1998;47(5):847-850. [48] 孔兆伟,傅浩坚,周碧珠,等.8周及12周游泳训练对大鼠血清瘦素水平的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2003,22(5): 511-514. [49] 胡振东,王德华.自愿转轮运动条件下雌性长爪沙鼠的体重、能量代谢和血清瘦素含量的变化[J].中国运动医学杂志,2007,26(5):605-608. [50] Hickey MS, Houmard JA, Considine RV, et al. Gender-dependent effects of exercise training on serum leptin levels in humans. Am J Physiol. 1997; 272(4 Pt 1):E562-566. [51] Zaccaria M, Ermolao A, Brugin E, et al. Plasma leptin and energy expenditure during prolonged, moderate intensity, treadmill exercise. J Endocrinol Invest. 2013; 36(6):396-401. [52] ] Plinta R, Olszanecka-Glinianowicz M, Drosdzol-Cop A, et al. The effect of three-month pre-season preparatory period and short-term exercise on plasma leptin, adiponectin, visfatin, and ghrelin levels in young female handball and basketball players. J Endocrinol Invest. 2012;35(6):595-601. [53] Kastin AJ, Pan W. Dynamic regulation of leptin entry into brain by the blood-brain barrier. Regul Pept. 2000; 92(1-3):37-43. [54] Kang S, Kim KB, Shin KO. Exercise training improves leptin sensitivity in peripheral tissue of obese rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;435(3):454-459. [55] 李琳燕,衣雪洁.运动对饮食性肥胖大鼠脂肪细胞瘦素受体基因表达的影响[J].山东体育学院学报,2008,24(4):64-67. [56] 宫华,高海宁,常波.运动和药物干预对2型糖尿病大鼠骨髓瘦素及其受体蛋白表达的影响[J].沈阳体育学院学报, 2014,33(4):67-71. [57] Kimura M, Tateishi N, Shiota T, et al. Long-term exercise down-regulates leptin receptor mRNA in the arcuate nucleus. Neuroreport. 2004;15(4):713-716. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [12] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| [13] | Bi Qingwei, Liu Chengpu, Li Yan, Zhao Wenwen, Han Mei. Structure analysis of platelet-rich fibrin derived from two centrifugation procedures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3534-3539. |
| [14] | Tian Guangzhao, Yang Zhen, Zha Kangkang, Sun Zhiqiang, Li Xu, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Liu Shuyun. Regulatory effect of decellularized cartilage matrix on macrophage polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3545-3550. |
| [15] | Zhou Anqi, Tang Yufei, Wu Bingfeng, Xiang Lin. Designing of periosteum tissue engineering: combination of generality and individuality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||