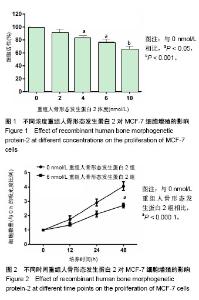
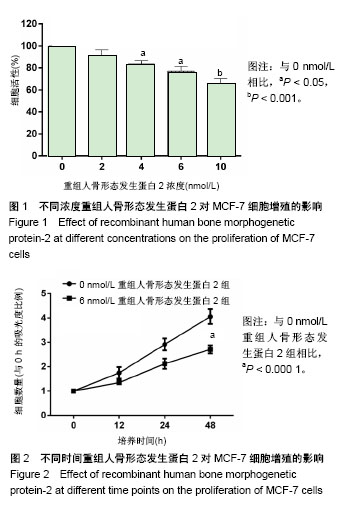
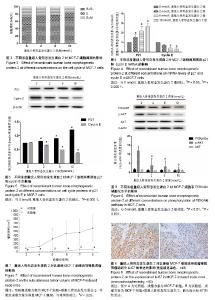
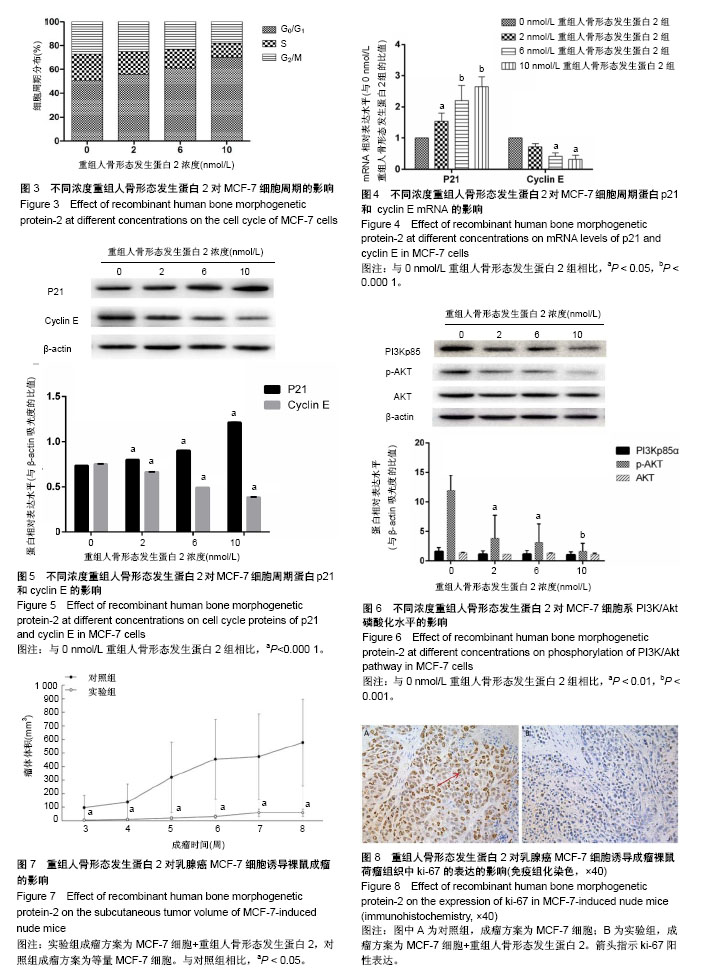
| [1] Urist MR. Bone: formation by autoinduction. Science. 1965;150 (3698):893-899.[2] Salazar VS, Gamer LW, Rosen V. BMP signalling in skeletal development, disease and repair. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(4): 203-221. [3] Kang MH, Kang HN, Kim JL, et al. Inhibition of PI3 kinase/Akt pathway is required for BMP2-induced EMT and invasion. Oncol Rep. 2009;22(3):525-534.[4] Lao L, Shen J, Tian H, et al. Secreted phosphoprotein 24kD (Spp24) inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017;51:51-55. [5] Li CS, Tian H, Zou M, et al. Secreted phosphoprotein 24 kD (Spp24) inhibits growth of human pancreatic cancer cells caused by BMP-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;466(2):167-172. [6] Yu JS, Cui W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: the role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development. 2016;143(17):3050-3060. [7] Faundez A, Tournier C, Garcia M, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein use in spine surgery-complications and outcomes: a systematic review. Int Orthop. 2016;40(6):1309-1319. [8] James AW, LaChaud G, Shen J, et al. A Review of the Clinical Side Effects of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2016;22(4):284-297. [9] Bodalia PN, Balaji V, Kaila R, et al. Effectiveness and safety of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 for adults with lumbar spine pseudarthrosis following spinal fusion surgery: A systematic review. Bone Joint Res. 2016;5(4):145-152. [10] Ghosh-Choudhury N, Woodruff K, Qi W, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 blocks MDA MB 231 human breast cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinase-mediated retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;272(3):705-711.[11] Katsuno Y, Hanyu A, Kanda H, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein signaling enhances invasion and bone metastasis of breast cancer cells through Smad pathway. Oncogene. 2008;27(49): 6322-6333. [12] Ye S, Park BH, Song KJ, et al. In vivo inhibition of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on breast cancer cell growth. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(3):E143-150.[13] Vavken J, Mameghani A, Vavken P, et al. Complications and cancer rates in spine fusion with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2). Eur Spine J. 2016;25(12): 3979-3989. [14] Tannoury CA, An HS2. Complications with the use of bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) in spine surgery. Spine J. 2014;14(3):552-559. [15] Young A, Mirarchi A. Soft Tissue Swelling Associated with the Use of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 in Long Bone Non-unions. J Orthop Case Rep. 2015;5(3):18-21. [16] Malham GM, Giles GG, Milne RL, et al. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins in Spinal Surgery: What Is the Fusion Rate and Do They Cause Cancer? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(22):1737-1742. [17] Skovrlj B, Koehler SM, Anderson PA, et al. Association Between BMP-2 and Carcinogenicity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(23): 1862-1871. [18] Wozney JM, Rosen V. Bone morphogenetic protein and bone morphogenetic protein gene family in bone formation and repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(346):26-37.[19] Wang Y, He T, Liu J, et al. Synergistic effects of overexpression of BMP?2 and TGF?β3 on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(6):5514-5520. [20] Zheng Y, Wang X, Wang H, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and migration through downregulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35(6):5189-5198. [21] Zhao X, Wang Q, Yang S, et al. Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis by targeting calcineurin in the xenograft model of human breast cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;781:60-68.[22] Noël A, De Pauw-Gillet MC, Purnell G, et al. Enhancement of tumorigenicity of human breast adenocarcinoma cells in nude mice by matrigel and fibroblasts. Br J Cancer. 1993;68(5): 909-915.[23] Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115-132.[24] Fontanella C, Fanotto V, Rihawi K, et al. Skeletal metastases from breast cancer: pathogenesis of bone tropism and treatment strategy. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2015;32(8):819-833. [25] Sciubba DM, Goodwin CR, Yurter A, et al. A Systematic Review of Clinical Outcomes and Prognostic Factors for Patients Undergoing Surgery for Spinal Metastases Secondary to Breast Cancer. Global Spine J. 2016;6(5):482-496. |