Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (34): 5552-5558.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2318
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation of injectable tantalum oxide-loaded brushite bone cement and investigation on its radiocapacity performance
Xing Yuying1, He Yuying1, Jiang Ningning1, Zhu Ruijie1, He Ran1, Qi Yangkun1, Wang Kejing2, Li Guangda1
1School of Medical Technology and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, Henan Province, China; 2School of Basic Medical Science, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2019-09-26Revised:2019-09-28Accepted:2020-02-26Online:2020-11-08Published:2020-09-11 -
Contact:Li Guangda, PhD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Medical Technology and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, Henan Province, China -
About author:Xing Yuying, School of Medical Technology and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, Henan Province, China He Yuying, School of Medical Technology and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation, Nos. 81402225, U1304805; Key Scientific and Technological Project of Henan Province, No. 182102311114; Young Backbone Teachers Project in Henan Higher Education Institution, No. 2018GGJS050; Student Research Training Program from Hennan Province, No. 201810464022.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xing Yuying, He Yuying, Jiang Ningning, Zhu Ruijie, He Ran, Qi Yangkun, Wang Kejing, Li Guangda. Preparation of injectable tantalum oxide-loaded brushite bone cement and investigation on its radiocapacity performance[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5552-5558.
share this article
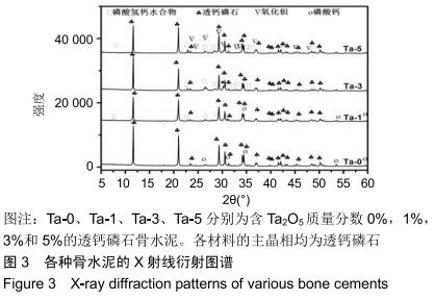
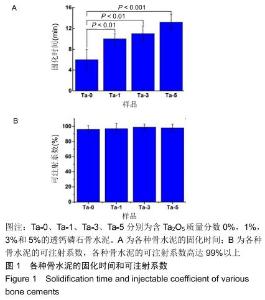
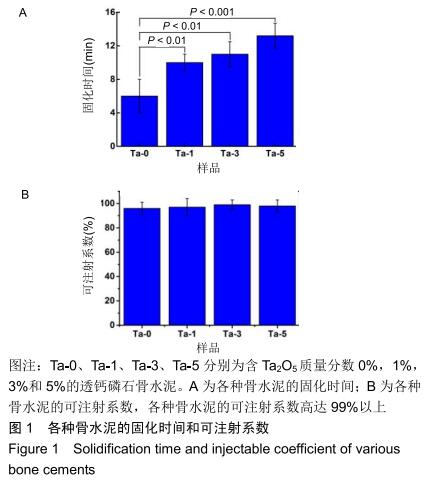
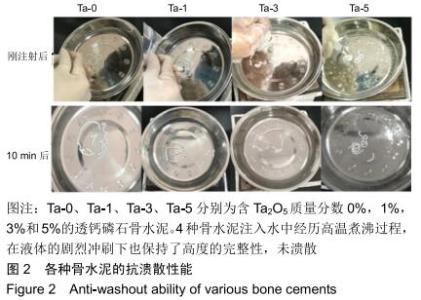
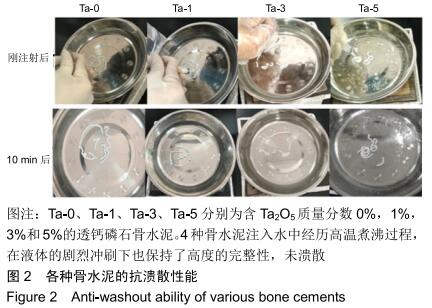
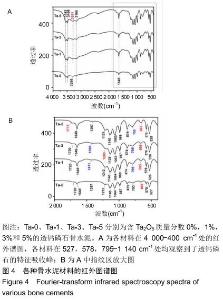
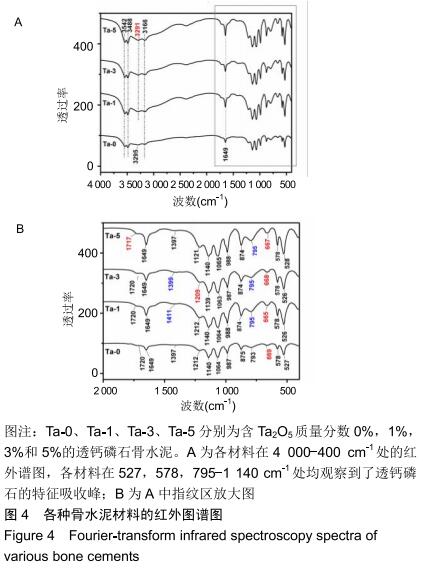
