Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 20-26.doi: 10.12307/2022.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes combined with chondroitinase ABC for treating spinal cord injury in rats
Xie Xingqi, Hu Wei, Tu Guanjun
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2021-02-05Revised:2021-02-07Accepted:2021-03-13Online:2022-01-08Published:2021-10-23 -
Contact:Tu Guanjun, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Xie Xingqi, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Guidance Program of the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, No. 201602857 (to TGJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Xingqi, Hu Wei, Tu Guanjun. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes combined with chondroitinase ABC for treating spinal cord injury in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 20-26.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
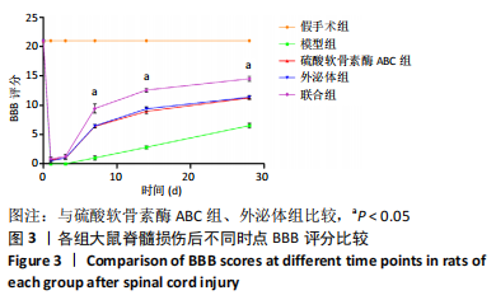
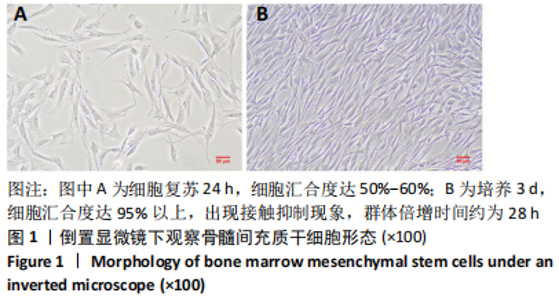
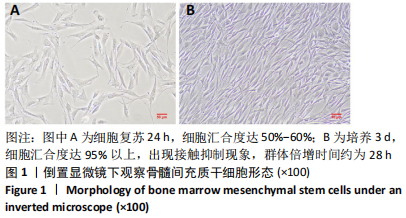
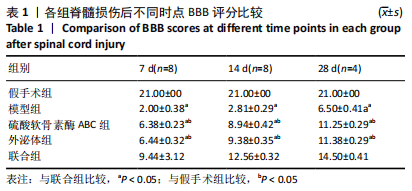
2.3 后肢运动功能评分 脊髓损伤后1 d各组大鼠后肢运动功能完全丧失,3 d后逐渐不同程度恢复,见图3。联合组脊髓损伤后7 d可见双后肢多关节节律运动,14 d可见掌面承重、后肢负重位,28 d可见后肢协调运动,见图3。各组脊髓损伤后1,3 d的BBB评分差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。脊髓损伤后第7,14,28天,ChABC组、外泌体组、联合组BBB评分显著高于模型组,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明治疗均有效。联合组BBB评分显著高于ChABC组、外泌体组,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。ChABC组和外泌体组间BBB评分差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表1。结果说明,BMSCs-Exo联合ChABC能协同发挥作用,促进脊髓损伤大鼠后肢运动功能恢复。"
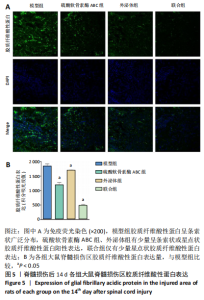
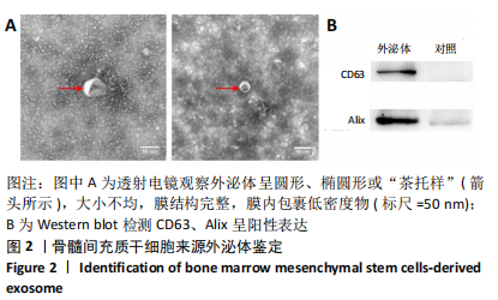
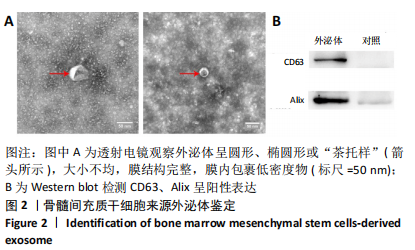
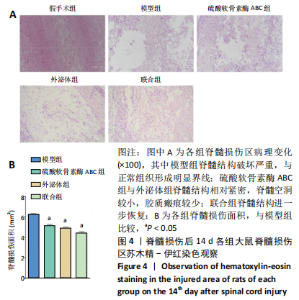
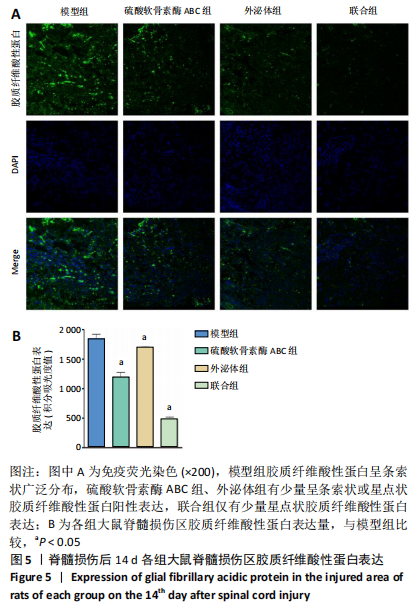
2.5 免疫荧光检测胶质纤维酸性蛋白表达 各组均有胶质纤维酸性蛋白阳性表达,主要集中于脊髓损伤区边缘。模型组胶质纤维酸性蛋白呈条索状广泛分布;ChABC组、外泌体组有少量呈条索状或星点状胶质纤维酸性蛋白阳性表达;联合组仅有少量星点状胶质纤维酸性蛋白表达,见图5A。与模型组、ChABC组、外泌体组比较,联合组胶质纤维酸性蛋白表达显著降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,ChABC组、外泌体组胶质纤维酸性蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05);与外泌体组比较,ChABC组胶质纤维酸性蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05),见图5B。结果说明,BMSCs-Exo联合ChABC能减少大鼠脊髓损伤后胶质瘢痕的形成,有利于神经元和轴突再生。"
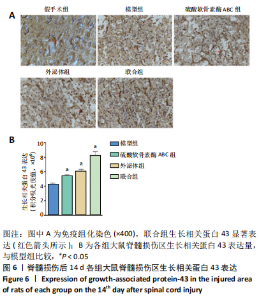
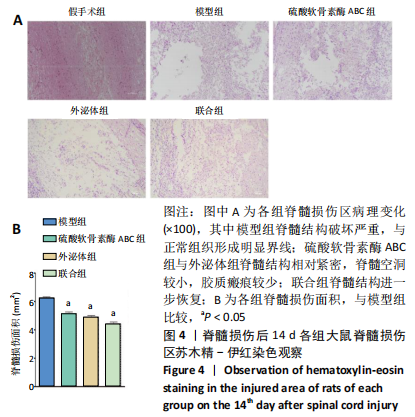
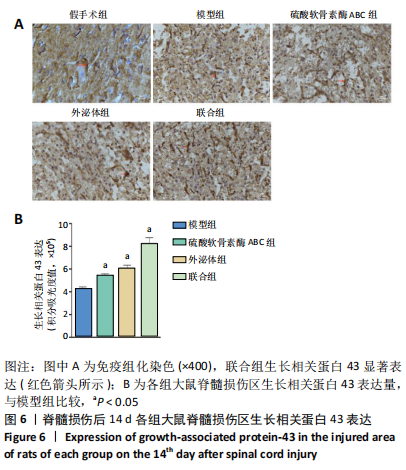
2.6 免疫组化检测生长相关蛋白43表达 各组均可见生长相关蛋白43阳性细胞,见图6A。联合组生长相关蛋白43显著表达,与其余各组比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。与模型组比较,ChABC组、外泌体组生长相关蛋白43表达增加(P < 0.05);与ChABC组比较,外泌体组生长相关蛋白43表达亦增加(P < 0.05),见图6B。结果说明,BMSCs-Exo联合ChABC能显著提高大鼠脊髓损伤后生长相关蛋白43表达,从而促进损伤神经元和轴突的修复与再生。 2.7 生物相容性 BMSCs-Exo和ChABC注射入大鼠模型后,未见伤口延迟愈合、感染、免疫排斥反应等不良影响,具有良好的生物相容性和转化意义。"
