Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (33): 5400-5406.doi: 10.12307/2022.716
Previous Articles Next Articles
Skeletal muscle function and exercise regulating cognitive function of the older adults
Xiao Youding1, Gao Qianjin2, Wang Erli3
- 1Department of Physical Education of Shanghai Jian Qiao University, Shanghai 201306, China; 2College of Physical Education, Shijiazhuang University, Shijiazhuang 050035, Heibei Province, China; 3Hebei Vocational College of Public Security Police, Shijiazhuang 050020, Heibei Province, China
-
Received:2021-10-27Accepted:2021-12-04Online:2022-11-28Published:2022-03-31 -
Contact:Wang Erli, Associate professor, Hebei Vocational College of Public Security Police, Shijiazhuang 050020, Heibei Province, China -
About author:Xiao Youding, Master, Department of Physical Education of Shanghai Jian Qiao University, Shanghai 201306, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xiao Youding, Gao Qianjin, Wang Erli. Skeletal muscle function and exercise regulating cognitive function of the older adults[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5400-5406.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
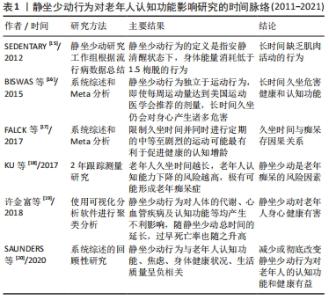
2.1 衰老与骨骼肌功能 2.1.1 老年骨骼肌结构及功能的退化是引发继发性衰老的重要因素 众所周知,衰老会使机体出现不可避免的结构和功能的降低,称为原发性衰老,而由于后天的疾病或不良生活方式等因素引起的机体功能的进一步降低,则称为继发性衰老,继发性衰老会在原发性衰老的基础上显著降低身体功能、缩短寿命,但如果采取一定的措施进行干预,继发性衰老是可以减少或避免的。因此,应通过倡导健康的生活方式等举措延迟或避免继发性衰老的产生,以实现健康增龄。研究表明骨骼肌在维持人体正常功能中发挥重要作用,老年骨骼肌结构及功能的紊乱是引发继发性衰老的重要因素[8]。因此,改善骨骼肌功能是延缓衰老的重要举措,而增加身体活动水平则是改善骨骼肌功能的重要手段。 实际上骨骼肌功能的重要性长期被人们所忽视,BENNIE等[9]对欧洲28万人的调查显示,经常进行抗阻训练的人不足17%,尤其大多数老年人没有足够的力量训练。那么为什么肌肉力量对中老年人的健康非常重要呢?这是因为骨骼肌除了为人体活动提供动力以外,还具有维持人体代谢正常、维持骨健康等重要功能[10]。如果不进行肌肉力量锻炼,骨骼肌功能衰退将会带来一系列的不确定风险,例如,跌倒,老年人腿部肌肉量减少和肌肉力量的下降会使跌倒的概率显著增加;糖代谢功能受损,骨骼肌是糖脂代谢的重要器官,肌肉量的流失会使胰岛素受体敏感性下降,容易导致胰岛素抵抗或糖尿病的发生;影响心血管健康,肌肉力量与心血管发病率呈反比关系,肌肉力量的下降可以导致心血管疾病发生,研究发现肌肉力量大的人的心血管疾病患病率会降低30%左右;影响寿命,骨骼肌功能降低会导致吞咽、消化、排泄等功能的减退,随之人体免疫能力也降低,这可能会引起各种各样的疾病发生,今天吃药明天住院,寿命会缩短[11]。这是因为骨骼肌占人体质量的40%左右,是人体质量最大的组织器官,是人体维持健康的关键储备。但是,随着增龄,肌肉也会出现衰老现象,只是正处于青壮年时期的身体有很强的代偿能力,不会出现跌倒或其他不适症状。据研究报告,人体从30岁开始,每年肌肉量会流失1%-5%,而当肌肉量流失达30%时将会影响肌肉的正常功能,流失量达到40%时将会威胁生命[12]。60岁以后,每年肌肉力量会下降5%左右,但是肌肉量和力量下降的程度也与是否经常进行体力活动有关,以一个体质量70 kg的青年人为例,30岁开始每年肌肉量正常流失0.7-3.5 kg,在没有任何运动干预措施的情况下,他到60岁时肌肉量的流失将会超过30%,这也意味着他将开始承受“腿老”带来的一系列风险。 2.1.2 运动能够延缓肌肉的衰老 研究显示运动能够延缓肌肉的衰老,对衰老骨骼肌具有改善效应,即使年龄大了,科学定期的力量训练也可以让你的肌肉获得新生[13]。肌肉体积增加了,力量大了,人体的功能能力改善,人也愿意动起来,随之有氧功率也会提高。力量的增加会使日常的生活能力提高,例如从床上或沙发上起来,如厕,外出购物,带小孩,上下楼梯,逛超市后提重物等等。力量的增加可有效防止意外受伤,腰背力量增大可防止腰背疼痛,大腿肌肉量增加可防止膝关节受伤,整个腿部力量提高可防止老年人跌倒,这些都说明了肌肉力量对健康生活的积极作用。抗阻力训练对疾病也有预防和治疗作用,例如对高血压、糖尿病、骨质疏松、关节炎、失眠、抑郁症、认知功能障碍等[14],尤其最新研究发现骨骼肌功能的变化对老年人脑健康有重要影响。 2.2 骨骼肌功能下降对老年认知功能的影响 2.2.1 静坐少动行为与认知功能下降相关 静坐少动行为和增龄性肌肉减少症都会使骨骼肌功能下降。静坐少动行为研究工作组对“静坐少动行为”的定义为:安静清醒状态下,坐位或卧位时,身体能量消耗低于1.5梅脱的行为。梅脱是评价运动强度的单位之一,所有看电视、听课、看书、坐卧等行为都属于1梅脱强度的活动[15]。