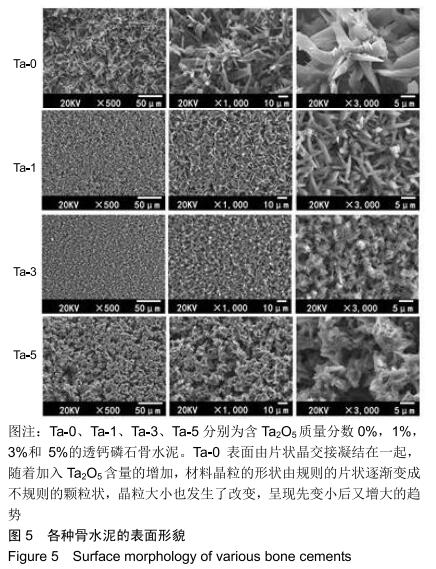
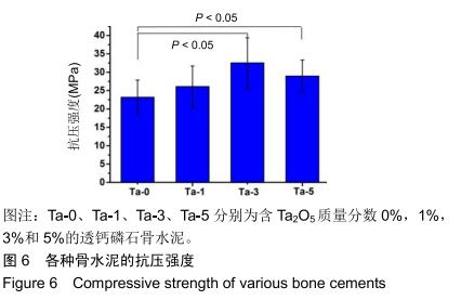
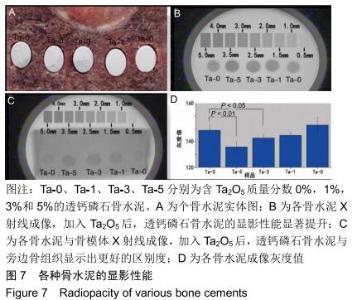
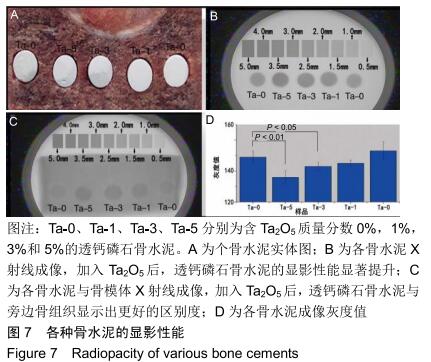
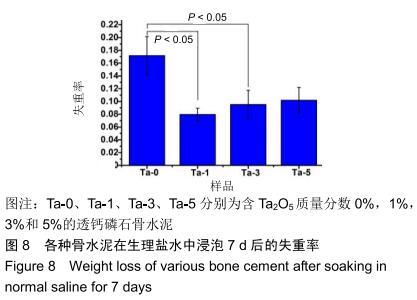
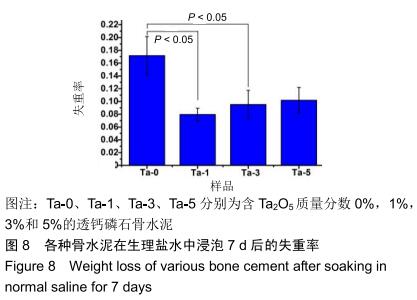
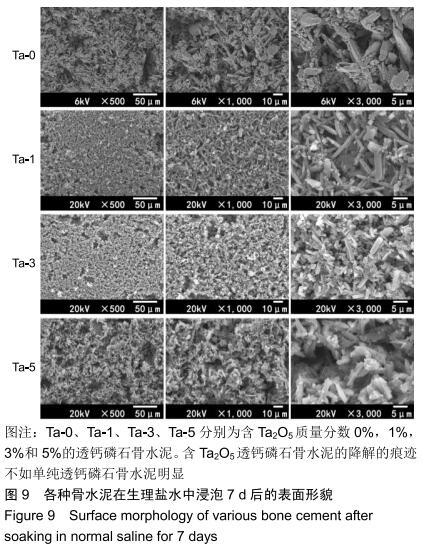
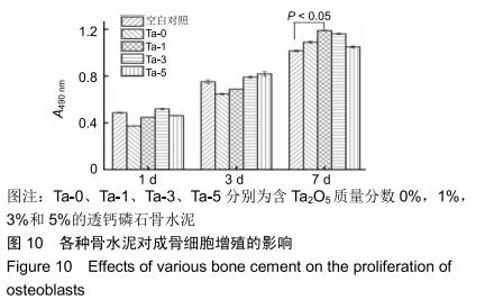
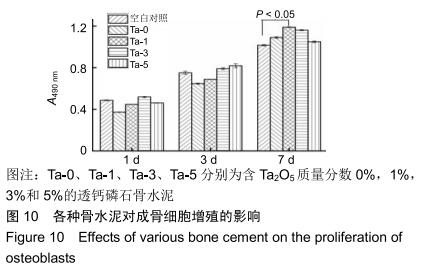
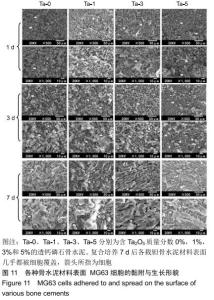
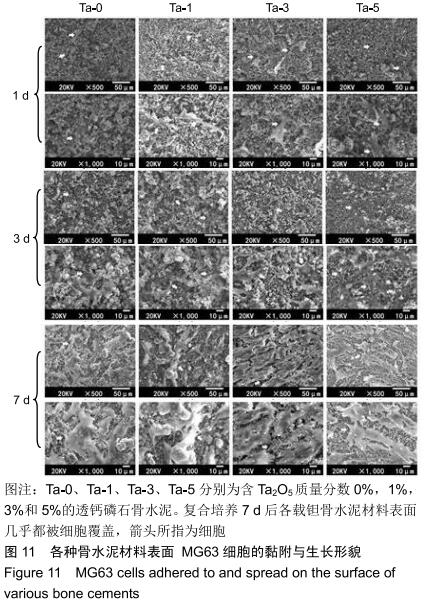
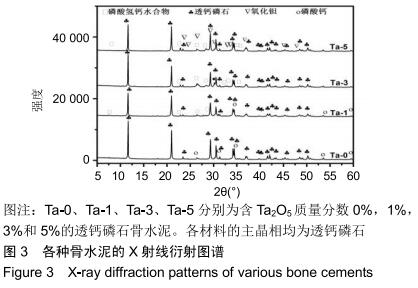
2.2 骨水泥的显微结构分析 图3为各骨水泥的X射线衍射谱图,各材料的主晶相均为透钙磷石[PDF# 09-0077],在加入Ta2O5的材料中观察到了极少量未反应的磷酸氢钙,在Ta-5中还检测到微量Ta2O5 [PDF#21-1198]。各材料红外谱图在527,578,795-1 140 cm-1处均观察到了透钙磷石的特征吸收峰[22],见图4;同时注意到与Ta-0相比,加钽材料的一些吸收峰出现了移动,793 cm-1处的峰(P-O-H平面外振动)蓝移到795 cm-1处[23],875 cm-1处的峰(P-O(H)伸缩振动)红移到874 cm-1 处[23],669 cm-1处的峰(结晶水)在Ta-1、Ta-2和Ta-3中分别红移至665,668和667 cm-1处[23]。 "
|
[1] JEONG J, KIM JH, SHIM JH, et al. Bioactive calcium phosphate materials and applications in bone regeneration. Biomater Res. 2019;23:4.
