Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (30): 4823-4830.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.30.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation of amphiphilic superparamagnetic composite particles with tumor targeted MRI contrast agent
Gu Jun-heng1, Zhang Qing-yun2, Zhang Wei3, Yang Xin-lin3
- 1 Department of Radiology, Tianjin Chest Hospital, Tianjin 300222, China
2 Department of Chemistry, Basic Section, Logistics University of Chinese People’s Armed Police Force, Tianjin 300309, China
3 Key Laboratory of Functional Polymer Materials, Ministry of Education, Institute of Polymer Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China
-
Revised:2014-06-24Online:2014-07-16Published:2014-08-08 -
Contact:Yang Xin-lin, M.D., Associate professor, Key Laboratory of Functional Polymer Materials, Ministry of Education, Institute of Polymer Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China -
About author:Gun Jun-heng, Associate chief physician, Department of Radiology, Tianjin Chest Hospital, Tianjin 300222, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 21374049; Innovation Team Fund of the Logistics University of Chinese People’s Armed Police Force, No. WHTD201307-2
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gu Jun-heng, Zhang Qing-yun, Zhang Wei, Yang Xin-lin. Preparation of amphiphilic superparamagnetic composite particles with tumor targeted MRI contrast agent[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(30): 4823-4830.
share this article
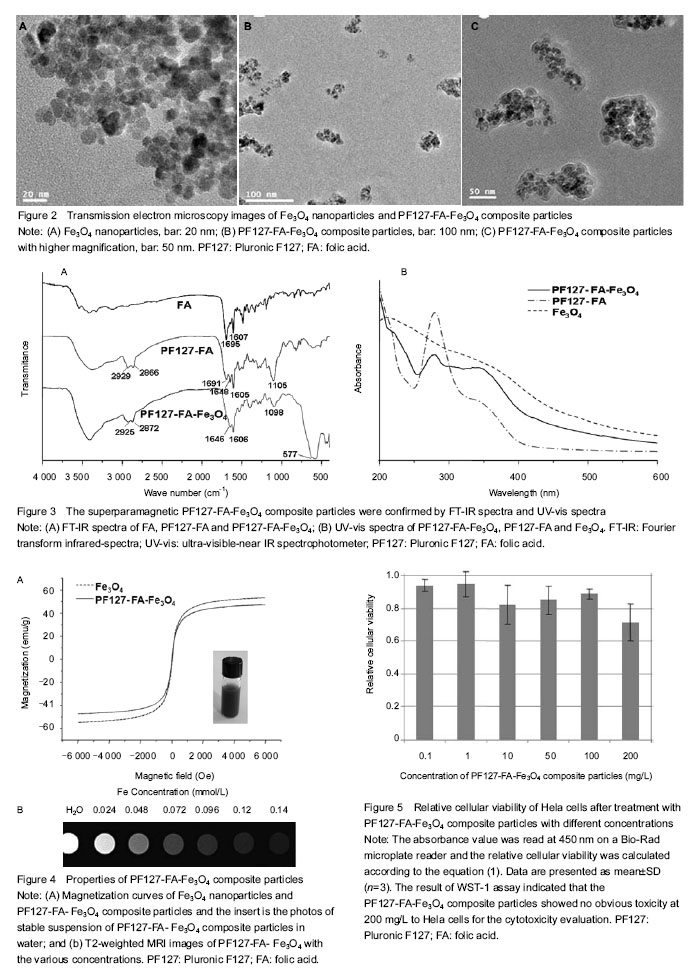
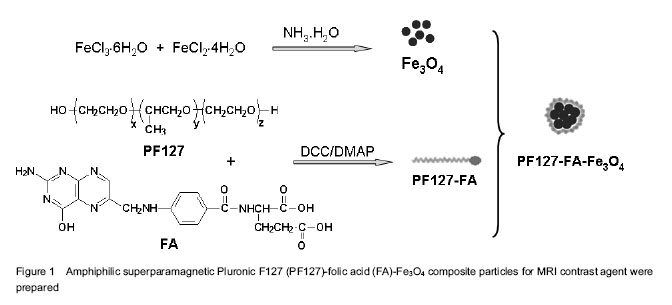
Preparation of PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles and characterization of their structures Since the magnetic nanoparticles without surface modification are prone to aggregate in the solvent due to their high specific surface area. Coating of magnetic nanoparticles with a polymer layer may prevent such aggregation, which also improves the chemical stability of the composite nanoparticles under rigid condition. In this work, magnetic Fe3O4 NPs were first prepared by the chemical co-precipitation of Fe3+/Fe2+ (2/1 in molar ratio) salts in an NH4OH solution at 60 ℃ via a well-known sol-gel process. Then PF127 was conjugated with FA by ester bonding between the hydroxyl groups of PF127 and the carboxylic acid groups of FA to give PF127-FA. Finally, superparamagnetic Fe3O4 NPs were coated with PF127-FA spontaneously to endow a possible tumor targeting and prevent the aggregation, as shown in Figure 1. The morphologies of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 NPs before and after coating with PF127-FA were characterized with transmission electron microscopy (Figure 2), which indicated that the size of Fe3O4 NPs was 10-20 nm (Figure 2A) and most of PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles had the slightly aggregated size of below 200 nm (Figure 2B). Further, Fe3O4 NPs aggregation coated with a thin film of PF127-FA conjugates is clearly observed in Figure 2C with a higher magnification. PF127-FA conjugate was synthesized via using the excessive molar ratios of FA to PF127 to ensure that at least one or two hydroxyl groups of PF127 were conjugated with the carboxylic acid groups of FA. The successful syntheses of PF127-FA conjugate and its coated superparamagnetic composite particles (PF127-FA-Fe3O4) were confirmed by Fourier transform infrared-spectra and Ultra-visible-near IR spectrophotometer in Figure 3. Fourier transform infrared spectrum of the PF127-FA conjugate in Figure 3A indicated the presence of the characteristics peaks at 1 691, 1 648 and 1 605/cm corresponding to the stretching vibrations from FA component together with the peaks at 2 929, 2 866 and 