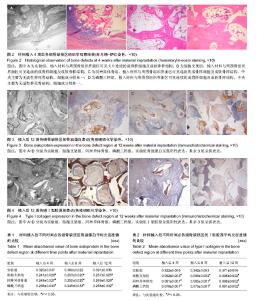
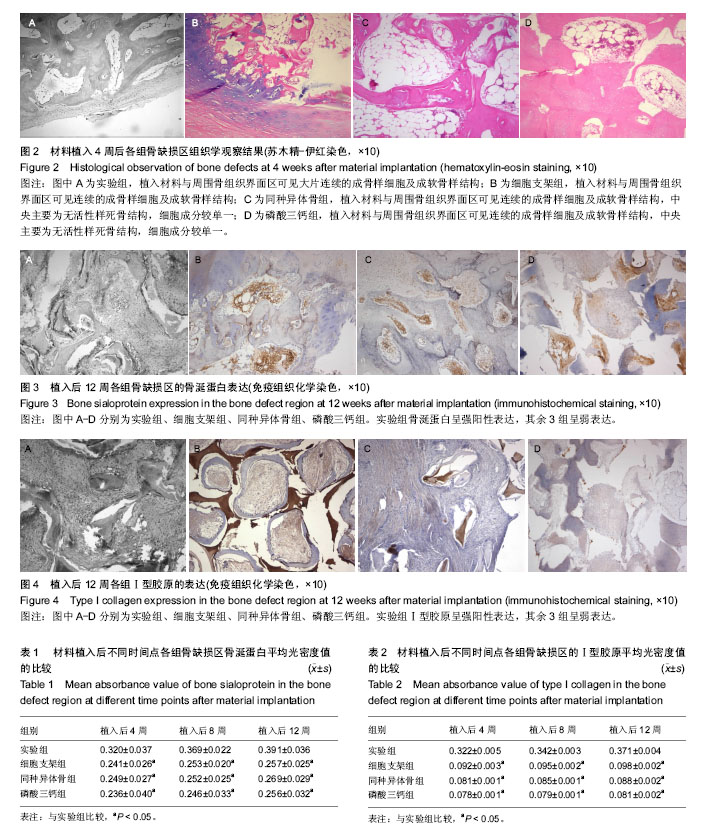
| [1] 王硕,韦兴.丝素蛋白复合物在骨缺损中的应用[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2015,4(5):415-419.[2] 王雷,余德涛.引导性骨再生膜管治疗骨缺损:怎样更好的走向临床?[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(42):7449-7454.[3] Fishero BA,Kohli N,Das A,et al.Current concepts of bone tissue engineering for craniofacial bone defect repair. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr.2015;8(1):23-30.[4] 王小志,何惠宇,杨楠,等.基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞复合同种异体骨修复绵羊极限骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(47): 8141-8148.[5] 许慧芬,何惠宇,唐小雪.物理联合化学或化学方法处理去抗原异种松质骨支架与骨髓间充质干细胞的细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(6):958-962.[6] 杨楠,何惠宇,胡杨,等.复合骨髓间充质干细胞同种异体支架骨修复羊髂骨极限缺损[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(16): 2859-2868.[7] 邬薇薇,胡杨,何惠字,等.BMP-2、bFGF基因转染的大鼠骨髓干细胞与牙胚细胞在体外混合培养对成牙基因的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2015,31(1):18-22.[8] 胡杨,盛磊,马莹,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子-慢病毒真核表达载体的构建及转染[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(6):1009-1014.[9] 杨楠.bFGF转染骨髓间充质干细胞附和支架材料的动物实验[D].新疆:新疆医科大学,2013:8-55.[10] 杨川博,何惠宇,崔杰,等.骨髓基质干细胞复合煅烧骨的皮下成骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(16):2883-2890. [11] Francisco JS,Moraes HP,Dias EP.Evaluation of the Image-Pro Plus 4.5 automatic counting of labeled nuclei by PCNA immunohistochemistry.Braz Oral Res.2004;18(2):100-104.[12] 臧程程,赵志颖,陈阵.人牙髓成牙本质细胞和神经组织中钠钙交换体1型通道蛋白的免疫组化研究[J],中华口腔医学杂志,2015, 50(10):627-630.[13] 许蕾,韩建国,李家锋.人BMP-2体外定向诱导犬BMSCs向成骨方向分化的实验研究[J].泰山医学院学报,2015,36(9):971-974.[14] 徐世旭,阳富春.骨形态发生蛋白的成骨作用及其在骨组织工程中的应用[J].医学综述,2008,14(2):193-195.[15] 安新玲,韩金祥,王世力.骨形态发生蛋白的研究进展[J].食品与药品,2009,11(11):69-73.[16] 王兴,崔鹏程,马瑞娜,等.rhBMP-2诱导异位软骨修复重建兔气管缺损的实验研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2011,11(10):1838-1840.[17] 肖后生,徐亮.骨形成蛋白在脊柱关节病中研究进展[J].安徽医学, 2011,32(2):226-228.[18] 杨丽,张荣华,朱晓峰,等.骨代谢与TGF-β1、BMP-2的关系[J].山东医药,2004,44(15):57-58.[19] Cui L,Yin S,Liu W,et al.Expanded adipose-derived stem cells suppress mixed lymphocyte reaction by secretion of prostaglandin E2.Tissue Eng.2007;13(6):1185-1195.[20] 孙兰英,王其宝,包崇云,等.碱性磷酸酶mRNA在体内组织工程骨中的表达[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2011,38(4):388-391.[21] 张丽君,丁焕文,王捷,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子基因转移对成骨细胞生长特性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007, 11(41):8238-8241.[22] Sun L,Wu L,Bao C,et al.Gene expressions of Collagen typeⅠ,ALP and BMP-4 in osteo-inductive BCP implants show similar pattern to that of natural healing bones.Mater Sci Eng C.2009;29(6):1829-1834.[23] Bourque WT,Hall BK,Gross M.The presence of several growth factors during the stage of fracture repair.J Bone Joint Surg(Br).1993;75(Supply):282-285.[24] 张鹏飞,史欣,袁梦桐,等.牙髓干细胞成骨诱导的新进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(31):6198-6200.[25] 袁林,曹凯华,童心.骨涎蛋白在不同类型种植体骨界面改建中的变化[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2012,22(6):319-322.[26] 李景辉,刘大勇,张方明,等.应用人恒牙牙髓干细胞与明胶支架构建组织工程骨的研究[J].北京口腔医学,2013,21(1):21-26.[27] 黄强,沈彬.Ⅰ型胶原与原发性骨质疏松的相关性研究进展[J].华西医学,2009,24(1):244-246.[28] Ong SJ,Jeon O,Yang HS,et al.Effects of culture conditions on steogenic differentiation in human esenchymal stem cells.J Microbiol Biotechnol.2007;17(7):1113-1119.[29] 夏欣一,崔英霞,杨滨,等.Ⅰ型胶原基因突变与成骨不全研究进展[J].中国优生与遗传杂志,2009,17(5):12-13.[30] 王征,毛克亚,侯喜君,等.多孔β-磷酸三钙修复骨缺损的实验研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2008,9(3):1136-1138.[31] 刘昌奎,谭新颖,罗金超,等.同种异体骨支架复合自体骨髓间充质干细胞修复下颌骨节段缺损动物模型的建立[J].口腔医学研究, 2015,31(1):27-30. |