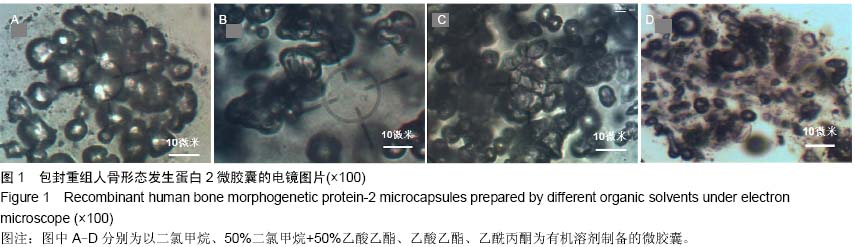
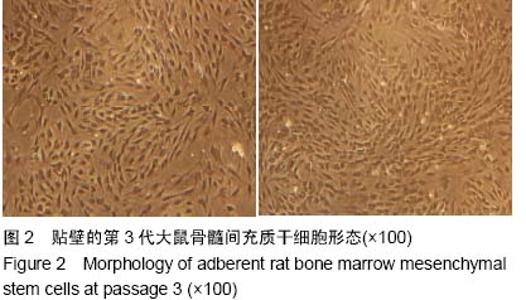
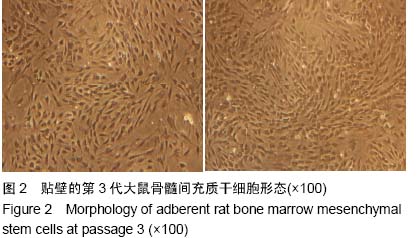
| [1] Lei L,Wang S,Wu H,et al.Optimization of release pattern of FGF-2 and BMP-2 for osteogenic differentiation of low-population density hMSCs.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015; 103(1):252-261.
[2] Lim SM,Eom HN,Jiang HH,et al.Evaluation of PEGylated exendin-4 released from poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres for antidiabetic therapy.J Pharm Sci. 2015; 104(1):72-80.
[3] Simon-Yarza T,Formiga FR,Tamayo E,et al.PEGylated-PLGA microparticles containing VEGF for long term drug delivery.Int J Pharm. 2013;440(1):13-18.
[4] Li X, Min S, Zhao X,et al. Optimization of entrapping conditions to improve the release of BMP-2 from PELA carriers by response surface methodology. Biomed Mater. 2014;10:015002.
[5] Vyslouzil J,Dolezel P,Kejdusova M,et al.Long-term controlled release of PLGA microparticles containing antidepressant mirtazapine. Pharm Dev Technol. 2014:1-8. [Epub ahead of print]
[6] Shah RB, Schwendeman SP. A biomimetic approach to active self-microencapsulation of proteins in PLGA.J Control Release. 2014;196:60-70.
[7] Ogbonna JD,Kenechukwu FC,Nwobi CS,et al.Formulation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of halofantrine-loaded solid lipid microparticles.Pharm Dev Technol. 2014:1-8.[Epub ahead of print]
[8] 林楚伟,周胜华,杜优优.全骨髓贴壁并差速传代分离纯化大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞:与密度梯度离心法的比较[J].中国组织工程与临床康复,2010,14(14):2508-2512.
[9] McKay WF,Peckham SM,Badura JM.A comprehensive clinical review of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (INFUSE Bone Graft). Int Orthop. 2007;31(6):729-734.
[10] Lebl DR.Bone morphogenetic protein in complex cervical spine surgery: A safe biologic adjunct? World J Orthop.2013; 4(2):53-57.
[11] Lad SP,Bagley JH,Karikari IO,et al. Cancer after spinal fusion: the role of bone morphogenetic protein.Neurosurgery. 2013; 73: 440-449.
[12] Calori GM,Donati D,Di Bella C,et al.Bone morphogenetic proteins and tissue engineering: future directions. Injury.2009; 40 Suppl 3:S67-76.
[13] Kempen DH,Kruyt MC, Lu L,et al.Effect of autologous bone marrow stromal cell seeding and bone morphogenetic protein-2 delivery on ectopic bone formation in a microsphere/ poly(propylene fumarate) composite.Tissue Eng Part A. 2009; 15(3):587-594.
[14] Kim SS,Gwak SJ,Kim BS.Orthotopic bone formation by implantation of apatite-coated poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/ hydroxyapatite composite particulates and bone morphogenetic protein-2.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008; 87(1):245-253.
[15] Zhao J,Wang S,Bao J,et al.Trehalose maintains bioactivity and promotes sustained release of BMP-2 from lyophilized CDHA scaffolds for enhanced osteogenesis in vitro and in vivo. PloS one.2013;8:e54645.
[16] White LJ, Kirby GT,Cox HC,et al.Accelerating protein release from microparticles for regenerative medicine applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(5):2578-2583.
[17] Chen L,Lu X,Li S,et al.Sustained delivery of BMP-2 and platelet-rich plasma-released growth factors contributes to osteogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells. Orthopedics.2012;35:e1402-1409.
[18] Hernandez A,Reyes R,Sanchez E,et al.In vivo osteogenic response to different ratios of BMP-2 and VEGF released from a biodegradable porous system. J Biomed Mater Res A.2012;100(9):2382-2391.
[19] Molavi O,Mahmud A,Hamdy S,et al.Development of a poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticle formulation of STAT3 inhibitor JSI-124: implication for cancer immunotherapy. Mol Pharm.2010;7(2):364-374.
[20] Zhang L,Lan X,Xu M,et al.Improvement in angiogenesis and osteogenesis with modified cannulated screws combined with VEGF/PLGA/fibrin glue in femoral neck fractures.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(4):1165-1172.
[21] Yan J,Yang S,Sun H,et al.Effects of releasing recombinant human growth and differentiation factor-5 from poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres for repair of the rat degenerated intervertebral disc.J Biomater Appl. 2013;29(1): 72-80.
[22] Gainza G,Aguirre JJ,Pedraz JL,et al.rhEGF-loaded PLGA-Alginate microspheres enhance the healing of full-thickness excisional wounds in diabetised Wistar rats. Eur J Pharm Sci.2013;50(3-4):243-252.
[23] Zou GK,Song YL,Zhou W,et al.Effects of local delivery of bFGF from PLGA microspheres on osseointegration around implants in diabetic rats.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012;114(3):284-289.
[24] Jelvehgari M, Montazam SH. Comparison of microencapsulation by emulsion-solvent extraction/ evaporation technique using derivatives cellulose and acrylate-methacrylate copolymer as carriers.Jundishapur J Nat Pharm Prod. 2012;7(4):144-152.
[25] Gupta V,Davis M,Hope-Weeks LJ,et al.PLGA microparticles encapsulating prostaglandin E1-hydroxypropyl-beta- cyclodextrin (PGE1-HPbetaCD) complex for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Pharm Res. 2011; 28(7): 1733-1749.
[26] Sheng Y,Yuan Y,Shan X,et al. Study on mass transfer behavior of hemoglobin-based nanocapsule surface. Sheng wu yi xue gong cheng xue za zhi = Journal of biomedical engineering.Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2008;25(4):879-884.
[27] Zhao J,Liu CS,Yuan Y,et al.Preparation of hemoglobin-loaded nano-sized particles with porous structure as oxygen carriers. Biomaterials.2007;28:1414-1422.
[28] Kim HK, Park TG. Microencapsulation of human growth hormone within biodegradable polyester microspheres: protein aggregation stability and incomplete release mechanism. Biotechnol Bioeng.1999;65(6):659-667. |