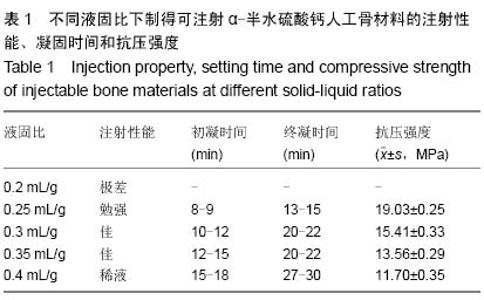
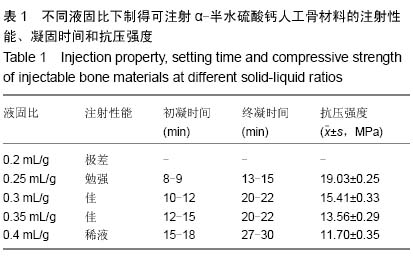
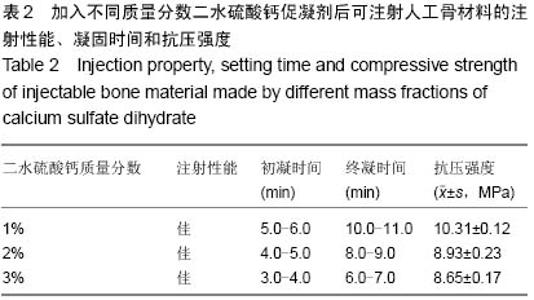
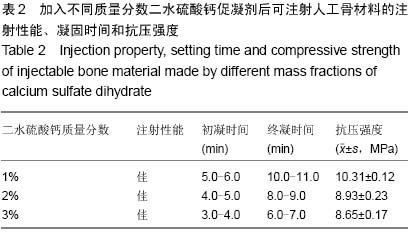
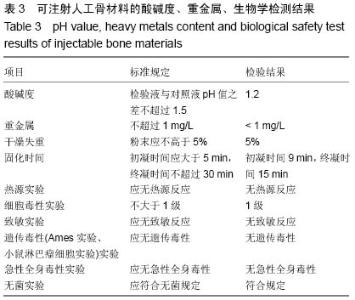
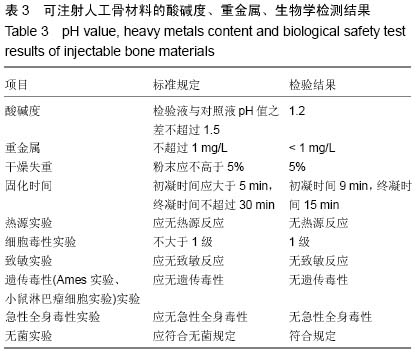
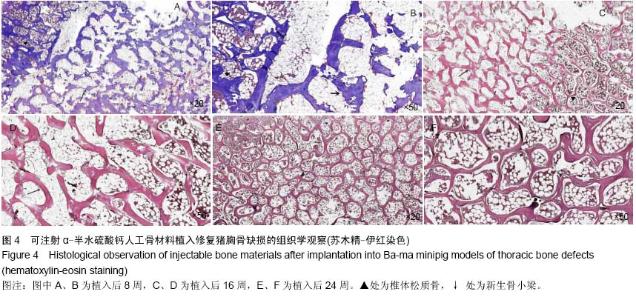
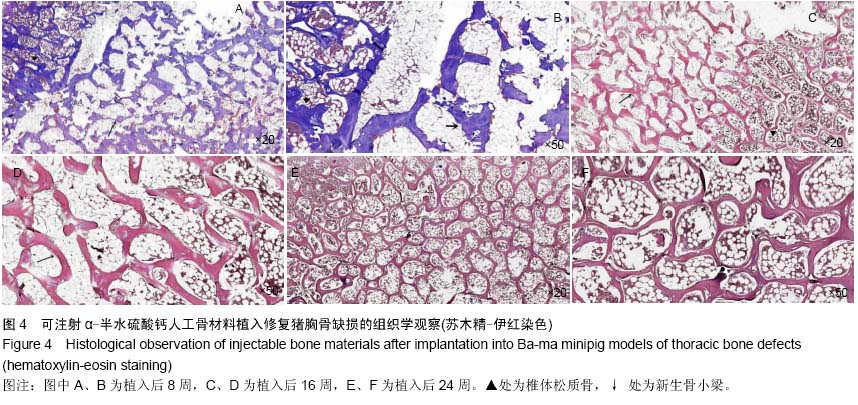
| [1] Temeno JS,Mikos AG.Injectable biodegradable materials for orthopedictissueengineering.Biomaterials.2000;21(23):2405-2412.
