Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (5): 752-758.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.05.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of resina draconis on Toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-kappaB and dendritic cell phenotypes in colitis rats
Li Nan1, Wang Xue-ming2, Ji Yang3, Shi Yu-ling1, Wang Xin1, Li Na1, Su Li1, Sha Li-na1
- 1 Department of Gastroenterology, the 309th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100091, China
2 Department of Pharmacy, the 309th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100091, China
3 Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Drug and Instrument Control, General Logistics Department of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100071,
China
-
Revised:2014-12-17Online:2015-01-30Published:2015-03-02 -
Contact:Li Nan, Department of Gastroenterology, the 309th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100091, China -
About author:Li Nan, M.D., Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Gastroenterology, the 309th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100091, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing, No. 717329
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Nan, Wang Xue-ming, Ji Yang, Shi Yu-ling, Wang Xin, Li Na, Su Li, Sha Li-na. Effects of resina draconis on Toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-kappaB and dendritic cell phenotypes in colitis rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(5): 752-758.
share this article
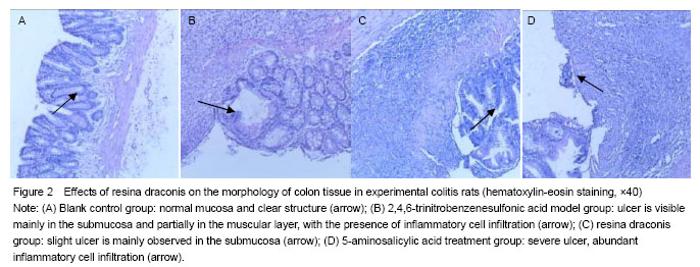
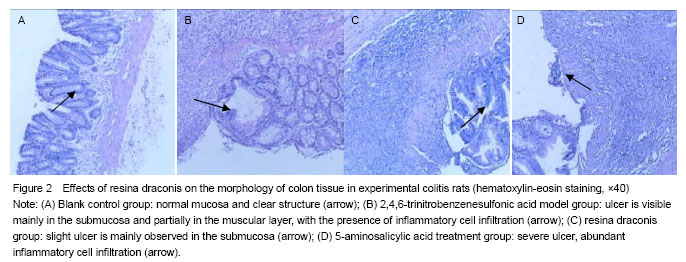
General condition following model induction In the TNBS model group, rat colitis specimens exhibited mucosal hyperemia, edema, erosions, necrosis, thickening intestinal wall and ulcer. Ulcer, inflammatory exudates and lymphoid hyperplasia were visible in the mucosa, submucosa and muscular layer. In the blank control group, intact smooth mucosa and clear structure of glandular organ were observed, without erosion or ulcer, with the presence of slight neutrophil infiltration. In the resina draconis and 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment groups, there were slight ulcer and partially intact glandular organ (Figure 2)."
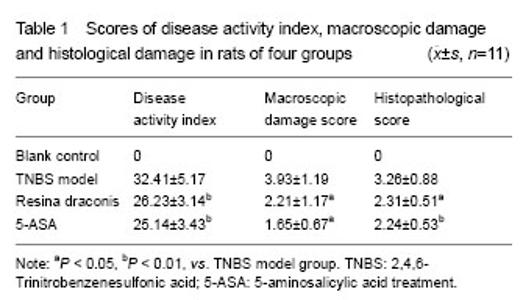
Disease activity index scoring Ulcer size was observed according to colonic mucosal damage index. Significant differences in weight changes were detected between the resina draconis and blank control groups (P=0.017, P=0.022, P=0.027), but there was no significant difference as compared TNBS model group with resina draconis and 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment groups (P=0.067, P=0.077). Disease activity index, macroscopic colonic damage score and histopathological score were significantly decreased in the resina draconis group compared with the model group (P < 0.05). Symptoms and tissue damages were obviously lessened in the 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment and resina draconis groups compared with the model group. Within 10 days, disease activity index scores were higher in the TNBS model group than those in the resina draconis and 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment groups (P=0.008, P=0.001; Table 1)."
