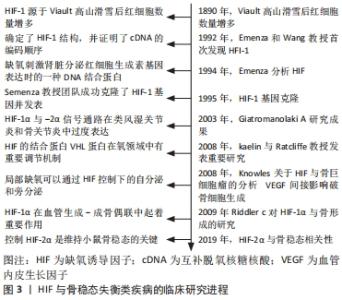
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (33): 5393-5399.doi: 10.12307/2022.778
Previous Articles Next Articles
Relationship between hypoxia-inducible factors and bone homeostasis disorders
Li Hongyuan1, Yang Liu2, Jin Xianhui1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Hengshui People’s Hospital, Hengshui 053000, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Yongchuan Hospital Affiliated to Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China
-
Received:2021-08-10Accepted:2022-01-06Online:2022-11-28Published:2022-03-31 -
Contact:Li Hongyuan, Department of Orthopedics, Hengshui People’s Hospital, Hengshui 053000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Li Hongyuan, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Hengshui People’s Hospital, Hengshui 053000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:Hebei Provincial Medical Key Research Project, No. 20150437 (to LHY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Hongyuan, Yang Liu, Jin Xianhui. Relationship between hypoxia-inducible factors and bone homeostasis disorders[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5393-5399.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
2.2 缺氧诱导因子的结构与生物学特性 缺氧诱导因子的作用主要体现在细胞氧稳态的维持方面,它主要包括缺氧诱导因子1,2,3的3个亚型,每个亚型都是由α与β亚基组成的异源二聚体[12-14]。现阶段,临床研究多集中在缺氧诱导因子1α因子方面,其是缺氧应答的主要调节因子。目前,已知的缺氧诱导因子1α的氧调节机制是:在正常的氧环境下,缺氧诱导因子1α经脯氨酰羟化酶羟基化后,被E3泛素连接酶蛋白修饰,再经蛋白酶体降解。但若是处于低氧环境时,细胞中的缺氧诱导因子1α因子将进入细胞核,诱导缺氧调节基因的激活,并进一步激活许多其他基因的表达[15-16],从而引起促进细胞转移和促进氧气供给等一系列的反应,见图4。"
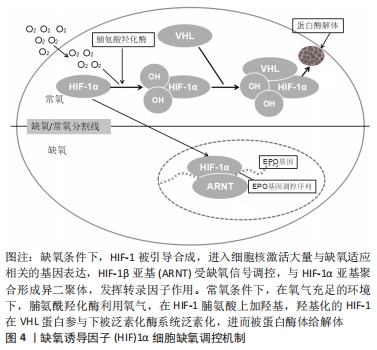
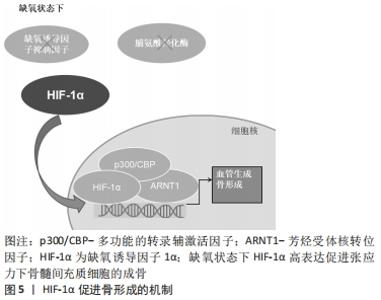
缺氧状态下,缺氧诱导因子1α的脯氨酰羟基化作用减弱,使得细胞核中的缺氧诱导因子1α不断积累,并通过缺氧诱导因子1的β亚基异源二聚体反式激活缺氧诱导因子反应基因,发挥出调节细胞凋亡、血管生成及能量代谢等多种作用[17]。除缺氧诱导因子1α以外,缺氧诱导因子2α也参与了机体的多种生物学过程,是与氧敏感相关的重要效应器[18-19]。缺氧诱导因子1α可以使骨细胞适应缺氧的微环境并促进其生长发育,而缺氧诱导因子2α的作用机制主要是在缺氧环境中调节骨细胞的分解代谢,与前者存在一些不同之处[20]。 缺氧诱导因子除了能对缺氧环境中的骨重塑进行调节外,还能对白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子等其他细胞因子进行调节[21]。同时,缺氧诱导因子还能对物理因素、金属离子及超声波等因素进行调节[22-23]。缺氧诱导因子调节所涉及的调控机制十分复杂,目前比较统一的研究观点有“缺氧诱导因子直接调控下游基因”“缺氧诱导因子通过调控HRMs来间接调控靶基因”两种途径完成对下游基因的调控[24]。 2.3 缺氧诱导因子对骨形成与骨重塑的调控机制 2.3.1 缺氧诱导因子对骨形成的作用机制 缺氧诱导因子1是调控组织细胞氧稳态的关键性核转录因子[25]。缺氧诱导因子α信号通路参与调节机体一系列的生理病理反应,尤以对血管形成及骨形成的调节作用最受学者关注。目前对于骨形成的具体机制尚未完全阐明,但可以确定其与组织和局部缺氧有重要联系[26-27]。有研究利用Cre-Flox重组酶技术,获得在成骨细胞中条件性敲除的小鼠VHL基因,导致小鼠缺氧诱导因子1α呈持续性高表达[28],结果显示此类小鼠的骨形成率明显高于正常小鼠。同时,在成骨细胞中条件性敲除缺氧诱导因子1α,会显著降低小鼠的骨量及血管数量,这表明调控缺氧诱导因子1α可进一步调节对骨形成有关键作用的骨量及血管数量。在缺氧应激条件下,成骨细胞过度表达的缺氧诱导因子1α能够促进骨形成,并增加长骨体积[29-30]。 缺氧诱导因子1α是氧感受器、正调节因子,缺氧诱导因子1α表达升高代表人骨细胞在缺氧环境下的生存能力提升。在骨形成过程中,缺氧诱导因子1α活性增强,可使缺氧条件下的细胞充分发挥效能,进而促进成骨细胞的增殖、迁移、黏附及血管生成[31]。缺氧信号通路是骨形成的重中之重,在骨形成过程中,缺血性、具有内缺氧区的生长板软骨细胞通过不断分裂增殖等一系列反应,最终完成矿化成骨[32]。而缺氧诱导因子1α便是这些软骨细胞存活的关键因子,只有缺氧诱导因子1α高表达,才能为骨形成创造条件,若是人为操控缺氧诱导因子1α通路,加速血管内皮生长因子与其他血管生成因子的过量分泌与合成,将会刺激长骨的血管生成,从而出现过度活跃的骨生成[33],见图5。"
