Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (43): 6951-6958.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.43.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Thermosensitive hydrogel with Aliskrien influence the heart function of rats with acute myocardial infarction
Chen Pan-pan, Li Xiao-yan, Jiang Xue-jun, Liu Yang
- Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2014-09-02Online:2014-10-15Published:2014-10-15 -
Contact:Li Xiao-yan, Chief physician, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Chen Pan-pan, Studying for master’s degree, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81170307
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Pan-pan, Li Xiao-yan, Jiang Xue-jun, Liu Yang. Thermosensitive hydrogel with Aliskrien influence the heart function of rats with acute myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(43): 6951-6958.
share this article
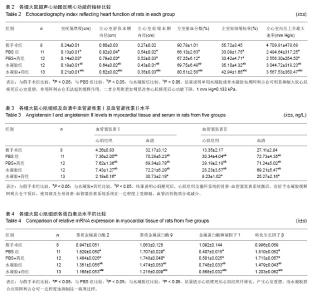
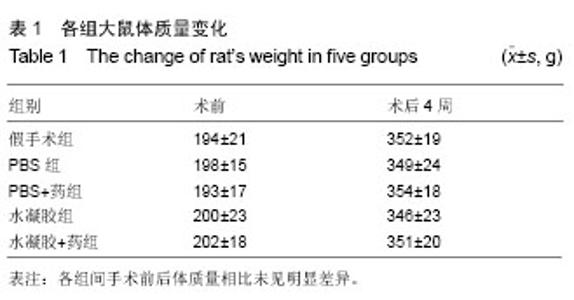
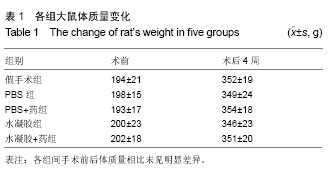
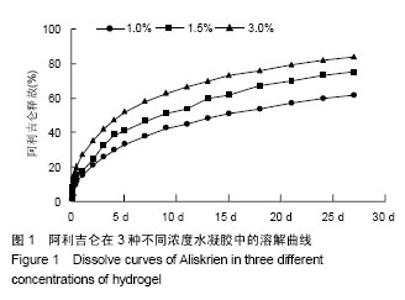
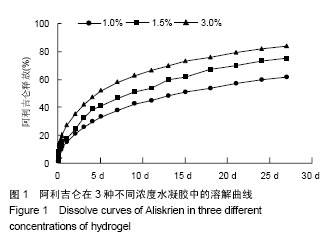
2.1 体外水凝胶控制释放阿利吉仑曲线 水凝胶可以控制其包裹的阿利吉仑的释放,20 d后仍可检测到药物从水凝胶中释放出来,并且随着水凝胶浓度的升高,其释放率降低,在3 d以后,3种不同浓度水凝胶的质粒释放率有明显差别(P < 0.05),见图1,本实验选用1.5%浓度的水凝胶。 2.2 各组实验动物一般情况 70只大鼠中,4只因为造模后3 d超声心动图显示梗死面积小于左心室周长的20%最终被排除出实验,3只因心肌梗死面积较大发生室颤而死亡,有7只可能因麻醉意外、手术出血过多或其他原因而死亡,最终存活56只。56只中假手术组8只、PBS组11只、PBS+药组12只、水凝胶组12只、水凝胶+药组13只。 2.3 各组实验动物体质量比较 实验过程中,各组大鼠毛发光泽,体态活泼,伤口愈合良好,无明显感染;食量及大便正常,无嗜睡现象。各组间手术前后体质量相比未见明显差异(表1)。 2.4 超声心动图及血流动力学检测 心肌梗死3 d,基线超声心动图显示4组之间室间隔厚度、左心室舒张末期内径、左心室收缩末期内径和左室射血分数、左室短轴缩短率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 心肌梗死后28 d,与假手术组相比,其余4组室间隔厚度、左室射血分数、左室短轴缩短率、左心室内压上升最大速率均有所下降(P < 0.05),左心室舒张末期内径、"
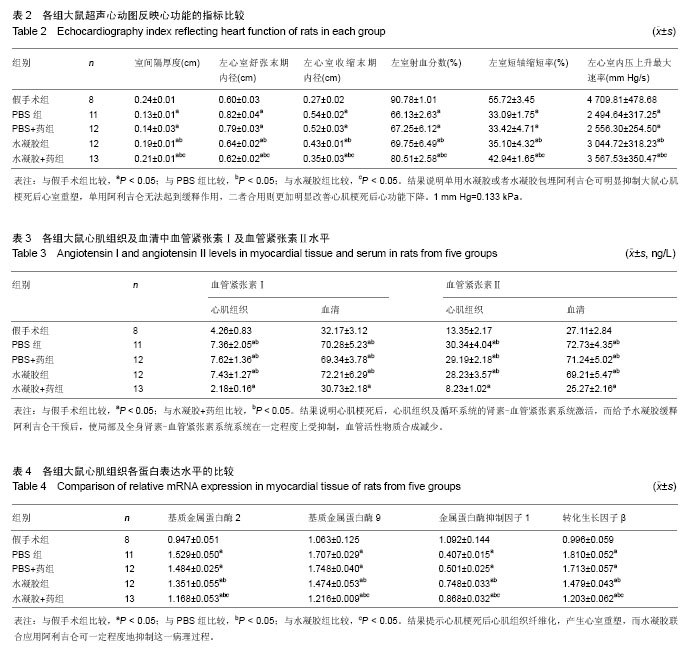
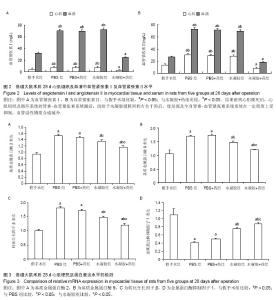
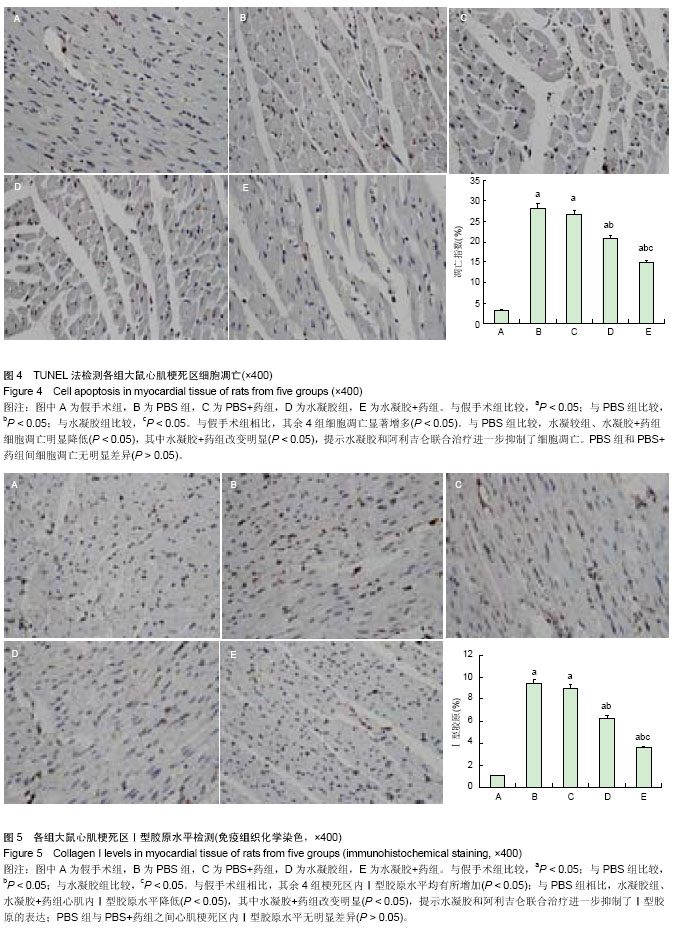
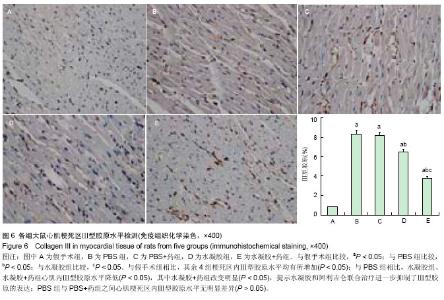
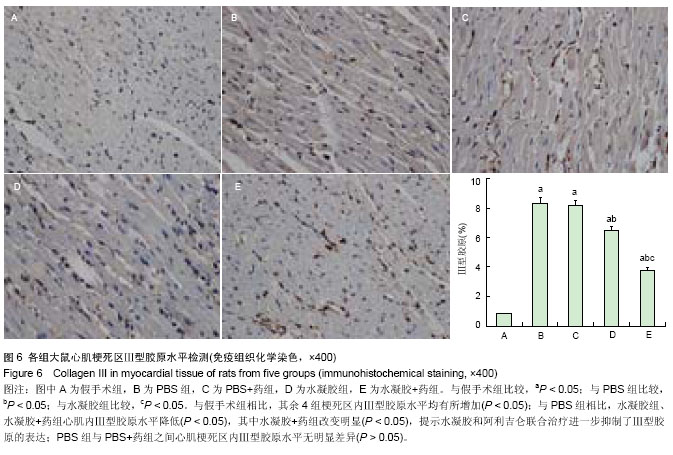