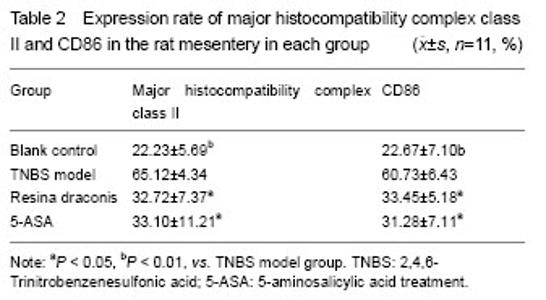
Dendritic cells surface markers major histocompatibility complex class II and CD86 expression in the mesenteric lymph node The expression of major histocompatibility complex class II and CD86 of dendritic cells surface markers in the mesenteric lymph node was significantly lower in the resina draconis group than those in the TNBS model group (Table 2). Expression rates of major histocompatibility complex class II and CD86 were the lowest in the blank control group. Expression rates of major histocompatibility complex class II and CD86 were greater in the TNBS model group than those in the blank control group (P=0.006, P=0.007). Expression rates of major histocompatibility complex class II and CD86 in the resina draconis group were significantly lower than those in the TNBS model group (P=0.021, P= 0.019), but still higher than those in the blank control group (P=0.006, P=0.001). Expression rates of major histocompatibility complex class II and CD86 in the 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group were significantly lower than those in the TNBS model group (P=0.015, P= 0.014), but higher than those in the blank control group (P= 0.077, P=0.032) (Table 2)."
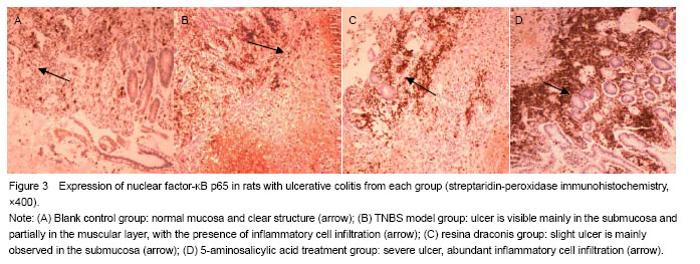
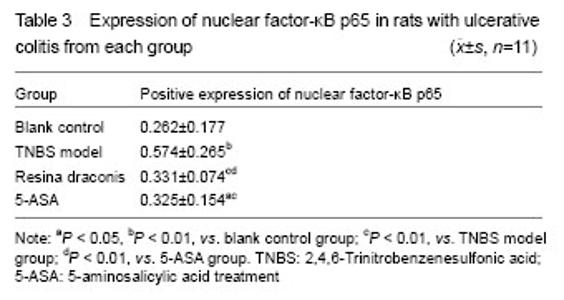
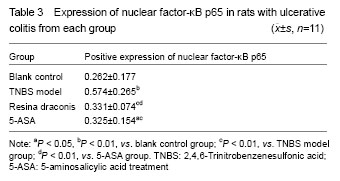
Effects of resina draconis on nuclear factor-κB p65 expression in rats with ulcerative colitis Yellow particles in the cytoplasm and/or nuclei were positive cells (Figure 3). Compared with the control group, nuclear factor-κB p65 expression was significantly higher in the TNBS model group, resina draconis group and 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group (P < 0.01, P < 0.05). Compared with the TNBS model group, nuclear factor-κB p65 expression was significantly lower in the resina draconis group and 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group (P < 0.01). Compared with the 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group, nuclear factor-κB p65 expression was lower in the resina draconis group (P < 0.01; Table 3)."