静坐少动行为使人体缺乏全身性的肌肉活动,肌肉长时间缺乏收缩可能会释放一系列的负面生化反应。研究表明,静坐少动的人分解血糖、胆固醇的功能不好,血糖和三酰甘油水平较高,这是糖尿病、心脏病及中风的罪魁祸首。老年人由于机体功能衰退容易静坐少动,研究发现老年人静坐少动行为与认知能力的降低相关,而且静坐少动行为独立于运动行为,即使运动量达到了美国运动医学会推荐的剂量,长时间久坐仍然会对身心产生诸多危害[16]。尽管久坐时间对痴呆发病率的归因风险尚不清楚,但FALCK 等[17]的回顾性研究证实,限制久坐时间并同时进行定期的中等至剧烈的运动可能最有利于促进健康的认知增龄。KU等[18]的前瞻性研究也证实久坐时间越长,老年人认知能力下降的风险越高,极有可能形成老年痴呆症。中国学者许金富等[19]运用可视化分析软件对2002-2017年之间发表的3 074篇论文进行了分析,发现静坐少动行为对人体的代谢、心血管疾病及认知功能等均产生不利影响,随静坐少动总时间的延长,过早死亡率也随之升高。SAUNDERS等[20]的系统性综述研究发现静坐少动行为与老年人认知功能、焦虑、身体健康状况、生活质量呈负相关,减少或彻底改变静坐少动行为对老年人的认知功能和健康有益。静坐少动行为对老年人认知功能影响研究的时间脉络,见表1。"
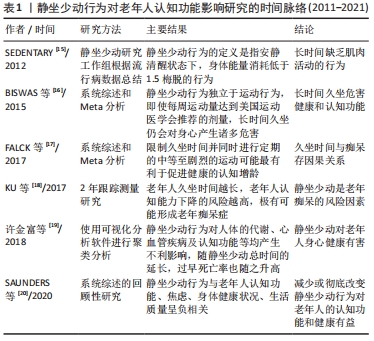
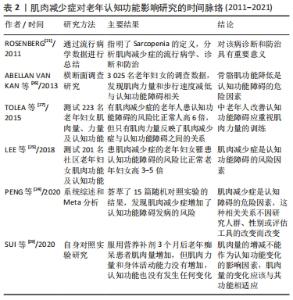
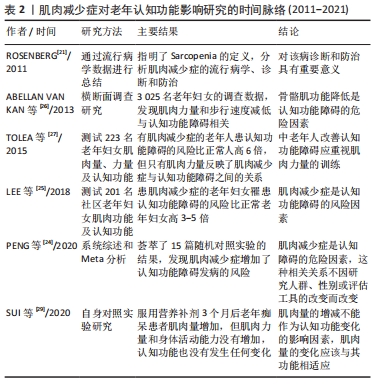
2.2.2 肌肉减少症使老年认知功能障碍的风险增加 “Sarcopenia”一词最早由美国学者ROSENBERG提出,该词源于希腊语,sarco 是肌肉的意思,penia是指流失或减少,合起来就是肌肉减少的意思,肌肉减少症是以肌肉量减少、肌力下降、肌肉功能降低为主要特征的与年龄相关的一种老年性疾病[21]。2019年肌肉减少症欧洲工作组将其定义为一种渐进的、全身性的肌纤维数量和质量的减少,肌肉力量下降、功能衰退,且伴有结缔组织和脂肪增多,导致机体功能和生活质量下降,不良事件风险增加,甚至死亡[22]。该病的发生、发展与诸多因素相关,包括遗传因素、增龄因素(活动能力受限、细胞凋亡、线粒体功能异常等)、内分泌疾病所致激素水平变化、营养不良、神经肌肉功能减退等[23]。 目前,研究一致认为骨骼肌功能降低(肌肉减少症)是老年人认知功能障碍的风险因素。例如,最近的一项系统综述和Meta分析荟萃了15篇随机对照试验的结果,发现肌肉减少症增加了认知功能障碍发病的风险(OR:2.85,95%CI:2.19-3.27),该研究的OR=2.85> 1,说明肌肉减少症是认知障碍的危险因素,作者指出这种相关关系不因研究人群、性别或评估工具的改变而改变[24]。韩国学者调查了201名老年韩国妇女的肌肉减少症和大脑认知能力之间的关系,使用简易认知功能量表(Mini-Mental State Examination,MMSE)测定认知功能, 肌肉减少症诊断采用亚洲工作组对肌肉减少症的定义标准,结果发现肌肉减少症的妇女罹患认知功能障碍的风险比正常妇女高3-5倍[25]。 肌肉减少症的诊断有3个要素,即肌肉量、力量和身体活动能力,但研究发现骨骼肌功能(肌肉力量和身体活动能力)是老年认知功能下降的风险因素,而肌肉量只作为参考因素。例如,ABELLAN等[26]对3 025名年龄75岁以上的法国妇女进行了横向研究,使用双能X线吸收测定法(DXA)测定肌肉量,用握力代表肌肉力量,6 m步行速度代表身体活动能力,使用简易认知功能量表测定认知功能,结果发现,有492名妇女患认知功能障碍;以“认知功能”为因变量,“肌肉量、握力及步行速度”为自变量,使用多元线性回归模型进行分析,发现握力(OR:1.81,95%CI:1.33-2.46)和步行速度(OR:2.42,95%CI:1.72-3.40)与认知功能障碍相关,OR值均大于1,说明骨骼肌功能降低是认知功能障碍的危险因素,而肌肉量与认知功能之间不存在相关关系。另一个横向研究观察了肌肉减少症对认知功能的影响,研究对象是223名中老年人,使用握力计测定肌肉力量,生物电阻抗法测定肌肉量,蒙特利尔认知评估量表用来评估认知能力;研究结果发现,有肌肉减少症的个体患认知功能障碍的风险比正常人高6倍,但只有肌肉力量反映了肌肉减少症与认知功能障碍之间的关系,而肌肉量与认知功能障碍之间没有强的关联,所以作者建议中老年人改善认知功能障碍应重视肌肉力量的训练[27]。最近SUI等[28]的研究再次证明了肌肉力量和身体活动能力(步行速度)的降低是认知功能障碍的良好预测指标,尤其对思维判断、注意力、视觉空间学习和长期记忆等认知领域的影响更为显著。为了证实肌肉量与老年认知功能的关系,研究人员让46例老年痴呆症患者口服营养补剂增加肌肉量,然后测定肌肉力量、身体活动能力以及认知功能的变化,结果发现,服用营养补剂3个月后老年痴呆患者肌肉量增加,但肌肉力量和身体活动能力没有增加,认知功能也没有发生任何变化[29]。这个研究提示单纯肌肉量的增减不能作为认知功能变化的影响因素,肌肉量的变化应该与其功能相适应,也就是说,增加肌肉量应该以增加骨骼肌功能为目的。肌肉减少症对老年认知功能影响研究的时间脉络,见表2。"
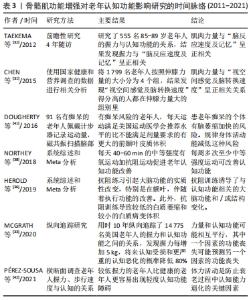
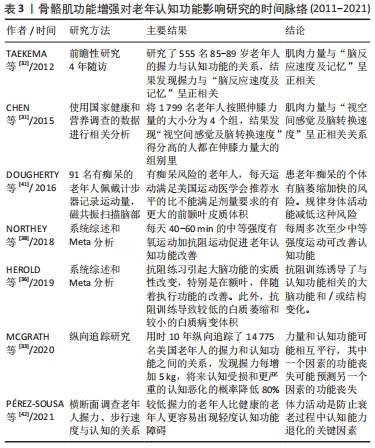
2.3 骨骼肌功能提高对老年认知功能的影响 2.3.1 骨骼肌功能与老年认知功能呈正相关 衰老会使骨骼肌功能下降,而运动能延缓或提高骨骼肌功能。2020年EMERENZIANI等[30]研究了老年人认知功能与骨骼肌功能之间的关系,并建立了回归方程,使用简易机体功能评估法(short physical performence battery,SPPB)测定老年人骨骼肌功能,使用简易精神状态检查量表(MMSE)测定老年人认知功能,使用多元线性回归模型进行分析,得到回归方程:MMSE=19.479+(1.548×SPPB)-(0.130×age),老年人的认知功能可以通过SPPB和年龄进行预测,因此,从回归方程看,骨骼肌功能与认知功能呈正相关关系。 很多研究证实了骨骼肌功能与认知功能之间的正相关关系。