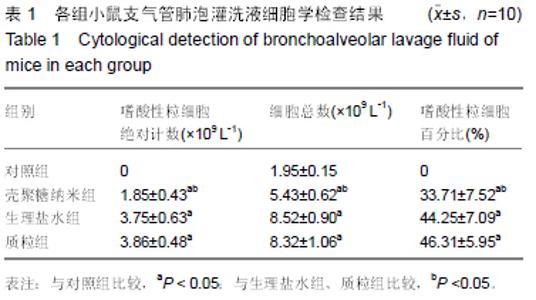
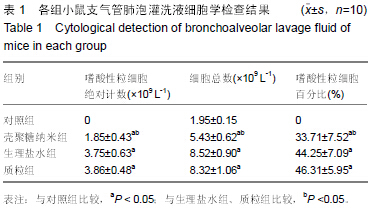
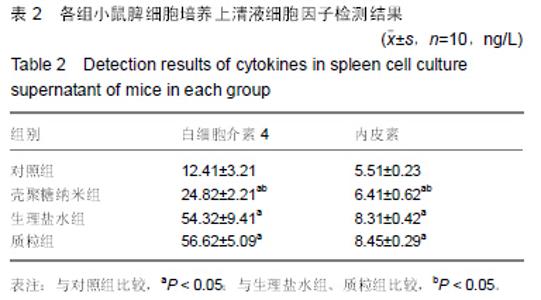
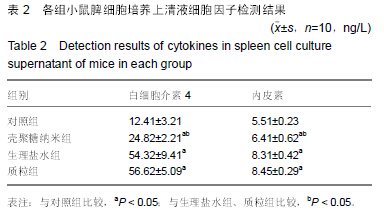
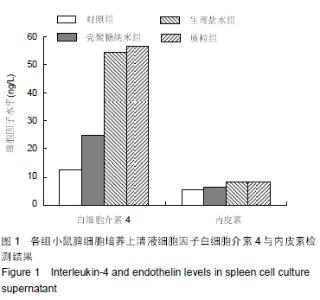
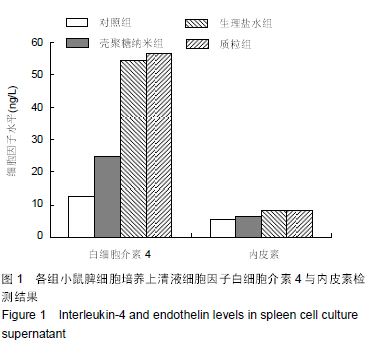
| [1] 刘金华,李岱容,陈涛,等.成立哮喘健康呼吸中心对哮喘患者健康行为影响的调查研究[J].重庆医学,2013,42(31):3801-3803.
[2] 周兰岛,解继胜,董光辉,等.百色市室内环境污染对儿童哮喘及哮喘样症状影响的流行病学调查[J].中国卫生统计,2013,30(3): 354-356.
[3] 陈虹,刘海沛,鲍一笑,等.哮喘易感基因多态性与哮喘预测指数阳性婴幼儿喘息的相关性[J].临床儿科杂志,2013,31(6): 547-550.
[4] 孙晓春,胡晓燕,王莉佳,等.氯喹对哮喘小鼠气道高反应性的抑制作用[J].南方医科大学学报,2015,35(1):12-16.
[5] Navarro CH,Moreno KJ,Arizmendi-Morquecho A,et al.Preparation and tribological properties of chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite coatings applied on ultra high molecular weight polyethylene substrate.J Plast Film Sheet.2012;28(4):279-297.
[6] Muraii S.Pulmonary arterial hypertension.Curr Opin Crit Care. 2006;12:228-234.
[7] 周雨田,徐军.12-烷基化壳聚糖纳米粒-反义内皮素转换酶核酸表达质粒的制备及其性质的研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2007, 27(11):20-26.
[8] 闫静静,郎轶咏,王强,等.壳聚糖微粒及纳米制剂在药剂学中的研究进展[J].医药导报,2011,30(9):1182-1187.
[9] 王春,杨连生,扶雄,等.壳聚糖基纳米载药微粒的研究进展[J].现代食品科技,2007,23(4):89-92.
[10] 王明力,赵德刚,陈汝材,等.纳米SiOx/单甘脂对壳聚糖保鲜涂膜改性的研究[J].食品科学,2007,28(3):96-99.
[11] 陈柔,王银松,杨晓英,等.乳糖酰化壳聚糖基自组装纳米载药体系的体外研究[J].功能材料,2011,42(1):59-62.
[12] 张吉星,毕娟,李慧,等.盐酸万古霉素缓释壳聚糖纳米粒-微粒系统的研制[J].药学服务与研究,2011,11(3):180-182.
[13] 徐江红,戴文佳,王正敏,等.黏膜免疫壳聚糖-多胺转运蛋白D (PotD)DNA纳米微粒对小鼠鼻咽部肺炎链球菌定植的保护作用研究[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志,2010,30(6):560-565.
[14] 苏丹.壳聚糖-siRNA分子纳米载体的制备、鉴定和基因沉默效应[D].第一军医大学,2007.
[15] 陈侠,李磊,鲜光军,等.壳聚糖纳米微粒对靶向转化生子因子-βⅡ型受体核酸适配子的缓释作用及其安全性研究[J].中华实验眼科杂志,2013,31(4):352-357.