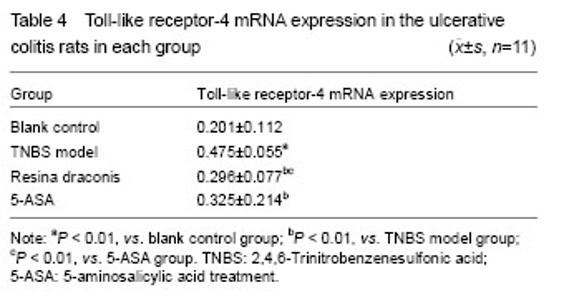
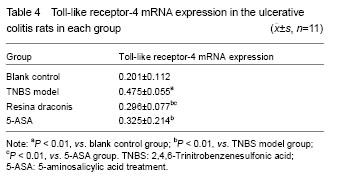
Effects of resina draconis on Toll-like receptor-4 mRNA expression in rats with ulcerative colitis Compared with the blank control group, Toll-like receptor-4 mRNA expression was significantly higher in the TNBS model group (P < 0.01). Compared with the TNBS model group, Toll-like receptor-4 mRNA expression was significantly lower in the 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group and resina draconis group (P < 0.01). Compared with the 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group, Toll-like receptor-4 mRNA expression was significantly lower in the resina draconis group (P < 0.01) (Table 4)."
| [1] Carrera E, Manzano R, Garrido E. Efficacy of the vaccination in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(9):1349-1353. [2] Xavier RJ, Podolsky DK. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 448(7152):427-434. [3] Diamante G, Dikstein R. Transcriptional control by NF-κB: elongation in focus. Biochim Biophysics Acta. 2013;1829 (9):937-945. [4] Lzcue A, Coombes JL, Powrie F. Regulatory T cells suppress systemic and mucosal immune activation to control intestinal inflammation. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:256-271. [5] Chen S, Zeng ZP, Li HZ, et al. Relationship between plasma level of leptin and the expression of leptin receptor in human adrenal tissues and tumors. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;19;90(38):2667-2670. [6] Petvises SO, Neill HC. Characterisation of dendritic cells arising from progenitors endogenous to murine spleen. PLoS One. 2014;14;9(2):e88311. [7] Li N, Wang XM, Wu K, et al. Influence of Compound Xuejie Enema on the Blood Rheology of Chronic Nonspecific Ulcerative Colitis. Zhongguo Quanke Yixue. 2006;9(24): 2073-2074. [8] Wang XM, Wu K, Shi YL, et al. Preparation and Clinical Application of Compound Xuejie enema. Zhongguo Yiyuan Yaoxue Zazhi. 2005;25(3):281. [9] Sobczak M, Zakraewski, Zakrzewski PK, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive action of the dimeric enkephalin peptide biphalin in the mouse model of colitis: New potential treatment of abdominal pain associated with inflammatory bowel diseases. Peptides. 2014;60:102-106. [10] Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, et al. Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest. 1993;69(2):238-249. [11] Tu P, Tsaip L, Lin Y, et al. Expression profile of Toll-like receptor mRNA in pigs co-infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and porcine circovirus type 2. Res Vet Sci. 2014;14(3):1-9. [12] Brenan M, Rees DJ. Sequence analysis or rat integrin alphaE1 and alphaE2 subunits: tissue expression reveals phenotypic similarities between intraepithelial lymphocytes and dendritic cells in lymph. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30(6): 1527-1537. [13] Tanaka K. Expression of Toll-like receptors in the intestinal mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;2(2):193-196. [14] Arasaradnam R, Nwokolo CU. Epiphenomenon of telomere lengths lessons from ulcerative colitis. Gut. 2012;61(10):1516. [15] Pulli B, Ali M, Forghani R, et al. Measuring myeloperoxidase activity in biological samples. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):1-10. [16] Zhang X, Ma J, Xu M, et al. Imbalance between CD205 and CD80/CD86 in dendritic cells in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. Thromb Res. 2014;19(14):1-10. [17] Haider J, Marisavljevic D, Stanisavljevicn, et al. BCL10 aberations and NF-kappa B activation involving p65 are absent or rare in primary gastric MALT lymphoma. Vojnosanit Preql. 2014;7(11):1040-1044. [18] Dimitrakopoulos GN, Dimtrakopoulou K, Maraziotis IA, et al. Supervised method for construction of microRNA-mRNA networks: application in cardiac tissue aging dataset. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;26(30):318-321. [19] Wang H, Ouyang Q, Hu RW. Establishment of rat colitis model induced by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Weichang Bingxue. 2001;6(1):7-10. [20] Yang XY, Yao L. Pharmacological action and clinical experience of dragon’s blood. Heilongjiang Yiyao. 