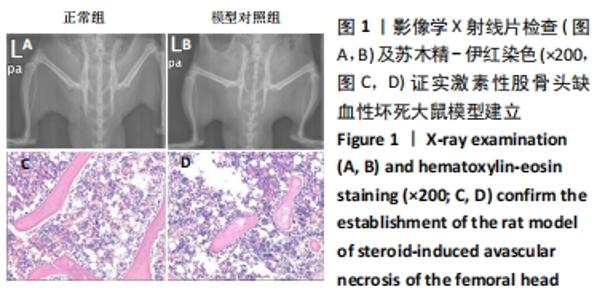
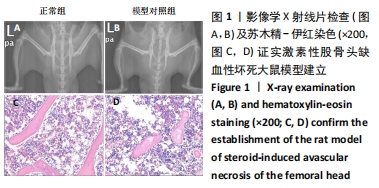
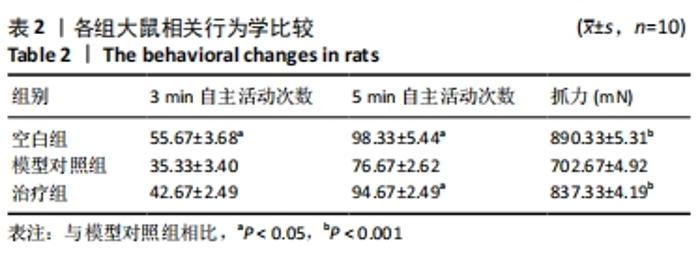
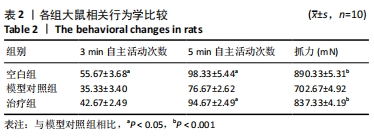
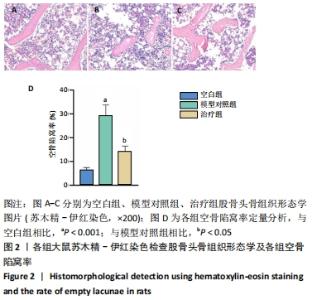
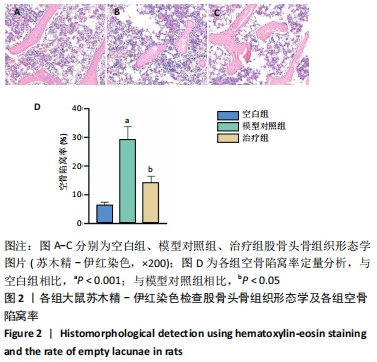
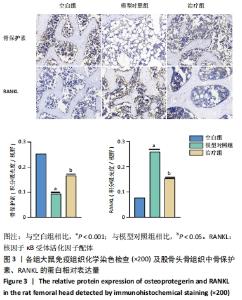
[1] FANG S, LI Y, CHEN P. Osteogenic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:45-55.
[2] XU HH, LI SM, FANG L, et al. Platelet-rich plasma promotes bone formation, restrains adipogenesis and accelerates vascularization to relieve steroids-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Platelets. 2021;32(7):950-959.
[3] SADILE F, BERNASCONI A, RUSSO S, et al. Core decompression versus other joint preserving treatments for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a meta-analysis. Br Med Bull. 2016;118(1):33-49.
[4] WANG A, REN M, WANG J. The pathogenesis of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A systematic review of the literature. Gene. 2018;671:103-109.
[5] 范思奇, 曾平, 农焦, 等. 通络生骨胶囊含药血清对破骨细胞及Toll样受体4/核因子κB信号通路的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(14):2155-2160.
[6] 张玲莉, 陈炳霖, 邹军. 运动影响骨转换:促进或抑制骨细胞/破骨细胞的发育和活性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(42):6838-6843.
[7] WANG C, MENG H, WANG Y, et al. Analysis of early stage osteonecrosis of the human femoral head and the mechanism of femoral head collapse. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14(2):156-164.
[8] 高彦淳, 冯勇, 张长青. 激素性股骨头坏死发生机制的研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2018,39(4):231-234.