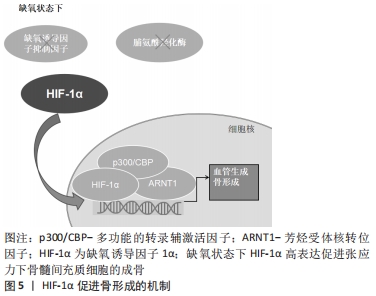
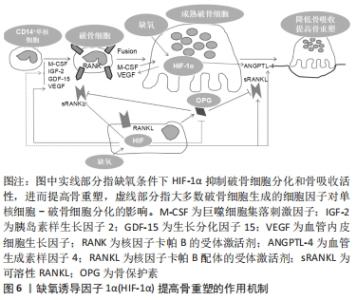
缺氧诱导因子1α下游众多的血管生成相关因子能诱导成骨细胞的分化与增殖,在骨形成中也有着重要的调控作用[34]。但目前研究认为缺氧诱导因子2α对骨生长发育的作用是微乎其微的[35-36],在肢芽间充质细胞仅敲除缺氧诱导因子1α,或是同时敲除缺氧诱导因子1α/2α,所导致的生长板异常情况几乎是相同的,推测缺氧诱导因子2α对生长板增殖分裂的作用可能并不是十分重要。缺氧诱导因子2α的作用主要体现在调控骨细胞分解代谢等方面。破骨细胞中缺氧诱导因子2α的表达显著上调,从而促进破骨细胞的成熟与分化,并引起进行性骨丢失,因此它可以被认为是骨形成的负调节因子[37]。 2.3.2 缺氧诱导因子对骨重塑的调控机制 骨代谢重塑的过程也是在缺氧状态下完成的,缺氧诱导因子1α作为氧稳态的关键性核转录因子,直接参与了骨重塑相关信号传导。与骨形成的作用机制相比,缺氧诱导因子1α在破骨细胞中又有着不同的作用机制。有研究指出,在一些恶性肿瘤中,肿瘤周围会出现严重的骨溶解,这种侵袭性病变的发生与破骨细胞中的缺氧诱导因子1α高表达存在一定联系[38-39]。而缺氧是破骨细胞形成和骨吸收的主要因素,白血病抑制因子下调脯氨酰羟基化酶并增加缺氧诱导因子1α的表达,从而增加破骨细胞活性及加速骨吸收[40]。故此,可利用破骨细胞中缺氧诱导因子1α表达的抑制作用来削弱破骨细胞活性,降低骨吸收,提高骨重塑[41-42],见图6。"
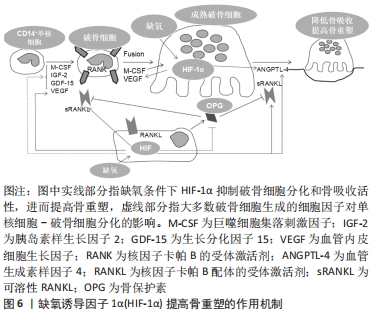
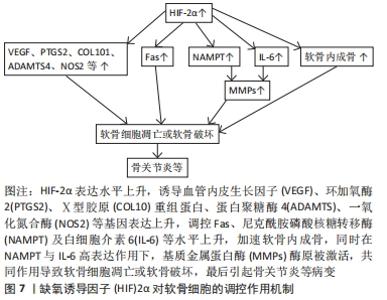
目前认为缺氧诱导因子1α在骨形成和骨重塑中的机制是不同的,但是具体原因尚不清楚,怀疑它可能受到骨微环境中细胞类型的影响[43]。 缺氧诱导因子2α与缺氧诱导因子1α对氧浓度敏感性不同,在骨形成、骨重塑中的功能作用也有一定的差异。在正常的生理条件下,缺氧诱导因子1α在血管生成与骨形成耦合中起着主导作用,同时缺氧诱导因子2α主要在破骨细胞的活化与分化中发挥作用。缺氧诱导因子2α在骨重塑方面的作用机制可能是依靠成骨细胞与破骨细胞间的相互调节来实现[44-45]。 2.4 缺氧诱导因子对骨稳态失衡类疾病的影响 2.4.1 关节炎 类风湿关节炎和骨关节炎是临床常见的、与骨稳态失衡有关的一类疾病,发病率很高,严重影响着患者的生活质量,而软骨损伤是这类疾病的致病特征。在软骨组织中,缺氧诱导因子1α具有促进软骨形成的能力,是软骨细胞分化早期重要的调控因子[46]。缺氧诱导因子直接影响着软骨细胞的存亡,在人骨髓细胞中,低氧状态下缺氧诱导因子1α能有效地诱导出软骨细胞,并使其适应骨骼间生长板的缺氧微环境。缺氧诱导因子2α的调节作用主要表现在软骨细胞分化的后期,影响软骨成骨和软骨退变,在骨关节炎患者软骨中的缺氧诱导因子2α呈明显高表达[47-48]。可见缺氧诱导因子1α与缺氧诱导因子2α的功能及分布存在不同。若将缺氧诱导因子1α看作是一种具有“保护”功能的调节因子,缺氧诱导因子2α则是一种对基因有“分解代谢”作用的调控因子。缺氧诱导因子2α由Epas1基因编码,能够调控软骨细胞靶基因表达,诱导软骨的凋亡[49]。缺氧诱导因子2α可调控炎性因子、基质分解酶类等各种分解代谢基因的表达,造成软骨破坏,并因此诱导骨关节炎等骨疾病的发生。已有研究指出[50],在骨关节炎建模小鼠的软骨细胞中缺氧诱导因子2α呈高表达状态,而缺失Epas1基因的小鼠出现软骨破坏被抑制的现象,提示可通过调控关节软骨细胞中Epas1基因表达,达到抑制软骨破坏的效果。缺氧诱导因子2α对软骨细胞的调控作用机制,见图7。"
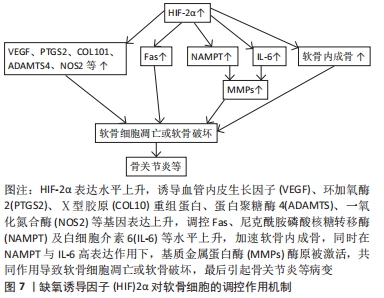

还有研究指出,基质金属蛋白酶家族中的MMP-13因子在正常软骨组织中呈低表达状态,但在关节炎患者的关节软骨中明显升高[51]。在某小鼠实验研究中,发现静水压力刺激小鼠软骨细胞后,其通过诱导缺氧诱导因子2α表达来增加MMP-13表达,进一步引起软骨退变,导致骨关节炎发生发展[52]。再者,血管内皮生长因子与缺氧诱导因子2α的表达也呈显著相关性,缺氧诱导因子2α通过调节血管内皮生长因子而引发骨肉瘤、骨关节炎等病变[53-54]。当缺氧诱导因子2α在软骨周围钙化层的高分化肥大软骨细胞中呈高表达状态时,会加速软骨细胞凋亡,上调血管内皮生长因子,进而加速软骨基质的降解,加重关节炎的发生与发展进程。此外,烟酰胺磷酸核糖转移酶作为一种降速酶,具有类炎症因子作用,是骨关节炎患者缺氧诱导因子2α的直接靶基因[55]。在关节软骨细胞中,烟酰胺磷酸核糖转移酶可以直接上调基质金属蛋白酶表达,激活缺氧诱导因子2α下游的分解代谢因子,这可能是骨关节炎的发病机制之一。再者,缺氧诱导因子2α还可通过上调脂肪酸合成酶基因表达,来刺激其介导的软骨细胞凋亡,并加速软骨成分破坏,引发关节炎等骨稳态失衡类疾病[56]。因此,抑制缺氧诱导因子2α表达将是防治关节炎等骨稳态失衡相关疾病的最新思路。 2.4.2 骨质疏松与骨折 骨质疏松的发生主要与成骨细胞数量、成骨功能及血管形成能力下降有关,而这些成骨及血管能力下降与缺氧诱导因子α信号通路改变有一定关系[57-58]。H型内皮细胞与骨形成密切相关,有研究通过特异性敲除小鼠内皮细胞VHL,激活了缺氧诱导因子α信号通路,促进了H型内皮细胞的增殖,抑制了骨量丢失、骨形成下降问题[59-60]。缺氧诱导因子α与雌激素缺乏性骨质疏松也有联系,常氧条件下雌激素、胰岛素生长因子等可积聚细胞内缺氧诱导因子α表达,进而激活相关的信号通路,但卵巢切除等因素会导致雌激素水平下降,抑制部分缺氧诱导因子α表达,引起骨量减少、骨密度下降,而注射缺氧诱导因子α通路激活剂后,可加速骨形成与血管形成,达到控制骨质疏松的目的[61]。 而骨质疏松导致的骨折在临床十分常见。骨折的愈合效果直接与血管生成和血液供应能力相关。金培程等[43]的研究显示,患者骨折约7 d缺氧诱导因子1α表达显著上升,且在同一时期,患者的骨痂增加,膜内化骨与软骨细胞也明显增长,可见缺氧诱导因子1α参与了一个或多个环节的调控,加速了骨折愈合。鉴于缺氧诱导因子1α信号通路在骨形成和血管形成方面的作用机制,今后需加强对相关药物的研究以增加缺氧诱导因子1α表达水平,促进血管生成和骨形成,同时还有可能加快骨折的愈合[62-63]。 2.4.3 骨肿瘤 骨肉瘤作为最常见的恶性原发性肿瘤病变,缺氧诱导因子1α在其中有预测microRNA-20b (miR-20b) 的靶基因作用,缺氧诱导因子1α的过表达影响了miR-20b在MG63细胞中的抑制作用,miR-20b增高可影响缺氧诱导因子1α的表达,下调VEGF通路蛋白,从而抑制肿瘤细胞的侵袭与增殖率[64]。