1 105/cm assigning to the stretching vibrations of CH2-bonds from PF127 chains. The Fourier transform infrared spectrum of PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles in Figure 3A had a new peak at 577 /cm attributing to the stretching vibration of Fe-O bond in Fe3O4 core together with all the characteristic peaks from PF127-FA conjugate. The UV-vis spectrum of PF127-FA in Figure 3B had a peak at 280 nm attributing to the characteristic absorbance of FA component, which was also clearly observed in the UV-vis spectrum of PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles. The mass ratio of PF127-FA conjugate was determined by thermal gravimetric analysis as 27.2 wt% in the resultant PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles. All these results indicated that PF127-FA conjugate was successfully coated onto the Fe3O4 NPs. The properties of PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles were characterized The presence of magnetite on PF127-FA-Fe3O4 was proven by a superconducting quantum interference device magnetometer. The magnetization curves of Fe3O4 and PF127-FA-Fe3O4 were measured at room temperature as shown in Figure 3A. The magnetic hysteresis loops were S-like curves, while the saturation magnetization of PF127-FA-Fe3O4 was 47.35 emu/g with near zero of magnetic remanence. This value was smaller than that of bulk Fe3O4 (53.9 emu/g), which was due to the coating of PF127-FA on Fe3O4. The results indicated that there was almost no remaining magnetization when the external magnetic field was removed, suggesting that PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles exhibited a superparamagnetic behavior. These superparamagnetic PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles could be dispersed stably as shown in the inserted photograph in Figure 4A. To check the MRI efficiency of PF127-FA-Fe3O4 as a tumor targeting contrast agent, T2-weighted signal intensities were measured with a clinical 3.0 T magnetic resonance scanner using iron concentrations ranging from 0 to 0.14 mmol/L at room temperature. Relaxivity values are calculated through the curve fitting of 1/T2 relaxation time (/ms) versus the iron concentrations (mmol/L). The iron content of PF127-FA-Fe3O4was estimated as 32 wt% by atomic absorption spectrometry. The T2 relaxivity was increased dramatically with the increasing of the iron concentrations in PF127-FA-Fe3O4. The linear function equation of Y=0.124 667 ×10-5 + 0.02494 X (R=0.9974, n=6) was obtained with iron concentration as x-axis and 1/T2 as y-axis. The transverse r2 relaxivities was obtained as 0.025×106/mol/s from the slope of linear. Figure 4B showed the T2-weighted MRI images of PF127-FA-Fe3O4 with the various iron concentrations. PF127-FA-Fe3O4 had a significant change of light intensity with the changes of iron concentration. These superparamagnetic composite particles with FA conjugating may find a potential application for special detection of cancers. The cytotoxicity of PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles was valued by WST assay As a MRI contrast agent, the potential toxicity PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles should be concerned for its further application in biomedical fields. In order to examine the cytotoxicity of PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles, Hela cells were incubated 24 hours with PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles in the concentration range from 0.1 to 200 mg/L. The result of WST-1 assay indicated that the PF127-FA-Fe3O4 composite particles showed no obvious toxicity at 200 mg/L to Hela cells for the cytotoxicity evaluation as shown in Figure 5. This confirmed their low levels of cytotoxicity."