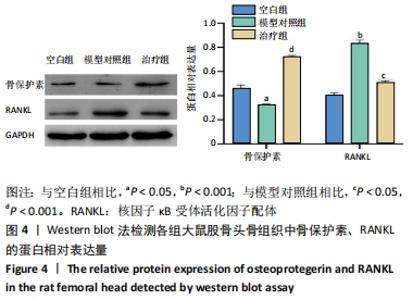
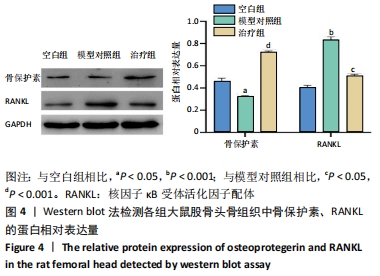
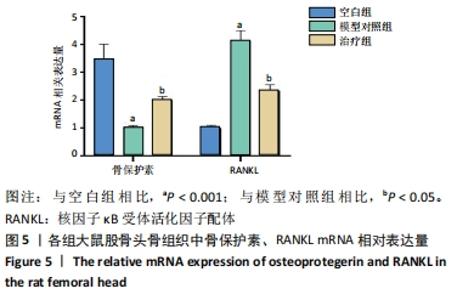
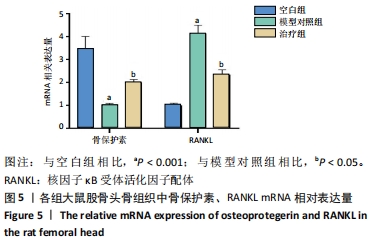
[9] 刘建军, 陈欣, 张兵刚, 等. 生血补髓方对激素性股骨头缺血性坏死模型大鼠血清OPG、RANK、RANKL含量的影响[J]. 甘肃中医药大学学报,2020,37(2):30-34.
[10] KWAN TS, PELLETIER JP, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. The differential expression of osteoprotegerin (OPG) and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL) in human osteoarthritic subchondral bone osteoblasts is an indicator of the metabolic state of these disease cells. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008;26(2):295-304.
[11] 孙光华, 廖瑛, 廖源, 等. 电针对去卵巢大鼠关节软骨退变及软骨下骨骨质疏松的影响[J]. 针刺研究,2018,43(12):781-787.
[12] 马遇原, 刘娣, 刘君伟, 等. 温针灸对膝关节骨性关节炎软骨下骨中OPG、RANKL蛋白表达的影响[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报,2020, 42(7):683-687.
[13] 陈志礼, 卢锦钊, 罗伟华, 等. 内热针联合偏振光对腰椎间盘突出症患者腰腿疼痛及血清MMP-3、MMP-7的影响[J]. 广东医科大学学报,2021,39(2):164-166.
[14] 付彪斌. 内热针软组织松解术治疗肩周炎临床观察[J]. 中医临床研究,2020,12(23):101-104.
[15] 刘武, 戴甫成, 张维, 等. 内热针联合体外冲击波对腰背肌筋膜炎疗效及血清SP和TNF-α水平的影响[J]. 系统医学,2020,5(17):34-37.
[16] 董俊球, 胡云, 刘名锋. 内热针治疗股骨头缺血性坏死48例[J]. 实用中医药杂志,2017,33(8):969-970.
[17] 黑晓燕, 许建峰, 朱仕强, 等. 内热针疗法对兔膝骨性关节炎软骨下骨中骨保护素及核因子κB受体活化因子表达的影响[J]. 针刺研究,2021,44(8):1-10.
[18] 莫湘涛, 董正, 朱俊博, 等. 温针灸配合股骨头坏死愈胶囊对中期股骨头缺血性坏死患者髋关节功能及影像学指标的影响[J]. 上海针灸杂志,2020,39(1):70-74.
[19] 郭胜男. 温针灸治疗早期股骨头坏死30例临床疗效观察[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2015.
[20] YUE J, WAN F, ZHANG Q, et al. Effect of glucocorticoids on miRNA expression spectrum of rat femoral head microcirculation endothelial cells. Gene. 2018;651:126-133.
[21] XU J, GONG H, LU S, et al. Animal models of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head-a comprehensive research review up to 2018. Int Orthop. 2018;42(7):1729-1737.