有研究提出,软骨肉瘤中有新血管的生成,这与缺氧诱导因子1α过表达相关,提示缺氧诱导因子1α是软骨肉瘤中与肿瘤新血管生成相关的恶性标志物,缺氧诱导因子1抑制治疗可能干预软骨肉瘤中的血管生成[65]。还有研究指出,缺氧诱导因子2PUT表达水平与骨肉瘤组织中的缺氧诱导因子2α呈正相关性,在MG63细胞中,缺氧诱导因子2PUT表达的下调导致缺氧诱导因子2α的mRNA表达水平随之降低,提示缺氧诱导因子2PUT 可能是骨肉瘤中缺氧诱导因子2α的调节剂[66]。 2.4.4 钙磷代谢紊乱 钙磷代谢紊乱多是指长期不规律的生活饮食造成患者营养不良以及体内电解质紊乱,从而影响骨发育与骨代谢,引发骨软化症等骨代谢病。钙代谢与磷代谢密切相关,与体内酸碱平衡关系密切,与成纤维细胞生长因子23也密切相关[67-68]。成纤维细胞生长因子23是一种重要的钙磷代谢调节因子,骨软化症便是由于成纤维细胞生长因子23过量表达而引起钙磷代谢紊乱造成的代谢性骨病,该病的临床表现主要为进行性的肌无力、骨痛和骨折等[69]。目前临床对此类疾病的发生机制尚未完全阐明,但怀疑缺氧诱导因子1α的过度激活可能会促进成纤维细胞生长因子23转录及血管形成,而应用缺氧诱导因子1α抑制剂可降低缺氧诱导因子1α与成纤维细胞生长因子23表达水平,这也将是今后防治钙磷代谢性骨病的新思路[70]。"

| [1] SUN YL, PARK KH, YU HG, et al. Controlling hypoxia-inducible factor-2α is critical for maintaining bone homeostasis in mice. Bone Res. 2019;7(2):210-223. [2] HELEN K. Hypoxic regulation of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption activity. Hypoxia. 2015;3(3):73-82. [3] DOMENE C, JORGENSEN C, Schofield CJ. Mechanism of molecular oxygen diffusion in a hypoxia-sensing prolyl hydroxylase using multiscale simulation. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142(5)2253-2263. [4] 张丹,任利玲.缺氧诱导因子1α在组织工程成骨和成血管中的作用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(4):504-508. [5] SHOMENTO SH, CHAO W, CAO X, et al. Hypoxia‐inducible factors 1α and 2α exert both distinct and overlapping functions in long bone development. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109(1):196-204. [6] HAHNE M, SCHUMANN P, MURSELL M, et al. Unraveling the role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-2α in the adaption process of human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) to hypoxia: redundant HIF-dependent regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Microvasc Res. 2018;116(16):34-44. [7] DELGADO C JESUS. Osteocytes and their messengers as targets for the treatment of multiple myeloma. J Bone Miner Metab. 2017;15(1):49-56. [8] GORDON J, MONTECINO MA, AQEILAN RI, et al. Epigenetic pathways regulating bone homeostasis: potential targeting for intervention of skeletal disorders. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014;12(4):496-506. [9] STEGEN S, CARMELIET G. Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible transcription factors and oxygen-sensing prolyl hydroxylases in bone development and homeostasis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hy. 2019;28(4):328-335. [10] ZOU D, ZHANG Z, HE J, et al. Blood vessel formation in the tissue-engineered bone with the constitutively active form of HIF-1α mediated BMSCs. Biomaterials. 2012;33(7):2097-2108. [11] XU J, SUN Y, WU T, et al. Enhancement of bone regeneration with the accordion technique via HIF-1/VEGF activation in a rat distraction osteogenesis model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2):1268-1276. [12] 李昭,王学彬.