[2] 贾婉萍,董伟,彭宏峰,等.烧结法制备掺镁透钙磷石骨水泥[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(22):3445-3450.
[3] 闫玉婷.掺锶透钙磷石骨水泥修复牙槽骨缺损的实验研究[D].唐山:华北理工大学,2017.
[4] SHIRALIZADEH S, NASR-ISFAHANI H, KEIVANLOO A, et al. Radiopaque nanocomposites based on biocompatible iodinated N-phenyl amide-modified methyl methacrylate/ acrylic acid copolymer. J Polym Res. 2017;24(11):186-198.
[5] WANG XY, TAN L, LIN X, et al. Photoelectric guided navigation unilateral puncture of the percutaneous kyphoplasty in treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2018;32(2):203-209.
[6] WU TT, YANG S, SHI HS, et al. Preparation and cytocompatibility of a novel bismuth aluminate/calcium phosphate cement with high radiopacity.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018;29(9):149.
[7] PAZARCEVIREN AE, EVIS Z, KESKIN D. Resorbable PCEC/gelatin-bismuth doped bioglass-graphene oxide bilayer membranes for guided bone regeneration.Biomed Mater. 2019;14(3):035018.
[8] WANG T, YIN P, YANG Y, et al. Effect of element iodine on thecellmembrane transportability of fluorescent polymers and lysosome-targeted cell imaging.ACS Sustain Chem Eng.2019; 7(6):6295-6303.
[9] YAZDANPANAH A, MOZTARZADEH F. Synthesis and characterization of Barium-Iron containing magnetic bioactive glasses, the effect of magnetic component on structure and in vitro bioactivity.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2018;176:27-37.
[10] WU TT, YANG S, LU TL, et al. Strontium ranelate simultaneously improves the radiopacity and osteogenesis of calcium phosphate cement.2019;14(3):035005.
[11] KANT R, GUPTA BD. Fiber-Optic SPR based acetylcholine biosensor using enzyme functionalized Ta2O5 nanoflakes for alzheimer’s disease diagnosis.J Lightwave Technol. 2018; 36(18):4018-4024.
[12] HOEKSTRA JW, VAN DEN BEUCKEN JJ, LEEUWENBURGH SC, et al. Tantalumpentoxide as a radiopacifier in injectable calcium phosphate cements for bone substitution.Tissue Eng Part C Methods.2011; 17(9): 907-913.
[13] 苏可欣,季平,王涵,等.3D打印多孔钽种植体对骨整合影响的实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018,36(3):291-295.
[14] MEIDANCHI A, JAFARI A. Synthesis and characterization of high purity Ta2O5 nanoparticles by laser ablation and its antibacterial properties.Opt Laser Technol.2019;111:89-94. [15] GUO YN, WANG XF, WANG CC, et al. Structural characteristics and bioactivity of Sr doped Ta2O5 nanorods on tantalum by a facile two step hydrothermal method.J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. 2018;28(6):2473-2483.
[16] XU J, BAO XK, FU T, et al. In vitro biocompatibility of a nanocrystalline beta- Ta2O5 coating for orthopaedic implants. Ceram Int.2018;44(5):4660-4675.
[17] ANG LM, ZHOU BB, LIU ZG, et al. Surface hydroxylation regulates cellular osteogeneses on TiO2 and Ta2O5 nanorod films.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2018;167:213-219.
[18] 蒋剑涛,施忠民.钽在软骨损伤修复中的研究进展及临床应用[J].国际外科学杂志,2018,45(7):473-477.
