[1] 李伟,曾建成.骨肿瘤血管的靶向治疗系统[J].西部医学,2008,20(5):1104-1105.
[2] DAI Y, GUO H, CHU L, et al. Promoting osteoblasts responses in vitro and improving osteointegration in vivo through bioactive coating of nanosilicon nitride on polyetheretherketone. J Orthop Translat. 2019;24:198-208.
[3] ZHANG Q, MESNER LD, CALABRESE GM, et al. Genomic variants within chromosome 14q32.32 regulate bone mass through MARK3 signaling in osteoblasts. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(7):e142580.
[4] TANAKA M, DYKES SS, SIEMANN DW. Inhibition of the Axl pathway impairs breast and prostate cancer metastasis to the bones and bone remodeling. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2021;38(3):321-335.
[5] 曹德云,王艳铭,刘丽,等.氯膦酸二钠联合骨化三醇治疗绝经后骨质疏松的疗效及对血清IGF-BP-3、SHBG的影响[J].西部医学,2020,32(2):238-241.
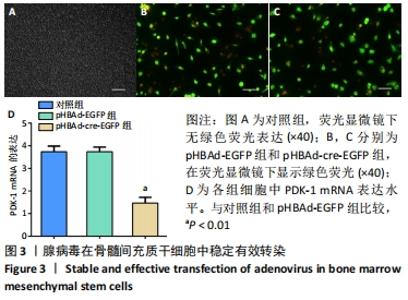
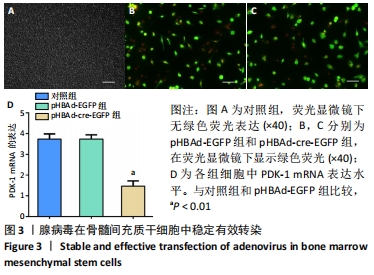
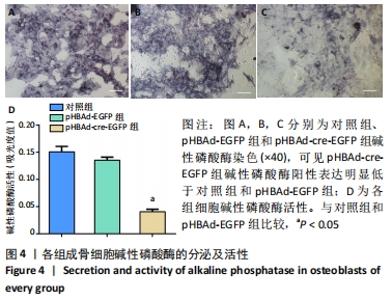
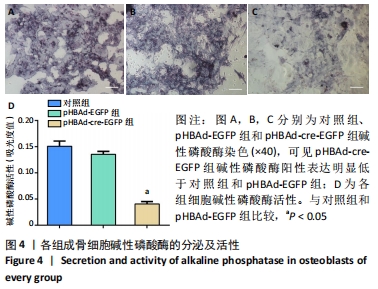
[6] BAI Y, ZHANG Q, CHEN Q, et al. Conditional knockout of the PDK-1 gene in osteoblasts affects osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(7):5432-5445.
[7] AGAS D, SABBIETI MG, MARCHETTI L, et al. FGF-2 enhances Runx-2/Smads nuclear localization in BMP-2 canonical signaling in osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(11):2149-2158.
[8] WANG H, ZHANG Z, YAN Z, et al. PD-L1, PDK-1 and p-Akt are correlated in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020;29(7):785-792.
[9] ULICI V, HOENSELAAR KD, AGOSTON H, et al. The role of Akt1 in terminal stages of endochondral bone formation: angiogenesis and ossification. Bone. 2009;45(6): 1133-1145.
[10] 刘康,白亦光,陈竹,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养及鉴定[J].川北医学院学报,2013,28(2):103-106.
[11] DAI Y, ZHENG C, LI H. Inhibition of miR-23a-3p promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2019. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29497.
[12] BALESTRA AC, KOUSSIS K, KLAGES N, et al. Ca2+ signals critical for egress and gametogenesis in malaria parasites depend on a multipass membrane protein that interacts with PKG. Sci Adv. 2021;7(13):eabe5396.
[13] LI ZS, HUNG LY, MARGOLIS KG, et al. The α isoform of cGMP-dependent protein kinase 1 (PKG1α) is expressed and functionally important in intrinsic primary afferent neurons of the guinea pig enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021;33(8):e14100.
[14] WANG M, WANG J, LIU M, et al. Fluvastatin protects neuronal cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity with decreasing oxidative damage and increasing PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021;73(4):515-521.
[15] DONG Y, MENG F, WANG Z, et al. Construction and application of a human scFv phage display library based on Cre‑LoxP recombination for anti‑PCSK9 antibody selection. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(2):708-718.
[16] CHEN CV, JORDAN CL, BREEDLOVE SM. Testosterone works through androgen receptors to modulate neuronal response to anxiogenic stimuli. Neurosci Lett. 2021;753:135852.
[17] SHOOP S, MARIA Z, CAMPOLO A, et al. Glial Growth Factor 2 Regulates Glucose Transport in Healthy Cardiac Myocytes and During Myocardial Infarction via an Akt-Dependent Pathway. Front Physiol. 2019;10:189.
[18] 陈巧玲,白亦光,别俊,等.靶向抑制Akt对成骨细胞分化PI3K/Akt信号通路调控的研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2020,37(12):2123-2128.
[19] BRUDERER M, RICHARDS RG, ALINI M, et al. Role and regulation of RUNX2 in osteogenesis. Eur Cell Mater. 2014;28:269-286.
[20] WANG C, LIAO H, CAO Z. Role of Osterix and MicroRNAs in Bone Formation and Tooth Development. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:2934-2942.
|