缺氧诱导因子1α在风湿性疾病中的研究进展[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2018,22(1):54-57. [13] HAI G, HONG Z, WU J, et al. The key role of microtubules in hypoxia preconditioning-induced nuclear translocation of HIF-1α in rat cardiomyocytes. Peer J. 2017;5(3):e3662. [14] SARTORI-CINTRA AR, MARA CS, ARGOLO DL, et al. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) expression by interleukin-1β (IL-1 β), insulin-like growth factors I (IGF-I) and II (IGF-II) in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Clinics. 2012;67(1):35-40. [15] FAYED HA, BARAKAT BM, ELSHAER SS, et al. Antiosteoporotic activities of isoquercitrin in ovariectomized rats: role of inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;865(5):172785. [16] 邵进,张岩,王治,等.低氧诱导因子1α参与骨发育及骨代谢调控的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(3):349-355. [17] 解友邦,侯艳,杨红艳,等.HIF-1α对K562细胞血管生成相关因子的影响[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2019,27(5):1476-1481. [18] 谢虎,李永忠,郭风劲,等.骨肉瘤中低氧诱导因子2α(HIF-2α),骨桥蛋白(OPN),血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)的表达及其临床意义[J].中国实验诊断学,2011,15(1):117-119. [19] RYU JH, SHIN Y, HUH YH, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α regulates Fas-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis during osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(3):440-450. [20] SAITO T, FUKAI A, IKEDA T, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) controls sequential steps of endochondral ossification during skeletal growth and osteoarthritis progression. Bone. 2009,44(1):41-42. [21] 赵光宗,方军,丁刚,等.拉喹莫德抑制成骨细胞中缺氧诱导因子2α的表达及其功能[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(7):917-924. [22] 周文婷.HIF-1活性调控机制的研究进展[J].生理科学进展,2020, 51(6):443-448. [23] YOON D, PASTORE YD, DIVOKY V, et al. Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1 Deficiency Results in Dysregulated Erythropoiesis Signaling and Iron Homeostasis in Mouse Development. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(35): 25703-25711. [24] 张申尧,董克芳,王凡.红景天苷抵抗骨细胞凋亡的作用和对绝经后骨质疏松患者的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2020,36(22): 3624-3629. [25] 宋亚琼,周播江.低氧诱导因子1在调控骨骼肌缺氧时能量代谢发生适应性变化的机制研究进展[J].解剖学报,2017,48(2):236-240. [26] 张俊宇,何鹏杰,程傲,等.缺氧复氧环境对成骨细胞自噬水平的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2019,99(11):844-849. [27] YU TM, WEN MC, LI CY, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in infiltrating inflammatory cells is associated with chronic allograft dysfunction and predicts long-term graft survival. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28(3):659-670. [28] 谢杨丽,翁士军,易玲娴,等.成年期软骨中敲除Vh1加速小鼠老年及不稳定所致骨性关节炎的进程[C].中华医学会第七次全国骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病学术会议论汇编,2013:258. [29] 李晓娟,吴华,李浩,等.缺氧环境通过HIF-1α/YAP信号促进大鼠生长板软骨细胞表型维持[J].