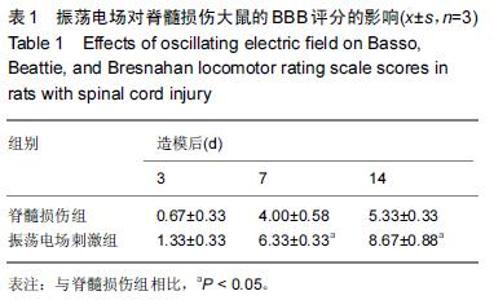
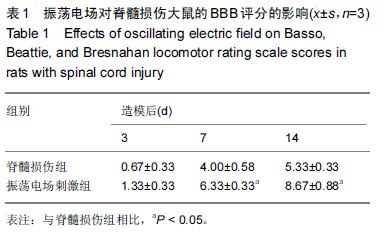
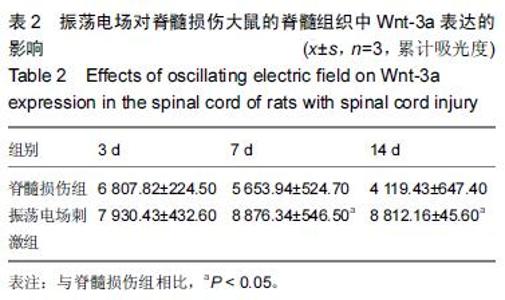
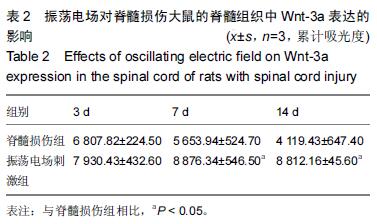
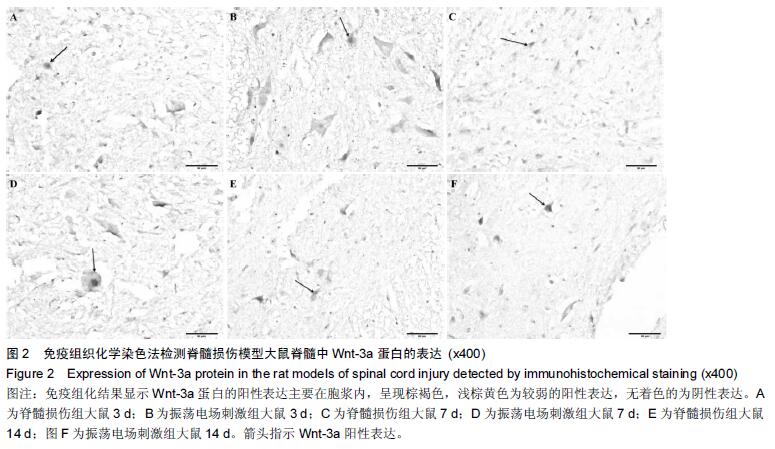
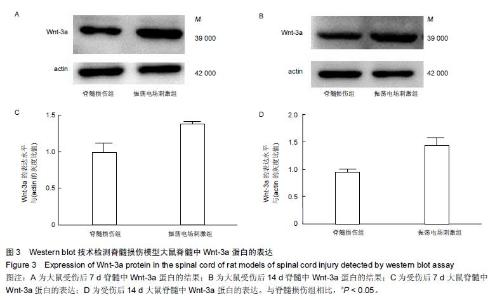
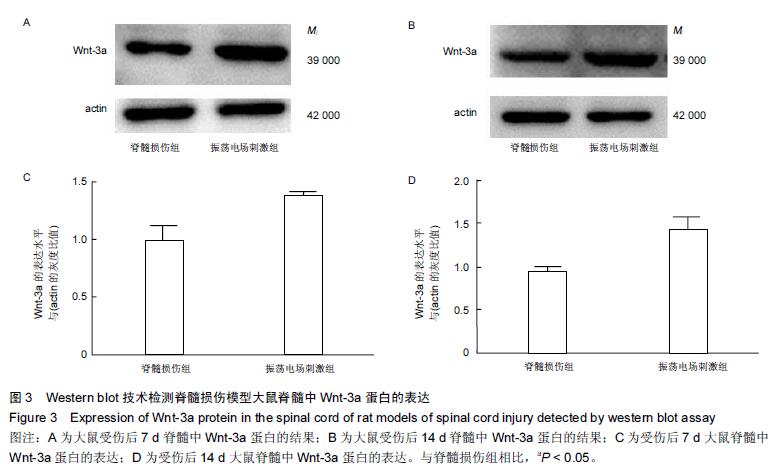
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (18): 2648-2654.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.18.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of oscillating electric field on Wnt-3a expression and motor function in the injured rat spinal cord
Huang Xian-jia1, Qian Jun1, Zhang Kun-kun1, Pan Wei-dong2, Jing Jue-hua1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230601, Anhui Province, China; 2Institute of Electrical Engineering, Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing 100190, China
-
Received:2016-03-03Online:2016-04-29Published:2016-04-29 -
Contact:Jing Jue-hua, M.D., Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230601, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Huang Xian-jia, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230601, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81471273; the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province, No. 1408085MH184
Cite this article
Huang Xian-jia, Qian Jun, Zhang Kun-kun, Pan Wei-dong, Jing Jue-hua. Effects of oscillating electric field on Wnt-3a expression and motor function in the injured rat spinal cord[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(18): 2648-2654.
