Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (28): 4539-4545.doi: 10.12307/2022.311
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and regulatory mechanism of microRNA in bone tissue repair around dental implants
Yang Qiongqiong1, Li Ping2, Wang Qian3
- 1Department of Prosthodontics; 2Department of Pathology, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 3Oral Disease Research Key Laboratory of Guizhou Tertiary Institution, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-04-21Accepted:2021-05-26Online:2022-10-08Published:2022-03-23 -
Contact:Li Ping, Master, Professor, Department of Pathology, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China Wang Qian, MD, Associate professor, Oral Disease Research Key Laboratory of Guizhou Tertiary Institution, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Yang Qiongqiong, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Qiongqiong, Li Ping, Wang Qian. Role and regulatory mechanism of microRNA in bone tissue repair around dental implants[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4539-4545.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 miRNAs在骨组织修复中的作用机制 牙种植被认为是治疗患者牙列缺损或牙列缺失的一种良好方法,成功率高达98%。种植体的稳定性是决定种植体植入成功的重要因素之一,对种植体的整体性和种植体即刻负重起重要作用。种植体的稳定性分为2种:初级稳定性和次级稳定性。初级稳定性是一种机械现象,而次级稳定性是骨重建的结果。 研究表明,骨密度、种植体的大小和设计、植入扭矩和手术技术等因素可能会影响种植体的初级稳定性[14-16],而次级稳定性主要取决于种植体固定结构周围的骨化[17]。骨发育是成骨细胞分化增强和破骨细胞分化减弱的过程,一旦失衡,就会影响种植体的稳定性,进而导致牙种植失败的发生,因此,揭示调控成骨细胞和破骨细胞活性的基因具有重要意义。 间充质干细胞是在自我更新的同时还可以分化成骨、软骨和其他组织的多能干细胞,这2个过程都受到遗传和表观遗传机制的调控,研究表明miRNAs在这些过程中也起着关键作用[18]。植入物表面充满相对不成熟的间充质细胞后,建立的局部环境(异体特征、炎症和机械状态等)和全身因素(生长因子水平、细胞因子水平和骨髓间充质干细胞的数量等)与诱导成骨和影响骨整合密切相关。结果是在植入物表面、植入物和骨之间的间隙内以及沿着现有骨的外科边缘可预测地形成骨,见图3。"
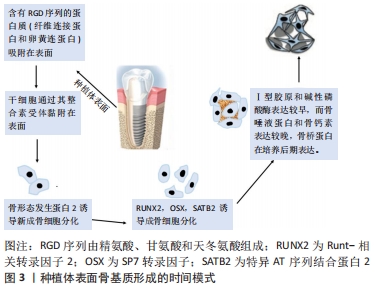
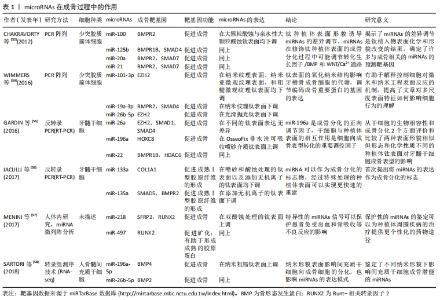
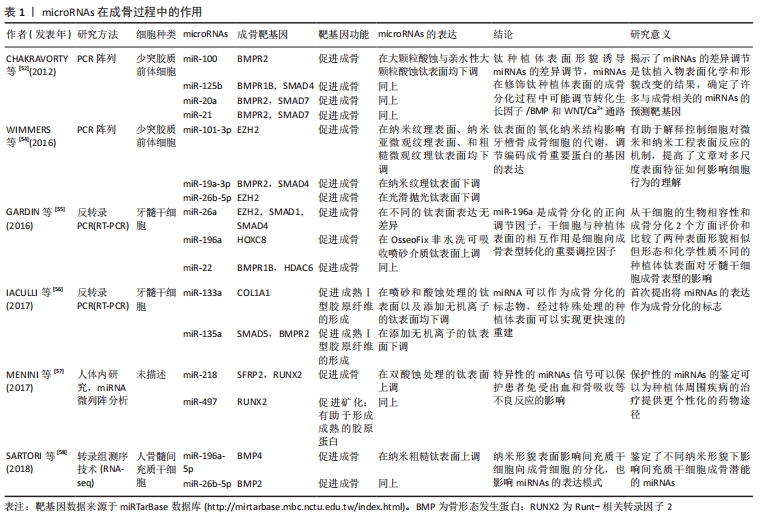
在人体的整个生命周期中,骨吸收与骨形成相耦合,由于成骨细胞和破骨细胞活性的耦合,这种重塑过程也活跃地发生在牙种植体表面。 一般来说,miRNAs通过直接抑制翻译或通过去烯基化和随后降解各种信使RNA靶点来发挥其生物学功能。在调节成骨细胞的增殖和分化时,它们精确地控制许多骨相关基因的激活或抑制。最近,越来越多的转录因子被证实对精确控制骨骼发育有重要贡献,其中Runt-相关转录因子2(RUNX family transcription factor 2,Runx2)及其下游分子Osterix转录因子在前成骨细胞向成熟成骨细胞和骨细胞分化过程中激活一系列基因,是最重要的成骨细胞特异性转录因子。 Runx2是骨限制性转录因子,属于Runt结构域基因家族成员之一,除了限制间充质干细胞向骨细胞、成骨细胞、成软骨细胞的分化,对脂肪细胞的分化也具有抑制作用[19]。Runx2协同增加成骨基因表达,包括骨钙素、骨桥蛋白、Ⅰ型胶原、骨唾液蛋白和碱性磷酸酶[20-22]。此外,Runx2的过度表达能够促进干细胞向成骨细胞分化,并上调细胞外基质蛋白,从而影响骨的形成和发育[23]。miRNAs可以通过直接靶向Runx2基因与Runx2相互作用,也可以影响其他增强或抑制Runx2表达水平的基因。miR-103a是一种机械敏感的miRNA,通过在转录后水平靶向Runx2抑制成骨细胞活性和细胞外基质矿化[24]。miR-204和miR-211通过降低Runx2蛋白水平在成骨过程中发挥负作用,促进人骨髓间充质干细胞的脂肪生成[25]。在最近的人类牙齿干细胞成骨分化模型中,Runx2的表达水平被miR-218下调[26]。CHEN等[27]的实验证实间充质干细胞的成骨分化可被miR-628-3p抑制,Runx2是miR-628-3p的靶标,在其3′UTR端有2个靶结合区域,miR-628-3p的过表达不仅可在信使RNA水平,还可在蛋白水平降低Runx2的表达[27]。 Osterix位于Runx2的下游,含有锌指结构,是Runx2的靶基因。由于其通过结合特定的富含GC的序列来增强几种成骨因子的表达,所以在成骨和胚胎骨骼发育中扮演着必不可少的角色。GAO等[28]报道,miR-143在非小细胞肺癌、乳腺癌等多种肿瘤中作为一种抑制因子,可以直接结合到Osx的3′-UTR,负调控人骨髓间充质干细胞的Osterix的表达。miRNA-637通过直接靶向Osterix来维持脂肪细胞和成骨细胞之间的平衡,miRNA-143和miRNA-145可通过靶向osterix抑制成骨分化[29]。