骨科,2019,10(2):134-139. [30] WANG Y, WAN C, DENG L, et al. The hypoxia-inducible factor α pathway couples angiogenesis to osteogenesis during skeletal development. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(6):1616-1626. [31] 刘晓东,邓廉夫,王君,等.低氧诱导因子1α在骨形成过程中对成骨细胞功能的调控作用[J].中华医学杂志,2007,87(47):3357-3361. [32] SCHROEPPEL JP, CRIST JD, ANDERSON HC, et al. Molecular regulation of articular chondrocyte function and its significance in osteoarthritis. Histol Histopathol. 2011;26(3):377-394. [33] 侯婧瑛,于萌蕾,郭天柱,等.缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(7):985-990. [34] BROWN ST, KELLY KF, DANIEL JM, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-2 alpha is required for the development of the catecholaminergic phenotype of sympathoadrenal cells. J Neurochem. 2009;110(2):622-630. [35] DUCO K, LEJLA M, MARISKA V, et al. Nur77 variants solely comprising the amino-terminal domain activate hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and affect bone marrow homeostasis in mouse and man. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(39):15070-15083. [36] MERCERON C, LEVI B, GIACCIA A J, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2α is a negative regulator of osteoblastogenesis and bone mass accrual. Bone Res. 2019;7(1):91-104. [37] ZHANG X, PRASADAM I, FANG W, et al. Chondromodulin-1 ameliorates osteoarthritis progression by inhibiting HIF-2α activity. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(11):1970-1980. [38] LEE J Y, LEE K, LEE K, et al. Pharmacokinetic Characterization of LW6, a Novel Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α (HIF-1α) Inhibitor in Mice. Molecules. 2021;26(8):2226. [39] HIRAGA T, KIZAKA-KONDOH S, HIROTA K, et al. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 expression enhance osteolytic bone metastases of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67(9):4157-4163. [40] 谢瑞燕,方雪玲, HAMZE I RAGE,等.红景天苷上调HIF-1α减轻高糖诱导的大鼠肾小球内皮细胞损伤[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019, 35(2):237-242. [41] 杨梦思,周娜,王志钢,等.转录因子HIF-1α及其信号通路在疾病发生中的作用研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2016,32(8):8-13. [42] JOHNSON RW, SCHIPANI E, GIACCIA AJ. HIF targets in bone remodeling and metastatic disease. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;150(150):169-177. [43] 金培程,程正江.闭合复位髓内钉固定治疗股骨干骨折对VEGF, HIF-1α表达的影响[J].现代医学,2020,320(2):53-58. [44] 闫奇奇,郝丽,张森.慢性肾脏病患者血清FGF23水平与钙磷代谢及临床相关性[J].安徽医科大学学报,2020,48(2):201-206. [45] SCHIPANI E, WU C, RANKIN EB, et al. Regulation of bone marrow angiogenesis by osteoblasts during bone development and homeostasis. Front Endocrinol. 2013;4(85):1-6. [46] RYU JH, YANG S, SHIN Y, et al. Interleukin-6 plays an essential role in hypoxia-inducible factor 2α-induced experimental osteoarthritic cartilage destruction in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;63(9):2732-2743. [47] 范凯健,吴菁,李钦,等.