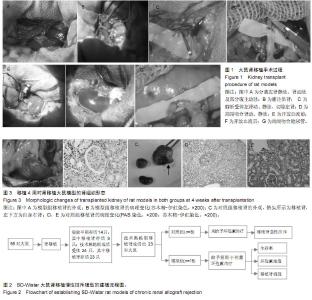
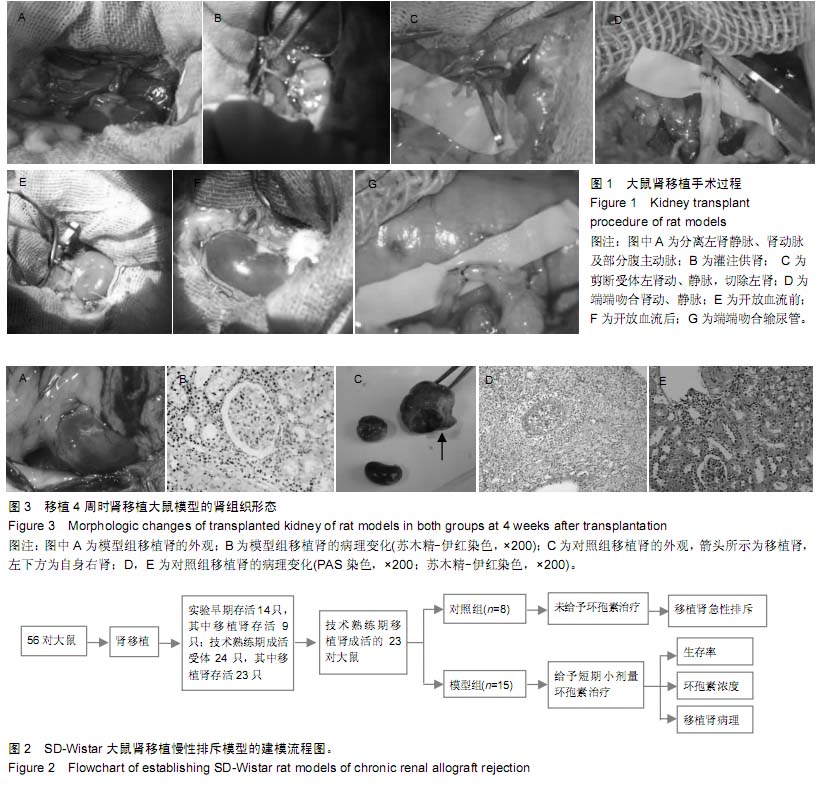
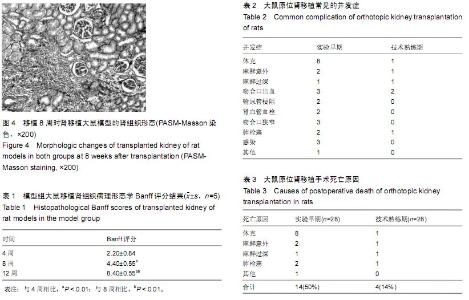
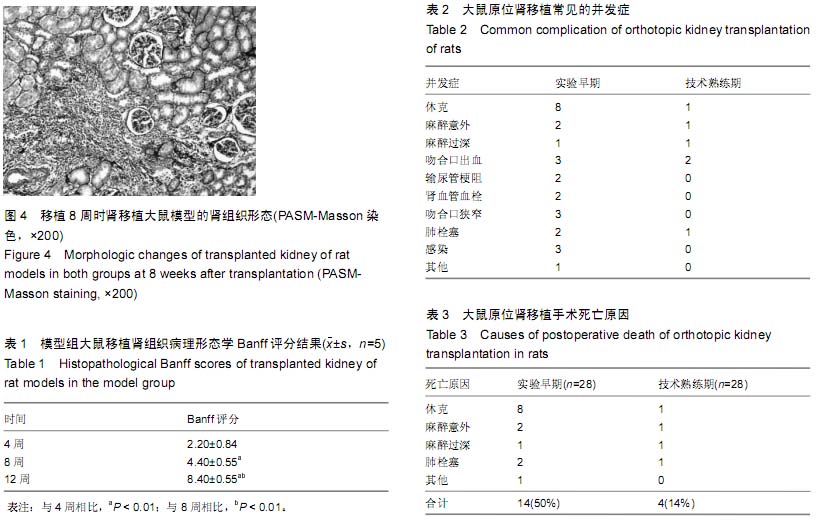
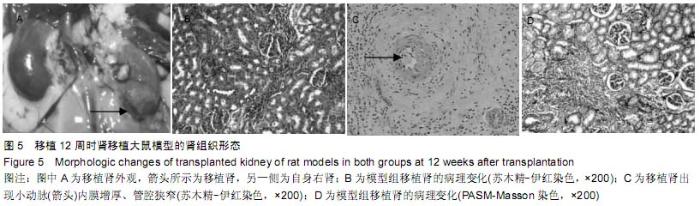
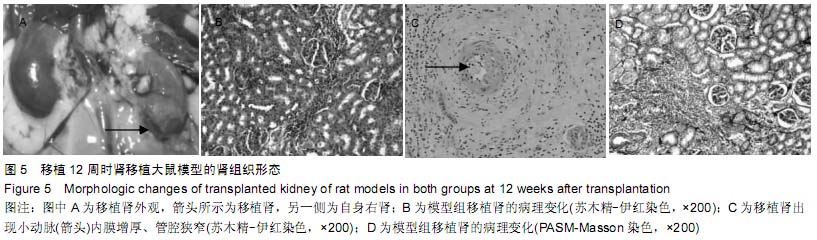
| [1] Howard RJ, Patton PR, Reed AI, et al. The changing causes of graft loss and death after kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2002;73(12):1923-1928.
[2] Diamond JR, Tilney NL, Frye J, et al. Progressive albuminuria and glomerulosclerosis in a rat model of chronic renal allograft rejection. Transplantation. 1992;54(4):710-716.
[3] Yilmaz S, Paavonen T, Häyry P. Chronic rejection of rat renal allografts. II. The impact of prolonged ischemia time on transplant histology. Transplantation. 1992;53(4): 823-827.
[4] Soots A, Lautenschlager I, Krogerus L, et al. An experimental model of chronic renal allograft rejection in the rat using triple drug immunosuppression. Transplantation. 1998;65(1):42-46.
[5] Rintala JM, Savikko J, Rintala SE, et al. FK778 ameliorates post-transplant expression of fibrogenic growth factors and development of chronic rejection changes in rat kidney allografts. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23(11):3446-3455.
[6] Pascual J. Concentration-controlled everolimus (Certican): combination with reduced dose calcineurin inhibitors. Transplantation. 2005;79(9 Suppl):S76-79.