| [1] ECKERT MJ, MARTIN MJ. Trauma: Spinal Cord Injury. Surg Clin North Am. 2017;97(5):1031-1045. [2] 吴周睿,朱元贵,程黎明,等.SCI与修复的关键科学问题——第81期“双清论坛”综述[J].中国科学基金,2013,27(3):147-153. [3] LEE H, MCKEON RJ, BELLAMKONDA RV. Sustained delivery of thermostabilized chABC enhances axonal sprouting and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(8): 3340-3345. [4] BRADBURY EJ, CARTER LM. Manipulating the glial scar: chondroitinase ABC as a therapy for spinal cord injury. Brain Res Bull. 2011;84(4-5):306-316. [5] TESTER NJ, PLAAS AH, HOWLAND DR. Effect of body temperature on chondroitinase ABC’s ability to cleave chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycans. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85(5):1110-1118. [6] MORTAZAVI MM, HARMON OA, ADEEB N, et al. Treatment of spinal cord injury: a review of engineering using neural and mesenchymal stem cells. Clin Anat. 2015;28(1):37-44. [7] FILIPPI M, BOIDO M, PASQUINO C, et al. Successful in vivo MRI tracking of MSCs labeled with Gadoteridol in a Spinal Cord Injury experimental model. Exp Neurol. 2016;282:66-77. [8] BOIDO M, RUPA R, GARBOSSA D, et al. Embryonic and adult stem cells promote raphespinal axon outgrowth and improve functional outcome following spinal hemisection in mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2009;30(5):833-846. [9] ZACHAR L, BAČENKOVÁ D, ROSOCHA J. Activation, homing, and role of the mesenchymal stem cells in the inflammatory environment. J Inflamm Res. 2016;9:231-240. [10] COFANO F, BOIDO M, MONTICELLI M, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Spinal Cord Injury: Current Options, Limitations, and Future of Cell Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11):2698. [11] CHEN X, LI Y, WANG L, et al. Ischemic rat brain extracts induce human marrow stromal cell growth factor production. Neuropathology. 2002; 22(4):275-279. [12] THÉRY C, ZITVOGEL L, AMIGORENA S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(8):569-579. [13] 万然,史旭,刘京松,等.间充质干细胞分泌组治疗SCI的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(7):1088-1095. [14] REN Z, QI Y, SUN S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Hope for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(23):1467-1478. [15] ALLEN AR. Surgery of experimental lesion of spinal cord equivalent to crush injury of fracture dislocaion of spinal colum. JAMA. 1911;57(4): 878-880. [16] 王琳,裴双,郭斌,等.骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体用于大鼠SCI修复的初步探索[J].中国病理生理杂志,2018,34(5):862-869. [17] GOLDSTEIN M, WATKINS S. Immunohistochemistry. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2008;Chapter 14:Unit 14.6. [18] GAZDIC M, VOLAREVIC V, HARRELL CR, et al. Stem Cells Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1039. [19] LIU AM, CHEN BL, YU LT, et al. Human adipose tissue- and umbilical cord-derived stem cells: which is a better alternative to treat spinal cord injury? Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(12):2306-2317. [20] JIN MC, MEDRESS ZA, AZAD TD, et al. Stem cell therapies for acute spinal cord injury in humans: a review. Neurosurg Focus. 