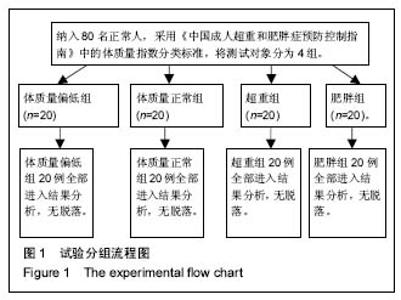
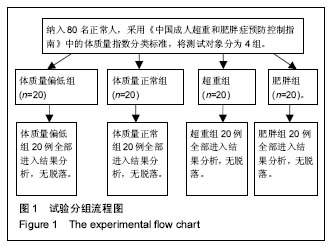
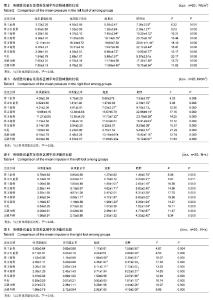
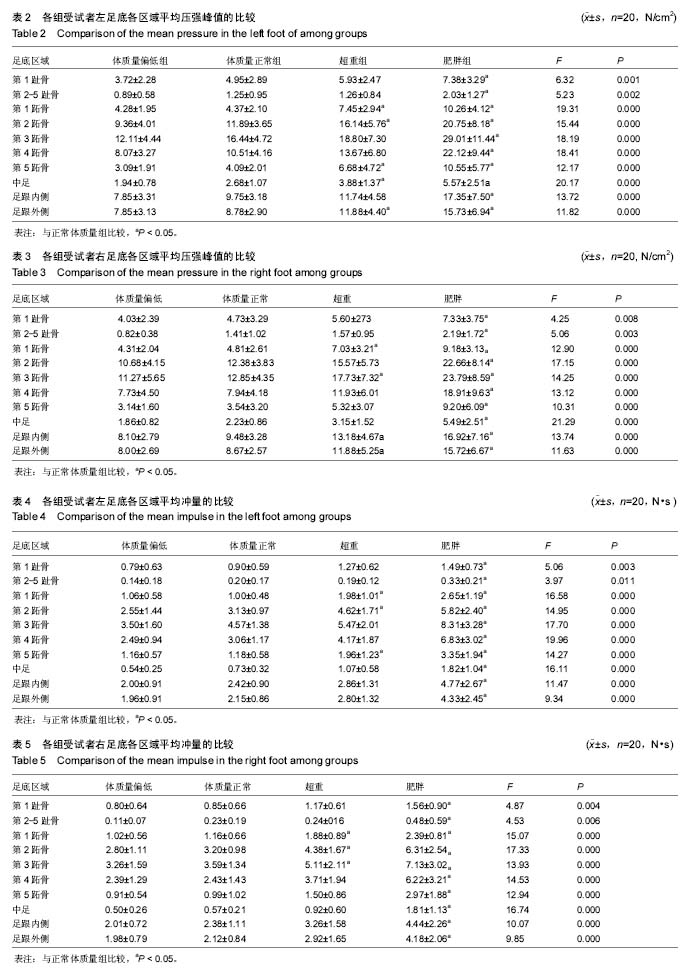
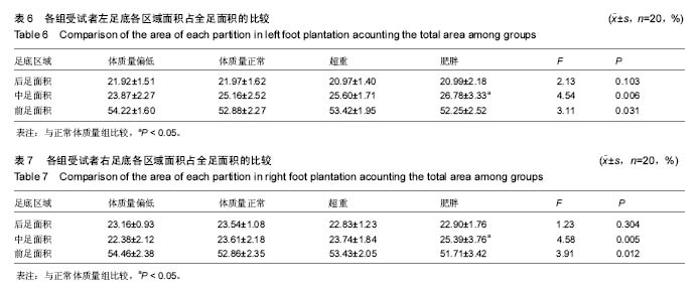
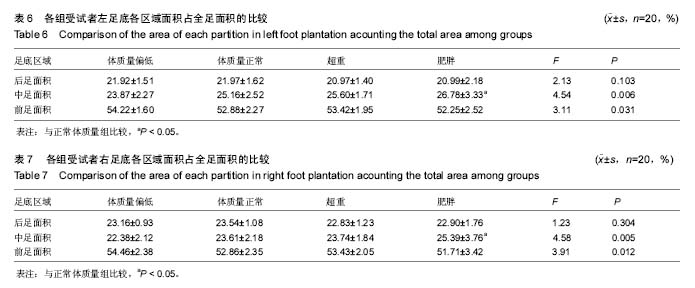
| [1] 岳童,倪朝民,刘孟,等. 脑卒中患者足底压力与步行能力的相关性分析[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2015,37(5):353-356.[2] 元香南,李晓婷,李菡婷,等. 步行模式下肌电生物反馈性功能性电刺激对脑卒中患者即刻足底压力的影响[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2015,21(10):1191-1196.[3] 李文霞,罗祥蓉,曹瑛,等.糖尿病周围神经病变患者足底压力与步态的变化[J].广东医学,2017,38(6):859-863.[4] 尹海滨,郭见平,牛英群.男大学生左足正常右足外八字步态足底压力特征分析[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2013, 35(6): 452-455.[5] 谢翠华,张倩,符霞军,等.糖尿病病人足底压力峰值与糖尿病足底压力性溃疡发生的相关性研究[J]. 护理研究, 2016,30(3):918-921.[6] 孔德刚,高虹,王璐.太极拳运动对老年人足底压力的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(5):2029-2031.[7] 徐珊珊.临床护士长期行走站立足底压力与肌肉骨骼损伤的调查分析[J]. 护理实践与研究,2016,13(9):90-92.[8] 黄萍,钱念东,齐进,等. 拇外翻发病危险因素与足底压力特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(42):6351-6356.[9] 孙育欣,潘晓华.高跟鞋与足弓的关系[J].海南医学,2013,24(5): 48-751.[10] Bennetts CJ, Owings TM, Erdemir A, et al. Clustering and Classification of Regional Peak Plantar Pressures of Diabetic Feet. J Biomech. 2013;46(1):19-25.[11] 何红,徐国丽,陈会平.糖尿病足周围神经病变病人降低足底压力护理干预措施的研究进展[J].护理研究,2015,29(9C):3338-3340.[12] 孔德刚,高虹,王璐.扁平足与正常足男大学生足底压力及步态特征比较[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2013, 34(6): 680-682, 685.[13] 周利明,姜伟星,刘清涛.背负不同负荷对儿童行走时足底压力的影响[J].河北医学,2014,20(7):1173-1176.[14] 刘程程,元香南,张立新,等. 老年人与健康大学生平地行走时足底压力特征比较[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2015, 21(5): 544-548.[15] 殷青霞.青年人自然行走状态下足底压力分类特征数据探究[J].电脑知识与技术,2016,12(7):192-194.[16] 杨洁,倪朝民.足底压力及其临床康复应用研究进展[J].中国临床保健杂志,2014,17(3):329-331.[17] 王彦斐,程如意.不同年资临床护士的足底压力步态分析[J].西部中医药,2014,27(10):162-163.[18] 李慧,任旭,常慧,等.沈阳市城市职业人群体重自评调查结果分析[J].中国健康教育,2015,31(7):664-667.