左心室收缩末期内径增加(P < 0.05)。与PBS组相比,水凝胶组、水凝胶+药组室间隔厚度、左室射血分数、左室短轴缩短率、左心室内压上升最大速率明显增加 (P < 0.05),左心室舒张末期内径、左心室收缩末期内径显著减小(P < 0.05),且水凝胶+药组改变较明显(P < 0.05)。PBS+药与PBS组相比各项指标差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 以上结果说明单用水凝胶或者水凝胶包埋阿利吉仑可明显抑制大鼠心肌梗死后心室重塑,单用阿利吉仑无法起到缓释作用,二者合用则更加明显改善心肌梗死后心功能下降(表2)。 2.5 心肌组织及血清血管紧张素Ⅰ及血管紧张素Ⅱ水平 心肌梗死28 d后,与假手术组相比,PBS组、PBS+药组、 水凝胶组心肌组织和血清中的血管紧张素Ⅰ及血管紧张素Ⅱ水平均升高(P < 0.05),而水凝胶+药组则降低(P < 0.05),见表3、图2。 以上结果说明心肌梗死后,心肌组织及循环系统的肾素-血管紧张素系统激活,而给予水凝胶缓释阿利吉仑干预后,使局部及全身肾素-血管紧张素系统系统在一定程度上受抑制,血管活性物质合成减少。"
| [1] van der Linde D,Konings EE,Slager MA,et al.Birth prevalence of congenital heart disease worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(21):2241-2247. [2] Abbate A,Biondi-Zoccai GG,Baldi A.Pathophysiologic role of myocardial apoptosis in post-infarction left ventricular remodeling. J Cell Physiol. 2002;193(2):145-153. [3] Cohn JN,Ferrari R,Sharpe N.Cardiac remodeling--concepts and clinical implications: a consensus paper from an international forum on cardiac remodeling. Behalf of an International Forum on Cardiac Remodeling.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35(3):569-582. [4] Kloner RA,Rezkalla SH.Cardiac protection during acute myocardial infarction: where do we stand in 2004?J Am Coll Cardiol.2004;44(2):276-286. [5] Savoia C,Volpe M.Angiotensin receptor modulation and cardiovascular remodeling. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst.2011;12(3):381-284. [6] Ferrario CM.Role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and proinflammatory mediators in cardiovascular disease.Am J Cardiol.2006;98(1):121-128. [7] Mentz RJ,Bakris GL,Waeber B,et al.The past,present and future of renin-angiotensin aldosterone system inhibition.Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(5):1677-1687. [8] Vijayaraghavan K,Deedwania P. Renin-angiotensin- aldosterone blockade for cardiovascular disease prevention. Cardiol Clin.2011;29(1):137-156. [9] Cohn JN.Reducing cardiovascular risk by blockade of the renin-angiotensin- aldosterone system.Adv Ther. 2007;24(6): 1290-304. [10] Horký K.Does the rennin inhibitor aliskiren offer promising novel opportunities in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases?Vnitr Lek.2007;53(4):364-370. [11] Van Tassell BW,Munger MA.Aliskiren for renin inhibition: a new class of antihypertensives.Ann Pharmacother. 