CHEN等[31]横向研究了1 799名老年人(> 60岁)的伸膝力量与“视空间感觉及脑转换速度”的关系,伸膝力量使用肌力矩测定仪测定,“视空间感觉及脑转换速度”使用数字符号转换实验(digit symbol substitution test,DSST)测定,然后将1 799名老年人按照伸膝力量的大小分为4个组,结果发现“视空间感觉及脑转换速度”得分高的人都在伸膝力量大的组别里,表明肌肉力量与“视空间感觉及脑转换速度”呈正相关关系。TAEKEMA等[32]研究了555名85-89岁老年人的握力与认知功能的关系,结果发现握力与“脑反应速度及记忆”呈正相关。MCGRATH等[33]用时10年纵向追踪了14 775名美国老年人的握力和认知功能之间的关系,发现握力每增加5 kg,将来认知受损和更严重的认知恶化的概率降低80%(OR:0.97,95%CI: 0.93-0.99)。力量能力和认知功能可能相互平行,其中一个因素的功能丧失可能预测另一个因素的功能丧失。作者建议,握力可用于评估老年人的认知状态,应随时监测认知功能障碍患者的力量能力。握力反映了前臂和手部的肌肉力量,与全身肌肉力量相关性较高,通常用握力代表全身的肌肉力量情况。 2.3.2 不同运动方式引起的骨骼肌功能改善对认知功能有积极影响 力量训练(或称抗阻训练)能够提高老年人肌肉力量,肌肉力量的改善对认知功能和脑健康有积极影响[34-35]。例如,研究表明力量训练能够增加大脑额叶皮质的厚度,并伴随着执行功能的改善,此外,力量训练还能够降低大脑白质萎缩和减小白质病变的体积[36]。研究还发现6个月的高强度抗阻运动不仅能够提高老年轻度认知功能障碍患者的认知能力,而且还能在运动干预后至少12个月内保护容易患痴呆的海马区不退化[37]。力量训练对脑的这些正向效益均是通过肌肉力量的提高来实现的。 不同运动方式均对骨骼肌有良好的刺激作用。在有关运动与认知功能的研究中,研究最多最早的是有氧运动。有氧运动可提高心肺适能和外周骨骼肌利用氧气的能力。大量的研究证明长期有氧运动可增加老年人前额叶皮质的体积,延缓海马回等脑区的萎缩,同时增强记忆和改善大脑的执行功能[38]。执行功能与大脑前额叶有关,是大脑的高级功能,执行功能是指一个人对自己的记忆、注意、逻辑推理、加工速度等认知过程进行抑制、转换、刷新和调整,从而完成一个特定的目标或任务,如外出购物[39]。 综合众多研究结论,康复专家建议老年人应按照美国运动医学会《身体活动指南》推荐的运动方案进行锻炼,有氧运动与力量训练相结合,即每周不低于150 min的中低强度有氧运动结合每周2次中等以上强度的力量训练[40]。每周完成推荐运动量的老年人往往有较大的脑量,易患痴呆的脑区萎缩率明显降低,认知功能得到改善[41-42]。骨骼肌功能增强对老年认知功能影响研究的时间脉络,见表3。"
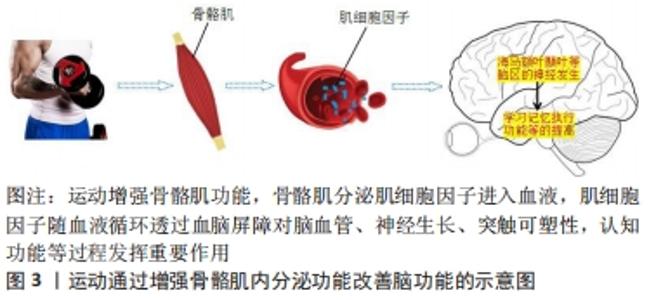
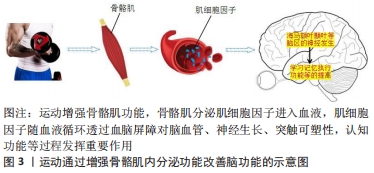
骨骼肌功能的提高除了直接或间接影响老年认知功能以外,还能够通过分泌肌细胞因子对脑血管形成、神经生长、突触可塑性等过程发挥重要作用。 2.4 骨骼肌内分泌功能增强对脑健康的影响 骨骼肌即是人体运动的动力器官,又是人体重要的内分泌器官,肌肉可通过自分泌、旁分泌和远距分泌等形式分泌多种肌细胞因子,作用于骨骼、脂肪、肝脏、肠道和大脑等组织器官,影响其代谢和功能,维持机体稳态。肌细胞因子的发现为骨骼肌与其他器官的相互作用提供了一种全新模式。目前“骨骼肌-肠道菌群”“骨骼肌-肝脏”以及“骨骼肌-大脑”研究越来越成为人们关注的热点。运动增强骨骼肌功能,骨骼肌分泌肌细胞因子进入血液,肌细胞因子随血液循环透过血脑屏障对脑血管形成、神经生长、突触可塑性、认知功能等过程发挥重要调节作用[43],见图3。"

2.4.1 PGC-1α-FNDC5/Irisin-BDNF通路 Irisin(鸢尾素)是2012年新发现的一种骨骼肌释放的激素,其与脂肪组织的棕色化有关,鸢尾素的发现给人们对肥胖的治疗带来了新的希望,由于2012年发表在《自然》杂志上的这篇论文称其是彩虹女神,所以人们将其命名鸢尾素[44]。研究人员发现,经过锻炼之后的肌肉会先分泌一种叫过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因1α(peroxisome proliferater activated receptor gamma coactivator-1α,PGC-1α)的蛋白,其调节的下游蛋白III型纤连蛋白组件包含蛋白5(type Ⅲ domain-containingprotein 5,FNDC5)可以通过自身剪切而形成鸢尾素进入血液。Irisin作用的靶器官组织是白色脂肪,它一方面可以将白色脂肪转变为棕色脂肪(棕色化),成为产热效率极高的棕色脂肪后,使肥胖者体内多余能量得以减少,另一方面被棕色化的脂肪组织大量消耗体内的葡萄糖和脂肪等,当它自身储存能量物质消耗殆尽,身体其他部位储存的白色脂肪就成为它的新燃料,呈现出星火燎原之势[45]。 除了Irisin对新陈代谢的有益作用外,研究还发现运动不仅在骨骼肌中诱导了Irisin的表达,而且也诱导了海马回中的FNDC5和脑源性神经营养因子(brain-derived neurophic factor,BDNF)的表达,海马回是大脑中与记忆和空间意识有关的中枢[46]。CHOI等[47]的研究表明,运动诱导成人海马回神经发生与FNDC5和脑源性神经营养因子的增加相关,有助于改善阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型的认知能力。重要的是,通过腺病毒载体将重组FNDC5外周注入肝脏,提高了血液Irisin的水平,循环的Irisin诱导了海马回中脑源性神经营养因子和其他神经保护基因的表达[48]。这一发现说明Irisin可以穿过血脑屏障影响大脑中相关保护因素的基因表达,这一发现也意味着Irisin在脑科学领域具有巨大治疗前景,鼓舞着人们进一步研究Irisin与海马体的作用以及认知功能的改善。因此,有很多研究测定了Irisin水平与认知功能之间的关系,发现Irisin水平与老年人较好的认知功能正相关[49-50],所有上述研究结果都说明可能存在“肌肉-大脑”内分泌环。运动诱导的肌源性Irisin释放进入血液为PGC1α、FNDC5和海马脑源性神经营养因子的表达之间提供了联系。 2.4.2 CathepsinB和脑源性神经营养因子调节 组织蛋白酶cathepsinB属溶酶体水解蛋白酶家族的成员,是骨骼肌细胞分泌的肌细胞因子。