Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (17): 2782-2788.doi: 10.12307/2022.551
Effect of estrogen on bone remodeling and root resorption during orthodontics
Cheng Yi, Liu Ting, Guo Yujing, Sun Xiaotong, Bi Lan, Zhang Ronghe
- Department of Orthodontics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2021-04-28Revised:2021-05-11Accepted:2021-06-23Online:2022-06-18Published:2021-12-27 -
Contact:Zhang Ronghe, Master, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthodontics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Cheng Yi, Master candidate, Department of Orthodontics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cheng Yi, Liu Ting, Guo Yujing, Sun Xiaotong, Bi Lan, Zhang Ronghe. Effect of estrogen on bone remodeling and root resorption during orthodontics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2782-2788.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
2.1 雌激素对正畸牙移动的作用 牙周膜连接类牙骨质和牙槽骨,是一层机械敏感的纤维软组织。牙周组织将正畸力从牙齿传递到牙槽骨,并为骨改建提供稳定的微环境。机械力作用下,细胞因子在张力侧和压力侧不均匀释放,牙槽骨发生骨改建[1],从而正畸牙齿发生移动。 正畸牙移动与骨改建有关,因此推测所有影响骨改建和雌激素变化的因素都可能影响正畸牙移动。在大鼠模型中,牙齿移动可以分成3个阶段:第1阶段,初始牙齿移动;第2阶段,延迟牙齿移动;第3阶段,牙齿移动的线性增加。雌激素水平发生改变时,骨改建效果也出现差异,而且机械力下牙齿移动速率也出现变化。有研究显示,对大鼠上颌第一磨牙28 d持续加力,发现去卵巢组牙齿移动速度明显快于对照组[2],表明去卵巢后大鼠雌激素减少,骨改建增加,正畸力作用下牙齿移动速率增加[3]。周翊飞等[4]研究并对比灌服避孕药与等量生理盐水对实验大鼠的作用,发现大鼠服用避孕药后雌激素增加,机械力作用下骨改建速率下降;实验表明雌激素水平上升,正畸牙移动速率减慢。有研究通过自身对照的方法对12例14-18岁月经初潮的女性患者进行分析发现,患者在月经周期(雌激素水平低)加载正畸力后尖牙向远中移动距离大于排卵期(雌激素水平高)[5]。不同生理周期雌激素分泌量差异较大,正畸牙移动速率也会发生相应改变。以上文献说明雌激素的含量与骨代谢及正畸牙移动速率呈负相关关系。 在临床正畸治疗过程中,正畸医生应该获得患者的完整病历信息,对于不同生理周期或者其他因素引起雌激素水平波动的女性患者,应当考虑正畸牙移动速率异常的情况,制定更合理的治疗计划并加载合适的正畸力,这样可以提高矫治效率且避免副反应,达到更好的矫治效果。 2.2 雌激素对骨改建的作用"
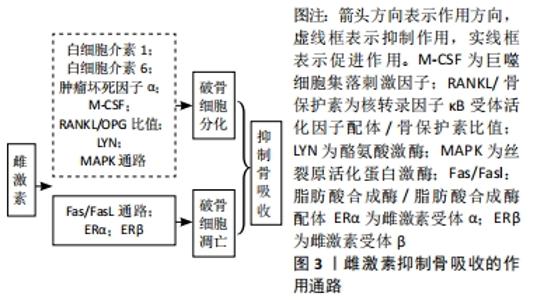
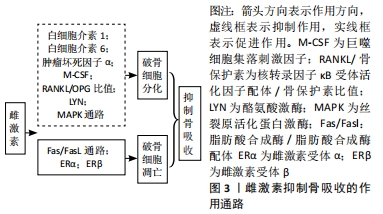
2.2.1 雌激素抑制骨吸收 破骨细胞是唯一的骨吸收细胞。骨吸收作用能启动旧骨基质的清除和新骨的重塑,使骨重塑周期保持稳态化。在绝经期雌激素缺乏会导致骨密度下降,组织学染色显示牙槽骨密度降低、破骨细胞数量减少,若补充雌激素上述情况则可减轻。 雌激素可抑制破骨细胞的分化。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator for nuclear factor kappa B ligand,RANKL)是破骨细胞分化的必需因子。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子与巨噬细胞集落刺激因子受体结合活化磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,PI3K)和生长因子受体结合蛋白2基因,进一步诱导蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,AKT)和细胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular regulated protein kinase,ERK)传导通路,促进破骨细胞分化[6]。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子可诱导骨髓表达核转录因子κB受体活化因子(receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand,RANK)受体,RANK与RANKL相互作用后促进破骨细胞分化。