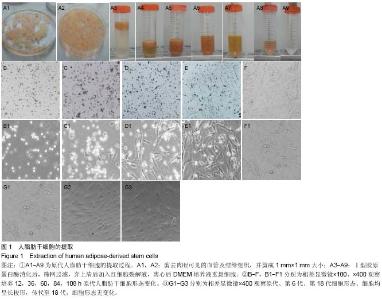
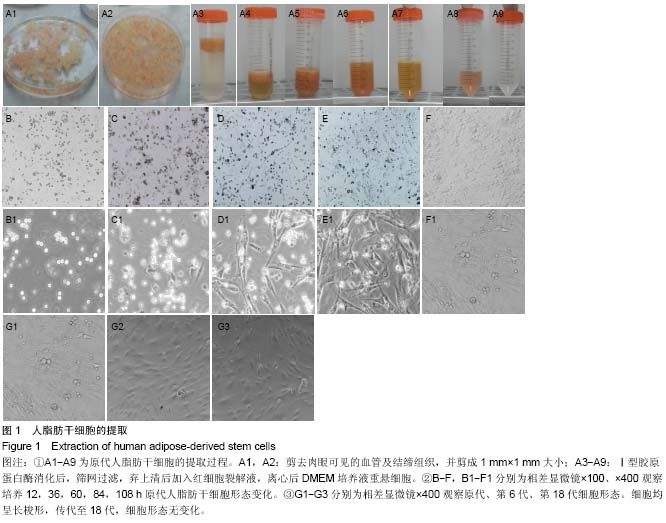
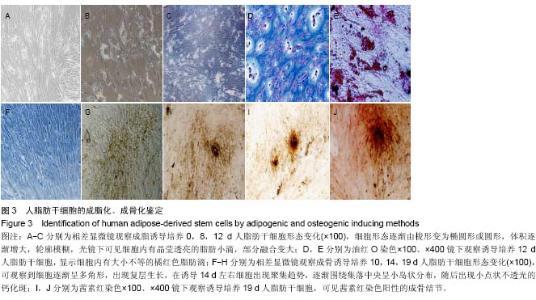
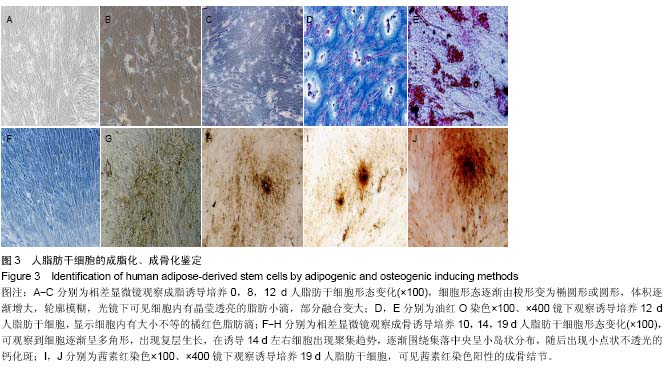
| [1] Harris CM, Laughlin R. Reconstruction of hard and soft tissue maxillofacial defects. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2013 Mar;21(1):127-138.
[2] Zhu W, Nelson CM. Adipose and mammary epithelial tissue engineering. Biomatter. 2013;3(3). pii: e24630.
[3] Park A, Kim WK, Bae KH. Distinction of white, beige and brown adipocytes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2014;6(1):33-42.
[4] Wu J, Boström P, Sparks LM, et al. Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in mouse and human. Cell. 2012;150(2):366-376.
[5] Ma J, Both SK, Yang F, et al. Concise review: cell-based strategies in bone tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(1):98-107.
[6] Handel M, Hammer TR, Hoefer D. Adipogenic differentiation of scaffold-bound human adipose tissue-derived stem cells (hASC) for soft tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2012;7(5): 054107.
[7] Handel M, Hammer TR, Hoefer D. Adipogenic differentiation of scaffold-bound human adipose tissue-derived stem cells (hASC) for soft tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2012;7(5): 054107.
[8] 林立新, 黄勇, 王玉婷, 等. 不同部位脂肪源性干细胞的生物学特性比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(27): 4992-4997.
[9] Cawthorn WP, Scheller EL, MacDougald OA. Adipose tissue stem cells meet preadipocyte commitment: going back to the future. J Lipid Res. 2012;53(2):227-246.
[10] Toyserkani NM, Christensen ML, Sheikh SP, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: New Treatment for Wound Healing. Ann Plast Surg. 2015;75(1):117-123.
[11] Ntambi JM, Young-Cheul K. Adipocyte differentiation and gene expression. J Nutr. 2000;130(12):3122S-3126S.
[12] Fève B. Adipogenesis: cellular and molecular aspects. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;19(4):483-499.
[13] Lee RH, Kim B, Choi I, et al. Characterization and expression analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow and adipose tissue. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2004; 14(4-6): 311-324.
[14] 唐少锋,刘承杏,姬林松,等.兔脂肪干细胞的体外分离培养特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(10): 1844-1848.
[15] Bodle JC, Teeter SD, Hluck BH, et al. Age-related effects on the potency of human adipose-derived stem cells: creation and evaluation of superlots and implications for musculoskeletal tissue engineering applications. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2014;20(12):972-983.
[16] Wang W, Chen L, Zhang C, et al. Experimental study on osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells treated with different concentrations of dexamethasone. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;25(12): 1486-1492.
[17] Yoshimura K, Suga H, Eto H. Adipose-derived stem/progenitor cells: roles in adipose tissue remodeling and potential use for soft tissue augmentation. Regen Med. 2009; 4(2):265-273.
[18] Park E, Patel AN. Changes in the expression pattern of mesenchymal and pluripotent markers in human adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Biol Int. 2010;34(10): 979-984.
[19] Nishiwaki S, Nakayama T, Saito S, et al. Efficacy and safety of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells for supporting hematopoiesis. Int J Hematol. 2012;96(3):295- 300.
[20] Han C, Zhang L, Song L, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a better cell source for nervous system regeneration. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(2): 329-337.
[21] 朱希山,台卫平,施薇,等.骨髓和脂肪来源间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(36): 6683-6686.
[22] 田霖,孙筱放,刘海波,等.人脂肪干细胞的分离培养与生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,(32):5946-5952.
[23] Yang C, Xing X, Xu D, et al. Effects of adipose-derived stem cells-hyaluronic acid composite on healing of wound combined with radiation injury. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;25(12):1499-1503.
[24] Ren ZW, Zhao Z, Wang Y, et al. Study on differentiation of rat adipose tissue-derived stromal cells into Schwann-like cells. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011;27(4): 385-388. |