[7] Kahan BD. Potential therapeutic interventions to avoid or treat chronic allograft dysfunction. Transplantation. 2001;71(11 Suppl):SS52-57.
[8] Tedesco Silva H Jr, Pinheiro Machado P, Rosso Felipe C, et al. Immunotherapy for De Novo renal transplantation: what's in the pipeline? Drugs. 2006;66(13):1665-1684.
[9] Press RR, de Fijter JW, Guchelaar HJ. Individualizing calcineurin inhibitor therapy in renal transplantation--current limitations and perspectives. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(2): 176-186.
[10] Wali RK, Weir MR. Chronic allograft dysfunction: can we use mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors to replace calcineurin inhibitors to preserve graft function? Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2008;13(6):614-621.
[11] Silber SJ, Crudop J. Kidney transplantation in inbred rats. Am J Surg. 1973;125(5):551-553.
[12] Solez K, Colvin RB, Racusen LC, et al. Banff 07 classification of renal allograft pathology: updates and future directions. Am J Transplant. 2008;8(4):753-760.
[13] Fisher B, Lee S. Microvascular surgical techniques in research, with special reference to the renal transplantation in the rat. Surgery. 1965;58(5):904-914.
[14] Yin JL, Pilmore HL, Yan YQ, et al. Expression of growth arrest-specific gene 6 and its receptors in a rat model of chronic renal transplant rejection. Transplantation. 2002; 73(4):657-660.