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子还可以激活蛋白激酶B、原癌基因及细胞外信号调节激酶传导通路并与RANKL相互作用,促进破骨细胞分化[7]。雌激素则通过抑制巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的表达,进而抑制破骨细胞分化。 RANKL-RANK-骨保护素传导通路是促进增殖、分化和存活的主要调节系统[8]。研究显示,由牙周膜细胞和骨衬细胞产生的RANKL为破骨细胞生成和正畸牙移动提供了动力[9]。在炎症条件下破骨细胞分化也依赖RANKL[10-11],因此RANKL是特异性诱导破骨细胞生成的重要因子。另外,骨保护素对RANKL功能的调节作用至关重要。最近动物实验研究表明,成骨细胞是骨改建中骨保护素的主要来源[12-13]。骨保护素是一种诱饵受体,能与RANKL结合,抑制RANK与RANKL的相互作用,调控破骨细胞的增殖、分化与凋亡,影响其生理功能。有实验研究证实,RANKL及骨保护素在介导破骨细胞的分化及生成有关键作用,为骨吸收疾病的靶向治疗提供依据[14-15]。有实验证明,压力增加成骨细胞和RANKL表达,降低了骨保护素的表达,而张力则相反[1]。RANKL/骨保护素升高可增加破骨细胞的分化,也解释了机械力作用下压力侧比张力侧骨组织破坏严重。雌激素上调骨保护素及下调RANKL的表达,从而抑制破骨细胞的分化。 雌激素还可以通过减少牙槽骨及牙周组织中分泌的白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6等因子,进而抑制破骨细胞的分化。白细胞介素1是激活破骨细胞并增加其分化的重要因子。在合适的微环境下,白细胞介素1可能通过激活小眼球转录因子诱导破骨细胞分化[16]。肿瘤坏死因子α在激活下游丝裂原活化蛋白激酶磷酸化后直接影响骨细胞中RANKL的活性并增加破骨细胞的分化[17]。WU等[18]明确了肿瘤坏死因子α促进RANKL诱导破骨细胞形成的机制,即肿瘤坏死因子α可以经由PI3K/AKT信号通路上调外周血B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白的表达,促进RANKL介导的破骨细胞生成。这也为治疗炎症性骨疾病指明了方向。利用嵌合小鼠经12 d正畸牙移动实验后[19],结果显示正畸牙移动过程中,肿瘤坏死因子α可以促进破骨细胞形成,增加骨吸收。此外,在此过程中肿瘤坏死因子α的表达可能较低,肿瘤坏死因子α反应性基质细胞促进肿瘤坏死因子α形成,这对破骨细胞的形成起重要作用。白细胞介素6激活酪氨酸蛋白激酶2(JAK2)/信号转导与转录激活因子(STAT3)传导通路诱导RANKL表达,促进破骨细胞分化[20]。细胞培养并染色检测破骨细胞的形成,并探讨应用酪氨酸蛋白激酶2特异性抑制剂(AG490)阻碍骨细胞JAK2/STAT3通路。结果显示,白细胞介素6可以通过激活酪氨酸蛋白激酶2和RANKL促进破骨细胞分化[21]。白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α及白细胞介素6在破骨细胞分化中的作用也进一步说明RANK/RANKL/骨保护素调控系统是在诱导骨吸收过程中有关键作用。 此外,绝经后雌激素由于破骨细胞过度的分化和活性而加速骨质流失,增加了绝经后妇女患骨质疏松症的概率。有研究发现雌激素对人破骨细胞分化蛋白质组的影响表现为上调酪氨酸激酶(LYN),其具有抗破骨作用。实验研究显示,与对照组相比,酪氨酸激酶基因敲除组中雌激素抑制破骨细胞作用,提示酪氨酸激酶是雌激素抑制破骨细胞存活、分化及功能影响的关键递质[22],这也为骨质疏松的进一步研究提供支持。近年来有些研究通过药物影响雌激素水平,进而调节破骨细胞功能以减少骨质疏松的骨丢失。如款冬酮可以抑制破骨细胞分化和促进破骨细胞凋亡[23]。 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路激活后可以上调核转录因子κB,诱导肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素β、白细胞介素6、诱导型一氧化氮合酶和环氧化酶2等表达,这是正畸牙移动的关键步骤[24]。现已发现3种主要丝裂原活化蛋白激酶传导通路:p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路、Jun氨基端激酶通路和细胞外信号调节激酶通路,其中前两者是应激活性蛋白激酶[25]。雌激素可以经多个位点参与丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路。如雌激素水平下降,过量的肿瘤坏死因子α及白细胞介素1可以激活p36α丝裂原活化蛋白激酶传导通路,增强RANKL和白细胞介素6的表达,从而促进破骨细胞的分化[26]。 雌激素促进破骨细胞的凋亡:雌激素不仅可以抑制破骨细胞的分化,还可以促进破骨细胞凋亡[27]。已有实验表明,雌激素通过脂肪酸合成酶/脂肪酸合成酶配体传导通路增加破骨细胞受体相互作用蛋白140的表达,促进破骨细胞的凋亡[28]。通过微阵列分析,KIM等[29]阐明了雌激素与雌激素受体α结合后减少了“氧化磷酸”和线粒体复合物Ⅰ基因的表达,减弱呼吸作用并减少破骨细胞数目,促进初期破骨细胞前体细胞的线粒体凋亡,加快破骨细胞凋亡。另外雌激素与雌激素受体β结合后可以作用于破骨细胞,诱导其凋亡[30],见图3,表1。"
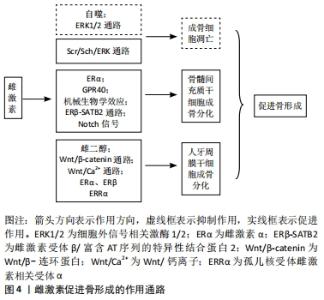
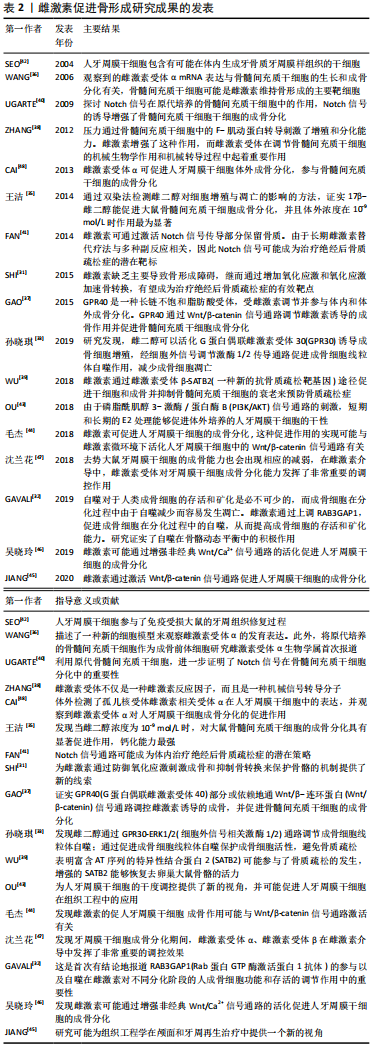
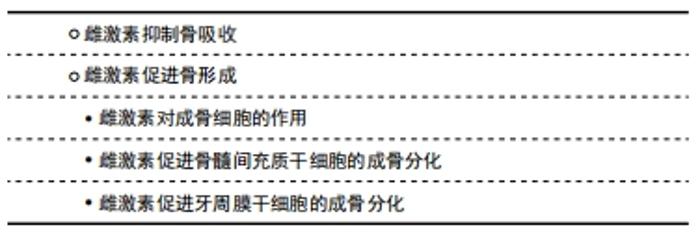