基质金属蛋白酶13在软骨重塑和关节炎中的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2018,34(5):607-611. [48] GIATROMANOLAKI A, SIVRIDIS E, MALTEZOS E, et al. Upregulated hypoxia inducible factor-1α and -2α pathway in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rrd. Ther. 2003;5(4):193-201. [49] 李启芳,王祥瑞.HIF-1α和HIF-2α对基因表达的调控[J].国际病理科学与临床杂志,2005,25(5):447-449. [50] YIN ZN, FAN J, XIA WB. Tumor-induced osteomalacia. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2018;4(4):119-127. [51] 苏永蔚,周山健,肖大伟,等.负载miRNA-27b的BMSCs来源的外泌体治疗实验性骨关节炎[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(8):59-67. [52] 张涛,徐枫,高明丽,等.右美托咪定对肺癌小鼠低氧时HIF-1α信号通路的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2019,39(9):1132-1134. [53] COIMBRA IB, JIMENEZ SA, HAWKINS DF, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha expression in human normal and osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2004;12(4):336-345. [54] 王莹,吴成爱,阎国强,等.胶原蛋白酶诱发兔膝关节骨性关节炎软骨组织中HIF2α表达上调[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(11): 1318-1322. [55] 韩巧巧,王艳玲,朱月春木.NADPH氧化酶与HIF-α在肿瘤中的相互调控[J].命的化学,2016,36(5):691-697. [56] ZHANG, FANG N, LUO W, et al. Role of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2015;82(3):144-147. [57] MIYAMOTO T. Mechanism underlying post-menopausal osteoporosis: HIF1α is required for osteoclast activation by estrogen deficiency. Keio J Med. 2015;64(3):44-47. [58] RIDDLE RC, KHATRI R, SCHIPANI E, et al. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in angiogenic–osteogenic coupling. J Mol Med. 2009;87(6): 583-590. [59] LI L, QU Y, JIN X, et al. Protective effect of salidroside against bone loss via hypoxia-inducible factor-1α pathway-induced angiogenesis. Sci Rep. 2016;25(6):32131. [60] 倪晓琳,夏维波.肿瘤性骨软化症的致病机制及治疗方法[J].中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志,2020,13(6):547-555. [61] WAGEGG M, GABER T, LOHANATHA FL, et al. Hypoxia promotes osteogenesis but suppresses adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stromal cells in a hypoxia-inducible factor-1 dependent manner. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):46483. [62] SHAO J, ZHANG Y, YANG T, et al. HIF-1α disturbs osteoblasts and osteoclasts coupling in bone remodeling by up-regulating OPG expression. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2015;51(51):808-814. [63] ONUORA S. Osteoarthritis: Cartilage matrix stiffness regulates chondrocyte metabolism and OA pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(9):504. [64] MING L, DAN W, NING L. MicroRNA-20b downregulates HIF-1α and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Res. 2016;23(5):257-266. [65] KOUVARAS E, CHRISTONI Z, SIASIOS I, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor in cartilage tumors. Biotech Histochem. 