2011; 24(2): 265-266. [21] Xia PF, Ding LY. The research progress of dragon's blood. Hebei Zhongyiyao Xuebao. 2006;21(1):40-43. [22] Li N, Wang XM, Gao LC, et al. Experimental study of resina draconis in protecting intestinal mucous membrane barrier in burned rats. Zhongguo Zhongxuyi Jiehe Xiaohua Zazhi. 2010;18(6):351-354. [23] Li N, Wang XM, Wu K, et al. Experimental study of resina draconis on rats with ulcerative colitisin. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xiaohua Yiyuan. 2007;15(6):377-379. [24] Creticos PS. Advances in synthetic peptide immuno- regulatory epitopes. World Allergy Organ J. 2014;7(1):30. [25] Wang J, Wang X, Hussain S, et al. Distinct roles of different NF-κB subunit s in regulating inflammatory and T cell stimulatory gene expression in dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2007;178(11):6777-6788. [26] Zhou HG, Chen HB, Wu MH. Viewing from the toll-like receptor/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway to explore the immunomodulatory mechanism of Chinese drugs. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. 2010;30(8):884-888. [27] Yu S, Tang S, Mayer GD, et al. Interactive effects of ultraviolet-B radiation and pesticide exposure on DNA photo-adduct accumulation and expression of DNA damage and repair genes in Xenopus laevis embryos. Aquat Toxicol. 2014;12(4):256-266. [28] Tan W, Huang W, Gu X, et al. IL-17F/IL-17R interaction stimulates granulopoiesis in mice. Exp Hematol. 2008; 36(11): 1417-1427. [29] Ahmed S, Shaffer A, Geddes T, et al. Evaluation of optimal RNA extraction method from human carotid atherosclerotic plaque. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2014;5(14):1-9. |
| [1] | Sun Kexin, Zeng Jinshi, Li Jia, Jiang Haiyue, Liu Xia. Mechanical stimulation enhances matrix formation of three-dimensional bioprinted cartilage constructs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [3] | Yang Yitian, Wang Lu, Yao Wei, Zhao Bin. Application of the interaction between biological scaffolds and macrophages in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [4] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [5] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [6] | Tang Haotian, Liao Rongdong, Tian Jing. Application and design of piezoelectric materials for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [7] | Xu Yan, Li Ping, Lai Chunhua, Zhu Peijun, Yang Shuo, Xu Shulan. Piezoelectric materials for vascularized bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [8] | Li Xinyue, Li Xiheng, Mao Tianjiao, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Three-dimensional culture affects morphology, activity and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [9] | Li Xiaoyin, Yang Xiaoqing, Chen Shulian, Li Zhengchao, Wang Ziqi, Song Zhen, Zhu Daren, Chen Xuyi. Collagen/silk fibroin scaffold combined with neural stem cells in the treatment of traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 890-896. |
| [10] | Yuan Bo, Xie Lide, Fu Xiumei. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote the repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [11] | Qin Yuxing, Ren Qiangui, Li Zilong, Quan Jiaxing, Shen Peifeng, Sun Tao, Wang Haoyu. Action mechanism and prospect of bone microvascular endothelial cells for treating femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 955-961. |
| [12] | Xiong Bohan, Yu Yang, Lu Xiaojun, Wang Xu, Yang Tengyun, Zhang Yaozhang, Liao Xinyu, Zhou Xiaoxiang, He Lu, Li Yanlin. Research progress in promoting tendon to bone healing during anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 779-786. |
| [13] | Zhang Min, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin. Application potential of naringin in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 787-792. |
| [14] | Ning Ziwen, Wang Xu, Shi Zhengliang, Qin Yihua, Wang Guoliang, Jia Di, Wang Yang, Li Yanlin. Meniscal injury repair methods for non-blood supply area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 420-426. |
| [15] | Zong Mingrui, Liu Haiyan, Li Bing, Wu Xiuping. Application of carboxymethyl chitosan in tissue engineering of stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 447-452. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||