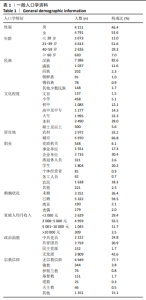
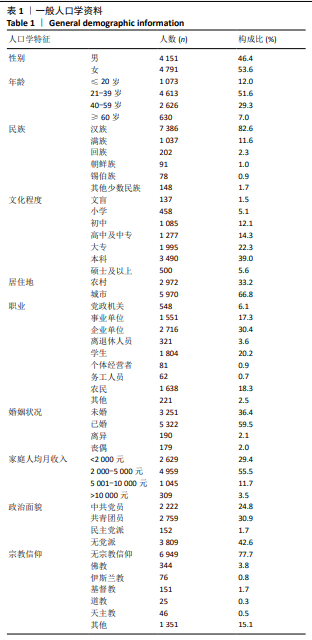
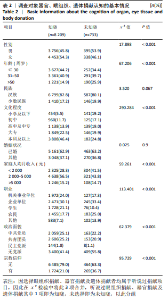
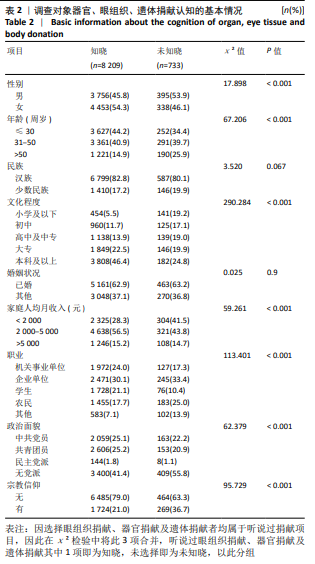
[1] 杜妍莹,孙俐,吕毅.天津市大学生器官捐献认知、态度及意愿调查[J].医学与社会,2018,31(9):59-62.
[2] 廖晨歌.中国遗体器官捐献困境解析及对策研究[J].中国卫生事业管理,2016,33(10):766-767, 794.
[3] 吴珍,高玲玲,陈雪莲,等.广东省流动人口的器官捐献意愿及其影响因素的调查[J].器官移植,2016,7(1):53-56.
[4] 江文诗, Gomez MP, Paez G,等.数据之美-聚焦全球器官捐献发展趋势[J].中华移植杂志 (电子版),2019,13(1):28-33.
[5] 石炳毅.继往开来,中国器官移植的发展现状-在2018年中华医学会器官移植学年会上的报告[J].器官移植,2019,10(1):32-35.
[6] 黄伟,司晶,徐哲,等.移植医院协调员队伍建设及工作流程探讨[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2016,37(4):670-673.
[7] GÓMEZ MP, BLANCA P, MANYALICH M. International Registry in Organ Donation and Transplantation--2013. Transplant Proc,2014,46(4): 1044-1048.
[8] 缪群芳,葛文杰,王艳岭.浙江省民众对遗体捐献的认知、态度及意愿调查[J].医学与哲学,2019,40(15):41-45,74.
[9] 胡冬梅.医务工作者、医学生及民众对器官捐献的认知、态度及意愿的调查研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2015.
[10] ALANAZI LF, ALDOSSARI SH, GOGANDY MA, et al. Attitude, beliefs and awareness towards corneal donation in Saudi Arabia. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2019;33(2):121-129.
[11] 张恒诚,郑佳男,刘文华,等.江苏地区器官捐献态度和意愿调查及对策分析[J].南京医科大学学报(社会科学版),2015,15(5): 339-343.
[12] 周粤佳,冀笑琰,强美英.中国高校学生身后器官捐献意愿的Meta分析[J].医学与哲学,2019,40(8):22-25.
[13] 赵玉霞,静香芝,章涵.信阳市民遗体器官捐献意愿及其影响因素[J].河南预防医学杂志,2019,30(11):872-874.
[14] 徐奇,聂立婷,胡金凤,等.济南市护士及护生器官捐献认知水平及意愿[J].护理学杂志,2019,34(11):83-86.
[15] 贾丽娜,肖奇贵,杨勤玲,等.西北地区公民逝世后器官捐献者家属捐献意愿影响因素分析[J].中国医学伦理学,2019,32(4):474-478.
[16] 耿子翔,牛天赋,杲舒畅,等.烟台市居民器官捐献意愿影响因素调查分析及新宣传模式的构思[J].器官移植,2018,9(6):445-450.
[17] 刘萌,马伟,伊向仁,等.济南市城市社区不同自理能力老年人养老意愿及其影响因素[J].中国公共卫生,2016,32(10):1301-1308.
[18] 李勇.器官移植捐献认知度和意愿度的研究及建议[J].西昌学院学报(自然科学版),2019,33(1):96-100.
[19] 王天霄,宋立锦,王童,等.济南市城镇居民器官捐献认知态度调查[J].中国公共卫生,2014,30(5):645-647.
[20] 梁盛美,梁玉婷,马美刚,等.南宁市居民对器官捐献的认知度与认可度的调查分析[J].医学信息,2019,32(10):129-132+135.
[21] GILL J, ROSE C, LESAGE J, et al. Use and outcomes of kidneys from donation after circulatory death donors in the United States. J Am Soc Nephrol,2017,28(12):3647-3657.
[22] 潘杰,王海峰,张东航,等.公民逝世后潜在供者器官捐献效率的影响因素分析[J].中国医院管理,2015,35(8):62-64.
[23] 金宗兰,陈萍萍,廖贵益,等.合肥地区居民公民逝世后器官捐献意愿及其影响因素分析[J].中华移植杂志(电子版),2019,13(4): 302-305.
[24] 方程钰,沈桑露,苏文静,等.器官捐献教育对大学生认知和态度影响[J].中国高等医学教育,2019(10):49, 95.
[25] 林建锋,刘维,黄君婷,等.家庭视角下器官捐献现状及对策—基于湖南省长沙市、浙江省温州市的实证调研[J].温州医科大学学报,2020,50(1):84-87.
[26] 李咏馨,厉培培,吴梦晗,等.器官移植和捐献认知度和意愿度的研究分析[J].通化师范学院学报,2017,38(2):39-41.
[27] 郑恒.国外器官捐献的经济激励、市场制度及改革启示[J].南方经济,2016(4):99-115.
[28] 周德霞,刘剑.中国人体器官捐献同意模式探讨[J].医学与社会, 2017,30(3):62-65.
[29] 吴鹏,李梦绮,张祖志,等.渗透生命教育的解剖教学对医学新生生命态度及器官捐献意愿的影响[J].锦州医科大学学报(社会科学版),2019,17(5):18-21.
[30] 张晓曼,冯雷.运用心理危机干预缓解中国器官捐献文化敏感性[J].器官移植,2019,10(1):84-87.
[31] 阎茹,邱鸿钟,黄海.大学生器官捐献意愿的文化心理特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(4):600-605.
[32] 张文馨,滕沙,彭晓,等.器官捐献和移植教育影响医学生认知和态度的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(5):810-814.
[33] 叶航,郑恒.器官捐献的激励机制与匹配理论[J].社会科学战线, 2017,(8):40-50.
[34] 梁永晴,陈唯,张湛,等.广州市某高校学生对器官捐献的认知、态度及意愿调查[J].医学与社会,2017,30(3):48-50, 61.
[35] 曹翠萍,黄海.构建中国人体器官捐献社会宣教系统的策略[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(2):300-304.
|