Osterix已被证明是miR-485-5p的直接靶点,在PCR分析和Western blot实验中,进一步证实了Osterix可能受到miR-485-5p的负调控[30]。miR-96成骨细胞分化的调节也是以Osterix为靶基因来进行的,miR-96的过表达对间充质干细胞向成骨分化具有抑制作用[31]。 骨形态发生蛋白/Smads信号通路是间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中的关键信号通路之一,而miRNAs可以调控其中的关键效应分子,进而影响骨重建。骨形态发生蛋白是转化生长因子β超家族的重要成员,是一种有效的成骨剂,通过已知的Smad依赖性骨形态发生蛋白信号通路刺激间充质骨祖细胞向成骨细胞成熟。GAN等[32]的研究显示miRNA-140-5p通过直接结合骨形态发生蛋白2的3’-UTR负调控斑马鱼和人的骨形态发生蛋白2的表达。向斑马鱼胚胎中微量注射miRNA-140-5p可导致胚胎性骨发育异常,通过重新导入骨形态发生蛋白2 mRNA可挽救胚胎性骨发育异,但骨形态发生蛋白2 mRNA不能完全消除miRNA-140-5p诱导的缺陷,对此的一种解释可能是由于miRNA-140-5p也可能调控其他与骨和软骨形成相关的基因。研究表明,miR-542-3p直接靶向骨形态发生蛋白7,抑制其蛋白翻译,从而下调蛋白激酶B和生存素的磷酸化,从而激活半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3,从而导致成骨细胞凋亡。此外,miR-542-3p还可能由于骨形态发生蛋白7水平的降低而阻碍Smad依赖性骨形态发生蛋白信号通路,从而导致小鼠颅骨原代成骨细胞分化受损[33]。MiR-195-5p通过靶向性重组人骨形态发生蛋白受体1A抑制牙周炎患者牙周间充质干细胞成骨。有研究还发现miR-195-5p受机械载荷的调节,参与机械载荷诱导的成骨分化[34]。 研究发现,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路也是间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中的关键信号通路之一。在成骨细胞分化过程中,人间充质干细胞中miR-16-2-3p(也称为miR-16-2*)的表达显著降低,而其过度表达通过直接靶向Wnt5a 信使RNA阻断Wnt信号通路而损害成骨细胞分化[35]。最近发现Wnt5a的表达也受到miR-38的抑制,并且与信使RNA 3′UTR的结合阻碍了间充质干细胞的成骨分化[36]。miR-26a和miR-26b对Wnt信号通路转导的激活主要通过负调控糖原合酶激酶3β的表达来完成,最终促进间充质干细胞向成骨分化[37-38],同时,miR-26对脂肪来源的间充质干细胞的成骨分化也具有负调控作用。 细胞和组织附着在异体表面是骨结合研究的中心焦点,整合素信号对种植体黏附间充质细胞的分化至关重要[39]。整合素家族在体内参与了间充质干细胞成骨分化调控的过程。内源性生长因子、细胞因子和来自细胞外基质的信号,主要通过整合素相互作用。整合素的表达受miRNA调控,miRNAs可通过局灶性黏附激酶改变或阻断整合素信号。整合素使局灶性黏附激酶磷酸化[40],局灶性黏附激酶进一步介导细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2和p38的活化,而p38的活化可以激活Runx2,从而促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨分化。WU等[41]在成骨分化过程中检测了miR-152-3p的表达,发现miR-152-3p的表达随时间的推移而降低。miR-152-3p下调可能通过增强人牙周膜干细胞的活力、增加碱性磷酸酶含量以及通过直接靶向整合素α5上调人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化相关基因的表达来促进人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化。 成骨-血管生成耦联也积极参与了骨组织的修复。骨是一种高度血管化的组织,其发育、重塑和再生过程中,依赖于成骨细胞、内皮细胞及血管生成之间的协同作用。越来越多的证据进一步表明,miRNAs在正常血管生成中既可以充当适应血管生长的正调节因子,也可以作为抵抗血管生成的负调节因子。 一项分析小鼠成肌间充质细胞中miR-9功能的研究证实了miR-9在成骨细胞分化中的作用。通过显著降低DKK1重组蛋白的表达,而不是其mRNA的表达,miR-9刺激碱性磷酸酶活性和成骨细胞矿化,以及一些成骨细胞标记基因的表达,如Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙素和骨唾液蛋白[42]。YANG等[43]的研究显示miR-497-195簇的表达在CD31hiEmcnhi内皮细胞中较高,在内皮细胞中沉默miR-497-195的小鼠显示出较少的CD31hiEmcnhi血管和较低的骨量。而此前RAMASAMY等[44]研究表明这种内皮细胞具有介导血管周围骨祖细胞分化的功能。YAN等[45]研究发现抗mir-138能够改善成骨-血管生成耦联,显著促进内源性骨和血管生成相关基因和蛋白质的表达,在含有antimir-138植体的周围形成大量富含新生血管的新生骨。WU等[46]对犬牙种植体周围炎的研究显示了高浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α诱导骨髓间充质干细胞中miR-27a表达下调,miR-27a可以通过促进早期标志物(Runx2和骨形态发生蛋白2)和晚期标志物(骨钙素和Ⅰ型胶原α1链)的表达来改善体外对骨形成有抑制作用的肿瘤坏死因子α从而正向调节成骨-血管生成偶联。正如作者以前的研究所报道的,miR-155和miR-33a-5p可以分别通过靶向细胞因子信号传导抑制蛋白1和特异AT序列结合蛋白2的表达来调节肿瘤坏死因子α抑制的成骨分化[47]。除了促进成骨外,研究还发现miR-27a可以通过上调血管内皮生长因子和血管生成素1的水平以及导管的形成来表现出明显的血管生成活性。这种成骨和血管生成的耦合有利于骨形成[48],它们可以促进内源性成骨和并血管生成。 机械压力和炎症状态也影响骨诱导,这就是初始稳定性和无感染环境对牙种植的成功至关重要的原因。MiRNAs与调节细胞对机械压力的反应密切相关,特别是miR-146a和最近的miR-33-5p[49-50]。MiRNAs在炎症中的作用主要通过调节其细胞和分子靶点被广泛认识,并且细节不断出现。