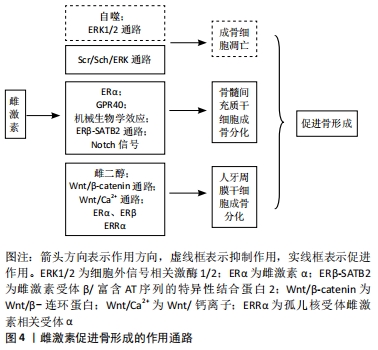
2.2.2 雌激素促进骨形成 雌激素对成骨细胞的作用:雌激素可以通过促进生成促进转化生长因子β、胰岛素样生长因子Ⅰ、骨形态发生蛋白6等因子,促进间充质细胞向成骨细胞分化。雌激素缺乏导致的成骨功能受损和骨改建,氧化应激增强此作用。有研究指出,雌激素缺乏导致小鼠骨组织氧化应激,抗氧化酶水平和活性降低,而抗氧化剂N-乙酰-L-半胱氨酸治疗改变去卵巢引起的成骨和骨转换异常[31]。结果表明,雌激素缺乏阻碍骨形成,而通过增加氧化应激加速骨转换,提示雌激素抑制氧化应激作用,增加成骨细胞活性。 GAVALI等[32]研究证实,在成骨细胞分化过程中,雌激素上调Rab蛋白GTP酶激活蛋白1抗体后可促进自噬减少成骨细胞的凋亡,延长其生存时间。还有研究发现,雌二醇可以活化G蛋白偶联雌激素受体30诱导成骨细胞增殖,经细胞外信号调节激酶1/2传导通路促进成骨细胞线粒体自噬作用,减少成骨细胞凋亡[33]。此外,雌激素激活Src/Shc/ERK传导通路,下调Jun氨基端激酶,进而改变转录因子活性,抑制成骨细胞凋亡,延长成骨细胞寿命。成骨细胞增加,骨量增多,正畸牙齿移动速率下降。 雌激素促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化:骨髓间充质干细胞是有较强自我更新和多向分化潜能的间充质干细胞,来源广泛,是组织工程技术理想的种子细胞,其骨向分化潜能可实现牙周组织再生,在人类医学中的应用前景广阔[34]。有动物实验证实,10-9 mol/L的雌激素促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的能力最强[35]。WANG等[36]也观察到雌激素受体α mRNA的表达与进行性骨髓间充质干细胞的生成和成骨分化有关,骨髓间充质干细胞可能是雌激素维持骨形成的主要靶细胞。 G蛋白偶联受体40受雌激素调节并介导体内体外成骨分化。有研究发现,G蛋白偶联受体40可能经Wnt/β-catenin传导通路作为雌激素诱导成骨分化的内源性启动子发挥作用[37]。机械刺激与雌激素是促进骨髓间充质干细胞活性的两个关键因素。有实验表明,机械力通过F-肌动蛋白转导促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和分化,雌激素增强了这种作用,说明雌激素在调控骨髓间充质干细胞的机械生物学效应和机械转导过程中起重要作用[38]。有研究表明,雌激素通过诱导雌激素受体β与富含AT序列的特异性结合蛋白2(Special AT-rich sequence binding protein 2,SATB2)基因-488位的雌激素反应元件结合来介导SATB2的上调,而SATB2在调节骨髓间充质干细胞的干性、自噬和抗衰老方面具有潜在的作用[39]。结果表明,雌激素可能经由雌激素受体β-SATB2传导通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的干性和成骨,并减少衰老,抑制骨质流失。Notch信号可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和分化[40]。体外细胞实验发现,雌激素通过增加Jagged1的表达增强骨髓间充质干细胞中的Notch信号,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和分化[41],提示雌激素可以通过激活Notch信号增加骨量,Notch信号也为绝经后骨质疏松症研究打开新思路。因此,以上文献说明雌激素可以通过多种途径激活并调控骨髓间充质干细胞的干性、增殖及分化,但具体的机制尚不明确,仍需进一步研究。 雌激素促进牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化:牙周膜干细胞由SEO等[42]于2004年首次从人类牙周组织中分离,与骨髓和牙髓间充质干细胞有类似的生物学特征,并维持着牙周组织的动态平衡,是目前牙周组织再生最具潜力的种子细胞。 牙周膜干细胞体外长期培养过程中,其干性作用逐渐下降,并伴随增殖、分化能力下降,凋亡增加,雌二醇能促进人牙周膜干细胞增殖,改变细胞周期,增加其干性相关基因表达,促进其成骨分化。而且,在此过程中PI3K/AKT传导通路可能有促进作用。因此,雌二醇的此种作用可能会增加牙周膜干细胞在组织工程中的应用[43]。 Wnt/β-catenin传导通路在调控胚胎发育和细胞增殖以及骨形成中都至关重要。国内国外研究均证实,在微环境下,雌激素可激活人牙周膜干细胞中Wnt/β-catenin传导通路,促进人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化[44-45]。有研究显示,加入雌激素后人牙周膜干细胞成骨相关指标表达量上调,而抑制经典Wnt/Ca2+通路后相关指标表达量不变[46],推测雌激素可能激活非经典Wnt/Ca2+传导通路,进而促进人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化。提示雌激素可以活化经典及非经典的Wnt/Ca2+传导通路并促进人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化,但二者间的作用机制尚不明确,仍需进一步研究。大量研究证实,雌激素受体α及雌激素受体β可以影响牙周膜干细胞成骨分化过程。沈兰花等[47]研究并对比卵巢切除组与假手术组中大鼠的成骨能力(体质量、骨密度等),发现雌性激素减少后牙周膜干细胞成骨能力下降并且雌激素受体在其中也起到重要的调节作用。CAI等[48]通过分离人牙周膜干细胞证实了其多向分化的能力。研究显示在人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的后期阶段,雌激素相关受体α的表达明显增加,此外以雌激素相关受体α为靶点的重组慢病毒介导的miRNA转染显著抑制碱性磷酸酶的活性、矿化能力和成骨相关基因的mRNA表达,表明雌激素相关受体α可促进人牙周膜干细胞体外成骨分化。以上文献说明雌性激素可以增加人牙周膜干细胞干性并通过多种通路及媒介促进成骨分化,但他们之间的相互作用尚需研究,见图4,表2。"
