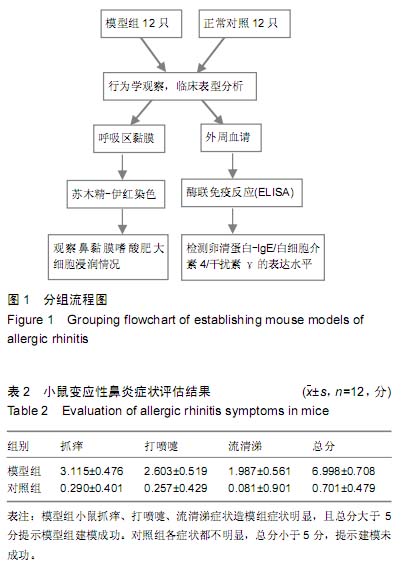
| [1] Kay AB. Advances in immunology-Allergy and allergic diseases-First of two parts. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(1):30-37.
[2] Cui Z, Zhang H. Analysis of HLA-DRB1 polymorphism for patienets with allergic rhinitis of Han people in Xinjiang. Xinjiang Yixueyuan Xuebaio. 2010;3:011.
[3] Sánchez-Velasco P, Mendizábal L, Antón EM, et al. Association ofhypersensitv tothe nematode Anisakis simplex with HLA class II DRB1* 1502-DQB1* 0601 haplotype. Human Immunol. 2000;61(3):314-319.
[4] Qi M, Wei H, Zhu Q, et al. Association between atopy for PlatanusAcerifolia pollen and HLA-DRB1 alleles. Linchuang Jianyan Zazhi. 2006;6:002.
[5] 邢志敏,于德林.蒿属花粉过敏变应性鼻炎与HLA-DRB基因多态性的相关性研究[J].临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志,2001,15(5):199-201.
[6] Yunlian C, Yangbing YYX. Analysis of HLA-DQB1 polymorphism for patienets with allergic rhinitis of Uygur and Han people in Xinjiang. Linchuag Erbiyanhouke Zazhi. 2011; 14:008.
[7] Munthe-Kaas MC, Carlsen KL, Carlsen KH, et al. HLADr-Dq haplotypes and the TNFA-308 polymorphism: associations with asthma and allergy. Allergy. 2007;62(9):991-998.
[8] Baraniuk JN. Pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997;99(2):S763-S772.
[9] Li Y, Yang G, Jia Y, et al. Genetic polymorphism in the second exon of HLA-DRB1 in cervical cancer. Clin Oncol Cancer Res. 2010;7(1):27-32.
[10] 刘恩岐,尹海林,顾为望.医学实验动物学[J].遗传,2008,30(7): 918-918.
[11] Gerlai R. Zebra fish: an uncharted behavior genetic model. Behav Genet. 2003;33(5):461-468.
[12] Fülöp AK, Földes A, Buzás E, et al. Hyperleptinemia,visceral adiposity,and decreased glucose tolerance in mice with a targeted disruption of the histidine decarboxylasegene. Endocrinology. 2003;144(10):4306-4314.
[13] 吉晓滨,邓家德,王磊,等.变应性鼻炎红细胞免疫功能的实验观察[J].中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,2007,13(11):788-790.
[14] 田理,贾德蓉,刘敬.力克敏喷剂治疗过敏性鼻炎实验研究[J].中医耳鼻喉科学研究杂志,2007,6(3):28-30.
[15] 于海玲,孙连平,曲香芝,等.通鼻胶囊对急性炎症和免疫性炎症的影响[J].延边大学医学学报,2006,29(1):27-29.
[16] 杨军,邓秋,周芸,等.实验性变应性鼻炎中鼻黏膜组胺的测定[J].首都医科大学学报,2006,27(1):109-112.
[17] 佘文煜,董震.普仑司特对实验性变应性鼻炎鼻黏膜组织重塑的影响[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2006,41(7):483-487.
[18] 王向东,韩德民,周兵,等.变应性鼻炎白细胞祖代细胞和相关细胞因子的检测及意义[J].耳鼻咽喉:头颈外科,2004,10(2):95-97.
[19] 张志明,孙树岩,季文樾.真菌性抗原致变应性鼻炎豚鼠模型建立[J].中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,2005,12(5):313-315.
[20] 余洪猛,文三立.豚草花粉变应原致过敏性鼻炎豚鼠模型的建立[J].上海实验动物科学,2001,21(4):212-214.
[21] Kumar RK, Herbert C, Foster PS. The“classical”ovalbumin challenge model ofasthma in mice. Curr Drug Target. 2008; 9(6):485-494.
[22] Shirakawa T, Li A, Dubowitz M, et al. Association between atopy and variantsof the β subunit of the high-affinity immunoglobulin E receptor. Nat Genet. 1994;7(2):125-130.
[23] Stern ME, Siemasko K, Gao J, et al. Role of interferon-γ in a mouse model of allergic conjunctivitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46(9):3239-3246.
[24] 林志荣,王维刚,严惠敏,等.卵清蛋白诱导129Sv小鼠建立哮喘模型的方法[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2011,33(9):964-968.
[25] 肖淑华,刘阳阳,魏连海,等.肥大细胞的研究进展[J].生理科学进展,2011,42(2):104-107.
[26] 洪娟,黄建明.嗜酸性粒细胞趋化因子与鼻变应性疾病[J].国际耳鼻喉头颈外科杂志,2006,30(4):251-254.
[27] Ismaïl A, Bousaffara R, Kaziza J, et al. Polymorphism in transporter antigen peptides gene (TAP1) associated with atopy in Tunisians. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997;99(2): 216-223.
[28] Moffatt MF, Traherne JA, Abecasis GR, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism and linkage disequilibrium within the TCR alpha/delta locus. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;9(101)1-9.
[29] Kim JJ, Kim MS, Lee JH, et al. STAT6 gene polymorphisms in allergic rhinitis.Genomics Inform. 2004;2:126-130.
[30] Chae S, Park Y, Li C, et al. Analysis of the variations in IL-28RA gene and their association with allergic rhinitis. Exp Mol Med. 2006;38(3):302.
[31] Lee SM, Gao B, Dahl M, et al. Decreased FoxP3 gene expression in the nasal secretions from patients with allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;140(2):197-201.
[32] Sogut A, Yilmaz O, Kirmaz C, et al. Regulatory-T, T-helper1, and T-helper2 cell differentiation in nasal mucosa of allergic rhinitis with olive pollen sensitivity. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011;157(4):349-353. |