先天免疫也影响骨愈合的初始阶段,其中几个方面受到miRNA功能控制的不同基因的影响[51]。 从以上研究证据可以看出,miRNAs是成骨过程中强有力的转录后调控因子,这些miRNAs可以直接靶向编码成骨过程中主要信号通路成分的基因来调节骨重建。许多miRNAs通过直接靶向编码成骨因子基因的信使RNA抑制成骨,还有一些miRNAs通过直接靶向编码负性成骨因子基因的信使RNA促进成骨。虽然一些miRNAs已被证明在骨修复中调节成骨分化,但许多初步研究都是描述性的,尚未在与植入物表面相关的研究中得到证实。此外,miRNAs也可以调节成骨-血管生成耦联,阐明控制成骨细胞分化和血管生成的分子机制对于改善骨相关疾病的治疗具有重要意义。 2.2 miRNAs与牙种植体表面形貌 种植体的表面形貌在骨结合中起着很重要的作用,不同形貌的种植体表面,其miRNAs的表达不同,对种植体表面成骨分化机制的影响也不同。大多数钛种植体粗糙表面相较于光滑表面显示出更有利的骨整合。 有一项研究使用人类细胞发育与分化miRNA PCR阵列研究了88个与干细胞分化相关的miRNAs[52],将miRNAs在大颗粒酸蚀和亲水性大颗粒酸蚀钛表面的表达与在光滑钛表面的表达进行比较。对差异调节的miRNAs的统计分析表明,与光滑表面相比,亲水性大颗粒酸蚀和大颗粒酸蚀表面分别有35和32个miRNAs表达下调,其中31个被下调的miRNAs在亲水性大颗粒酸蚀和大颗粒酸蚀中是共同的,miR-215和miR-125b是亲水性大颗粒酸蚀和大颗粒酸蚀表面高度下调的基因之一;相反,亲水性大颗粒酸蚀和大颗粒酸蚀表面分别有10和9个miRNAs表达上调,其中8个上调的miRNAs在亲水性大颗粒酸蚀和大颗粒酸蚀中是共同的。这些结果表明,miRNAs的表达影响着不同形态钛种植体表面成骨分化的遗传机制。此外,这些miRNAs在修饰钛种植体表面的成骨分化过程中可能调节转化生长因子β/骨形态发生蛋白和WNT/Ca2+途径,进一步证实了OLIVARES-NAVARRETE等[53]的发现,即转化生长因子β/骨形态发生蛋白和WNT/Ca2+信号途径在这些表面的成骨细胞成熟中起着重要的控制作用。 WIMMERS等[54]利用新技术制备纳米钛表面,分析了4种不同钛表面-光滑抛光表面、纳米纹理表面、纳米亚微观纹理表面和粗糙微观纹理表面的miRNAs表达。从人骨祖细胞中分离出54个总RNA,将细胞置于培养皿上10 d,制备信使RNA和miRNA的微阵列杂交。对于miRNA微阵列,选择了720个人类miRNA探针,研究鉴定了32个在实验组间差异表达的miRNAs。实时定量PCR分析在实验组中差异表达的6个miRNAs:miR-31-3p、miR-134、miR-136-3p、miR-376C-3p、miR-494和miR-424-5p,它们分别与成骨(miR-31-3p、miR-136-3p、miR-376C-3p和miR-424-5p)、凋亡(miR-494和miR-134)以及细胞生长和增殖(miR-134)相关。此研究结果显示,许多mRNAs和miRNAs可以作为表面修饰的结果被调节,钛表面的氧化纳米结构影响牙槽骨成骨细胞的代谢,调节编码成骨重要蛋白的基因的表达。 为了评估对成脂和成骨分化有影响的9种成熟miRNAs的表达,GARDIN 等[55]将从人牙髓中提取的细胞植入两种类型的牙种植体中,这2种植体的微观形貌相似,但纳米形貌和化学性质不同,实验组为OsseoFix非水洗可吸收喷砂介质,对照组为氧化铝喷砂/酸蚀的种植体。提取总RNA后,获得mRNAs的实时PCR阵列。用RT-PCR方法对所选mirna进行分析,miRNAs表现出与成骨分化相关的差异表达,其中miR-196a表达上调,并在Hox基因表达的调控中起重要作用,作者的结论是,他们的研究结果将证实miR-196a是成骨分化的正向调节因子。 经过特殊处理的钛种植体表面miRNAs的表达对人牙髓干细胞的成骨分化有着一定程度的影响,IACULLI等[56]用喷砂和酸蚀表面的钛盘(对照组)和添加无机离子的实验盘(实验组)来区分已知成骨miRNAs(miR-133a、miR-133b和miR-135a)的表达,用牙髓干细胞进行实时PCR检测miRNA的表达水平。实验结果显示,相比对照组,实验组miR-133a、miR-133b和miR-135a表现出更明显的下调。该研究表明,miRNAs可以作为成骨分化的标志物,分化的诱导严格依赖于钛的存在,而不是支持因子的存在,经过特殊处理的种植体表面可以实现更快速的骨结合。 为了评估经过不同表面处理的种植体周围组织的miRNA表达,MENINI等[57]选定了7例患者(女4例,男3例)在无牙区接受2个相邻的种植体,一种是用商业纯钛(Ⅳ级)制成的经双酸蚀处理的骨灰石植入物(实验组),整个种植体表面都进行了处理;另一种是具有相同双酸蚀表面处理的全骨灰石植入物(对照组),但处理范围没有延伸到冠状面3 mm,随后对7例患者的周围软组织(包括上皮和结缔组织)进行微创取样,并通过miRNA微阵列进行分析。将miRNA分别与测量的临床参数(探查时出血、骨吸收、探查深度、植入物类型和斑块指数)进行比较,并根据其与所比较表面的相关性进行火山图统计分析。研究结果表明:miR-33,miR-134,miR-200和miR-378在细胞增殖、干细胞募集和分化、成骨和炎症中起调节作用;miR-30,miR-197,miR-218,miR-548和miR-613在成骨和软骨内稳态中起调节作用;let-7f,miR-425和miR-548在炎症中起调节作用;miR-517,miR-525,miR-624,miR-3128,miR-3658,miR-3692,miR-3912,miR-3920,miR-4683和miR-4690在炎症、细胞增殖和软骨内稳态中起调节作用。 具有纳米形貌的表面有可能改善骨组织修复的反应,从而缩短时间,同时增加植入物周围的骨形成,改善骨质量较低的区域。SARTORI等[58]在反应离子刻蚀法制备的纳米粗糙玻璃圆盘(实验组)和光滑表面圆盘(对照组)上评估miRNAs的表达模式,用人间充质干细胞检测碱性磷酸酶活性、实时荧光定量PCR和转录组测序技术(RNA-seq)分析miRNA的表达,共发现117个miRNAs差异表达,有45个miRNAs表达上调,72个miRNAs表达下调,其中,一些miRNAs与成骨基因的调控有关,如miR-135b-5p、miR-122-5p、miR-196a-5p、miR-26b-5p和miR-148b-3p。该研究表明,具有纳米粗糙形貌的表面显示出通过表达与成骨基因相关的miRNAs来改善骨组织修复反应的潜力,并且显示出一些miRNAs可以帮助控制骨组织修复过程。以上研究通过不同的方法描述了miRNAs的表达,但没有进一步探讨它们在骨重建中的作用见表1。"