[2] Ooms EM,Wolke JG,van der Waerden JP,et al.Trabecular bone response to injectable calcium phosphate (Ca-P) cement.J Biomed Mater Res.2002;61(1):9-18.
[3] DormansJP,Dormans NJ.Use of percutaneous in tramedullary decompression and medical grade calcium sulphate pellets for treatment of unicameral bone cysts of the calcaneus in children.Orthopedics.2004;27(1):137-140.
[4] Girardi FP,Cammisa FP.The effect of bone graft extenders to enhance the performance of iliaccrest grafts in instrumented lumbar spine fusion.Orthopedics.2003;26(5):545.
[5] 注册号国药管械(进)字2002第3461400号(更)[医疗器械产品8美国osteoset人工骨.
[6] 注册号国食药监械(进)字2004第3460504号[医疗器械产品]英国医用硫酸钙sitmulna.
[7] 葛亮,苟三怀,杨四川,等.复合纳米人工骨的注射、凝固及其机械性能研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2006,3(5):4-8.
[8] 游永刚,唐辉,陈克久,等.硫酸钙在骨修复治疗中的作用[J].中国矫形外科志,2008,16(16):1245-1247.
[9] 张世民,吕刚.骨缺损修复中复合型可注射型骨替代材料的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(51): 10117-10120.
[10] 李志宏,黄姝杰,关静,等.可注射骨修复材料研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009,23(11):1382-1387.
[11] Turner H,Urban R,Tomlinson M,et al.Early restoration of bone following vertebroplasty using a high strength injectable calcium sulfate bone graft substitute compared to polymethylmethac- rylate.Spine J. 2004;4(5):106-107.
[12] Turner TM,UrbanRM,HallDJ,et al.Osseous healing using injectable calcium sulfate-based putty for the delivery of demineralized bonematrix and cancellous bone chips. Orthopedics.2003;26:s57175.
[13] Thomas MV,Puleo DA.Calcium sulfate: properties and clinical applications. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2009;88(2): 597−610.
[14] Hing KA,Wilson LF,Buckland T.Comparative performance of three ceramic bone graft substitutes.Spine J.2007;7(4): 475−490.
[15] 郑万荣,张巨松,杨洪永,等.转晶剂、晶种和分散剂对α半水石膏晶体粒度、形貌的影响[J].非金属矿,2006,29(4):1-4.
[16] 牟国栋.半水石膏水化过程中的物相变化研究[J].硅酸盐学报,2002, 30(4):532-535.
[17] 陈华.医用外科级α-半水硫酸钙的研制及其相关研究[D].北京:军医进修学院,2006.
[18] 岳文海,王志.α-半水石膏晶形转化剂作用机理的探讨[J].武汉工业大学学报,1996,18(2):1-4.
[19] 牟国栋,马吉生,施倪承.两种半水石膏形态特征的电子显微镜研究及其形成机理的探讨[J].矿物岩石,2000,20(3):9-13.
[20] 法国石膏工业学会著.石膏(物理一化学,生产一应用)[M].北京:中国建筑工业出版社,1987.
[21] 陈怡坚.可注射硫酸钙骨水泥产品的开发研究[D].浙江:浙江大学, 2012.
[22] Yoshikawa H,Myoui A.Bone tissue engineering with porous hydroxyapatite ceramics. J Artif Organs.2005;8(3):131-136.
[23] Guarnieri R,Aldini NN,Pecora G,et al.Medial-grade calcium sulfate hemihydrate (surgiplaster) in healing of a human extractionsocket--histologic observation at 3 months: a case report.IntJOralMaxillofacImplants.2005;20(4): 636-641.
[24] Dreesmmal H.Ueberknoehe Pnlombieunrg.Bietrkinehir. 1892; 9:804-810.
[25] Mastrogiacomo M,Muraglia A,Komlev V,et al.Tissue engineering of bone: search for a better scaffold.OrthodCraniofac Res.2005; 8(4):277-284.
[26] Kelly CM,Wilkins RM,Gitelis S,et al.The use of a surgical grade calcium sulfate as a bone graft substitute: results of a multicenter trial.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(382):42-50.
[27] Oh CW,Kim PT,Ihn JC.The use of calcium sulfate as a substitute.J Orthop Surg. 1998;2:1-10. |