2007; 41(3):456-464. [12] Volpe M,Battistoni A,Chin D,et al.Renin as a biomarker of cardiovascular disease in clinical practice.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.2012;22(4):312-317. [13] 罗芳.生物医用水凝胶材料的研究进展[J].广东化工,2011,38(8): 104-105. [14] Wu DQ,Wang T,Lu B,et al.Fabrication of Supramolecular Hydrogels for Drug Delivery and Stem Cell Encapsulation. Langmuir.2008;24(18):10306-10312. [15] McMurray JJ,Adamopoulos S,Anker SD,et al.ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(14):1787-1847. [16] Gallagher GL,Jackson CJ,Hunyor SN.Myocardial extracellular matrix remodeling in ischemic heart failure.Front Biosci.2007;12:1410-1419. [17] Jiang XJ,Wang T,Li XY,et al.Injection of a novel synthetic hydrogel preserves left ventricle function after myocardial infarction.J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;90(2):472-477. [18] Riccioni G.Aliskiren in the treatment of hypertension and organ damage.Cardiovasc Ther.2011;29(1):77-87. [19] Abramov D,Carson PE.The role of angiotensin receptor blockers in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2012;13(3):317-327. [20] McMurray JJ,Pitt B,Latini R,et al.Aliskiren Observation of Heart Failure Treatment(ALOFT)Investigators. Effects of the oral direct renin inhibitor aliskiren in patients with symptomatic heart failure.Circ Heart Fail.2008;1(1):17-24. [21] Pilz B,Shagdarsuren E,Wellner M,et al.Aliskiren, a human renin inhibitor, ameliorates cardiac and renal damage in double-transgenic rats.Hypertension. 2005;46(3):569-576. [22] Puig JG,Schunkert H,Taylor AA,et al.Evaluation of the dose--response relationship of aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor, in an 8-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study in adult patients with stage 1 or 2 essential hypertension.Clin Ther. 2009;31(12): 2839-2850. |