这些研究结果表明,异基因表面的特性可能会影响miRNAs的表达,最终影响来自周围组织的细胞反应,如改变贴壁细胞或邻近细胞的骨诱导基因的表达。微/纳米结构与未经处理的表面或抛光的表面相比,对成骨细胞的增殖和分化具有更好的促进作用,在微纳米尺度上合理设计表面形貌将会是是控制和引导细胞响应的有力工具。了解特定miRNA调节成骨细胞分化的机制,以及可调节其表达的刺激物,对开发新的治疗药物,指导人们的生活方式具有重要意义。为了发现新的miRNAs并了解它们在基因靶点上的复杂分子活性,还需要进一步的研究。 2.3 miRNAs与骨组织修复的应用研究 研制成骨能力强、成骨强度高的生物医用钛种植体是临床的必然要求。WU等[59]采用微弧氧化技术制备钛盘,以提供超亲水表面,并将miRNA脂质复合物添加到孔中进行细胞传递。当用增强成骨活性的miR-29b和对抑制内源性成骨的miR-138有抑制作用的抗miR-138使Ti表面功能化时,在上调成骨表达和增强碱性磷酸酶产生方面,观察到明显刺激间充质干细胞成骨分化,胶原分泌和细胞外基质矿化。SHAO等[60]采用全骨髓贴壁法培养骨髓间充质干细胞,通过非病毒转染制备miR-122修饰的细胞片,并与微弧氧化钛植入物复合构建基因修饰的组织工程植入物,并通过扫描电子显微镜观察其表面形态,植入物的体外成骨活性通过碱性磷酸酶、天狼星红、茜素红染色、聚合酶链反应和蛋白质印迹分析来确定。在成骨诱导的第3天,实验组的Runx2、osterix、骨钙素、胶原蛋白Ⅰ、碱性磷酸酶和骨形态发生蛋白2的相对表达水平分别为2.0,3.1,4.6,3.2,10.5和4.5,分别是空白对照组的2倍。结果表明,miR-122修饰显著增强了板的体外成骨活性,改性后的种植体表面与丰富的细胞和细胞外基质紧密结合,有效促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。该研究认为将微弧氧化钛植入物与miR-122修饰片复合构建基因修饰的组织工程植入体是可行的。LIU等[61]的研究选择了3种不同表面修饰的钛植入物来检查它们对人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨的功能,包括微弧氧化等,所有这些表面修饰的钛植入物都能促进成骨分化。然而,钛种植体的微弧氧化表面显示出更强大的促进成骨分化的作用。 研究结果表明,微弧氧化涂层诱导的成骨分化可能是通过ERK1/2-miR-1827途径实现的。新型miRNA功能化钛种植体能增强成骨活性,有望使临床骨种植体界面的骨结合更加快速和牢固。"

| [1] DE-UGARTE L, SERRA-VINARDELL J, NONELL L, et al. Expression profiling of microRNAs in human bone tissue from postmenopausal women. Hum Cell. 2018;31(1):33-41. [2] CAKOUROS D, GRONTHOS S. Epigenetic regulators of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell lineage determination. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020; 18(5):597-605. [3] LANZILLOTTI C, DE MATTEI M, MAZZIOTTA C, et al. Long non-coding RNAs and microRNAs interplay in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:646032. [4] PETERS LJF, FLOEGE J, BIESSEN EAL, et al. MicroRNAs in chronic kidney disease: four candidates for clinical application. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(18):6547. [5] FRÖHLICH LF. Micrornas at the interface between osteogenesis and angiogenesis as targets for bone regeneration. Cells. 2019;8(2):121. [6] LEE RC, FEINBAUM RL, AMBROS V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843-854. [7] LI Y, ZENG Q, QIU J, et al. MiR-183-5p Promotes proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis in breast cancer cells through negatively regulating four and a half LIM protein 1. J Breast Cancer. 2020;23(4): 355-372. [8] SAHA S, AIN R. MicroRNA regulation of murine trophoblast stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Life Sci Alliance. 2020;3(11): e202000674. [9] EZHILARASAN D. MicroRNA interplay between hepatic stellate cell quiescence and activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;885:173507. [10] LI R, WU H, JIANG H, et al. FBLN5 is targeted by microRNA‑27a‑3p and suppresses tumorigenesis and progression in high‑grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2020;44(5):2143-2151. [11] FENG Q, ZHENG S, ZHENG J. The emerging role of microRNAs in bone remodeling and its therapeutic implications for osteoporosis. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(3):BSR20180453. [12] ZHA JP, WANG X Q, DI J. MiR-920 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone mesenchymal stem cells by targeting HOXA7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):254. [13] FENG L, ZHANG JF, SHI L, et al. MicroRNA-378 suppressed osteogenesis of MSCs and impaired bone formation via inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:1017-1028. [14] MÖHLHENRICH SC, HEUSSEN N, MODABBER A, et al. Influence of bone density, screw size and surgical procedure on orthodontic mini-implant placement - part B: implant stability. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021;50(4):565-572. [15] GÓMEZ-POLO M, ORTEGA R, GÓMEZ-POLO C, et al. Does length, diameter, or bone quality affect primary and secondary stability in self-tapping dental implants? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;74(7): 1344-1353. [16] GEHRKE SA, GUIRADO JLC, BETTACH R, et al. Evaluation of the insertion torque, implant stability quotient and drilled hole quality for different drill design: an in vitro Investigation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29(6):656-662. [17] MEREDITH N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int J Prosthodont. 1998;11(5):491-501. [18] SHU T, HE L, WANG X, et al. Long noncoding RNA UCA1 promotes chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via miRNA-145-5p/SMAD5 and miRNA-124-3p/SMAD4 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;514(1):316-322. [19] KOMORI T. Runx2, an inducer of osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):313-323. [20] DONG M, JIAO G, LIU H, et al. Biological silicon stimulates collagen type 1 and osteocalcin synthesis in human osteoblast-like cells through the BMP-2/Smad/RUNX2 signaling pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016; 173(2):306-315. [21] CHENG F, YANG MM, YANG RH. miRNA-365a-3p promotes the progression of osteoporosis by inhibiting osteogenic differentiation via targeting RUNX2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(18):7766-7774. [22] ZHANG W, WU Y, SHIOZAKI Y, et al. miRNA-133a-5p inhibits the expression of osteoblast differentiation-associated markers by targeting the 3’ UTR of RUNX2. DNA Cell Biol. 2018;37(3):199-209. [23] KIDWAI F, EDWARDS J, ZOU L, et al. Fibrinogen induces RUNX2 activity and osteogenic development from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells. 2016;34(8):2079-2089. [24] ZUO B, ZHU J, LI J, et al. microRNA-103a functions as a mechanosensitive microRNA to inhibit bone formation through targeting Runx2. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(2):330-345. [25] ITO K, TOMOKI R, OGURA N, et al. MicroRNA-204 regulates osteogenic induction in dental follicle cells. J Dent Sci. 2020;15(4):457-465. [26] MELNIK S, GABLER J, DREHER SI, et al. MiR-218 affects hypertrophic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells during chondrogenesis via targeting RUNX2, MEF2C, and COL10A1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):532. [27] CHEN H, JI X, SHE F, et al. miR-628-3p regulates osteoblast differentiation by targeting RUNX2: Possible role in atrophic non-union. Int J Mol Med. 2017;39(2):279-286. [28] GAO Y, XIAO F, WANG C, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes osterix expression to regulate osteogenic differentiation by targeting miRNA-143 in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(8):6986-6996. [29] WANG C, LIAO H, CAO Z. Role of osterix and microRNAs in bone formation and tooth development. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:2934-2942. [30] ZHANG SY, GAO F, PENG CG, et al. miR-485-5p promotes osteoporosis via targeting Osterix. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(15):4792-4799. [31] LIU H, LIU Q, WU XP, et al. MiR-96 regulates bone metabolism by targeting osterix. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2018;45(6):602-613. [32] GAN S, HUANG Z, LIU N, et al. MicroRNA-140-5p impairs zebrafish embryonic bone development via targeting BMP-2. FEBS Lett. 2016; 590(10):1438-1446. [33] KUREEL J, DIXIT M, TYAGI AM, et al. miR-542-3p suppresses osteoblast cell proliferation and differentiation, targets BMP-7 signaling and inhibits bone formation. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(2):e1050. [34] CHANG M, LIN H, FU H, et al. MicroRNA-195-5p regulates osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells under mechanical loading. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(12):3762-3774. [35] DUAN L, ZHAO H, XIONG Y, et al. miR-16-2* Interferes with WNT5A to regulate osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(3):1087-1102. [36] LONG H, ZHU Y, LIN Z, et al. miR-381 modulates human bone mesenchymal stromal cells (BMSCs) osteogenesis via suppressing Wnt signaling pathway during atrophic nonunion development. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(7):470. [37] SU X, LIAO L, SHUAI Y, et al. MiR-26a functions oppositely in osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and ADSCs depending on distinct activation and roles of Wnt and BMP signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015; 6(8):e1851. [38] HU H, ZHAO C, ZHANG P, et al. miR-26b modulates OA induced BMSC osteogenesis through regulating GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;107:158-164. [39] OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, HYZY SL, BERG ME, et al. Osteoblast lineage cells can discriminate microscale topographic features on titanium-aluminum-vanadium surfaces. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014;42(12):2551-2561. [40] VISAVADIYA N P, KEASEY M P, RAZSKAZOVSKIY V, et al. Erratum to: integrin-FAK signaling rapidly and potently promotes mitochondrial function through STAT3. Cell Commun Signal. 