| [1] Thorek LJD, Chen AK, Czupryna J, et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging. Ann Biomed Eng. 2006;34(1):23-38. [2] Berry CC, Curtis ASG. Functionalisation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2003;36:R198-R206. [3] Ito A, Shinkai M, Honda H, et al. Medical application of functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J Biosci Bioeng. 2005; 100(1):1-11. [4] Chemla YR, Crossman HL, Poon Y. Ultrasensitive magnetic biosensor for homogeneous immunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:14268-14272. [5] Mornet S, Vasseur S, Grasset F, et al. Magnetic nanoparticle design for medical applications. Prog Solid State Chem. 2006;34(2):237-247. [6] Hatakeyama M, Kishi H, Kita Y, et al. A two-step ligand exchange reaction generates highly water-dispersed magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J Mater Chem. 2011;21:5959-5966. [7] Tassa C, Shaw SY, Weissleder R. Dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles: a versatile platform for targeted molecular imaging, molecular diagnostics, and therapy. Acc Chem Res. 2011;44:842-852. [8] Easo SL, Mohanan PV. Dextran stabilized iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and in vitro studies. Carbohyd Polym. 2013;92(1):726-732. [9] Xie J, Xu C, Kohler N, et al. Controlled pegylation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles for reduced non-specific uptake by macrophage cells. Adv Mater. 2007;19: 3163-3166. [10] Kim DK, Mikhaylova M, Wang FH, et al. Starch-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles as MR contrast agents. Chem Mater. 2003;15:4343-4351. [11] Quan Q, Xie J, Gao H, et al. HSA coated iron oxide nanoparticles as drug delivery vehicles for cancer therapy. Mol Pharm. 2011;8(5):1669-1676. [12] Kah JC, Chen J, Zubieta A, et al. Exploiting the protein corona around gold nanorods for loading and triggered release. ACS Nano. 2012;6(8):6730-6740. [13] Cifuentes-Rius A, de Puig H, Kah JC, et al. Optimizing the properties of the protein corona surrounding nanoparticles for tuning payload release. ACS Nano. 2013;7(11): 10066-10074. [14] Chen FH, Zhang LM, Chen QT, et al. Synthesis of a novel magnetic drug delivery system composed of doxorubicin- conjugated Fe3O4 nanoparticle cores and a PEG-functionalized porous silica shell. Chem Commun. 2010;46:8633-8635. [15] Ahmad T, Bae H, Rhee I, et al. Gold-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as a T2 contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging. J Nanosci Nanotechno. 2012;12(7):5132-5137. [16] Zhu J, Lu YJ, Li YG, et al. Synthesis of Au-Fe3O4 heterostructured nanoparticles for in vivo computed tomography and magnetic resonance dual model imaging. Nanoscale. 2014;6(1):199-202. [17] Larsen EK, Nielsen T, Wittenborn T, et al. Accumulation of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coated with variably sized polyethylene glycol in murine tumors. Nanoscale. 2012;4(7):2352-2361. [18] Huang C, Neoh KG, Kang ET. Combined ATRP and ‘Click’ chemistry for designing stable tumor-targeting superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir. 2011;28(1):563-571. [19] Aphesteguy JC, Jacobo SE. Synthesis of a soluble polyaniline-ferrite composite: magnetic and electric properties. J Mater Sci. 2007;42:7062-7068. [20] Wang HD, Luo WQ, Chen JC. Fabrication and characterization of thermoresponsive Fe3O4@PNIPAM hybrid nanomaterials by surface-initiated RAFT polymerization. J Mater Sci. 2012;47:5918-5925. [21] Wang SH, Shi XY, Antwerp MV, et al. Dendrimer-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for specific targeting and imaging of cancer cells. Adv Funct Mater. 2007;17:3043-3050. [22] Kabanov AV, Batrakova EV, Alakhov VY. Pluronic block copolymers as novel polymer therapeutics for drug and gene delivery. J Controlled Release. 2002;82(2-3):189-212. [23] Batrakova EV, Kabanov AV. Pluronic block copolymers: evolution of drug delivery concept from inert nanocarriers to biological response modifiers. J Controlled Release. 2008; 130(2):98-106. [24] Bromberg L. Polymeric micelles in oral chemotherapy. J Controlled Release. 2008;128(2):99-112. [25] Singh-Joy SD, McLain VC. Safety assessment of poloxamers 101, 105, 108, 122, 123, 124, 181, 182, 183, 184, 185, 188, 212, 215, 217, 231, 234, 235, 237, 238, 282, 284, 288, 331, 333, 334, 335, 338, 401, 402, 403, and 407, poloxamer 105 benzoate, and poloxamer 182 dibenzoate as used in cosmetics. Int J Toxicol. 2008;27:93-128. [26] Liang S, Wang Y, Yu J, et al. Surface modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: as a new carrier for bio-magnetically targeted therapy. J Mater Sci. 2007;18:2297-2302. [27] Sun C, Fang C, Stephen Z, et al. Tumor-targeted drug delivery and MRI contrast enhancement by chlorotoxin-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanomed. 