| [1] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [3] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [4] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [5] | Xu Yinqin, Shi Hongmei, Wang Guangyi. Effects of Tongbi prescription hot compress combined with acupuncture on mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, in degenerative intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 713-718. |
| [6] | Zhang Wenwen, Jin Songfeng, Zhao Guoliang, Gong Lihong. Mechanism by which Wenban Decoction reduces homocysteine-induced apoptosis of myocardial microvascular endothelial cells in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 723-728. |
| [7] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [8] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [9] | Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun. The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Su Liping, Lu Ziyang, Liu Li, Zhang Wei, Su Tianyuan, Hu Xiayun, Pu Hongwei, Han Dengfeng. C-jun, Cytc and Caspase-9 in the apoptosis of cerebellar granule neurons induced by diacetylmorphine in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3943-3948. |
| [12] | Zuo Zhenkui, Han Jiarui, Ji Shuling, He Lulu. Pretreatment with ginkgo biloba extract 50 alleviates radiation-induced acute intestinal injury in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3666-3671. |
| [13] | Zhang Liang, Ma Xiaoyan, Wang Jiahong. Regulatory mechanism of Shenshuai Yin on cell apoptosis in the kidney of chronic renal failure rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3672-3677. |
| [14] | Xie Yang, Lü Zhiyu, Zhang Shujiang, Long Ting, Li Zuoxiao. Effects of recombinant adeno-associated virus mediated nerve growth factor gene transfection on oligodendrocyte apoptosis and myelination in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3678-3683. |
| [15] | Liu Fang, Shan Zhengming, Tang Yulei, Wu Xiaomin, Tian Weiqun. Effects of hemostasis and promoting wound healing of ozone sustained-release hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3445-3449. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||