2019;46(3):E10. [21] CSOBONYEIOVA M, POLAK S, ZAMBORSKY R, et al. Recent Progress in the Regeneration of Spinal Cord Injuries by Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3838. [22] CURTIS E, MARTIN JR, GABEL B, et al. A First-in-Human, Phase I Study of Neural Stem Cell Transplantation for Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(6):941-950.e6. [23] LIAU LL, LOOI QH, CHIA WC, et al. Treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:112. [24] SHENDE P, SUBEDI M. Pathophysiology, mechanisms and applications of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;91:693-706. [25] ZURITA M, VAQUERO J. Functional recovery in chronic paraplegia after bone marrow stromal cells transplantation. Neuroreport. 2004; 15(7):1105-1108. [26] PAUL C, SAMDANI AF, BETZ RR, et al. Grafting of human bone marrow stromal cells into spinal cord injury: a comparison of delivery methods. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(4):328-334. [27] VAQUERO J, ZURITA M, OYA S, et al. Cell therapy using bone marrow stromal cells in chronic paraplegic rats: systemic or local administration? Neurosci Lett. 2006;398(1-2):129-134. [28] HELDRING N, MÄGER I, WOOD MJ, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles. Hum Gene Ther. 2015;26(8):506-517. [29] BAGNO L, HATZISTERGOS KE, BALKAN W, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Cardiovascular Disease: Progress and Challenges. Mol Ther. 2018;26(7):1610-1623. [30] LOU G, CHEN Z, ZHENG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(6):e346. [31] FORSBERG MH, KINK JA, HEMATTI P, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells and exo: progress and challenges. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:665. [32] ZHANG Y, WANG WT, GONG CR, et al. Combination of olfactory ensheathing cells and human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes sciatic nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(10):1903-1911. [33] LIEW LC, KATSUDA T, GAILHOUSTE L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: a glimmer of hope in treating Alzheimer’s disease. Int Immunol. 2017;29(1):11-19. [34] LIU W, WANG Y, GONG F, et al. Exosomes derived from bone mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by suppressing the activation of A1 neurotoxic reactive astrocytes. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(3):469-484. [35] ZHAO C, ZHOU X, QIU J, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit complement activation in rats with spinal cord injury. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:3693-3704. [36] LANKFORD KL, ARROYO EJ, NAZIMEK K, et al. Intravenously delivered mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes target M2-type macrophages in the injured spinal cord. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0190358. [37] LI C, JIAO G, WU W, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit neuronal apoptosis and promote motor function recovery via the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(11):1373-1383. [38] PEKNY M, PEKNA M. Astrocyte intermediate filaments in CNS pathologies and regeneration. J Pathol. 