2019;94(4):283-289. [66] WANG Y, YAO J, MENG H, et al. A novel long non-coding RNA, hypoxia-inducible factor-2α promoter upstream transcript, functions as an inhibitor of osteosarcoma stem cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2015; 11(4):2534-2540. [67] 滑雅娜,鲁芙爱,王永福. HIF-1相关信号通路及其在自身免疫性疾病中作用[J].中国免疫学杂志,2019,35(8):1013-1017. [68] YANG G, SUN Q, TENG Y, et al. PTEN deficiency causes dyschondroplasia in mice by enhanced hypoxia-inducible factor 1α signaling and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Development. 2008;135(21):3587-3597. [69] 陈焕,张燕,刘梦思,等.肢端肥大症患者骨转换标记物和骨平衡变化及其影响因素分析[J].中华医学杂志,2021,101(33):2600-2605. [70] 杨庆诚,曾炳芳,施忠民,等.组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂对骨肉瘤侵袭性及HIF-1α表达的影响[J].肿瘤,2008,28(6):472-475. [71] ZHOU XF, GUO XJ, CHEN M, et al. HIF-3α promotes metastatic phenotypes in pancreatic cancer by transcriptional regulation of the RhoC-ROCK1 signaling pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 2018;16(1):124-134. [72] ZULKIFLI AF, TOSHIHARU Y, OSAMU O. Deterioration of alveolar development in mice with both HIF-3α knockout and HIF-2α knockdown. BMC Res Notes. 2018;11(1):449-452. [73] ANDO H, NATSUME A, IWAMI K, et al. A hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-3α splicing variant, HIF-3α4 impairs angiogenesis in hypervascular malignant meningiomas with epigenetically silenced HIF-3α4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;433(1):139-144. [74] LI QF, WANG XR, YANG YW, et al. Hypoxia upregulates hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-3alpha expression in lung epithelial cells: characterization and comparison with HIF-1alpha. Cell Res. 2006;16(6):548-558. [75] CHEN WC, CHI CH, CHUANG CC, et al. Three novel EXT1 and EXT2 gene mutations in taiwan patients with multiple exostoses. J Formos Med Assoc. 2006;105(5):434-437. [76] RUAN W, CAO L, CHEN Z, et al. Novel exostosin-2 mutation identified in a Chinese family with hereditary multiple osteochondroma. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(4):4383-4389. [77] LEMOS MC, PETER K, CHRISTIE PT, et al. A novel EXT1 splice site mutation in a kindred with hereditary multiple exostosis and osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metat. 2005,90(9):5386-5392. [78] BAASANJAV S, JAMSHEER A, KOLANCZYK M, et al. Osteopoikilosis and multiple exostoses caused by novel mutations in LEMD3 and EXT1 genes respectively - coincidence within one family. BmC Med Genet. 2010;11(1):110. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Zhang Jingxin, Liu Linfeng, Zhang Shiwen, Lin Jie. Molecular mechanism of magnesium ion promoting bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5384-5392. |
| [3] | Zhao Dun, Fang Bin, Yi Chunzhi, He Mincong, Zheng Jiaqian, Li Yue. Effects of total flavonoids of Rhizoma drynariae on bone remodeling and expression of bone morphogenetic protein-2, vascular endothelial growth factor and CD31 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4638-4642. |