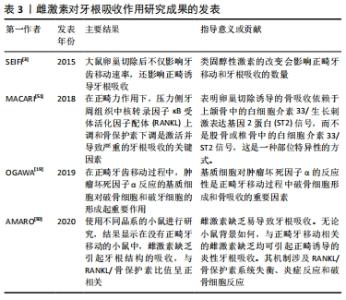
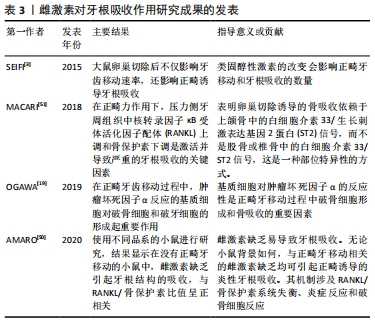
2.3 雌激素对正畸诱导牙根吸收的影响及机制 机械力作用过程中,受压侧的牙周膜细胞坏死,透明带形成,牙停止运动。在清除透明带的过程中,单核巨噬细胞和多核巨细胞可能会破坏由成牙骨质细胞组成的牙根外层,甚至牙本质也可能受到影响。牙本质的吸收是不可逆转的,并且对牙齿结构破坏严重。 有研究表明,雌激素缺乏及其对骨代谢的影响会影响牙齿移动和牙根吸收的速度。正畸牙移动增加了牙根吸收的风险,也是正畸中的常见副反应[49]。正畸牙移动诱导牙根吸收被认为是正畸诊疗中的多因素并发症,如力的大小与方向、个体差异和激素水平等。 雌激素有抑制牙根吸收及促进牙根再生的能力,这种能力可以很好地保护正畸治疗中的牙根。据报道,雌激素缺乏后,破牙骨质细胞增加牙根吸收的速度及范围。破牙骨质细胞具有与破骨细胞相似的生物学特征,在正畸牙移动过程中产生因子,如RANKL、白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子等可以促进破牙骨质细胞的分化和激活,从而诱导牙根吸收。因此,雌激素的骨保护作用与抑制破牙因子、促进破牙细胞分化有关。例如在正畸治疗中,力作用下肿瘤坏死因子α诱导破牙细胞形成,导致牙根破坏[19]。SIRISOONTORN等[2]在卵巢切除组与未切除组大鼠的磨牙加力实验中,去卵巢组近中根部可见宽而浅的吸收凹坑;在远中根部可观察到较深的吸收凹坑,分布在牙根的颈部、中部和根尖的1/3处,说明在压力作用下,雌激素减少可以促进正畸牙根吸收。这种吸收的差异可能是牙根的角度和形态差异导致骨改建不平衡的结果。雌激素经由RANKL-RANK-骨保护素传导通路对牙根吸收修复后期的破牙骨质细胞产生抑制作用。雌激素还可以诱导增加成牙骨质细胞活性,促进牙根及周围牙周组织吸收陷窝的再生。细胞外信号调节激酶1/2传导通路可能是雌激素促进成牙骨质细胞活性的途径之一。 临床上,正畸治疗导致的牙根吸收难以避免,雌激素替代治疗能否促进牙根的修复再生,对患者及正畸发展有重要的意义[50]。有研究使用不同品系的小鼠进行研究,结果显示在没有牙齿移动的BALB/C小鼠中,雌激素引起的牙根吸收程度与RANKL/骨保护素比值为正比例关系[51]。在两种品系小鼠中,正畸牙移动后缺乏雌激素均可诱发正畸诱导的炎性牙根吸收,其机制包括RANKL/骨保护素失衡、炎症反应和破牙细胞反应。在正畸力作用下,压力侧牙周组织中RANKL上调和骨保护素下调是激活并导致严重的牙根吸收的关键因素[52]。尽管雌激素对骨组织的作用已得到公认,但关于其对正畸诱导的牙根吸收的影响的信息较少。见表3。"
| [1] VANSANT L, CADENAS DS LLANO-PERUL M, VERDONCK A, et al. Expression of biological mediators during orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;95:170-186. [2] SIRISOONTORN I, HOTOKEZAKA H, HASHIMOTO M, et al. Tooth movement and root resorption; The effect of ovariectomy on orthodontic force application in rats. Angle Orthod. 2011;81(4):570-577. [3] SEIFI M, EZZATI B, SAEDI S, et al. The effect of ovariectomy and orchiectomy on orthodontic tooth movement and root resorption in wistar rats. J Dent (Shiraz). 2015;16(4):302-309. [4] 周翊飞,郑茜,毛杰,等.口服避孕药对大鼠正畸牙牙周组织改建的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(4):542-547. [5] 王斌,杨曦,周建萍,等.青少年女性月经周期不同阶段加力对正畸牙移动的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(15):2332-2337. [6] AMARASEKARA DS, YUN H, KIM S, et al. Regulation of osteoclast differentiation by cytokine networks. Immune Netw. 2018;18(1):e8. [7] ROSS FP, Teitelbaum SL. αvβ3 and macrophage colony-stimulating factor: partners in osteoclast biology. Immunol Rev. 