Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (19): 2986-2992.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.19.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Pedicle screw fixation through Wiltse approach combined with injectable calcium sulfate bone cement for single-level thoracolumbar fracture
Zhan Fang-biao1, Wang Shi-jun2, Cheng Jun1, Feng Shi-long1, Xie Li-zhong1, Li Bo1, Zhang You1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Chongqing Three Gorges Central Hospital, Chongqing 404000, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, First Hospital, Peking University, Beijing 100034, China
-
Online:2017-07-08Published:2017-08-10 -
Contact:Wang Shi-jun, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Hospital, Peking University, Beijing 100034, China -
About author:Zhan Fang-biao, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Chongqing Three Gorges Central Hospital, Chongqing 404000, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhan Fang-biao, Wang Shi-jun, Cheng Jun, Feng Shi-long, Xie Li-zhong, Li Bo, Zhang You. Pedicle screw fixation through Wiltse approach combined with injectable calcium sulfate bone cement for single-level thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2986-2992.
share this article
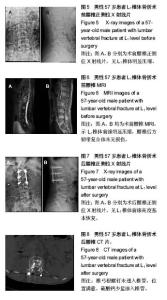
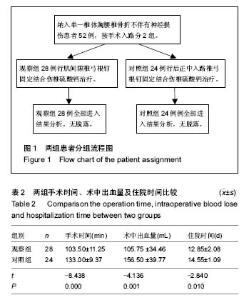
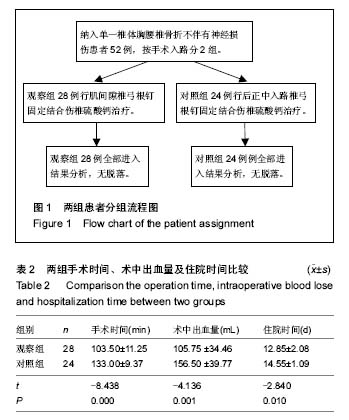
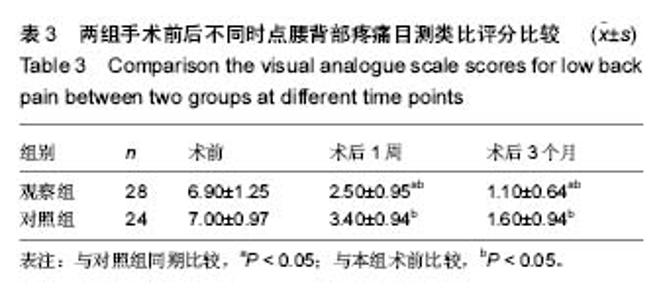
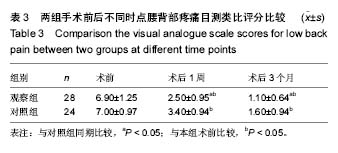
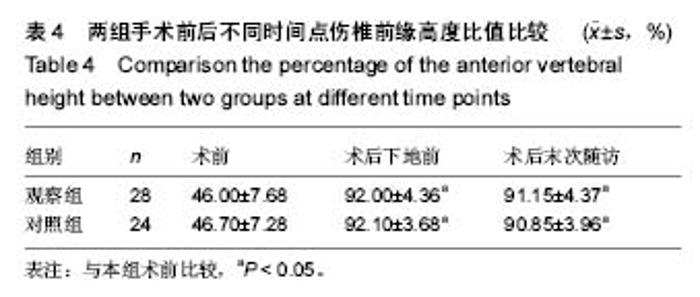
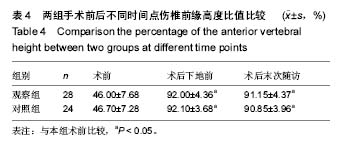
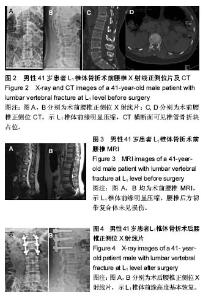
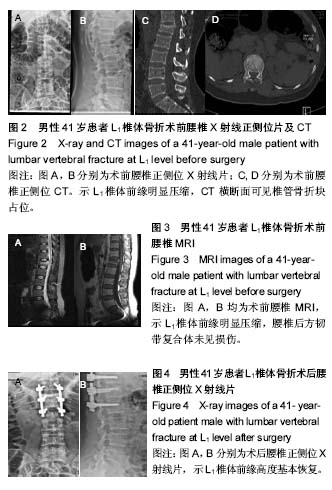
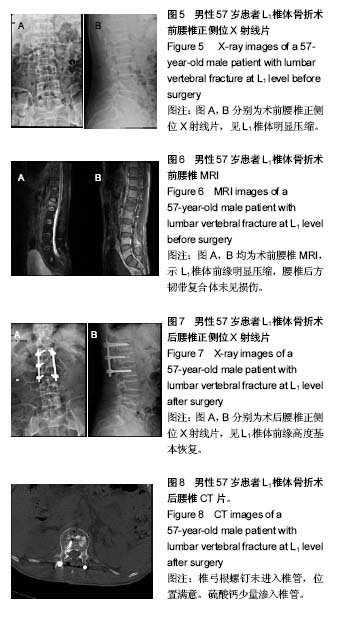
病例2:患者,57岁男性,因高处坠落伤致腰背部疼痛8 h入院。入院行腰椎正侧位X射线片、MR检查提示L1椎压缩性骨折,疼痛目测类比评分7分。患者采用椎旁肌间隙入路并椎弓根钉棒系统内固定结合伤椎注入硫酸钙治疗,治疗后3 d复查腰椎正侧位X射线片及腰椎CT。腰椎CT可见硫酸钙少量渗入椎管,患者无神经症状,治疗后3个月随访疼痛目测类比评分0分,骨折愈合良好,内固定未见松动及断钉断棒,见图5-8。 2.5 不良事件 本组52例患者中术后腰椎CT扫描发现无螺钉误入椎管,所有患者术后均无切口感染,切口积血等并发症。术后CT发现2例患者出现硫酸钙渗入椎管,发生率4%(2/52),但术后均无神经症状,术后3个月复查时硫酸钙已完全吸收。所有患者随访期间未出现螺钉松动、断裂。 2.6 可能影响结果的因素 本研究2组患者手术并非由同一组手术医生完成,因此术中出血量、手术时间及伤椎复位效果可能有人为偏倚。"
| [1] 杨民,徐祝军,丁国正,等. 后路椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗相邻两节段胸腰椎骨折[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2012,28(6):500-504. [2] 钟远鸣,付拴虎,李智斐,等. 单双侧椎弓根螺钉内固定并后路腰椎体间融合修复腰椎退行性疾病的系统评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(9):1353-1360.[3] Kim BG, Dan JM, Shin DE. Treatment of thoracolumbar fracture. Asian Spine J. 2015;9:133-146.[4] Wood KB, Buttermann GR, Phukan R, et al. Operative compared with nonoperative treatment of a thoracolumbar burst fracture without neurological deficit: a prospective randomized study with follow-up at sixteen to twenty-two years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97:3-9.[5] Ko SB, Lee SW. Result of posterior instrumentation without fusion in the management of thoracolumbar and lumbar unstable burst fracture. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27: 189-195. [6] Jeon CH, Lee YS, Youn SJ, et al. Factors affecting postural reduction in posterior surgery for thoracolumbar burst fracture. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28:E225-230.[7] Kawaquehi Y, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery. A histologic and enzymatic analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21:941-944.