| [4] | Lu Qigui, Xie Pingjin, Luo Zhen, Li Feilong, Chen Qunqun, Chai Shengting. MicroRNA-20b-5p effects on cartilage and subchondral bone angiogenesis in early-stage osteoarthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4658-4665. |
| [5] | Yang Qiongqiong, Li Ping, Wang Qian. Role and regulatory mechanism of microRNA in bone tissue repair around dental implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4539-4545. |
| [6] | Gong Yuqing, Yao Wei, Li Ran. Osteoimmunological effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha in alveolar bone remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4242-4251. |
| [7] | Chen Qiaoling, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Lin Tao, Luo Xuwei. Osteoblast differentiation after conditional knockout of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 gene from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3785-3789. |
| [8] | Yu Xiaofan, Jiang Huijiao, Tan Xiaowu, Wu Xiangwei. Expression of vasohibin-1 and other factors after the co-culture of two kinds of Echinococcus granulosus protoscolex and endothelial progenitor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3892-3896. |
| [9] | Fan Danyang, Fu Runze, Mi Jiajing, Liu Chunyan. Expression and role of cannabinoid receptors during bone remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 283-288. |
| [10] | Tian Xinbao, Xu Jianfeng, Huang Yuan, Lai Zheying, Li Xiaolong, Liu Xiaoli, Lin Ruizhu, Zhu Ning. Internal heat-type acupuncture inhibits osteoblast viability and promotes bone formation in a rat model of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2642-2648. |
| [11] | Chen Yiyuan, Yang Qian, Wu Saixuan, Zhang Mi, Dong Ming, Liu Tingjiao, Niu Weidong. The role of spleen tyrosine kinase in bone remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2446-2453. |
| [12] | Li Jingyu, Su Yingying, Bai Ding. Morphological characteristics of subchondral bone in a mouse model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1692-1698. |
| [13] | Zheng Xiaolong, He Xiaoming, Gong Shuidi, Pang Fengxiang, Yang Fan, He Wei, Liu Shaojun, Wei Qiushi. Bone turnover characteristics in patients with alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 657-661. |
| [14] | Zhang Qunhui, Li Yimei, Zhang Dejun. Hypoxia-inducible factor and coronary heart disease: antagonism and protection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5729-5734. |
| [15] | Xiao Sha, Gao Chengzhi, Zhou Dongping. Comparison of three kinds of bone replacement materials in the treatment of bone defects around the mandibular posterior teeth with immediate implantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5495-5500. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||