2005;208:88-105. [8] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):19-26. [9] YANG CY, JEON HH, ALSHABAB A, et al. RANKL deletionc in periodontal ligament and bone lining cells blocks orthodontic tooth movement. Int J Oral Sci. 2018;10(1):3. [10] DANKS L, KOMATSU N, GUERRINI MM, et al. RANKL expressed on synovial fibroblasts is primarily responsible for bone erosions during joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(6):1187-1195. [11] TSUKASAKI M, KOMATSU N, NAGASHIMA K, et al. Host defense against oral microbiota by bone-damaging T cells. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1-11. [12] TSUKASAKI M, ASANO T, MURO R, et al. OPG production matters where it happened. Cell Rep. 2020;32(10):108124. [13] CAWLEY KM, BUSTANANTE-GOMEZ NC, GUHA AG, et al. Local production of osteoprotegerin by osteoblasts suppresses bone resorption. Cell Rep. 2020; 32(10):108052. [14] TONG X, GU J, SONG R, et al. Osteoprotegerin inhibit osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by enhancing autophagy via AMPK/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2018; 120(2):1630-1642. [15] OHNUMA K, KASAGI S, UTO K, et al. MicroRNA-124 inhibits TNF-α and IL-6 induced osteoclastogenesis. Rheumatol Int. 2019;39(4):689-695. [16] KIM JH, JIN HM, KIM K, et al. The mechanism of osteoclast differentiation induced by IL-1. J Immunol. 2009;183:1862-1870. [17] MARALEH A, KITAURA H, OHORI F, et al. TNF-α directly enhances osteocyte RANKL expression and promotes osteoclast formation. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1-12. [18] WU L, GUO Q, YANG J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes osteoclast formation Via PI3K/Akt pathway-mediated blimp1 expressio upregulation. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(6):1308-1315. [19] OGAWA S, KITAURA H, KISHIKAWA A, et al. TNF-α is responsible for the contribution of stromal cells to osteoclast and odontoclast formation during orthodontic tooth movement. PLoS One. 2019;14(10):e223989. [20] MCGREGOR NE, MURAT M, ELANGO J, et al. IL-6 exhibits both cis- and trans-signaling in osteocytes and osteoblasts, but only trans-signaling promotes bone formation and osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2019; 294(19):7850-7863. [21] WU Q, ZHOU X, HUANG D, et al. IL-6 Enhances osteocyte-mediated osteoclastogenesis by promoting JAK2 and RANKL activity in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(4):1360-1369. [22] GAVALI S, GUPTA MK, DASWANI B, et al. LYN, a key mediator in estrogen-dependent suppression of osteoclast differentiation, survival, and function. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(3):547-557. [23] RYOO G, MOON YJ, ChOI S, et al. Tussilagone promotes osteoclast apoptosis and prevents estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;531(4):508-514. [24] CHUANG S, CHEN C, CHOU Y, et al. G Protein-coupled estrogen receptor mediates cell proliferation through the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway in murine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18):6490. [25] YUR J, LOREZ JM. Understanding MAPK Signaling Pathways in Apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2346. [26] THOUVEREY C, CAVERZASIO J. Ablation of p38α MAPK signaling in osteoblast lineage cells protects mice from bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency. Endocrinology. 2015;156(12):4377-4387. [27] LIU G, Lu Y, MAIZ, et al. Suppressing MicroRNA-30b by estrogen promotes osteogenesis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2019; 2019:1-13. [28] PIAO H, CHU X, LV W, et al. Involvement of receptor interacting protein 140in estrogen-mediated osteoclasts differentiation, apoptosis, and bone resorption. J Physiol Sci. 2017;67(1):141-150. [29] KIM H, PONTEF, NOOKAEW I, et al. Estrogens decrease osteoclast number by attenuating mitochondria oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production in early osteoclast precursors. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):11933. [30] CRUZOE-SOUZA M, SASSO-CERRI E, CERRI PS. Immunohistochemical detection of estrogen receptor β in alveolar bone cells of estradiol-treated female rats: possible direct action of estrogen on osteoclast life span. J Anat. 2009;215(6):673-681. [31] SHI C, WU J, YAN Q, et al. Bone marrow ablation demonstrates that estrogen plays an important role in osteogenesis and bone turnover via an antioxidative mechanism. Bone. 2015;79:94-104. [32] GAVALI S, GUPTA MK, DASWANI B, et al. Estrogen enhances human osteoblast survival and function via promotion of autophag. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019;1866(9):1498-1507. [33] 孙晓琪.雌二醇通过G蛋白偶联雌激素受体30(GPR30)/ERK1/2信号通路调节MC3T3-E1细胞线粒体自噬的分子机制研究[A]//中国营养学会、亚太临床营养学会、江苏省科学技术协会、中国疾病预防控制中心营养与健康所、农业农村部食物与营养发展研究所、中国科学院上海营养与健康研究所.营养研究与临床实践——第十四届全国营养科学大会暨第十一届亚太临床营养大会、第二届全球华人营养科学家大会论文摘要汇编[C].