2017;15(1):11. [41] WU D, MA L. Downregulating microRNA-152-3p promotes the viability and osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via targeting integrin alpha 5. Arch Oral Biol. 2020;120:104930. [42] LIU X, XU H, KOU J, et al. MiR-9 promotes osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting DKK1 gene expression. Mol Biol Rep. 2016;43(9):939-946. [43] YANG M, LI CJ, SUN X, et al. MiR-497-195 cluster regulates angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis by maintaining endothelial Notch and HIF-1α activity. Nat Commun. 2017;8:16003. [44] RAMASAMY SK, KUSUMBE AP, WANG L, et al. Endothelial Notch activity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone. Nature. 2014;507 (7492):376-380. [45] YAN J, CHANG B, HU X, et al. Titanium implant functionalized with antimiR-138 delivered cell sheet for enhanced peri-implant bone formation and vascularization. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018; 89:52-64. [46] WU X, GU Q, CHEN X, et al. MiR-27a targets DKK2 and SFRP1 to promote reosseointegration in the regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(1):123-134. [47] WU T, XIE M, WANG X, et al. miR-155 modulates TNF-α-inhibited osteogenic differentiation by targeting SOCS1 expression. Bone. 2012; 51(3):498-505. [48] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014; 507(7492):323-328. [49] HUANG Y, CRAWFORD M, HIGUITA-CASTRO N, et al. miR-146a regulates mechanotransduction and pressure-induced inflammation in small airway epithelium. FASEB J. 2012;26(8):3351-3364. [50] WANG H, SUN Z, WANG Y, et al. miR-33-5p, a novel mechano-sensitive microRNA promotes osteoblast differentiation by targeting Hmga2. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23170. [51] NAQVI AR, ZHONG S, DANG H, et al. Expression profiling of LPS responsive miRNA in primary human macrophages. J Microb Biochem Technol. 2016;8(2):136-143. [52] CHAKRAVORTY N, IVANOVSKI S, PRASADAM I, et al. The microRNA expression signature on modified titanium implant surfaces influences genetic mechanisms leading to osteogenic differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(9):3516-3523. [53] OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, HYZY SL, HUTTON DL, et al. Role of non-canonical Wnt signaling in osteoblast maturation on microstructured titanium surfaces. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(6):2740-2750. [54] WIMMERS FERREIRA MR, RODRIGO FERNANDES R, FREIRE ASSIS A, et al. Oxidative nanopatterning of titanium surface influences mRNA and microRNA expression in human alveolar bone osteoblastic cells. Int J Biomater. 2016;2016:9169371. [55] GARDIN C, FERRONI L, PIATTELLI A, et al. Non-washed resorbable blasting media (NWRBM) on Titanium Surfaces could Enhance Osteogenic Properties of MSCs through increase of miRNA-196a and VCAM1. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2016;12(5):543-552. [56] IACULLI F, DI FILIPPO ES, PIATTELLI A, et al. Dental pulp stem cells grown on dental implant titanium surfaces: an in vitro evaluation of differentiation and microRNAs expression. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(5):953-965. [57] MENINI M, DELLEPIANE E, BALDI D, et al. Microarray expression in peri-implant tissue next to different titanium implant surfaces predicts clinical outcomes: a split-mouth study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017; 28(9):e121-e134. [58] SARTORI EM, MAGRO-FILHO O, SILVEIRA MENDONÇA DB, et al. Modulation of micro RNA expression and osteoblast differentiation by nanotopography. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(2):269-280. [59] WU K, SONG W, ZHAO L, et al. MicroRNA functionalized microporous titanium oxide surface by lyophilization with enhanced osteogenic activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(7):2733-2744. [60] SHAO D, WANG C, SUN Y, et al. Effects of oral implants with miR‑122‑modified cell sheets on rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(1):1537-1544. [61] LIU L, ZENG D, CHEN Y, et al. Microarc oxidation surface of titanium implants promote osteogenic differentiation by activating ERK1/2-miR-1827-Osterix. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020;56(4):296-306. |
| [1] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [2] | Wang Qin, Shen Cheng, Liao Jing, Yang Ye. Dapagliflozin improves renal injury in diabetic nephropathy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1216-1222. |
| [3] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [4] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [5] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [7] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [8] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [9] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [10] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [11] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [12] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | Hu Weifan, Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Sun Yang, Zhao Fengchao. Overexpression of miR-25 downregulates titanium particle-induced osteoclast differentiation through the NFATc1 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 682-687. |
| [14] | Xu Jing, Yan Yongmin, Cai Mengjie . miR-373 inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by downregulating transforming growth factor beta type II receptor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 756-761. |
| [15] | Huang Chuanjun, Zou Yu, Zhou Xiaoting, Zhu Yangqing, Qian Wei, Zhang Wei, Liu Xing. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in RADA16-BDNF hydrogel promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||