[8] Danneels LA, Vanderstraeten GG, Cambier DC, et al. CT imaging of trunk muscles in chronic low back pain patients and healthy control subjects. Eur Spine J. 2000;9:266-272. [9] Datta G, Gnanalingham KK, Peterson D, et al. Back pain and disability after lumbar laminectomy. Is there a relationship to muscle retraction? Neurosurgery. 2004;54:1413-1420.[10] .Wiltse LL, Bateman JG, Hutchinson RH, et al. The paraspinal sacrospinalis-splitting approach to the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1968;50(5):919-926. [11] Wiltse LL, Spencer CW. New uses and refinements of the paraspinal approach to the lumbar spine.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1988;13:696-706.[12] Olivier E,Beldame J,Ould Slimane M,et al. Comparison between one midline cutaneous incision and two lateral incisions in the lumbar paraspinal approach by Wiltse:a cadaver study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006;28:494-497. [13] Wiltse LL. The paraspinal sacrospinalis-splitting approach to the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973: 48-57.[14] Ni WF, Huang YX, Chi YL, et al. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for neurologic intact thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23:530-537.[15] Samama CM, Langeron O, Rosencher N, et al. Aprotinin versus placebo in major orthopedic surgery: a randomized, doubleblinded, dose-ranging study. Anesth Analg. 2002;95: 287-293. [16] Koutsoumbelis S, Hughes AP, Girardi FP, et al. Risk factors for postoperative infection following posterior lumbar instrumented arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93: 1627-1633.[17] Schoenfeld AJ, Ochoa LM, Bader JO, et al. Risk factors for immediate postoperative complications and mortality following spine surgery: a study of 3475 patients from the National surgical quality improvement program. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:1577-1582. [18] Gejo R, Matsui H, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Serial changes in trunk muscle performance after posterior lumbar surgery. Spine. 1999;24:1023-1028. [19] Kim DY, Lee SH, Chung SK, et al. Comparison of multifidus muscle atrophy and trunk extension muscle strength: percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation. Spine. 2005;30:123-129. [20] Kumbhare D, Parkinson W, Dunlop B. Validity of serum creatine kinase as a measure of muscle injury produced by lumbar surgery. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008;21(1):49-54.[21] Foley KT,Gupta SK, Justis JR, et al . Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation of the lumbar spine. Neurosurg Focus. 2001;10(4):1-8.[22] Lee JK, Jang JW, Kim TW, et al. Percutaneous short-segment pedicle screw placement without fusion in the treatment of thoraclumbar burst fractures: is it effective? Comparative sdudy with opne short-segment pedicle screw fixation with posterolateral fusion. Acta Neurochir. 2013;155(12):2305-2312.[23] Garfin SR, Fardon DF. Emerging technologies in spine surgery. Spine J. 2002;2(20):1-4. [24] Ringel F, Stoffel M, Stuer C, et al. Minimally invasive transmuscular pedicle screw fixation of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Neurosurgery 2006;59(4 Suppl 2):ONS361-366; discussion ONS366-367. [25] Schizas C, Michel J, Kosmopoulos V, et al. Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw insertion in percutaneous posterior transpedicular stabilization. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(5):613-617.[26] Perisinakis K, Theocharopoulos N, Damilakis J, et al. Estimation of patient dose and associated radiogenic risks from fluoroscopically guided pedicle screw insertion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(14):1555-1560.