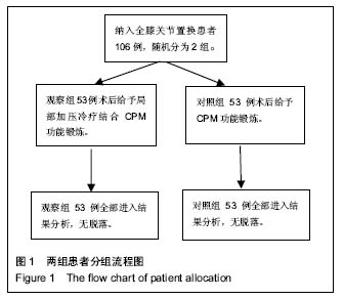
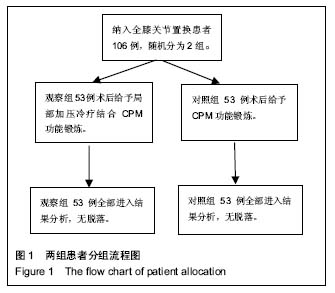
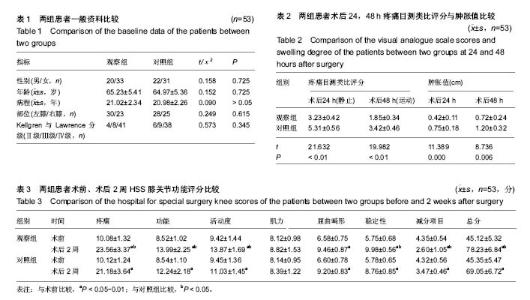
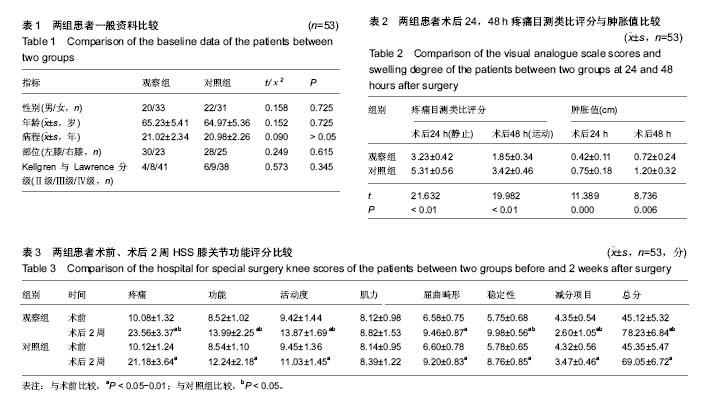
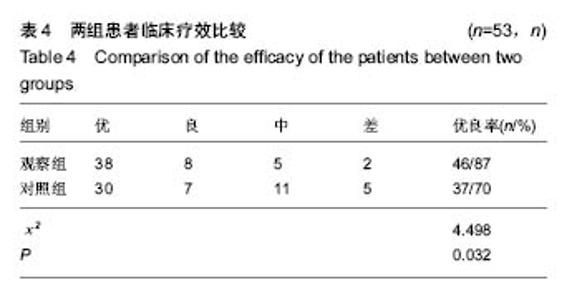
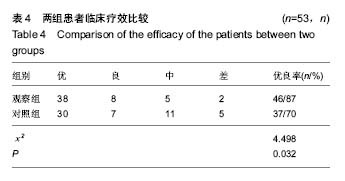
| [1] Joshi RN, White BP, Murray-Weir M, et al. Prospective Randomized Trial of the Efficacy of Continuous Passive Motion Post Total Knee Arthroplasty: Experience of the Hospital for Special Surgery. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(12): 2364-2369.[2] 谭建国.全膝关节置换术患者术后应用连续股神经阻滞联合浸润麻醉的镇痛效果评估[J].海南医学院学报, 2016,22(13): 1450-1453.[3] 李建会,吴涛,边仁秀,等.康复机器人辅助步行训练对全膝关节置换术后患者功能恢复的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2012, 34(11):806-809.[4] Schinksy MF, McCune C, Bonomi J. Multifaceted Comparison of Two Cryotherapy Devices Used After Total Knee Arthroplasty: Cryotherapy Device Comparison. Orthop Nurs. 2016;35(5): 309-316.[5] Scharf HP. CORR Insights®: does advanced cryotherapy reduce pain and narcotic consumption after knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(11): 3424-3425.[6] Huskission EC. Measurement of pain. J Rheumatol. 1982;9(5): 768-769.[7] Insall JN,Ranawat CS,Aglietti P,et al.A comparison of models of totle knee replacement prostheses.J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 1976;58:754-765.[8] 牛雪飞,苏辉棠.关节松动术联合物理因子治疗全膝关节置换术后膝关节活动受限的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2015,37(10):776-777.[9] Mau-Moeller A, Behrens M, Finze S, et al. The effect of continuous passive motion and sling exercise training on clinical and functional outcomes following total knee arthroplasty: a randomized active-controlled clinical study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014;12:68.[10] 吴晴晴,聂艳芳,袁秋娟. 髋关节置换术后皮牵引与冰敷结合CPM机疗效对比分析[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2011,23(9): 796-797.[11] Baloch N, Zubairi AJ, Rashid RH, et al. Effect of continuous passive motion on knee flexion range of motion after total knee arthroplasty. J Pak Med Assoc. 2015;65(11 Suppl 3): S32-34.[12] 张剑君. 旋转平台及后稳定固定平台假体在人工膝关节置换术的临床治疗分析[J].海南医学院学报,2013,19(12): 1723-1725.[13] Mumith A, Pavlou P, Barrett M, et al. Enhancing Postoperative Rehabilitation Following Knee Arthroplasty Using a New Cryotherapy Product: A Prospective Study. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2015;6(4): 316-321.[14] Wittig-Wells D, Johnson I, Samms-Mcpherson J, et al. Does the use of a brief cryotherapy intervention with analgesic administration improve pain management after total knee arthroplasty? Orthop Nurs. 2015;34(3): 148-153.