2008;3:495-505. [28] Yang Y, Jiang JS, Du B, et al. Preparation and properties of a novel drug delivery system with both magnetic and biomolecular targeting. J Mater Sci. 2009;20:301-307. [29] Scarberry KE, Dickerson EB, McDonald JF, et al. Magnetic nanoparticlepeptide conjugates for in vitro and in vivo targeting and extraction of cancer cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:10258-10262. [30] Lee HY, Li Z, Chen K, et al. PET/MRI dual-modality tumor imaging using arginine–glycine–aspartic (RGD)-conjugated radiolabeled iron oxide nanoparticles. J Nucl Med. 2008;49: 1371-1379. [31] Zhang J, Rana S, Srivastava RS, et al. On the chemical synthesis and drug delivery response of folate receptor-activated, polyethylene glycol-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2008;4:40-48. [32] Sun C, Sze R, Zhang M. Folic acid–PEG conjugated superparamagnetic nanoparticles for targeted cellular uptake and detection by MRI. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;78:550-557. [33] Yang XQ, Pilla S, Grailer JJ, et al. Tumor-targeting, superparamagnetic polymeric vesicles as highly efficient MRI contrast probes. J Mater Chem. 2009;19:5812-5817. [34] Wang L, Neoh KG, Kang ET, et al. Multifunctional polyglycerol-grafted Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles for targeting ovarian cancer cells. Biomaterials. 2011;32: 2166-2173. |
| [1] | Zhang Houjun, Jiang Shengyuan, Deng Bowen, Liu Gang, Bai Huizhong, Tao Jingwei, Fan Xiao, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Mechanism by which tetramethylpyrazine improves inflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1701-1707. |
| [2] | Xing Guoyi, Sun Legang, Ma Xiangrui, Wang Wenlong. Regulation of Sema3A on oral mesenchymal stem cell function [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1626-1633. |
| [3] | Lin Lingqi, Chen Jin, Qian Kun, Zhao Liang, Shi Yijie. Preparation and in vitro release of manganese-based metal-organic framework materials loaded with baicalin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5475-5481. |
| [4] | Li Hongyuan, Yang Liu, Jin Xianhui. Relationship between hypoxia-inducible factors and bone homeostasis disorders [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5393-5399. |
| [5] | Wang Zijie, Tian Zhihui, Wu Jiayuan. Signal peptide-CUB-epidermal growth factor-like domain protein family as coreceptors/ligands is involved in embryonic development and disease development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5209-5216. |
| [6] | Gong Yuqing, Yao Wei, Li Ran. Osteoimmunological effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha in alveolar bone remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4242-4251. |
| [7] | Chen Qiaoling, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Lin Tao, Luo Xuwei. Osteoblast differentiation after conditional knockout of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 gene from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3785-3789. |
| [8] | Yan Nan, Wu Yanlong, Tang Xiaohui, Zhang Xiaoyan, Wang Hui, Yang Tianze, Zhou Maochun, Wang Zhengdong, Yang Xiaoxia. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells may alleviate brain damage caused by the microglial overactivation in the cortex around ischemic site of stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3790-3795. |
| [9] | Chen Sheng, Yang Yan, Ding Liang, Ye Chuanjin, Zhang Lei, Xia Shu, Li Huiling, Huang Xiaofeng. Establishment and identification of an immortalized oral cancer-related fibroblast line [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3808-3813. |
| [10] | Liu Chao, Zeng Zhaomu, Wen Xichao, Wu Wensong, Sun Chengyuan, Zheng Kebin. Role and clinical application prospects of exosomal non-coding RNAs in the occurrence and development of glioma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3928-3936. |
| [11] | Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Zhao Wanhua, Lin Yushi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Important role of exosomes-mediated hypoxia-related signaling pathways in the occurrence and progression of diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3065-3070. |
| [12] | Min Keting, Zhang Yiguo, Yang Hao, Lü Xin. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells on negative regulation of immune response of myeloid-derived suppressor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3084-3089. |
| [13] | Yin Liang, Zhang Mingxue, Li Jianan, Jiang Feng. Inducing macrophage polarization to M2 anti-inflammatory type reduces oxidative damage in diabetic retinopathy mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2685-2689. |
| [14] | Yang Yang, Liu Jiajia, Xue Jianhua, Liu Yunfei, Yao Yu. Correlation between interleukin 23/helper T17 cell axis and lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2190-2195. |
| [15] | Zhong Yulan, Zhou Xiangxiang, Gan Xin. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 1979-1984. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||