[27] Rampersaud YR, Foley KT, Shen AC, et al. Radiation exposure to the spine surgeon during fluoroscopically assisted pedicle screw insertion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(20):2637-2645.[28] Vaccaro AR,Lehman RA Jr,Hurlbert RJ,et al. A new classification of thorocolumbar injuries:the importance of injury morphology,the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex,and neurologic status. Spine. 2005;30(20):2325-2333.[29] Huskisson EC. Measurement of pain. Lancet. 1974;2(7889): 1127-1131. [30] 高生,李慧章,席平昌,等.硫酸钙椎体成形术联合椎弓根钉内固定治疗创伤性胸腰椎骨折的前瞻性研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(7):586-588.[31] Siebenga J, Leferink VJM, Segers MJM, et al. Treatment of traumatic thoracolumbar spine fractures: a multicenter prospective randomized study of operative versus nonsurgical treatment. Spine. 2006;31:2881-2890. [32] Weber BR, Grod D, Dvorak J, et al. Posterior surgical approach to the lumbar spine and its effect on the multifidus muscle. Spine. 1997;22:1765-1772.[33] Kim DY, Lee SH, Chung SK, et al. Comparison of multifidus muscle atrophy and trunk extension muscle strength: percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation. Spine. 2004;30:123-129.[34] Li HJ, Yang L, Xie H, et al. Surgical outcomes of mini-open Wiltse approach and conventional open approach in patients with single-segment thoracolumbar fractures without neurologic injury. J Biomed Res. 2015;29(1):76-82.[35] 崔威,张勇鹏,张斌.椎弓根钉经椎旁肌间隙置入修复胸腰椎骨折:矫正效果及生物相容性随访[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(22):3513-3518.[36] 张兆川,马超,吴德慧,等. 椎弓根螺钉椎旁肌间隙与后正中入路内固定修复胸腰椎骨折:稳定性比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(40): 6451-6458.[37] 鲍海星,徐宏光.椎旁肌间隙入路并伤椎单侧置钉治疗不稳定型胸腰椎骨折[J].颈腰痛杂志,2016,37(4):339-341.[38] 王洪伟,周跃,李长青,等.经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的生物力学及临床研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(9) :932-937.[39] 王洪伟,周跃,李长青,等.经伤椎与跨伤椎万向钉置钉固定脊柱骨折的生物力学对比研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2010,26(12) : 1105-1108.[40] Kurui TG. Posterior fixation of thoracolumbar burst fracture: shout-segment pedicle fixation versus long-segment instumenation. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;188(6):485-488.[41] Liao JC, Fan KF, Keorochana G, et al. Transpedicular grafting after short-segment pedicle instrumentation for thoracolumbar burst fracture: calcium sulfate cement versus autogenous iliac bone graft. Spine. 2010;35(15):1482-1488.[42] Liao JC, Fan KF, Chen WJ, et al. Posterior instrumentation with transpedicular calcium sulphate graft for thoracolumbar burst fracture. Int Orthop. 2009;33(6):1669-1675.[43] Walsh WR, Morberg P, Yu Y, et al. Response of a calcium sulfate bone graft substitute in a confined cancellous defect. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;406(1):228-236. [44] Hu GF, Xiao LW, Fu H, et al. Study on injectable and degradable cement of calcium sulphate and calcium phosphate for bone repair. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010; 21(2):627-634.[45] Bu BX, Wang MJ, Liu WF, et al. Short-segment posterior instrumentation combined with calcium sulfate cement vertebroplasty for thoracolumbar compression fractures: Radiographic outcomes including nonunion and other complications. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015; 101: 227-233. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||