[15] Yanagita M. The role of the vitamin K-dependent growth factor Gas6 in glomerular pathophysiology. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2004;13(4):465-470.
[16] Coito AJ, Kupiec-Weglinski JW. Extracellular matrix proteins: bystanders or active participants in the allograft rejection cascade? Ann Transplant. 1996;1(3):14-18.
[17] Wu KS, Hung YJ, Lee CH, et al. The Involvement of GAS6 Signaling in the Development of Obesity and Associated Inflammation. Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:202513.
[18] Mackenzie HS, Tullius SG, Heemann UW, et al. Nephron supply is a major determinant of long-term renal allograft outcome in rats. J Clin Invest. 1994;94(5):2148-2152.
[19] Kujal P, Vernerová Z. 5/6 nephrectomy as an experimental model of chronic renal failure and adaptation to reduced nephron number. Cesk Fysiol. 2008;57(4):104-109.
[20] Kriz W. Podocyte is the major culprit accounting for the progression of chronic renal disease. Microsc Res Tech. 2002;57(4):189-195.
[21] 辛宇鹏,卢一平,张秀辉,等.大鼠原位异体肾移植硬化加快模型的建立[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2004,35(2):267-270.
[22] Mihatsch MJ, Ryffel B, Gudat F. The differential diagnosis between rejection and cyclosporine toxicity. Kidney Int Suppl. 1995;52:S63-69.
[23] Bennett WM, DeMattos A, Meyer MM, et al. Chronic cyclosporine nephropathy in renal transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1996;28(4):2100-2103.
[24] Wiecek A, Nowicki M, Kokot F, et al. Acute failure of the transplanted kidney--pathophysiology, diagnosis and prevention. Ann Transplant. 1996;1(4):5-9.
[25] Katznelson S, Wilkinson A, Rosenthal TR, et al. Cyclosporine-induced hemolytic uremic syndrome: factors that obscure its diagnosis. Transplant Proc. 1994;26(5):2608- 2609.
[26] 刘小友,于立新,付绍杰,等.大鼠肾移植急性排斥反应模型的建立[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2005,26(11):730-732.
[27] Paul LC. Functional and histologic characteristics of chronic renal allograft rejection. Clin Transplant. 1994;8(3 Pt 2): 319-323.
[28] Häyry P, Isoniemi H, Yilmaz S, et al. Chronic allograft rejection. Immunol Rev. 1993;134:33-81.
[29] Paul LC. Animal models of chronic heart and kidney allograft rejection. Transplant Proc. 1993;25(2):2080-2081.
[30] Paul LC, Hayry P, Foegh M, et al. Diagnostic criteria for chronic rejection/accelerated graft atherosclerosis in heart and kidney transplants: joint proposal from the Fourth Alexis Carrel Conference on Chronic Rejection and Accelerated Arteriosclerosis in Transplanted Organs. Transplant Proc. 1993;25(2):2022-2023.
[31] Kirklin JK, Bourge RC, McGiffin DC. Recurrent or persistent cardiac allograft rejection: therapeutic options and recommendations. Transplant Proc. 1997;29(8A):40S-44S.
[32] Steinbrüchel DA. Pathogenesis and mechanisms of graft rejection in concordant xenotransplantation with special reference to hamster-to-rat cardiac transplantation. APMIS Suppl. 1996;58:5-45.
[33] Yilmaz S, Taskinen E, Häyry P, et al. Protocol core biopsy as intermediate efficacy end-point in chronic kidney allograft rejection. Transplant Proc. 1996;28(1):491-493.
[34] Demetris AJ, Murase N, Lee RG, et al. Chronic rejection. A general overview of histopathology and pathophysiology with emphasis on liver, heart and intestinal allografts. Ann Transplant. 1997;2(2):27-44.
[35] Cramer DV, Chapman FA, Makowka L. Prevention of vascularized allograft and xenograft rejection in rodents by brequinar sodium. Transplant Proc. 1993;25(3 Suppl 2): 23-28.
[36] Wanders A, Akyürek ML, Waltenberger J, et al. Impact of ischemia time on chronic vascular rejection in the rat--effects of angiopeptin. Transplant Proc. 1993;25(2):2098-2099. |