[19] LI GD, ZHANG N, ZHAO ST, et al. Fe-doped brushite bone cements with antibacterial property. Mater Lett. 2018;215(1): 27-30.
[20] LOCA D, SOKOLOVA M, LOCS J, et al. Calcium phosphate bone cements for local vancomycin delivery. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2015;49:106-113.
[21] GAO CX, LIU HI, YANG HI, et al. Fabrication and characterization of injectable calcium phosphate-based cements for kyphoplasty.Mater Technol.2015;30:B256-263.
[22] 李光大,常乔婉,赵三团,等.纳米Fe3O4对透钙磷石骨水泥的理化性能影响研究[J].功能材料,2013,44(16):1977-1981.
[23] ALI TS, LEE SL, RAFAQAT H. Injectable magnesium-doped brushite cement for controlled drug release application.J Mater Sci.2016;51:7427-7439.
[24] DADKHAH M, PONTIROLI L, FIORILLI S, et al. Preparation and characterisation of an innovative injectable calcium sulphate based bone cement for vertebroplasty application.J Mater Chem A Mater.2017;5:102-115.
[25] LIU JQ, LI JY, YE JD, et al.S etting behavior, mechanical property and biocompatibility of anti-washout wollastonite/ calcium phosphate composite cement.Ceram Int. 2016;42(12): 13670-13681.
[26] FALEH T, ZEESHAN S, JAKE B. Dicalcium phosphate cements, brushite and monetite.Acta Biomater. 2012;8(2): 474-487.
[27] 靳正国,郭瑞松,侯信,等.材料科学基础[J].天津:天津大学出版社, 2015:243-247.
[28] 刘梦璐.石墨烯对磷酸钙骨水泥材料体外成骨活性的影响[D].新乡:河南师范大学,2018.
[29] 何仕诚,滕皋军,邓钢,等.添加不同类型、比例的显影剂后骨水泥性能的变化[J].介入放射学杂志,2006,15(4):238-241.
[30] 郑召民,郭家伟,催力扬,等.磷酸钙骨水泥的显影性及生物力学实验研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(9):696-699.
[31] 郑勇.多功能性多孔BaSO4@PDA/I-CD/Ag纳米粒子骨水泥显影剂的制备及性能研究[D].苏州:苏州大学附属第一医院,2017.
[32] 王红美.掺氟-10%掺锶透钙磷石骨水泥制备及其成骨能力研究[D].唐山:华北理工大学,2018.
[33] 郭良煜,郭卫春.磷酸镁骨水泥及其复合物在骨修复应用的研究进展[J].医学研究杂志,2019,48(1):159-162.
[34] 黄田,郑南生,张育专,等.磷酸钙骨水泥/纤维蛋白胶复合材料填充桡骨缺损的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(52): 7829-7835. |
| [1] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [2] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [3] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [5] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [6] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [7] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [8] | Zhang Guomei, Zhu Jun, Hu Yang, Jiao Hongwei. Stress of three-dimensional finite element models of E-MAX porcelain inlay [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 537-541. |
| [9] | Cheng Jun, Tan Jun, Zhao Yun, Cheng Fangdong, Shi Guojia. Effect of thrombin concentration on the prevention of postoperative cerebrospinal leakage by fibrin glue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 570-575. |
| [10] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [11] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [12] | Ye Haimin, Ding Linghua, Kong Weihao, Huang Zutai, Xiong Long. Role and mechanism of hierarchical microchanneled bone scaffolds in promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 621-625. |
| [13] | Yu Langbo, Qing Mingsong, Zhao Chuntao, Peng Jiachen. Hot issues in clinical application of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in orthopedics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 449-455. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Wang Xinting, Xu Dandi, Zhang Junxia, Su Hailong Wang Qi. Stability of load-bearing cross barrier of different arch structures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3838-3843. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||