2016年MOON等[51]发现了一条连接肌肉与大脑海马回的信号通路(cathepsinB-BDNF信号通路),他们发现小鼠运动时升高了血液循环中的cathepsinB,cathepsinB随血液循环穿过血脑屏障促进海马回中脑源性神经营养因子表达和刺激了神经发生。在小鼠模型中的这些发现后来在恒河猴和人体试验中得到了进一步验证,长期运动训练促进骨骼肌分泌cathepsinB进入血液,cathepsinB穿过血脑屏障,诱导海马回脑源性神经营养因子增加,调节突触可塑性、神经元间的连接和记忆改善[52]。另一个实验显示,小鼠用甲酰胺核苷酸处理1周后,小鼠的海马回神经发生和认知功能改善[53]。甲酰胺核苷酸是AMP依赖的蛋白激酶(Adenosine 5‘-monophosphate (AMP)- activated protein kinase,AMPK)信号通路激活剂,可激活AMPK信号通路,这个实验证实了运动可能是通过激活骨骼肌中的AMPK信号通路诱导cathepsinB的分泌,cathepsinB穿过血脑屏障,与运动引起的认知功能改进相关[54]。而敲除cathepsinB的小鼠海马回神经发生和空间学习记忆均受到损害[55]。 2.4.3 脑源性神经营养因子的作用 神经元既能生成营养因子,维持所支配组织的正常代谢与功能,同时也接受神经营养因子的支持,以维持其正常的形态和功能。神经营养因子可产生于其他组织(例如骨骼肌)和神经胶质细胞,它们在神经末梢经由受体进入末梢,在逆向轴浆运输抵达胞体,从而支持神经元的生长、发育和功能完整。目前已发现并分离的神经营养因子主要有神经生长因子、脑源性神经营养因子、神经营养因子3及神经营养因子4/5等。脑源性神经营养因子在神经元生长、神经可塑性(大脑根据经验改变和适应的能力)以及神经功能维持中发挥重要作用,在中枢神经系统分布广泛,诸如海马区域、纹状体等表达较多,其调节多巴胺能神经细胞的再生和功能正常。研究发现,老年人通过有氧运动可以改善海马区域的萎缩,而且这种结构的改善常伴随脑源性神经营养因子的增多及认知功能提高[56]。运动与脑源性神经营养因子及认知功能之间的阳性相关已被广泛研究,并在青少年和老年人群中得到证实[57]。脑源性神经营养因子是与成年人神经元生长有关的重要神经营养因子,大脑在成年期可以通过新的神经元的生长,增加神经元可塑性,提高脑储备。神经元的生长仅发生在部分的脑区(其中经常被研究的是海马区),因此可能是记忆和学习能力改善的重要机制。有规律的运动可以通过脑源性神经营养因子促进部分大脑区域的神经发生,从而长期维持记忆[58],并且最新研究发现力量训练对长期保持海马神经可塑性,维护脑健康意义重大[59]。 虽然运动、脑源性神经营养因子、神经发生和记忆之间的联系在动物模型中得到了很好的描述,但运动在人类脑健康方面尚需进一步探索。人们正在积极研究运动诱发的神经发生,作为神经和精神障碍疾病(如阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病和抑郁症)的一种潜在疗法。 上述介绍的几种肌细胞因子主要与运动调控脑健康密切相关,其中很多机制尚未明确,进一步深入研究有望为老年人认知功能的保持及相关疾病的治疗提供新思路。"

| [1] CASTELLS-SáNCHEZ A, ROIG-COLL F, DACOSTA-AGUAYO R, et al. Exercise and fitness neuroprotective effects: molecular, brain volume and psychological correlates and their mediating role in healthy late-middle-aged women and men. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:615247. [2] LIU-AMBROSE T, BARHA C, FALCK RS. Active body, healthy brain: Exercise for healthy cognitive aging. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019;147:95-120. [3] BEKER N, GANZ A, HULSMAN M, et al. Association of cognitive function trajectories in centenarians with postmortem neuropathology, physical Health, and other risk factors for cognitive decline. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2031654. [4] CHEN FT, HOPMAN RJ, HUANG CJ, et al. The effect of exercise training on brain structure and function in older Adults: a systematic review based on evidence from randomized control trials. 2020;9(4):914. [5] 魏胜敏,高前进.运动对各年龄阶段人群脑健康的影响及机制研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(1):67-69. [6] PEDERSEN BK. Physical activity and muscle-brain crosstalk. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(7):383-392. [7] SCISCIOLA L, FONTANELLA RA, SURINA, et al. Sarcopenia and cognitive function: role of myokines in muscle brain cross-talk. Life (Basel). 2021; 11(2):173. [8] BENNIE JA, DE COCKER K, TITTLBACH S. The epidemiology of muscle strengthen-ing and aerobic physical activity guideline adherence among 24,016 German adults. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021;31(5):1096-1104. [9] BENNIE JA, DE COCKER K, SMITH JJ, et al. The epidemiology of muscle strengthen-ing exercise in Europe: A 28-country comparison including 280,605 adults. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):e0242220. [10] PARRY HA, ROBERTS MD, KAVAZIS AN. Human skeletal muscle mitochondrial adaptations following resistance exercise training. Int J Sports Med. 2020;41(6):349-359. [11] MCLEOD JC, STOKES T, PHILLIPS SM. Resistance exercise training as a primary countermeasure to age-related chronic disease. Front Physiol. 2019;10:645. [12] WILKINSON DJ, PIASECKI M, ATHERTON PJ. The age-related loss of skeletal muscle mass and function: Measurement and physiology of muscle fibre atrophy and muscle fibre loss in humans. Ageing Res Rev. 2018;47:123-132. [13] 首健, 陈佩杰, 肖卫华. 运动对老年骨骼肌的改善效应及其机制[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(9):1140-1145. [14] FRAGALA MS, CADORE EL, DORGO S, et al.Resistance training for older adults: position statement from the national strength and conditioning association. J Strength Cond Res. 2019;33(8):2019-2052. [15] SEDENTARY BRN. Letter to the editor: standardized use of the terms “sedentary” and “sendentary beviours” . Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2012;37(3):540-542. [16] BISWAS A, OH PI, FAULKNER GE, et al. Sedentary time and it’s association with risk for disease incidence, mortality, and hospitalization in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intem Med. 2015; 162(2):123. [17] FALCK RS, DAVIS JC, LIU-AMBROSE T. What is the association between sedentary behaviour and cognitive function? A systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(10):800-811. [18] KU PW, LIU YT, LO MK, et al. Higher levels of objectively measured sedentary behavior is associated with worse cognitive ability: Two-year follow-up study in community-dwelling older adults. Exp Gerontol. 2017;99:110-114. [19] 许金富,陈海春.国际静坐少动行为研究的知识图谱分析[J].山东体育学院学报,2018,34(6):109-116. [20] SAUNDERS TJ, MCISAAC T, Douillette K, et al. Sedentary behaviour and health in adults: an overview of systematic reviews. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020;45(10 (Suppl. 2)):S197-S217. [21] ROSENBERG IH. Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance. Clin Geriatr Med. 2011;27(3):337-339. [22] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019; 48(1):16-31. [23] BIčIKOVá M, MáčOVá L, JANDVOá D, et al. Movement as a positive modulator of aging. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(12):6278. [24] PENG TC, CHEN WL, WU LW, et al. Sarcopenia and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2020; 39(9):2695-2701. [25] LEE I, CHO J, HONG H, et al. Sarcopenia is associated with cognitive impairment and depression in elderly korean women. Iran J Public Health. 