中国营养学会、亚太临床营养学会、江苏省科学技术协会、中国疾病预防控制中心营养与健康所、农业农村部食物与营养发展研究所、中国科学院上海营养与健康研究所:中国营养学会,2019:2. [34] Uder C, Brückner S, Winkler S, et al. Mammalian MSC from selected species: features and applications. Cytometry A. 2018;93(1): 32-49. [35] 王洁,张鹏,代庆刚,等.雌激素对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2014,23(6):654-660. [36] WANG Q, YU J, ZHAI H, et al. Temporal expression of estrogen receptor alpha in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;347(1):117-123. [37] GAO B, HUANG Q, JIE Q, et al. Dose-response estrogen promotes osteogenic differentiation via GPR40 (FFAR1) in murine BMMSCs. Biochimie. 2015;110:36-44. [38] ZHANG M, CHEN F, WANG A, et al. Estrogen and its receptor enhance mechanobiological effects in compressed bone mesenchymal stem cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;195(5):400-413. [39] WU G, XU R, ZHANG P, et al. Estrogen regulates stemness and senescence of bone marrow stromal cells to prevent osteoporosis via ERβ-SATB2 pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(5):4194-4204. [40] UGARTE F, RYSER M, THIEME S, et al. Notch signaling enhances osteogenic differentiation while inhibiting adipogenesis in primary human bone marrow stromal cells. Exp Hematol. 2009;37(7):867-875. [41] FAN J, YANG L, MENG G, et al. Estrogen improves the proliferation and differentiation of hBMSCs derived from postmenopausal osteoporosis through notch signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;392(1-2):85-93. [42] Seo B, MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet. 2004; 364(9429):149-155. [43] OU Q, WANG X, WANG Y, et al. Oestrogen retains human periodontal ligament stem cells stemness in long-term culture. Cell Prolif. 2018;51(2): e12396. [44] 毛杰,周翊飞,吴晓玲,等. 雌激素介导下Wnt/β-catenin传导通路调控人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研,2018,22(13):2087-2092. [45] JIANG B, XU J, ZHOU Y, et al. Estrogen enhances osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells by activating the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Craniofac Surg. 2020;31(2):583-587. [46] 吴晓玲,郑茜,吕佳岭,等.雌激素微环境下非经典Wnt/Ca2+传导通路调控人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的研究[J].口腔医学研究, 2019,35(1):33-37. [47] 沈兰花,张瑞,孟玲娜.雌激素受体对去势大鼠牙周膜干细胞成骨分化能力的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2018,34(4):448-451. [48] CAI C, YUAN G, HUANG YE, et al. Estrogen-related receptor α is involved in the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human periodontal ligaments. Int J Mol Med. 2013;31(5):1195-1201. [49] LI T, ZHOU Z, WANG H, et al. Effects of estrogen on root repair after orthodontically induced root resorption in ovariectomized rats. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020;158(2):247-263. [50] AMARO ERS, ORTIZ FR, DORNELES LS, et al. Estrogen protects dental roots from orthodontic-induced inflammatory resorption. Arch Oral Biol. 2020;117:104820. [51] MACARI S, MADEIRA MFM, LIMA ILA, et al. ST2 regulates bone loss in a site dependent and estrogen‐dependent manner. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(10): 8511-8521. [52] 朱倩,蔡萍.雌激素对正畸骨改建相关细胞因子的影响[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2014,41(6):694-698. [53] 姜欢,胡敏.正畸牙移动相关牙根吸收研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2011, 27(2):168-169. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [4] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [6] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [7] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [8] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [9] | Hu Weifan, Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Sun Yang, Zhao Fengchao. Overexpression of miR-25 downregulates titanium particle-induced osteoclast differentiation through the NFATc1 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 682-687. |
| [10] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [11] | Yang Sidi, Wang Qian, Xu Nuo, Wang Ronghan, Jin Chuanqi, Lu Ying, Dong Ming. Biodentine enhances the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts through upregulating bone morphogenetic protein-2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 516-520. |
| [12] | Wang Jiajia, Liu Jie, Wang Min. Establishing a murine model of experimental apical periodontitis induced by Fusobacterium nucleatum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 176-181. |
| [13] | Feng Dongfei, He Hongxu, Xie Qi, Zhang Lili, Zhou Hui, Li Wei. Selection of key genes related to biological functions and regulation pathway in periodontal reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 253-259. |
| [14] | Cao Wei, Mao Furong, Hu Xiaohua, Yang Xiaohong. N-6 methyladenosine RNA methylation regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 266-270. |
| [15] | Wu Saixuan, Zhang Mi, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Regulatory role of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in bone homeostasis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 271-275. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||