2004;204(4):428-437. [39] 熊薇,袁娅金,张桂仙,等.中枢神经系统损伤后胶质瘢痕形成的机制及其对神经修复的影响[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2020,42(10): 1876-1883. [40] AZIZI M, FARAHMANDGHAVI F, JOGHATAEI MT, et al. ChABC-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: A comprehensive study on biocompatibility, functional recovery, and axonal regeneration in animal model of spinal cord injury. Int J Pharm. 2020;577:119037. [41] XIA T, HUANG B, NI S, et al. The combination of db-cAMP and ChABC with poly(propylene carbonate) microfibers promote axonal regenerative sprouting and functional recovery after spinal cord hemisection injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;86:354-362. [42] LIU X, WANG J, LI G, et al. Effect of combined chondroitinase ABC and hyperbaric oxygen therapy in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(1):25-30. [43] FÜHRMANN T, ANANDAKUMARAN PN, PAYNE SL, et al. Combined delivery of chondroitinase ABC and human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neuroepithelial cells promote tissue repair in an animal model of spinal cord injury. Biomed Mater. 2018;13(2):024103. [44] JANZADEH A, SARVEAZAD A, YOUSEFIFARD M, et al. Combine effect of chondroitinase ABC and low level laser (660nm) on spinal cord injury model in adult male rats. Neuropeptides. 2017;65:90-99. [45] SARVEAZAD A, BABAHAJIAN A, BAKHTIARI M, et al. The combined application of human adipose derived stem cells and chondroitinase ABC in treatment of a spinal cord injury model. Neuropeptides. 2017;61:39-47. [46] NOVOTNA I, SLOVINSKA L, VANICKY I, et al. IT delivery of ChABC modulates NG2 and promotes GAP-43 axonal regrowth after spinal cord injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011;31(8):1129-1139.
(责任编辑:MZH,ZN,JY)
|
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1316-1322. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1323-1329. |
| [3] | Kan Houming, Fan Lijun, Chen Xuetai, Shen Wen. Application of platelet-rich plasma in neuropathic pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1345-1353. |
| [4] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1183-1190. |
| [5] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1191-1197. |
| [6] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1033-1039. |
| [7] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1040-1046. |
| [8] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1053-1059. |
| [9] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1060-1067. |
| [10] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1086-1092. |
| [11] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1098. |
| [12] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1099-1104. |
| [13] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1122-1127. |
| [14] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1133-1140. |
| [15] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1141-1150. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||