2018;47(3):327-334. [26] ABELLAN VAN KAN G, CESARI M, GILLETTE-GUYONNET S, et al. Sarcopenia and cognitive impairment in elderly women: results from the EPIDOS cohort. Age Ageing. 2013;42(2):196-202. [27] TOLEA MI, GALVIN JE. Sarcopenia and impairment in cognitive and physical performance. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:663-671. [28] SUI SX, HOLLOWAY-KEW KL, HYDE NK, et al. Muscle strength and gait speed rather than lean mass are better indicators for poor cognitive function in older men. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):10367. [29] SUI SX, WILLIAMS LJ, HOLLOWAY-KEW KL, et al. Skeletal Muscle Health and Cognitive Function: A Narrative Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):255. [30] EMERENZIANI GP, VACCARO MG, IZZO G, et al. Prediction equation for estimating cognitive function using physical fitness parameters in older adults. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0232894. [31] CHEN WL, PENG TC, SUN YS, et al. Examining the association between quadriceps strength and cognitive performance in the elderly. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(32):e1335. [32] TAEKEMA DG, LING CHY, KURRLE SE, et al. Temporal relationship between handgrip strength and cognitive performance in oldest old people. Age Ageing. 2012;41:506-512. [33] MCGRATH R, VINCENT BM, HACKNEY KJ, et al. The longitudinal associations of handgrip strength and cognitive function in aging Americans. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21(5):634-639. [34] HORTOBáGYI T, GRANACHER U, FERNANDEZ-DEL-OLMO M, et al. Functional relevance of resistance training-induced neuroplasticity in health and disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;122:79-91. [35] DE LA ROSA A, OLASO-GONZALEZ G, ARC-CHAGNAUD C, et al.Physical exercise in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(5):394-404. [36] HEROLD F, TöRPEL A, SCHEGA L, et al. Functional and/or structural brain changes in response to resistance exercises and resistance training lead to cognitive improvements - a systematic review. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2019;16:10. [37] BROADHOUSE KM, SINGH MF, SUO C, et al. Hippocampal plasticity underpins long-term cognitive gains from resistance exercise in MCI. Neuroimage Clin. 2020;25:102182. [38] NORTHEY JM, CHERBUIN N, PUMPA KL, et al. Exercise interventions for cognitive function in adults older than 50: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(3):154-160. [39] GUADAGNI V, DROGOS LL, TYNDALL AV, et al. Aerobic exercise improves cognition and cerebrovascular regulation in older adults. Neurology. 2020;94(21):e2245-e2257. [40] PESCATELLO LS, ARENAR, RIEBE D, et al. ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. America: WoltersKluwer. 2013:27. [41] DOUGHERTY RJ, ELLINGSON LD, SCHULTZ SA, et al. Meeting physical activity recommendations may be protective against temporal lobe atrophy in older adults at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;4:14-17. [42] PÉREZ-SOUSA MÁ, DEL POZO-CRUZ J, OLIVARES PR, et al. Role for physical fitness in the association between age and cognitive function in older adults: a mediation analysis of the SABE colombia study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(2):751. [43] GOMARASCA M, BANFI G, LOMBARDI G. Myokines: The endocrine coupling of skeletal muscle and bone. Adv Clin Chem. 2020;94:155-218. [44] BOSTRöM P, WU J, JEDRYVHOWSKI MP, et al. A PGC1α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;81(7382):463-468. [45] DE FREITAS GB, LOURENCO MV, DE FELICE FG. Protective actions of exercise-related FNDC5/-Irisin in memory and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2020;155(6):602-611. [46] BABAEI A, NOURSHAHI M, FANI M, et al. The effectiveness of continuous and interval exercise preconditioning against chronic unpredictable stress: Involvement of hippocampal PGC-1alpha/FNDC5/BDNF pathway. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;136:173-183. [47] CHOI SH, BYLYKBASHI E, CHATILA ZK, et al. Combined adult neurogenesis and BDNF mimic exercise effects on cognition in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. Science. 2018;361(6404):eaan8821. [48] LOPRINZI PD, FRITH E. A brief primer on the mediational role of BDNF in the exercise-memory link. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2019;39:9-14. [49] KUSTER OC, LAPTINSKAYA D, FISSLER P, et al. Novel blood-based biomarkers of cognition, stress, and physical or cognitive training in older adults at risk of dementia: preliminary evidence for a role of BDNF, Irisin, and the kynurenine pathway. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;59(3):1097-111. [50] PIGNATARO P, DICARLO M, ZERLOTIN R, et al. FNDC5/Irisin system in neuroinfla-mmation and neurodegenerative diseases: update and novel perspective. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1605. [51] MOON HY, BECK A, BERRON D, et al. Running-induced systemic cathepsinB secretion is associated with memory function. Cell Metab. 2016;24(2):332-340. [52] DE LA ROSA A, SOLANA E, CORPAS R, et al. Long-term exercise training improves memory in middle-aged men and modulates peripheral levels of BDNF and Cathep- sin B. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):3337. [53] KOBILO T, YUAN C, VAN PRAAG H. Endurance factors improve hippocampal neurogenesis and spatial memory in mice. Learn Me. 2011;18(2):103-107. [54] VALENZUELA PL, CASTILLO-GARCIA A, Morales JS, et al. Exercise benefits on Alzheimer’s disease: State-of-the-science. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;62:101108. [55] KIM S, CHOI JY, MOON S, et al. Roles of myokines in exercise-induced improvement of neuropsychiatric function. Pflugers Arch. 2019;471(3): 491-505. [56] VOSS MW, SOTO C, YOO S, et al. Exercise and Hippocampal Memory Systems. Trends Cogn Sci. 2019;23(4):318-333. [57] GHOLAMNEZHAD Z, BOSKABADY MH, JAHANGIRI Z. Exercise and Dementia. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1228:303-315. [58] RENDEIRO C, RHODES JS. A new perspective of the hippocampus in the origin of exercise-brain interactions. Brain Struct Funct. 2018; 223(6):2527-2545. [59] BROADHOUSE KM, SINGH MF, SUO C, et al. Hippocampal plasticity underpins long-term cognitive gains from resistance exercise in MCI. Neuroimage Clin. 2020;25:102182. [60] AARSLAND D. Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Dementia-Related Psychosis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2020; 81(5):AD19038BR1C. [61] GARCIA-HERMOSO A, CAVERO-REDONDO I, RAMIREZ-VéLEZ R, et al. Muscular Strength as a Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in an Apparently Healthy Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Data From Approximately 2 Million Men and Women. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;99(10):2100-2113. [62] CELIS-MORALES CA, WELSH P, LYALL DM, et al. Associations of grip strength with cardiovascular, respiratory, and cancer outcomes and all cause mortality: prospective cohort study of half a million UK Biobank participants. BMJ. 2018;361:k1651. [63] SOYSAL P, HURST C, DEMURTAS J, et al.Handgrip strength and health outcomes: Umbrella review of systematic reviews with meta-analyses of observational studies. J Sport Health Sci. 2021;10(3):290-295. |
| [1] | Tan Xinfang, Guo Yanxing, Qin Xiaofei, Zhang Binqing, Zhao Dongliang, Pan Kunkun, Li Yuzhuo, Chen Haoyu. Effect of uniaxial fatigue exercise on patellofemoral cartilage injury in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [5] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [6] | Gu Zhengqiu, Xu Fei, Wei Jia, Zou Yongdi, Wang Xiaolu, Li Yongming. Exploratory study on talk test as a measure of intensity in blood flow restriction training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1154-1159. |
| [7] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [8] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [9] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [10] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [12] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [13] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [14] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [15] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