[15] 马路遥,郭万首.膝关节置换术后冷疗的研究现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(3):253-256.[16] 马严刚.全膝关节置换术后应用关节周围局部注射镇痛的疗效评价[D].山东大学,2014.[17] 傅建珍.全膝关节置换术后康复锻炼中应用鸡尾酒疗法镇痛28例[J].临床医学,2012,2(11):93-94.[18] 乔玉宁,谢秋娟,丁敏华,等.早期肌力锻炼对人工全膝关节置换术患者康复的影响[J].上海护理,2014,14(5):14-16.[19] 韩向真. CPM 机辅助功能锻炼对全膝关节置换术后患者关节活动度的影响[J]. 护理实践与研究, 2015,12(10):142-142,143.[20] Tammachote N,Kanitnate S,Manuwong S,et al.Is Pain After TKA Better with Periarticular Injection or Intrathecal Morphine? Clin Orthop Relat Res.2013;471(6):1992-1999.[21] 申作柱.全膝关节置换术治疗重度膝关节骨性关节炎的临床疗效分析[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(14):224-225.[22] Koh IJ,Kang YG,Chang CB, et al.Does periarticular injection have additional pain relieving effects during contemporary multimodal pain control protocols for TKA?A randomised,controlled study. Knee. 2012;19(4):253-259.[23] 潘琳琳,朱小娟,董慧珍.膝关节骨性关节炎患者行全膝关节置换术后应用循环加压冷疗系统控制疼痛的临床研究[J].内蒙古医学杂志,2014,46(7):861-863.[24] 王健.人工膝关节置换围手术期规范化疼痛管理[D].南方医科大学,2014.[25] 李毅.髋关节置换术围手术期的深静脉血栓预防策略的研究[D].浙江大学,2013.[26] 贺文. 冷疗加压系统使用时间对行人工全膝关节置换术患者关节肿胀疼痛与睡眠质量的影响[J]. 国际护理学杂志,2016, 35(13):1732-1735.[27] 邓宝贵,全小明.冷疗对全膝关节置换术后出血量、疼痛、肿胀及睡眠质量的影响[J].护理研究(中旬版),2014,28(4):1311-1313.[28] 周清洁,彭贵凌,姜耀,等.骨折后Aircast冷疗与冰袋两种冰敷与解除疼痛效果的比较[J].实用医学杂志,2011,27(8):1454-1455.[29] 程明.围手术期系统康复治疗对全膝关节置换术后早期膝关节功能恢复的影响[D].泸州医学院,2014.[30] 余占洪,李素香,苏厂尧,等.冷敷疗法在膝关节置换术后临床应用及其影响因素的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2013, 7(5):719-721.[31] 高学宇,周章武.综合疗法治疗膝关节骨性关节炎研究进展[J].中医药临床杂志,2014,26(12):1316-1318.[32] 马丽红,张玲,吴秋霞.冷疗机持续冷敷在膝关节置换术后的应用研究[J].护理研究,2012,26(10):2739-2741.[33] Spreng UJ,Dahl V,Hjall A,et al.High-volume local infiltration analgesia combined with intravenous or local ketorolac+morphine compared with epidural analgesia after total knee arthroplasty.Br J Anaesth. 2010;105(5):675-682.[34] 郝建彬.全膝关节置换术治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床体会[J].中国实用医药,2013,8(7):51-52.[35] Chang CB, Cho WS. Pani manag ement protocols, peri-operative pain and patient satisfaction after total knee replacement:a multicentre study. Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012; 94(11):1511-1516.[36] 周树花,于清霞.人工全膝关节置换术患者的康复护理[J].中国社区医师,2014,30(34):151-152.[37] 戴繁林,张鹏,时晓亚,等.全膝关节置换术中注射鸡尾酒式镇痛混合剂对膝关节中期功能的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016, 31(4):359-361.[38] 胡华,王莉.人工膝关节置换术后康复锻炼的效果分析[J].现代护理,2015,13(17):98-100.[39] 吴明珑,田薇,刘洪娟. 人工全膝关节置换术后最佳冰敷时间及频率的研究[J]. 骨科, 2015, 6(3): 159-161.[40] 谢琪,刘慧,黄华扬,等.持续脉冲加压冷疗对膝关节镜术后早期功能障碍的影响[J].广东医学,2014,35(2):239-240. |