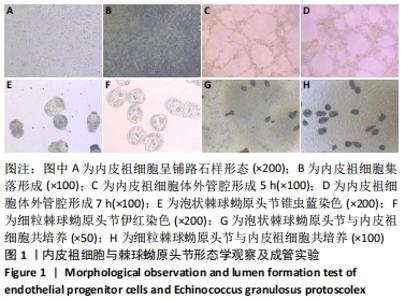
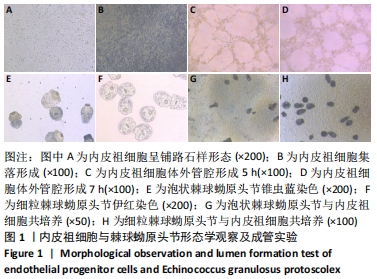
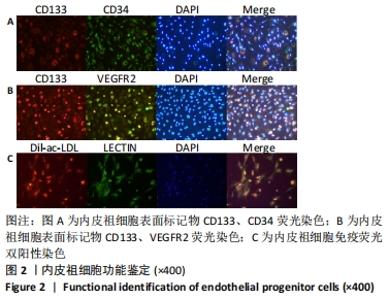
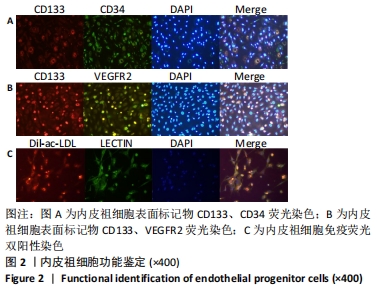
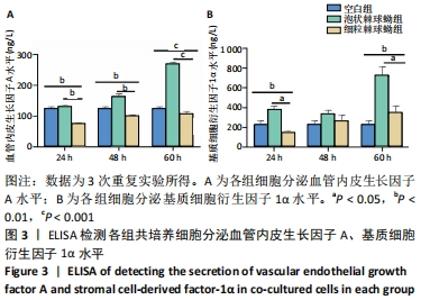
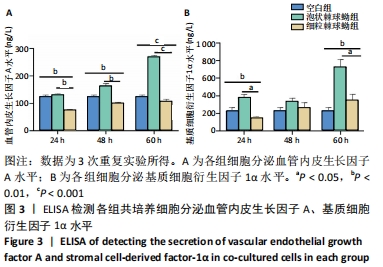
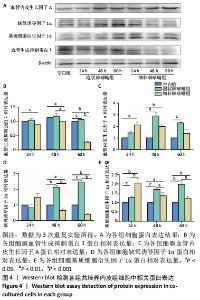
[1] 沈舒.泡型肝包虫病诊疗专家共识(2020版)[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2020,27(1):13-17.
[2] 苟平,王志鑫,胡陈亮,等.中国西部地区泡型、囊型包虫病手术治疗方式与术后并发症的回顾性分析[J].实用临床医药杂志,2019,23(3):33-37.
[3] 郭亚民,朱文君,赵顺云,等.复杂性肝棘球蚴病外科治疗策略研究进展[J].中国血吸虫病防治杂志,2018,30(6):705-708.
[4] 周启锋,任利,张灵强,等.肝泡状棘球蚴病动物模型的研究进展[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2017,33(11):2247-2250.
[5] 尼顿,米玛. 52例肝包囊虫病CT表现回顾性分析[J].西藏医药,2018,39(5): 64-65.
[6] 曾辉,刘明琪,泽仁措.肝囊型包虫病的超声图像分析[J].中国城乡企业卫生,2017,32(6):94-96.
[7] 张皓,李豪胜,杨茂江,等.肝细粒棘球蚴病的影像病理学对比分析[J].中国人兽共患病学报,2017,33(9):845-847.
[8] 黄玉洁,赵建卿,王健,等.多层螺旋CT及血管成像对肝泡状棘球蚴血管受侵的诊断价值[J].新疆医科大学学报,2015,38(10):1216-1219.