[16] 魏明,涂玲,梁颖红,等.臭氧暴露对哮喘大鼠CD4+CD25highFoxp3+调节性T淋巴细胞数量和Foxp3mRNA表达的影响[J].中华劳动卫生职业病杂志,2013,31(9):693-696.
[17] Witoon T,Chareonpanich M,Jumras Limtrakul J,et al.Size control of nanostructured silica using chitosan template and fractal geometry: effect of chitosan/silica ratio and aging temperature.J Solgel Sci Technol.2010;56(3):270-277.
[18] 李慧,方凤.062 内皮素在哮喘气道炎症与重建中的地位[J].国外医学:呼吸系统分册,2001,21(3):145-146.
[19] 李莹,纪霞,王海燕等.青岛地区支气管哮喘患者TNF-α基因rs1800629位点多态性与表达及TNF-α、内皮素水平相关研究[J].国际呼吸杂志,2013,33(3):165-169.
[20] 王鹏,李星晶,王丽华,等.嗜酸粒细胞趋化因子、干扰素-γ和内皮素1在支气管哮喘中的临床意义[J].热带医学杂志,2012,12(2): 190-192.
[21] 戴山林,黄茂,王虹,等.哮喘豚鼠内皮素、心钠素含量的变化及心钠素对内皮素含量的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2000,16(10): 906-908.
[22] Kong AG,Wang P,Zhang HG,et al.One-pot fabrication of magnetically recoverable acid nanocatalyst, heteropolyacids/chitosan/Fe3O4, and its catalytic performance.Appl Catal A Gen.2012;417:183-189.
[23] 周雨田,徐军.12-烷基化壳聚糖纳米粒包裹反义内皮素转换酶核酸表达质粒在哮喘基因治疗中的特征[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(5):829-833.
[24] 支亚丽.支气管哮喘患者血清一氧化氮、内皮素、白介素-10、白介素-6和免疫球蛋白E变化的研究[J].实用医学杂志,2007,23(9): 1323-1324.
[25] 徐红涛,王旻晨,杨亚安,等.内皮素-1对大鼠血管平滑肌表型转化和增殖的影响[J].解剖学杂志,2009,32(2):162-165.
[26] Zhao DH,Zhu YC,Li F,et al.Polymorph selection and nanocrystallite rearrangement of calcium carbonate in carboxymethyl chitosan aqueous solution: Thermodynamic and kinetic analysis.Mater Res Bull.2010;45(1):80.
[27] 汪婷,谢宇,赵杰,等.羟丙基壳聚糖纳米微粒的制备及其对Ni2+的吸附研究[J].环境污染与防治,2011,33(10):19-23.
[28] 李斐,金星明,沈晓明,等.壳聚糖TGF-β1纳米质粒构建及对卵清蛋白肠道过敏小鼠免疫调节效果[J].现代免疫学,2007,27(6): 470-476.
[29] 周少华,陈勇,洪艳,等.壳聚糖的纳米化及其生物学效应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(26):5190-5193.
[30] 代昭,张纪梅,黄文强,等.烷基化壳聚糖纳米微球的制备及其XPS光谱分析[J].离子交换与吸附,2008,24(1):40-46.
[31] 李菲菲,王秋雯,马列,等.复合转化生长因子-β1的磺化壳聚糖/聚赖氨酸纳米粒子的制备及其体外诱导干细胞分化性能[J].高分子学报,2013,(9):1177-1182.
[32] 李慧,董文凤,杜丽,等.凝集素化昔萘酸沙美特罗纳米粒-微粒的药效和药动学研究[J].第二军医大学学报,2013,34(11): 1220-1224.
[33] 周雨田.12-烷基化壳聚糖/反义内皮素转换酶RNA表达质粒复合体纳米粒在变应性气道炎症中的免疫调节作用[D].广州医学院, 2006.
[34] 刘文艳,陈文魁,周书林,等.过敏性哮喘患者新型免疫疗法治疗前后外周血IL-4及IL-5活性和IgE的变化[J].实用医学杂志,2003, 19(10):1084-1086.
[35] 梁文华,周兆山,吉中强,等.IL-4和IL-4R基因多态性与哮喘的相关性[J].中华医学遗传学杂志,2014,31(1):97-100.
[36] 朱晓萍,杨锡强,符州,等.IL-13和IL-4在哮喘发病中的作用及相互关系[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志,2004,24(7):519-522.
[37] 程静,梁红艳,姜晓峰,等.哮喘造模不同阶段的小鼠支气管肺泡灌洗液中IL-4、IL-12、IL-13的检测及意义[J].中国实验诊断学, 2013,17(4):643-646.
[38] 张嘉琳,陈虹,胡良平,等.白细胞介素4和10基因多态性与儿童哮喘的相关性及对细胞因子表达的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2002, 82(2):114-118.
[39] 黄花荣,吴敬芳.IFN-γ与IL-4基因多态性与儿童哮喘易感性及外周血IFN-γ、IL-4和IgE的关系[J].中国病理生理杂志,2010,26(9): 1769-1775.
[40] 李绍波,金小红,王昕昕,等.特异性免疫治疗对哮喘大鼠白细胞介素-10和转化生长因子-β1的影响[J].现代实用医学,2010,22(5): 495-497. |