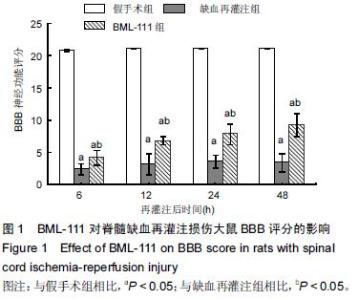
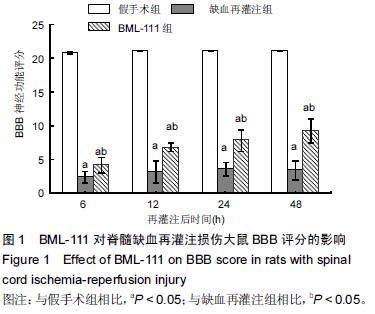
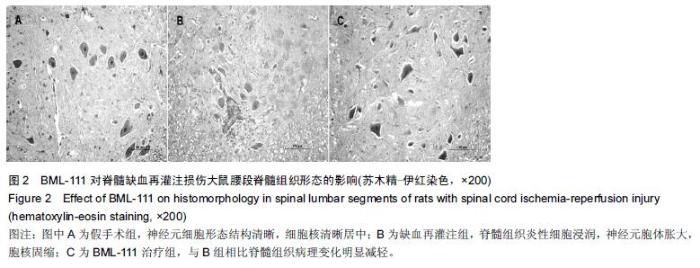
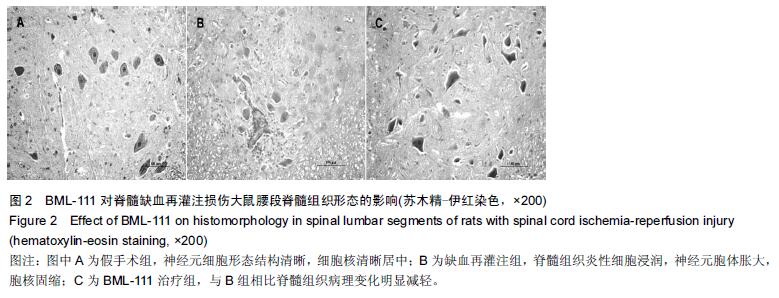
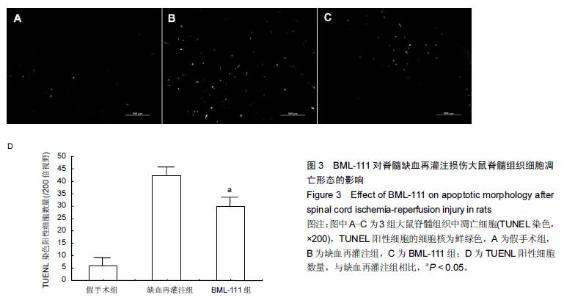
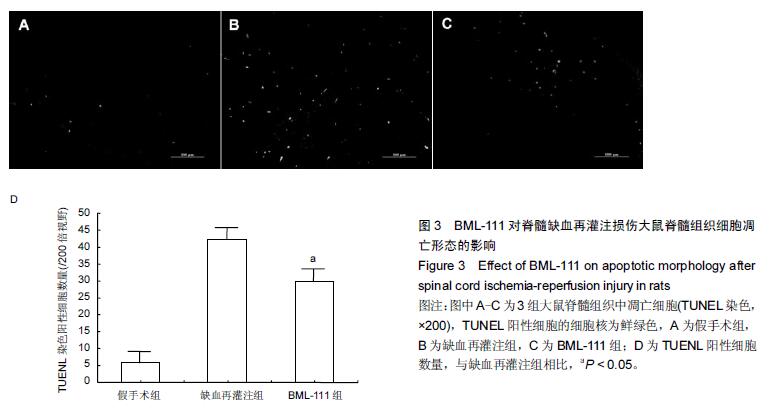
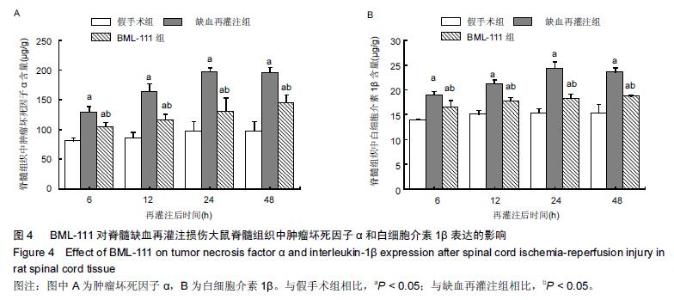
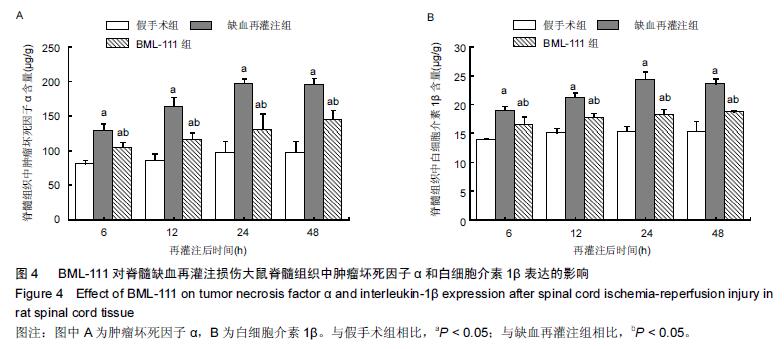
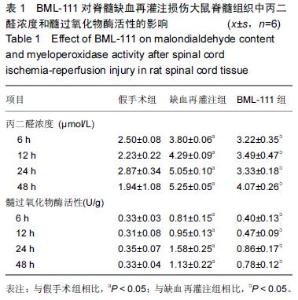
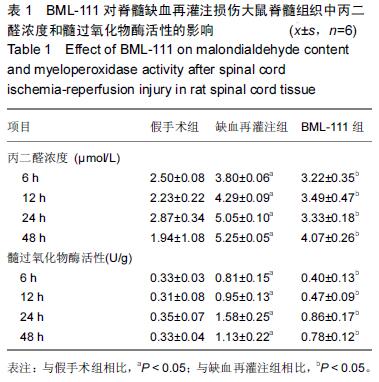
| [1] Zhang Q, Huang C, Meng B, et al. Acute effect of Ghrelin on ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat spinal cord. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(8):9864-9876. [2] Manzanero S, Santro T, Arumugam TV. Neuronal oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke: sources and contribution to cell injury. Neurochem Int. 2013;62(5): 712-718. [3] Li XQ, Lv HW, Tan WF, et al. Role of the TLR4 pathway in blood-spinal cord barrier dysfunction during the bimodal stage after ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2014;11:62. [4] Li XQ, Lv HW, Wang ZL, et al. MiR-27a ameliorates inflammatory damage to the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord ischemia: reperfusion injury in rats by downregulating TICAM-2 of the TLR4 signaling pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:25. [5] Wolfrum S, Nienstedt J, Heidbreder M, et al. Calcitonin gene related peptide mediates cardioprotection by remote preconditioning. Regul Pept. 2005;127(1-3):217-224. [6] Yamazaki M, Mochizuki M, Ikeda Y, et al. Clinical results of surgery for thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: operative indication of posterior decompression with instrumented fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31(13):1452-1460. [7] Wada T, Yao H, Miyamoto T, et al. Prevention and detection of spinal cord injury during thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic repairs. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;72(1):80-84; discussion 85. [8] Gewirtz A. Lipoxin analogs: novel anti-inflammatory mediators. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005;6(11): 1112-1115. [9] Gilroy DW, Lawrence T, Perretti M, et al. Inflammatory resolution: new opportunities for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(5):401-416. [10] Serhan CN, Chiang N, Van Dyke TE. Resolving inflammation: dual anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution lipid mediators. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(5):349-361. [11] Petasis NA, Akritopoulou-Zanze I, Fokin VV, et al. Design, synthesis and bioactions of novel stable mimetics of lipoxins and aspirin-triggered lipoxins. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005;73(3-4):301-321. [12] Celic T, Španjol J, Bobinac M, et al. Mn porphyrin-based SOD mimic, MnTnHex-2-PyP(5+), and non-SOD mimic, MnTBAP(3-), suppressed rat spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury via NF-κB pathways. Free Radic Res. 2014;48(12):1426-1442. [13] Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(1):1-21. [14] 于清波,邓剑锋,高大新,等.膝骨关节炎关节液中丙二醛、超氧化物歧化酶在玻璃酸钠注射前后的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(46):7528-7532. [15] 潘峰, 祝成亮,陶凤华,等.他克莫司后处理对缺血再灌注脊髓组织炎性反应的抑制作用[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2014,11(2):1-4. [16] Zivin JA, DeGirolami U. Spinal cord infarction: a highly reproducible stroke model. Stroke. 1980;11(2):200-202. [17] Picone AL, Green RM, Ricotta JR, et al. Spinal cord ischemia following operations on the abdominal aorta. J Vasc Surg. 1986;3(1):94-103. [18] Walters BC, Hadley MN, Hurlbert RJ, et al. Guidelines for the management of acute cervical spine and spinal cord injuries: 2013 update. Neurosurgery. 2013; 60 Suppl 1:82-91. [19] Bannenberg G, Serhan CN. Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators in the inflammatory response: An update. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1801(12):1260-1273. [20] Lee TH, Lympany P, Crea AE, et al. Inhibition of leukotriene B4-induced neutrophil migration by lipoxin A4: structure-function relationships. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991;180(3):1416-1421. [21] Li HB, Wang GZ, Gong J, et al. BML-111 attenuates hemorrhagic shock-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in rats. J Surg Res. 2013;183(2):710-719. [22] Lopez MS, Dempsey RJ, Vemuganti R. Resveratrol neuroprotection in stroke and traumatic CNS injury. Neurochem Int. 2015;89:75-82. [23] Gong G, Yuan LB, Hu L, et al. Glycyrrhizin attenuates rat ischemic spinal cord injury by suppressing inflammatory cytokines and HMGB1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012;33(1):11-18. [24] Izumi B, Nakasa T, Tanaka N, et al. MicroRNA-223 expression in neutrophils in the early phase of secondary damage after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett. 2011;492(2):114-118. |