[9] 蒲鹏,代静.多层螺旋CT在脊椎泡状棘球蚴病中的诊断价值[J].中国现代医生,2019,57(5):103-105.
[10] 徐睿,余鑫.肝泡型包虫病CT钙化特点及其临床应用价值[J].贵州医药, 2019,43(9):1459-1461.
[11] 赵小峰.人VASH_1蛋白结构和功能的生物信息学分析[J].生物技术,2015, 25(6):552-557.
[12] 高静,李晓岚,王敏哲,等.血管内皮生长因子、基质细胞衍生因子-1基因对人微血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移、凋亡的影响[J].安徽医药,2019,23(9): 1784-1789.
[13] 韩晓宇,师永红.低氧诱导因子-1α参与肿瘤血管形成的生物学机制研究进展[J].疾病监测与控制,2021,15(1):77-80.
[14] 杨锦锋,曾荣耀.血管内皮生长因子和缺氧诱导因子-1α的表达与原发性肝癌患者临床病理特征及预后的关系[J].中国慢性病预防与控制,2020, 28(12):924-927.
[15] 王威,张颖倩,李中轩,等.内皮祖细胞促进损伤血管再内皮化的机制[J].临床心血管病杂志,2019,35(8):763-767.
[16] 毛梅,王健瑜,汪丽,等.内皮祖细胞对急性损伤肺组织的抗炎作用[J].第三军医大学学报,2015,37(24):2444-2447.
[17] WANG X, ZHAO Z, ZHANG H, et al. Simultaneous isolation of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells derived from murine bone marrow. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(6):5171-5177.
[18] 桂显伟,姜慧娇,武杰,等.两种棘球绦虫原头节促进骨髓间充质干细胞钙化的差异性分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(1):38-43.
[19] 赵兴华.对肝泡状棘球蚴病患者CT图像特征的分析[J].当代医药论丛,2017, 15(3):133-135.
[20] 尹建海,沈玉娟,于爱萍,等.小鼠细粒棘球蚴体外促血管生成作用研究[J].中国血吸虫病防治杂志,2017,29(3):320-323.
[21] 郭黎姣,姜慧娇,韩欢欢,等.肝泡状棘球蚴组织中HIF-1α、VEGFA的表达及对血管生成的作用[J].中国人兽共患病学报,2019,35(7):639-646.
[22] 曾红春,王颖鑫,王俊华,等.CEUS评价大鼠肝泡状棘球蚴病灶血流灌注的动态演变[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2017,14(9):566-570.
[23] 陈曦,张先兵,李勋,等.内皮祖细胞修复血管损伤的研究[J].中国现代普通外科进展,2015,18(11):908-911.
[24] HAN X, JIANG G, SHI Q. Effects of antihyperglycemics on endothelial progenitor cells. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020;49(5):629-636.
[25] 林上进,程群.内皮祖细胞与骨折愈合[J].国际骨科学杂志,2016,37(1):31-35.
[26] WATANABE T, HOSAKA T, OHMORI-MATSUDA K, et al. High preoperative plasma vasohibin-1 concentration predicts better prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma. Health Sci Rep. 2018;1(6):e40.
[27] NINOMIYA Y, OZAWA S, OGUMA J, et al. Expression of vasohibin-1 and -2 predicts poor prognosis among patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Oncol Lett. 2018;16(4):5265-5274.
[28] MIKAMI S, OYA M, KOSAKA T, et al. Increased vasohibin-1 expression is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis of renal cell carcinoma patients. Lab Invest. 2017;97(7):854-862.
[29] SAITO M, SUZUKI Y, YANO S, et al. Proteolytic inactivation of anti-angiogenic vasohibin-1 by cancer cells. J Biochem. 2016;160(4):227-232.
[30] 曹宸,辜敏,刘文能.内皮祖细胞研究进展及其在肿瘤治疗中的潜在应用[J].西南国防医药,2019,29(4):508-510.
|