[22] CHANGJUN C, DONGHAI L, XIN Z, et al. Mid- to long-term results of modified non-vascularized allogeneic fibula grafting combined with core decompression and bone grafting for early femoral head necrosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):116.
[23] 曹华, 郑刚, 杨茜. 内热针配合髋关节灌注治疗髋关节滑膜炎效果观察[J]. 中外医学研究,2019,17(15):11-13.
[24] ZHOU M, XI J, CHENG Y, et al. Reprogrammed mesenchymal stem cells derived from iPSCs promote bone repair in steroid-associated osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):175.
[25] 梁锦锋, 单乐天, 李鸿文, 等. 平菇提取物对激素性股骨头坏死大鼠模型的药效作用研究[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报,2014,38(5):622-625.
[26] JIA YB, JIANG DM, REN YZ, et al. Inhibitory effects of vitamin E on osteocyte apoptosis and DNA oxidative damage in bone marrow hemopoietic cells at early stage of steroid-induced femoral head necrosis. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(4):1585-1592.
[27] PENG WX, YE C, DONG WT, et al. MicroRNA-34a alleviates steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head by targeting Tgif2 through OPG/RANK/RANKL signaling pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017; 242(12):1234-1243.
[28] 季德江, 冶尕西, 关淑婷, 等. 内热针在腰椎间盘突出症治疗中的应用探讨[J]. 湖北中医杂志,2019,41(8):40-42.
[29] 朱仕强, 许建峰, 黑晓燕, 等. 内热针干预膝骨性关节炎兔软骨下骨Ⅰ型胶原、基质金属蛋白酶3和骨桥蛋白的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(17):2636-2642.
[30] 万超, 朱小虎, 程宇核, 等. 内热针疗法对膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨细胞凋亡及Caspase-3和Caspase-9表达的影响[J]. 中国针灸,2019, 39(4):409-416.
[31] 温莎, 高谦, 范娇, 等. 内热针对家兔膝关节周围慢性软组织损伤肌筋膜血流速度的影响[J]. 宁夏医学杂志,2019,41(9):773-775.
[32] 张金晨, 林瑞珠, 田心保, 等. 内热针疗法对兔膝关节骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中华保健医学杂志,2020,22(3):119-121.
[33] 黄丽萍, 王刚, 高谦, 等. 内热针治疗早期股骨头缺血性坏死的临床疗效观察[J]. 解放军医学院学报,2020,41(12):1202-1205.
[34] PENG Y, LIN Y, HOU X, et al. Effect of mild hypothermia on behaviors of rats with intracerebral hemorrhage and the possible mechanism. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020;40(9):1359-1364.
[35] 赵鑫, 陈长军, 李东海, 等. 间隙连接蛋白-43调控骨组织细胞间平衡在激素性股骨头坏死中的研究进展[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2021,46(3):257-262.
[36] YASUDA H. Discovery of the RANKL/RANK/OPG system. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):2-11.
[37] LEMS WF. Fracture risk estimation may facilitate the treatment gap in osteoporosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(11):1943-1945.
[38] 赵希云, 张晓刚, 曹林忠, 等. 从脾肾论治骨质疏松症的OPG/RANK/RANKL信号调控机制[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(9): 1206-1210.
[39] 吉万波, 刘冠虹, 刘锦涛, 等. 骨重塑失衡与激素性股骨头坏死关系的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2013,19(24):4467-4470.
[40] SONG HM, WEI YC, LI N, et al. Effects of Wenyangbushen formula on the expression of VEGF, OPG, RANK and RANKL in rabbits with steroid-induced femoral head avascular necrosis. Mol Med Rep. 2015; 12(6):8155-8161.
[41] ZHAO JJ, WU ZF, WANG L, et al. MicroRNA-145 Mediates Steroid-Induced Necrosis of the Femoral Head by Targeting the OPG/RANK/RANKL Signaling Pathway. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e159805.
[42] 宋红梅, 魏迎辰, 李楠, 等. 温阳补肾方对兔激素性股骨头坏死组织中骨保护素和核因子-κB受体活化因子及其配体mRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(2):178-183. |