[19] Gravante G, Russo G, Pomara F, et al.Comparison of ground reaction forces between obese and control young adults during quiet standing on a baropodometric platform. Ciln Biomech. 2003;18(8):780-782.[20] 严励,王永慧,杨川,等.非糖尿病人群足底压力的研究[J].中山大学学报 (医学科学版),2006,27(2):197-202.[21] 张少伟,邹晓峰,陈民盛. 肥胖男性少年足底动态压力变化参数[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(33): 6262-6266.[22] 高艳玲,张志广,付磊磊.某县960例小学生扁平足患病情况及发生影响因素分析[J].实用预防医学,2014,21(10):1210-1212.[23] 蒋娅,李亚洁,谢翠华,等.2型糖尿病病人足底压力影响因素研究[J].护理研究,2013,27(12):4004-4006.[24] 魏秀丽,肖波涛,杨秀丽.手术室护士长时间站立时足底压力和肌肉骨骼受损情况的调查[J].解放军护理杂志,2016,33(10): 34-36.[25] 孟敏,蒋娅,谢翠华.糖尿病患者周围神经病变与足底压强的关系[J]. 护理学杂志, 2014, 29(11): 30-31.[26] 贾秀眉,王秋惠,徐芳.手术护士长时间站立足底压力和肌肉骨骼受损情况调查[J].医院管理论坛,2016,33(11):61-63.[27] 闫红光. 不同体质量指数成年女性穿高跟鞋行走步态特征分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(49):7349-7355.[28] 宋丽华,陈民盛.人体负重行走的生物力学研究及前景[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(41):7771-7774.[29] 李立,陈玉娟,翟凤鸣,等.长期从事太极拳运动老年人足底压力分布特征及平衡能力研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016,31(9):984-988.[30] 李冬玲,李远,李姗姗.平衡足底压力及稳定步态在早期糖尿病足防治[J].临床医学工程,2016 23(2):173-174.[31] 吴宝平,闰松华,张宽,等.大学生不同运动方式下的足底压力分布研究[J]. 北京生物医学工程,2016,35(2):161-179.[32] 杜天舒,成西侠,张春礼,等.前交叉韧带损伤患者动态足底压力变化[J].中国运动医学杂志,2016,35(6):520-526.[33] 蒋建新,蒋涵芝. 女生扁平足现状调查与及时干预矫正研究[J].继续医学教育,2016,30(2):99-100.[34] 张悠然.足部矫正器对扁平足患者步态的影响[J].西部皮革, 2014,36(19):39-46.[35] 边曙光,李俊,陈莹,等.扁平足矫正效果追踪评估系统设计[J].医疗卫生装备,2016,37(8):24-28.[36] 陈瑞巧.临床手法结合功能锻炼矫治生长发育儿童扁平足的探讨[J]. 数理医药学杂志,2016,29(11):1593-1595.[37] 陈善本,鲍琨,陈博昌.儿童足弓发育与扁平足的研究进展[J]. 临床小儿外科杂志,2016,15(6):610-613.[38] 苏宏伦,郭俊超孙,莫中军,等.个性化扁平足矫形鞋垫的生物力学研究[J]. 医用生物力学,2016,31(6):490-494.[39] 闫松华,谭国庆,刘志成.7-11岁肥胖儿童动态足底压力分布[J].医用生物力学,2010,25(2):118-123.[40] 魏东凌,张文,周琳.扁平足与正常足举重运动员足底压力分布对照研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2013,32(2):112-116.[41] 左建刚,胡海威,桑志成,等.拇外翻足并发第2跖骨头下疼痛的相关因素研究[J].中国骨伤,2017,30(1):51-56. |