share this article
| [1] Singh A, Tetreault L, Kalsi-Ryan S, et al. Global prevalence and incidence of traumatic spinal cord injury. Clin Epidemiol. 2014;6:309-331. [2] Devivo MJ. Epidemiology of traumatic spinal cord injury: trends and future implications. Spinal Cord. 2012;50(5):365-372. [3] Groah SL, Charlifue S, Tate D, et al. Spinal cord injury and aging: challenges and recommendations for future research. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;91(1):80-93. [4] Singh A, Tetreault L, Kalsi-Ryan S, et al. Global prevalence and incidence of traumatic spinal cord injury. Clin Epidemiol. 2014;6:309-331. [5] Rahimi-Movaghar V, Sayyah MK, Akbari H, et al. Epidemiology of traumatic spinal cord injury in developing countries: a systematic review. Neuroepidemiology. 2013;41(2):65-85. [6] Knútsdóttir S, Thórisdóttir H, Sigvaldason K, et al. Epidemiology of traumatic spinal cord injuries in Iceland from 1975 to 2009. Spinal Cord. 2012;50(2):123-126. [7] Frieden L, Winnegar AJ. Opportunities for research to improve employment for people with spinal cord injuries. Spinal Cord. 2012;50(5):379-381. [8] Shapiro S, Borgens R, Pascuzzi R, et al. Oscillating field stimulation for complete spinal cord injury in humans: a phase 1 trial. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005; 2(1):3-10. [9] Shapiro S. A review of oscillating field stimulation to treat human spinal cord injury. World Neurosurg. 2014; 81(5-6):830-835. [10] Cheng Zhang, Guanghao Zhang, Aihua Wang, et al. Oscillating field stimulation promotes recovery after spinal cord injury in rats: Assessment using behavioral, electrophysiological and histological evaluations. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015;2015:4594-4597. [11] Zhang C, Zhang G, Rong W, et al. Oscillating field stimulation promotes spinal cord remyelination by inducing differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells after spinal cord injury. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014; 24(6):3629-3636. [12] Radman T, Su Y, An JH, et al. Spike timing amplifies the effect of electric fields on neurons: implications for endogenous field effects. J Neurosci. 2007;27(11): 3030-3036. [13] Tator CH. Phase 1 trial of oscillating field stimulation for complete spinal cord injury in humans. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2(1):1; discussion 1-2. [14] Hamid S, Hayek R. Role of electrical stimulation for rehabilitation and regeneration after spinal cord injury: an overview. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(9):1256-1269. [15] Walters BC. Oscillating field stimulation in the treatment of spinal cord injury. PM R. 2010;2(12 Suppl 2):S286-291. [16] Jing JH, Qian J, Zhu N, et al. Improved differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells and neurological function after spinal cord injury in rats by oscillating field stimulation. Neuroscience. 2015;303:346-351. [17] Borgens RB, Toombs JP, Blight AR, et al. Effects of applied electric fields on clinical cases of complete paraplegia in dogs. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 1993; 5(5):305-322. [18] Ille F, Sommer L. Wnt signaling: multiple functions in neural development. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005;62(10): 1100-1108. [19] Yu JM, Kim JH, Song GS, et al. Increase in proliferation and differentiation of neural progenitor cells isolated from postnatal and adult mice brain by Wnt-3a and Wnt-5a. Mol Cell Biochem. 2006;288 (1-2):17-28. [20] Fehlings MG, Tator CH, Linden RD. The effect of direct-current field on recovery from experimental spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg. 1988;68(5):781-792. [21] Borgens RB, Toombs JP, Breur G, et al. An imposed oscillating electrical field improves the recovery of function in neurologically complete paraplegic dogs. J Neurotrauma. 1999;16(7):639-657. [22] Lu W, Yamamoto V, Ortega B, et al. Mammalian Ryk is a Wnt coreceptor required for stimulation of neurite outgrowth. Cell. 2004;119(1):97-108. [23] Lee SM, Tole S, Grove E, et al. A local Wnt-3a signal is required for development of the mammalian hippocampus. Development. 2000;127(3):457-467. [24] Lie DC, Colamarino SA, Song HJ, et al. Wnt signalling regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Nature. 2005;437(7063):1370-1375. [25] Davidson KC, Jamshidi P, Daly R, et al. Wnt3a regulates survival, expansion, and maintenance of neural progenitors derived from human embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2007;36(3):408-415. [26] Calegari F, Haubensak W, Haffner C, et al. Selective lengthening of the cell cycle in the neurogenic subpopulation of neural progenitor cells during mouse brain development. J Neurosci. 2005;25(28): 6533-6538. [27] Yamamoto S, Nagao M, Sugimori M, et al. Transcription factor expression and Notch-dependent regulation of neural progenitors in the adult rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 2001;21(24):9814-9823. [28] Yin ZS, Zu B, Chang J, et al. Repair effect of Wnt3a protein on the contused adult rat spinal cord. Neurol Res. 2008;30(5):480-486. [29] Zhou J, He H, Yang L, et al. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on bone mass and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in ovariectomized rats. Arch Med Res. 2012;43(4):274-282. [30] Wei LC, Ding YX, Liu YH, et al. Low-dose radiation stimulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling, neural stem cell proliferation and neurogenesis of the mouse hippocampus in vitro and in vivo. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012;9(3):278-289. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||